
ATARAX 2 mg/ml XAROPE

Pergunte a um médico sobre a prescrição de ATARAX 2 mg/ml XAROPE

Como usar ATARAX 2 mg/ml XAROPE
Introdução
Prospecto: informação para o utilizador
Atarax 2mg/ml xarope
hidroxizina, dihidrocloruro
Leia todo o prospecto detenidamente antes de começar a tomar este medicamento, porque contém informações importantes para si.
- Conserva este prospecto, porque pode ter que voltar a lê-lo.
- Se tiver alguma dúvida, consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico.
- Este medicamento foi-lhe prescrito apenas para si, e não deve dá-lo a outras pessoas, mesmo que tenham os mesmos sintomas que si, porque pode prejudicá-las.
- Se experimentar efeitos adversos, consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico, mesmo que se trate de efeitos adversos que não aparecem neste prospecto. Ver secção 4.
Conteúdo do prospecto
- O que é Atarax xarope e para que é utilizado
- O que precisa saber antes de começar a tomar Atarax xarope
- Como tomar Atarax xarope
- Possíveis efeitos adversos
- Conservação de Atarax xarope
- Conteúdo do envase e informação adicional
1. O que é Atarax xarope e para que é utilizado
Atarax é um medicamento ansiolítico que pertence a uma classe de compostos denominados difenilmetanos.
Atarax é utilizado no:
- tratamento sintomático da ansiedade em adultos maiores de 18 anos;
- tratamento sintomático do prurido em adultos, adolescentes e crianças a partir de 12 meses.
2. O que precisa saber antes de começar a tomar Atarax xarope
Não tome Atarax
- Se é alérgico (hipersensível) a hidroxizina dihidrocloruro ou a qualquer um dos outros componentes de Atarax, a cetirizina, a outros derivados da piperazina, a aminofilina ou a etilendiamina.
- Se padece de porfiria (grupo de distúrbios hereditários que afetam o sangue).
- Se o seu ECG (eletrocardiograma) mostra um problema do ritmo cardíaco chamado “prolongamento do intervalo QT”.
- Se tem ou teve uma doença cardiovascular ou se a sua frequência cardíaca é muito baixa.
- Se tem níveis baixos de sais no seu corpo (ex. nível baixo de potássio ou magnésio).
- Se está tomando certos medicamentos para problemas do ritmo cardíaco ou medicamentos que possam afetar o ritmo cardíaco (ver “Uso de Atarax com outros medicamentos”).
- Se algum familiar próximo faleceu subitamente por problemas cardíacos.
- Em caso de gravidez ou amamentação.
Advertências e precauções
- Se tem um elevado risco de convulsões.
- Se tem insuficiência hepática e se tem insuficiência renal moderada ou grave. Nesses casos, deve reduzir-se a dose de Atarax.
- Se sofre de glaucoma, obstrução do fluxo da bexiga urinária, diminuição da motilidade gastrointestinal, miastenia gravis ou demência.
- Atarax pode estar associado a um aumento do risco de distúrbios do ritmo cardíaco que podem ser ameaçadores para a vida. Por isso, informe o seu médico se tem qualquer problema cardíaco ou se está tomando qualquer outro medicamento, incluindo os adquiridos sem receita.
Procure atendimento médico imediato se, enquanto estiver em tratamento com Atarax, experimentar problemas cardíacos como palpitações, dificuldade para respirar ou perda da consciência. O tratamento com hidroxizina deve ser interrompido.
Outros medicamentos e Atarax
Comunique ao seu médico ou farmacêutico se está utilizando, utilizou recentemente ou pode ter que utilizar qualquer outro medicamento. Isso inclui qualquer medicamento adquirido sem receita. Atarax pode afetar ou ser afetado por outros medicamentos.
Atarax pode potenciar a ação depressora do sistema nervoso central se for utilizado conjuntamente com outros fármacos com propriedades depressoras ou anticolinérgicas. Nesses casos, deve adaptar-se a dose a cada paciente.
Atarax antagoniza os efeitos da betahistina e de fármacos anticolinesterasa.
Deve suspender-se o tratamento com Atarax pelo menos 5 dias antes de realizar um teste de alergia ou uma prova de provocação bronquial com metacolina, para evitar efeitos sobre os resultados.
Deve evitar-se a administração simultânea de Atarax com inibidores da monoamino oxidase.
Atarax contrarresta a ação pressora da adrenalina.
A administração conjunta com fármacos que possam provocar arritmias pode aumentar o risco de prolongamento QT e Torsades de Pointes (alterações de algumas medidas no eletrocardiograma).
Não tome Atarax se estiver tomando medicamentos para tratar:
- infecções bacterianas (ex. os antibióticos eritromicina, moxifloxacino, levofloxacino)
- infecções por fungos (ex. pentamidina)
- problemas cardíacos ou pressão arterial elevada (ex. amiodarona, quinidina, disopiramida, sotalol)
- psicose (ex. haloperidol)
- depressão (ex. citalopram, escitalopram)
- distúrbios gastrointestinais (ex. prucaloprida)
- alergia
- malária (ex. mefloquina e hidroxicloroquina)
- câncer (ex. toremifeno, vandetanib)
- abuso de medicamentos ou dor intensa (metadona)
Até à data, não foram detectadas mais interações com outros medicamentos.
Toma de Atarax com alimentos, bebidas e álcool
Não deve tomar álcool enquanto estiver em tratamento com este medicamento. A administração simultânea de hidroxizina e álcool pode produzir efeitos sobre o sistema nervoso central.
Gravidez e amamentação
Consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico antes de tomar qualquer medicamento. Atarax não deve ser tomado durante a gravidez.
Atarax não deve ser tomado durante a amamentação. Se o tratamento com Atarax for necessário, deve suspender-se a amamentação.
As seguintes reações podem aparecer em bebês recém-nascidos de mães que tomaram Atarax durante a última etapa da gravidez e/ou do parto, as quais se observaram imediatamente ou ao cabo de algumas horas após o nascimento: tremores, rigidez e/ou fraqueza muscular, dificuldade para respirar e retenção urinária (retenção de urina).
Condução e uso de máquinas
Atarax pode alterar a sua capacidade para conduzir ou manejar máquinas, porque pode produzir sonolência, diminuir a sua atenção ou diminuir a sua capacidade de reação. A ocorrência desses efeitos é mais provável no início do tratamento ou quando se aumenta a dose. Não conduza nem utilize máquinas se experimentar algum desses efeitos.
Pacientes de idade avançada
Não se recomenda utilizar este medicamento em pacientes de idade avançada, porque nesses pacientes o efeito do medicamento pode prolongar-se e pode aumentar o risco de efeitos adversos. Em caso de que seja necessário utilizar este medicamento em pacientes de idade avançada, recomenda-se iniciar o tratamento com a metade da dose recomendada.
Atarax contém benzoato de sódio, sacarose e etanol
Este medicamento contém menos de 1 mmol de sódio (23 mg) por 5 ml; isto é, é essencialmente “isento de sódio”.
Este medicamento contém 1,5 mg de benzoato de sódio em cada 5 ml, equivalente a 0,3 mg/ml.
Este medicamento contém sacarose. Se o seu médico lhe indicou que padece uma intolerância a certos açúcares, consulte com ele antes de tomar este medicamento. A sacarose pode prejudicar os dentes. A doses maiores de 6,5 ml de xarope, o conteúdo de sacarose deve ser tido em conta em pacientes com diabetes mellitus.
Este medicamento contém 4,75 mg de álcool (etanol) em cada 5 ml, que equivale a 0,95 mg/ml (0,095% p/v). A quantidade em 5 ml deste medicamento é equivalente a menos de 2 ml de cerveja ou 1 ml de vinho. A pequena quantidade de álcool que contém este medicamento não produz qualquer efeito perceptível.
3. Como tomar Atarax xarope
Siga exatamente as instruções de administração deste medicamento indicadas pelo seu médico. Em caso de dúvida, consulte novamente o seu médico ou farmacêutico.
Deve administrar-se a menor dose de Atarax que resulte eficaz e durante o menor tempo possível.
Adultos maiores de 18 anos:
- Para o tratamento sintomático da ansiedade: 50 mg (25 ml) por dia, repartidos em 3 doses. Recomenda-se administrar 12,5 mg (6,25 ml) pela manhã, 12,5 mg (6,25 ml) ao meio-dia e 25 mg (12,5 ml) à noite. O seu médico lhe indicará se precisa tomar uma dose maior à noite. Em casos mais graves, podem ser utilizadas até 100 mg (50 ml) por dia. A dose máxima diária é de 100 mg (50 ml) por dia.
- Para o tratamento sintomático do prurido: Recomenda-se começar com uma dose de 25 mg (12,5 ml) uma hora antes de deitar, e se for necessário, administrar doses de até 25 mg (12,5 ml) de 3 a 4 vezes por dia. A dose máxima diária é de 100 mg (50 ml) por dia.
Adolescentes e crianças a partir de 12 meses:
- Para o tratamento sintomático do prurido: De 1 a 2 mg (0,5 a 1 ml) por kg por dia, repartidos em várias doses. Em crianças de até 40 kg de peso, a dose máxima diária é de 2 mg (1 ml) por kg por dia. Em crianças de mais de 40 kg de peso, a dose máxima diária é de 100 mg (50 ml) por dia.
Não se recomenda utilizar este medicamento em pacientes de idade avançada (ver secção 2). Em caso de que seja necessário utilizar este medicamento, recomenda-se iniciar o tratamento com a metade da dose recomendada. O seu médico lhe prescreverá a menor dose possível. A dose máxima diária nesses pacientes é de 50 mg (25 ml) por dia.
Se tiver problemas de rim ou problemas de fígado, o seu médico pode indicar-lhe que tome uma dose mais baixa (ver “Advertências e precauções”).
A dose será adaptada dentro do intervalo de doses recomendado de acordo com a resposta do paciente ao tratamento.
Se acredita que o efeito de Atarax é demasiado forte ou demasiado fraco, consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico.
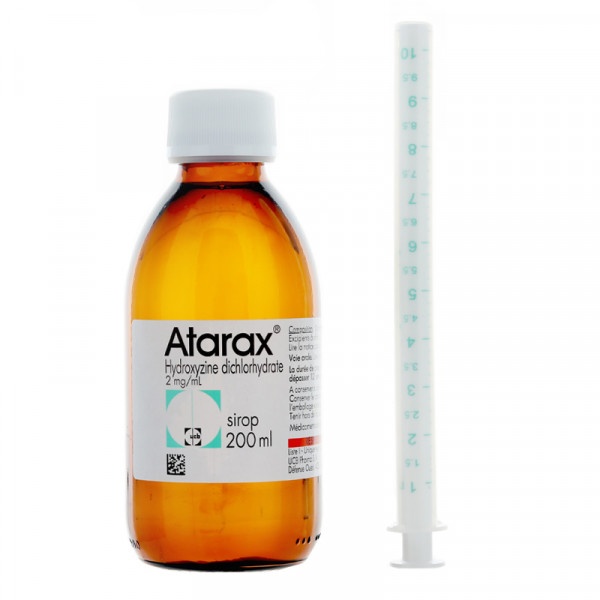
A quantidade de xarope é medida com uma seringa de 10 ml para administração oral, graduada cada 0,25 ml. Cada ml contém 2 mg de hidroxizina dihidrocloruro. Introduza a seringa incluída no envase no interior do frasco e extraia os ml correspondentes.
O xarope deve ser tomado antes das refeições, sozinho ou diluído em água ou sumo de frutas.
Se tomar mais Atarax do que deve
Se tomou demasiado Atarax, consulte imediatamente o seu médico ou farmacêutico ou ligue para o Serviço de Informação Toxicológica, telefone 915 620 420, especialmente se é uma criança que tomou demasiado. Em caso de sobredose, pode instaurar-se um tratamento sintomático. Pode realizar-se uma monitorização eletrocardiográfica (ECG), devido à possibilidade de um problema do ritmo cardíaco, como prolongamento do intervalo QT ou Torsade de Pointes.
Uma sobredosagem importante pode provocar náuseas, vómitos, taquicardia, febre, sonolência, reflexo pupilar alterado, tremor, confusão, alucinação, diminuição do nível de consciência, depressão respiratória, convulsões, diminuição da pressão arterial e arritmia cardíaca, incluindo bradicardia, podendo desembocar em um coma profundo e um colapso cardiorrespiratório.
Se esqueceu de tomar Atarax
Lembre-se de sempre tomar o seu medicamento.
Não tome uma dose dupla para compensar as doses esquecidas. Continue a tomar a sua dose normal quando lhe tocar.
Se interromper o tratamento com Atarax
O seu médico lhe indicará a duração do seu tratamento com Atarax. Não suspenda o tratamento antes.
Se tiver alguma outra dúvida sobre o uso deste medicamento, pergunte ao seu médico ou farmacêutico.
4. Possíveis efeitos adversos
Como todos os medicamentos, este medicamento pode produzir efeitos adversos, embora nem todas as pessoas os sofram.
Os seguintes efeitos adversos foram notificados em ensaios clínicos:
- sonolência, dor de cabeça, fadiga, secura da boca.
O efeito adverso frequente (que afeta pelo menos 1 de cada 100 pacientes) é sedação.
Os efeitos adversos pouco frequentes (que afetam pelo menos 1 de cada 1.000 pacientes) são: náuseas, malestar, febre, tontura, insónia, tremor, agitação e confusão.
Os efeitos adversos raros (que afetam pelo menos 1 de cada 10.000 pacientes) são: taquicardia, alterações na acomodação ou capacidade de ver a diferentes distâncias, visão borrosa, estreñimento, vómitos, hipersensibilidade, provas da função hepática anormais, convulsões, movimentos anormais involuntários (discinesia), desorientação, alucinações, retenção da urina, erupção eritematosa, erupção maculo-papular, dermatite, picazón e hipotensão.
Os efeitos adversos muito raros (que afetam menos de 1 de cada 10.000 pacientes) são: choque anafiláctico, broncoespasmo (estreitamento dos brônquios que provoca dificuldade para respirar), edema angioneurótico (inflamação da pele e mucosas), aumento da sudorese, erupção devido ao medicamento, pustulose exantémica aguda generalizada (tipo de reação alérgica que aparece em resposta a um medicamento, infecção ou doença), eritema multiforme, síndrome de Stevens-Johnson (estes dois últimos são distúrbios da pele devidos a uma reação alérgica ou infecção).
Os efeitos adversos de frequência não conhecida (não podem ser estimados a partir dos dados disponíveis) são: QT prolongado no eletrocardiograma, Torsades de Pointes (alteração do eletrocardiograma associada a taquicardias), hepatite, perda do conhecimento (síncope), doenças ampollares (por exemplo, necrólise epidérmica tóxica, pénfigo) e aumento de peso.
Deixe de tomar este medicamento e procure atendimento médico imediato se experimentar qualquer problema do ritmo cardíaco como palpitações, dificuldade para respirar ou perda da consciência.
Os seguintes efeitos adversos foram observados com cetirizina, o principal metabolito de hidroxizina: trombocitopenia (diminuição no número de plaquetas), agressividade, depressão, tic, distonia (contracções musculares), parestesia (sensação de formigueiro), crise oculógira (colocação dos olhos em uma posição fixa), diarreia, disúria (dificuldade para urinar), enurese (incontinência urinária), astenia, edema e aumento de peso.
Comunicação de efeitos adversos
Se experimentar qualquer tipo de efeito adverso, consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico, mesmo que se trate de possíveis efeitos adversos que não aparecem neste prospecto. Também pode comunicá-los diretamente através do Sistema Espanhol de Farmacovigilância de Medicamentos de Uso Humano: www.notificaram.es. Mediante a comunicação de efeitos adversos, você pode contribuir para fornecer mais informações sobre a segurança deste medicamento.
5. Conservação de Atarax xarope
Mantenha este medicamento fora da vista e do alcance das crianças.
Atarax deve ser conservado na sua caixa de cartão devido ao facto de que o princípio ativo hidroxizina dihidrocloruro é sensível à luz.
Não requer nenhuma temperatura especial de conservação.
Não utilize Atarax xarope após a data de validade que aparece no envase após “CAD”. A data de validade é o último dia do mês que se indica.
Os medicamentos não devem ser jogados fora pelos esgotos nem para o lixo. Deposite os envases e os medicamentos que não precisa no Ponto SIGRE da farmácia. Pergunte ao seu farmacêutico como se livrar dos envases e dos medicamentos que não precisa.
Desta forma, ajudará a proteger o meio ambiente.
6. Conteúdo do envase e informação adicional
Composição de Atarax xarope
- O princípio ativo é hidroxizina dihidrocloruro. Cada ml contém 2 mg de hidroxizina dihidrocloruro.
- Os outros componentes são: sacarose, benzoato de sódio, aroma de avelã, levomentol, etanol, água purificada.
Aspecto do produto e conteúdo do envase
Atarax xarope é apresentado em um frasco de vidro topázio com tampa à prova de crianças e com uma seringa para administração oral (Polietileno/Poliestireno) de 10 ml, graduada cada 0,25 ml. Cada envase tem 150 ml de xarope.
Titular da autorização de comercialização e responsável pela fabricação
Titular da autorização de comercialização:
UCB Pharma, S.A.
Praça de Manuel Gómez Moreno, s/n,
Edifício Bronze, Planta 5,
28020 Madrid
Espanha
Responsável pela fabricação:
NEXTPHARMA, SAS
17, Route de Meulan (Limay)
78250 - França
Data da última revisão deste prospecto:janeiro de 2023
A informação detalhada deste medicamento está disponível na página Web da Agência Espanhola de Medicamentos e Produtos Sanitários (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/

Quanto custa o ATARAX 2 mg/ml XAROPE em Espanha em 2025?
O preço médio do ATARAX 2 mg/ml XAROPE em dezembro de 2025 é de cerca de 1.92 EUR. Os valores podem variar consoante a região, a farmácia e a necessidade de receita. Confirme sempre com uma farmácia local ou fonte online para obter informações atualizadas.
- País de registo
- Preço médio em farmácia1.92 EUR
- Substância ativa
- Requer receita médicaSim
- Fabricante
- Esta informação é apenas para referência e não constitui aconselhamento médico. Consulte sempre um médico antes de tomar qualquer medicamento. A Oladoctor não se responsabiliza por decisões médicas baseadas neste conteúdo.
- Alternativas a ATARAX 2 mg/ml XAROPEForma farmacêutica: COMPRIMIDO, 25 mg cloridrato de hidroxizinaSubstância ativa: hydroxyzineFabricante: Ucb Pharma S.A.Requer receita médicaForma farmacêutica: COMPRIMIDO, 25 mgSubstância ativa: hydroxyzineFabricante: Bluefish Pharmaceuticals Ab (Publ)Requer receita médicaForma farmacêutica: COMPRIMIDO, 25 mgSubstância ativa: hydroxyzineFabricante: Neuraxpharm Spain S.L.Requer receita médica
Alternativas a ATARAX 2 mg/ml XAROPE noutros países
As melhores alternativas com o mesmo princípio ativo e efeito terapêutico.
Alternativa a ATARAX 2 mg/ml XAROPE em Польща
Alternativa a ATARAX 2 mg/ml XAROPE em Україна
Médicos online para ATARAX 2 mg/ml XAROPE
Avaliação de posologia, efeitos secundários, interações, contraindicações e renovação da receita de ATARAX 2 mg/ml XAROPE – sujeita a avaliação médica e regras locais.









