
ДАПАРОКС 33 мг/мл ОРАЛЬНИЙ РОЗЧИН У КРАПЛЯХ
Запитайте лікаря про рецепт на ДАПАРОКС 33 мг/мл ОРАЛЬНИЙ РОЗЧИН У КРАПЛЯХ

Інструкція із застосування ДАПАРОКС 33 мг/мл ОРАЛЬНИЙ РОЗЧИН У КРАПЛЯХ
Вступ
Опис: інформація для користувача
Daparox 33 мг/мл оральні краплі у вигляді розчину
пароксетин (месилат)
Вважно прочитати уважно весь опис перед тим, як почати приймати цей препарат,адже він містить важливу інформацію для вас.
- Зберігайте цей опис, оскільки вам може знадобитися знову його прочитати.
- Якщо у вас виникли питання, проконсультуйтеся з вашим лікарем або фармацевтом.
- Цей препарат призначений лише для вас і не слід давати його іншим людям, хоча їхні ознаки захворювання можуть бути однаковими, оскільки це може їм нашкодити.
- Якщо у вас виникнуть будь-які побічні ефекти, повідомте про це вашому лікарю або фармацевту. До них також входять можливі побічні ефекти, не згадані в цьому описі. Див. розділ 4.
Зміст опису:
- Що таке Daparox 33 мг/мл оральні краплі у вигляді розчину і для чого він використовується
- Що вам потрібно знати перед тим, як почати приймати Daparox 33 мг/мл оральні краплі у вигляді розчину
- Як приймати Daparox 33 мг/мл оральні краплі у вигляді розчину
- Можливі побічні ефекти
- Зберігання Daparox 33 мг/мл оральних крапель у вигляді розчину
- Зміст упаковки та додаткова інформація
1. Що таке Daparox 33 мг/мл оральні краплі у вигляді розчину і для чого він використовується
Пароксетин належить до групи антидепресантів, які називаються селективними інгібіторами зворотного захоплення серотоніну (СІЗС).
Daparox призначений для:
- Великого депресивного епізоду (періоди депресії)
- Обсесивно-компульсивного розладу (повторюваної обсесивної думки і/або дії)
- Розладу тривоги з і без агорафобії (аномальний страх покидати будинок, входити до
магазинів або страх відкритих просторів)
- Соціальної тривоги/соціальної фобії (ексагерований страх або уникнення будь-якої
соціальної ситуації)
- Розладу загальної тривоги (загальний страх з великою тривогою або нервовим станом)
2. Що вам потрібно знати перед тим, як почати приймати Дапарокс 33 мг/мл краплі для прийому всередину в розчині
Не приймайте Дапарокс, якщо
- вас алергійно на пароксетин або на будь-який інший компонентцього лікарського засобу (перелічені в розділі 6).
- ви приймаєте лікарські засоби для лікування депресії або хвороби Паркінсона(так звані інгібітори моноамінооксидази (МАО)).
- Ви можете використовувати пароксетин тільки якщо ви припинили приймати нереверсивні МАО не менше ніж за 14 днів до цього (наприклад, ізокарбоксазиді фенелзин).
- Якщо ви приймаєте оборотний МАО (наприклад, моклобемід, лінезолід, метилтіонін-хлорид – метиленовий синій), вам потрібно чекати не менше 24 годин перед прийняттям пароксетину.
- Навпаки, коли ви припиняєте приймати пароксетин, вам потрібно чекати не менше 7 днів перед початком прийому МАО.
- якщо ви приймаєте певний лікарський засіб (тіоридазин), який використовується для лікування важких психічних захворювань, таких як психоз. Пароксетин може викликати збільшення концентрації тіоридазину в крові, тому збільшується ризик виникнення побічних ефектів, викликаних тіоридазином. Одним із можливих побічних ефектів є нерегулярні серцеві скорочення (важка вентрикулярна аритмія) та раптова смерть (див. також розділ 2, "Інші лікарські засоби та Дапарокс").
- якщо ви приймаєте певний лікарський засіб, який використовується для лікування психозу (пімозид). Пароксетин може викликати збільшення концентрації пімозиду в крові, тому збільшується ризик виникнення одного з побічних ефектів пімозиду (див. розділ 2, "Інші лікарські засоби та Дапарокс").
Попередження та застереження
Порадьтеся з вашим лікарем або фармацевтом перед початком прийому Дапарокс.
Будьте особливо обережні з Дапарокс
- Якщо ви приймаєте певні лікарські засоби, які використовуються для лікування депресії або хвороби Паркінсона (МАО). Не приймайте пароксетин разом з цими лікарськими засобами.Ваш лікар призначить час, коли вам потрібно почати лікування пароксетином після припинення прийому цих МАО (див. розділ 2, "Не приймайте Дапарокс", та розділ 2, "Інші лікарські засоби та Дапарокс").
- Якщо у вас з'являються симптоми, такі як нетерпіння, гіперактивність або неможливість сидіти або стояти на місці(акатизія). Якщо це відбувається, зв'яжіться з вашим лікарем. Збільшення дози може бути шкідливим.
- Якщо ви починаєте відчувати симптоми серотонінового синдрому. Цей синдром проявляється як поєднання деяких з наступних симптомів: як неспокій (екстремальний), сплутаність, раздражливість, марення (галюцинації), потіння, тремор або озноб, збільшення рефлексів і м'язових скорочень (міоклон), висока температура, жорсткість (див. розділ 2, "Інші лікарські засоби та Дапарокс"). Якщо у вас з'являються будь-які з цих симптомів, негайно зв'яжіться з вашим лікарем і припиніть приймати пароксетин.
- Якщо у вас є або був (періоди) надмірної ейфорії або надмірної збудливості, яка викликає незвичайну поведінку (маніакальний стан). Якщо у вас є маніакальний період, може бути необхідним припинити лікування пароксетином.
- Якщо у вас є проблеми з печінкоюабо важкі проблеми з нирками. Можливо, ваш лікар буде потрібно коригувати дозу.
- Якщо у вас є цукровий діабет. Лікування пароксетином може змінити рівень цукру в крові, тому потрібно контролювати його. Можливо, буде потрібно коригувати дозу інсуліну або пероральних антидіабетичних засобів.
- Якщо у вас є або був епілепсія чи судоми. Пароксетин може викликати судоми (апоплексію), тому ваш лікар буде потрібно особливо уважно стежити за цим. Якщо у вас трапляються судоми (апоплексія), негайно зв'яжіться з вашим лікарем. Можливо, буде потрібно припинити лікування пароксетином.
- Якщо ви приймаєте лікування електроконвульсивною терапією (ЕКТ). Наразі досвід використання пароксетину під час лікування ЕКТ обмежений, тому ваш лікар буде потрібно особливо уважно стежити за цим.
- Якщо у вас є або був збільшення внутрішньоочного тиску(глаукома). Пароксетин може розширювати зіниці (мідріаз), що може привести до збільшення тиску в очах, тому ваш лікар буде потрібно особливо уважно стежити за цим.
- Якщо у вас є серцево-судинні захворювання. Безпека використання пароксетину не була досліджена у пацієнтів з цією хворобою, тому ваш лікар буде потрібно особливо обережно стежити за цим.
- Якщо ви особа похилого віку, використовуєте інші лікарські засобиабо маєте проблеми з печінкою(цироз), і внаслідок цього у вас є високий ризик низької концентрації солі (натрію) в крові. Пароксетин може знижувати концентрацію натрію в крові, що викликає слабкість і втому. Якщо це відбувається, зв'яжіться з вашим лікарем.
- Якщо у вас є збільшення ризiku кровотечабо якщо ви приймаєте інші лікарські засоби, які можуть збільшити ризик кровотеч, або якщо ви вагітні (див. "Вагітність, годування грудьми та фертильність"). Багато прикладів цих лікарських засобів - це ті, які використовуються для розрідження крові (антICOагулянти), певні лікарські засоби, які використовуються для лікування важких психічних захворювань або нудоти та блювоти (фенотіазини), лікарський засіб, який використовується для лікування шизофренії (клоzapін), ацетилсаліцилова кислота та певні лікарські засоби, які використовуються для лікування болю та запалення (НПЗ, як ібупрофен або інгібітори COX-2). Пароксетин може викликати аномальні кровотечі, тому ваш лікар буде потрібно особливо обережно стежити за цим (див. розділ 2, "Прийом інших лікарських засобів").
- Якщо у вас є проблеми з зором. Ваш лікар скаже вам, що не варто самому приймати цей лікарський засіб, якщо у вас є проблеми з зором. Попросіть вашого опікуна або друга контролювати дозу, яку вам потрібно.
- Якщо ви хочете припинити приймати пароксетин, ви можете відчувати симптоми абстиненції, особливо якщо лікування припиняється раптово (див. розділ 3, Якщо ви припиняєте лікування Дапарокс). Порадьтеся з вашим лікарем перед припиненням лікування пароксетином.
Думки про самогубство та погіршення депресії або тривоги
Якщо ви депресивні та/або маєте тривожний розлад, іноді ви можете мати думки про самозшкодження або самогубство. Це може збільшитися на початку прийому антидепресантів, оскільки всі ці лікарські засоби потребують часу для дії, зазвичай кілька тижнів, але іноді це може бути більше часу.
Це більш ймовірно:
- Якщо ви раніше мали думки про самогубство або самозшкодження.
- Якщо ви молодий дорослий. Інформація з клінічних досліджень показала збільшення ризику самогубних поведінок у молодих дорослих з психіатричними захворюваннями, які приймали антидепресанти.
Якщо у вас з'являються думки про самозшкодження або самогубство в будь-який момент, зв'яжіться з вашим лікарем або негайно зверніться до лікарні.
Це може бути корисно для вас пояснити близьким родичам або друзям, що ви депресивні або маєте тривожний розлад, і попросити їх прочитати цю інструкцію. Ви можете також попросити їх сказати вам, якщо вони думають, що ваша депресія або тривога погіршується, або якщо вони стурбовані змінами в вашій поведінці.
Деякі лікарські засоби з групи, до якої належить Дапарокс (так звані ІСРС/ІРН), можуть викликати симптоми сексуальної дисфункції (див. розділ 4). У деяких випадках ці симптоми зберігаються після припинення лікування.
Діти та підлітки
Пароксетин не повинен використовуватися у дітей та підлітках молодше 18 років. Ви повинні знати, що у пацієнтів молодше 18 років збільшується ризик побічних ефектів, таких як спроби самогубства, самогубчі думки та ворожість (головним чином агресивність, поведінка протистояння та гнів). Навіть так, ваш лікар може призначити пароксетин пацієнтам молодше 18 років, якщо вирішить, що це найкраще для них. Якщо лікар призначив пароксетин пацієнту молодше 18 років і ви хочете обговорити це рішення, відвідайте лікаря. Ви повинні повідомити лікаря, якщо будь-які з цих симптомів з'являються або погіршуються у пацієнтів молодше 18 років, які приймають пароксетин. Крім того, не встановлено з certainty, чи цей лікарський засіб впливає на зростання, зрілість та когнітивний або поведінковий розвиток у цій віковій групі.
Інші лікарські засоби та Дапарокс
Повідомте вашого лікаря або фармацевта, якщо ви приймаєте, нещодавно приймали або можете приймати будь-який інший лікарський засіб.
Існують інші лікарські засоби, чиї ефекти можуть бути змінені пароксетином. З іншого боку, ці лікарські засоби можуть впливати на ефективність пароксетину. Пароксетин може взаємодіяти з наступними лікарськими засобами:
- Лікарські засоби, які використовуються для лікування депресії або хвороби Паркінсона (МАО, як моклобемідабо ізокарбоксазид), харчовий добавок (Л-триптофан), лікарські засоби для мігрені (триптани, як суматриптан, алмотриптан), анальгетики (трамадол, бупренорфін, петидін), лікарський засіб, який використовується проти інфекцій (лінезолід), оборотний МАО, який діє як візуалізуючий агент перед операцією (метиленовий синій), інші селективні інгібітори зворотного захоплення серотоніну (ІСРС, як флуоксетин, сертралін), лікарські засоби, які використовуються для лікування психіатричних захворювань (літій, рисперидон), лікарський засіб, який використовується для лікування хронічного болю або в анестезії (фентаніл) та Живописний перець(Hypericum perforatum), трав'яний засіб для депресії. Одночасне використання цих лікарських засобів може викликати серотоніновий синдром (див. розділ 2, "Не приймайте Дапарокс" та розділ 2, "Попередження та застереження").
- Бупренорфіну поєднанні з налоксоном, заміщення лікування для залежності від опіоїдів.
- Лікування психозу (пімозид). Дослідження, проведені з одночасним використанням пароксетину та пімозиду, показали, що пароксетин може збільшувати кількість пімозиду в крові. Оскільки пімозид може викликати важкі побічні ефекти, такі як порушення серцевого ритму, ви не повинні використовувати пароксетин разом з пімозидом (див. розділ 2, "Не приймайте Дапарокс").
- Лікарські засоби інгібітори ферментів, як певні лікарські засоби, які використовуються для лікування депресії (кломіпрамін). Ваш лікар, ймовірно, призначить вам нижчу дозу, ніж зазвичай. Якщо ви будете використовувати пароксетин разом з індукторами ферментів (наприклад, карбамазепін, рифампіцин, фенобарбітал та фенітоїн), зазвичай не потрібно нижчої початкової дози, і ваш лікар буде коригувати наступні дози залежно від ефекту лікарського засобу.
- Через взаємодію з пароксетином може відбуватися подовження м'язового розслаблення м'язових розслаблювачів, які використовуються в анестезії, таких як мівакурій та суksamетоній.
- Комбінація лікарських засобів для лікування інфекції Синдром набутої імунодефіцитності (СНІД)(фосампренавірта ритонавір).
- Лікарські засоби, які використовуються для лікування хвороби Паркінсона (проклідин). Можуть збільшуватися ефекти та побічні ефекти проклідину. Якщо ви починаєте відчувати побічні ефекти, такі як сухість у роті, розмитість зору, запор та затримка сечі в сечовому міхурі через порушення його опорожнення, може бути потрібно зменшити дозу проклідину після консультації з лікарем.
- Певні лікарські засоби для лікування епілепсії(антikonvulsанти, як валпроат натрію). Хоча не було доведено прямого ефекту, ваш лікар буде потрібно особливо обережно призначати пароксетин пацієнтам з епілепсією.
- Лікарські засоби, які метаболізуються тим же ферментом, що й пароксетин, такі як деякі лікарські засоби для лікування депресії (трициклічні антидепресанти, як нортриптилінта дезіпрамін), певні лікарські засоби для лікування важких психічних захворювань, як антипсихотики (перфеназин, тіоридазинта рисперидон), лікарський засіб, який використовується для лікування синдрому дефіциту уваги та гіперактивності (атомоксетин), певні лікарські засоби для лікування порушень серцевого ритму (як флекайнідта пропафенон), певні лікарські засоби для лікування стенокардії та високого кров'яного тиску (метопролол), лікарський засіб, який використовується для лікування високого рівня холестерину (правастатин) та певні лікарські засоби для лікування важких психічних захворювань або нудоти та блювоти (фенотіазини). Можуть збільшуватися ефекти та побічні ефекти цих лікарських засобів. Не слід використовувати пароксетин та тіоридазин разом, оскільки ризик важких побічних ефектів, таких як порушення серцевого ритму (важка вентрикулярна аритмія) та раптова смерть (див. розділ 2, "Не приймайте Дапарокс").
- Таблеткові інгібітори згортання крові (антICOагулянти, як аценокумарол, фенпрокумон). Ефекти та побічні ефекти цих лікарських засобів можуть збільшуватися, а також ризик кровотечі. Ваш лікар буде потрібно особливо обережно стежити за вами та може бути потрібно коригувати дозу антICOагулянтів (див. розділ 2, "Попередження та застереження").
- Лікарські засоби, які використовуються для лікування раку легенів або проблем з фертильністю (тамоксифен).
- Лікарські засоби, які збільшують ризик кровотечі. Певні лікарські засоби, які використовуються для лікування важких психічних захворювань або нудоти та блювоти (фенотіазини, як хлорпромазин, перфеназин), лікарський засіб, який використовується для лікування шизофренії (клоzapін), певні лікарські засоби, які використовуються для лікування депресії (трициклічні антидепресанти, як кломіпрамін, дезіпрамін), ацетилсаліцилова кислота, лікарські засоби, які використовуються для лікування болю та запалення (НПЗ, як ібупрофенабо інгібітори COX-2, як рофекоксиб, целекоксиб) (див. розділ 2, "Попередження та застереження").
- Лікарські засоби, які використовуються для зниження кислотності шлунку (циметидин, омеprазол).
Використання Дапарокс з харчовими продуктами, напоями та алкоголем
Не слід споживати алкоголь та пароксетин одночасно.
Вагітність, годування грудьми та фертильність
Якщо ви вагітні або годуєте грудьми, вважаєте, що можете бути вагітною або плануєте вагітність, проконсультуйтеся з лікарем або фармацевтом перед прийняттям цього лікарського засобу.
Немає достатніх даних для визначення безпеки та ефективності використання пароксетину під час вагітності.
Деякі дослідження показали збільшення ризику вад серця у новонароджених дітей матерів, які приймали пароксетин у перші місяці вагітності. Ви та ваш лікар можете вирішити, чи краще змінити лікування на інший лікарський засіб або припинити пароксетин поступово. Однак, залежно від обставин, ваш лікар може порадити продовжувати лікування пароксетином.
Переконайтеся, що ваша акушерка та/або лікар знають, що ви приймаєте пароксетин. Якщо ви приймаєте Дапарокс на кінцевій стадії вагітності, може збільшитися ризик масивної вагінальної кровотечі після пологів, особливо якщо у вас є історія геморагічних розладів. Ваш лікар або акушерка повинні знати, що ви приймаєте Дапарокс, щоб能够и порадити вам.
Лікарські засоби, такі як пароксетин, можуть збільшувати ризик важкої хвороби у новонароджених, званої персистуючою гіпертензією легенів новонароджених (ПГЛН), коли їх приймають під час вагітності, особливо наприкінці вагітності, що робить немовлят більш дихаючими та блідими. Якщо це відбувається з вашим немовлям, негайно зв'яжіться з вашим лікарем або акушеркою. Якщо ви приймаєте пароксетин під час останніх 3 місяців вагітності, ваш новонароджений також може мати інші захворювання, які починаються впродовж перших 24 годин після пологів. Це включає проблеми з сном та харчуванням, дихальні проблеми, блідість, коливання температури, блювоту, тривалий плач, м'язову жорсткість або гіпотонію, апатію, тремор або нервозність. Якщо ваша дитина має будь-які з цих симптомів при народженні, зв'яжіться з вашим лікарем або акушеркою, які порадять вам.
Пароксетин проходить у невеликих кількостях до грудного молока. Якщо ви приймаєте пароксетин, обговоріть це з лікарем перед початком годування грудьми. Ви та ваш лікар можете вирішити, чи можете ви годувати грудьми, приймаючи пароксетин.
У дослідженнях на тваринах було показано, що пароксетин знижує якість сперми. Теоретично це може впливати на фертильність, хоча ще не відомо його вплив на людську фертильність.
Водіння автомобіля та використання машин
Пароксетин не впливає на здатність водити автомобіль або використовувати машини. Однак, цей лікарський засіб може викликати побічні ефекти (такі як розмитість зору, головокружіння, сонливість або сплутаність). Якщо ви відчуваєте будь-які з цих побічних ефектів, не водьте автомобіль та не керуйте інструментами або машинами, або будь-якою іншою діяльністю, яка вимагає уваги та концентрації. Це означає, що перед виконанням таких дій ви повинні спостерігати за вашою реакцією на пароксетин.
Дапарокс містить етанол (алкоголь), пропіленгліколь та натрій
Цей лікарський засіб містить 67 мг етанолу в кожних 20 краплях, що відповідає кількості 111 мг/мл (11% об./об.). Кількість в 20 краплях відповідає менш ніж 2 мл пива або 1 мл вина. Незначна кількість алкоголю в цьому лікарському засобі не матиме жодного помітного ефекту.
Цей лікарський засіб містить 490 мг пропіленгліколю в кожних 20 краплях, що відповідає 811 мг/мл.
Цей лікарський засіб містить менше 23 мг натрію (1 ммоль) на мл; це означає, що він практично "не містить натрію".
3. Як приймати Дапарокс 33 мг/мл краплі для прийому всередину у вигляді розчину
Слідкуйте точно інструкціям щодо застосування цього лікарського засобу, вказаним вашим лікарем. Про консультацію з вашим лікарем або фармацевтом, якщо у вас виникли питання.
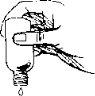 Пароксетин слід приймати переважно вранці разом з їжею.
Пароксетин слід приймати переважно вранці разом з їжею.
Принимайте пароксетин з водою, ніколи з іншого типу напою.
Пароксетин можна застосовувати за допомогою дозатора-крапельниці (доза 10 мг до 30 мг) або шприця (доза 40 мг до 60 мг).
Якщо ваш лікар рекомендує використовувати дозатор-крапельницю, виливайте необхідну кількість крапель у склянку, наповнену водою (200 мл), добре перемішайте суміш і випийте весь вміст склянки.
Щоб уникнути помилок при лічбі 40 крапель або більше, можливо, ваш лікар розгляне питання про призначення цього лікарського засобу у вигляді таблеток або використання шприця для введення пероральної суспензії (доза виражається в мл).
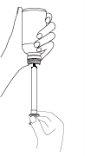
Якщо ваш лікар рекомендує використовувати шприц для прийому всередину, вставте наконечник шприця в пластикову крапельницю флакону, поверніть флакон догори дном і завантажте кількість мл, яку призначив лікар, всередину шприця. Випустіть вміст шприця у склянку, наповнену водою (200 мл), добре перемішайте і випийте весь вміст склянки.
Після кожного застосування промийте шприц водою і дайте йому висохнути на повітрі.
Рекомендована доза така:
- Епізод великої депресії
Рекомендована доза становить 20 мг (20 крапель) на добу. У нормальних умовах ви повинні почати відчувати полегшення протягом тижня, хоча ефекти можуть проявитися пізніше (наприклад, через два тижні). У разі недостатньої ефективності лікарського засобу ваш лікар може поступово збільшувати дозу з інтервалом 10 мг (10 крапель) до максимальної добової дози 50 мг (1,5 мл). Ваш лікар визначить період, протягом якого ви повинні продовжувати приймати краплі, який може тривати більше 6 місяців.
- Обсесивно-компульсивний розлад (ОКР)
Рекомендована доза становить 40 мг (1,2 мл) на добу, з початковою дозою 20 мг (20 крапель) на добу. У разі недостатньої ефективності лікарського засобу ваш лікар може поступово збільшувати дозу з інтервалом 10 мг (10 крапель). Максимальна добова доза становить 60 мг (1,8 мл). Ваш лікар визначить період, протягом якого ви повинні продовжувати приймати краплі, який може тривати кілька місяців або навіть більше.
- Тревожний розлад з агорафобією або без неї
Рекомендована доза становить 40 мг (1,2 мл) на добу, з початковою дозою 10 мг (10 крапель) на добу. У разі недостатньої ефективності лікарського засобу ваш лікар може поступово збільшувати дозу з інтервалом 10 мг (10 крапель). Максимальна добова доза становить 60 мг (1,8 мл). Початкова доза низька для уникнення загострення симптомів тревожного розладу на початку лікування. Ваш лікар визначить період, протягом якого ви повинні продовжувати приймати краплі, який може тривати кілька місяців або навіть більше.
- Соціальна тривожний розлад/фобія
Рекомендована доза становить 20 мг (20 крапель) на добу. У разі недостатньої ефективності лікарського засобу ваш лікар може поступово збільшувати дозу з інтервалом 10 мг (10 крапель). Максимальна добова доза становить 50 мг (1,5 мл). Ваш лікар визначить період, протягом якого ви повинні продовжувати приймати краплі, який може тривати довго, і протягом цього періоду лікування повинно бути періодично оцінено.
- Загальний тривожний розлад
Рекомендована доза становить 20 мг (20 крапель) на добу. У разі недостатньої ефективності лікарського засобу ваш лікар може поступово збільшувати дозу з інтервалом 10 мг (10 крапель). Максимальна добова доза становить 50 мг (1,5 мл). Ваш лікар визначить період, протягом якого ви повинні продовжувати приймати краплі, який може тривати довго, і протягом цього періоду лікування повинно бути періодично оцінено.
Пацієнти похилого віку
Рекомендована початкова доза для пацієнтів похилого віку така ж, як і початкова доза для інших дорослих пацієнтів, але максимальна добова доза не повинна перевищувати 40 мг (1,2 мл).
Застосування у дітей і підлітків
Пароксетин не повинен застосовуватися у дітей і підлітків молодше 18 років (див. розділ 2, "Діти та підлітки").
Пацієнти з нирковою або печінковою недостатністю
Якщо у вас є проблеми з печінкою або важка ниркова хвороба, ваш лікар повинен调整 дозу.
Тривалість лікування
Ваш лікар визначить період, протягом якого ви повинні продовжувати приймати пароксетин. залежно від вашої хвороби, ви можете потребувати приймати пароксетин протягом довгого часу. Ви повинні продовжувати приймати пароксетин протягом певного часу, навіть коли ваші симптоми зникнуть, щоб уникнути їх повернення. Не припиняйте лікування пароксетином без консультації з вашим лікарем.Якщо ви раптово припините лікування пароксетином, ви можете відчувати симптоми відміни, тому дозу слід поступово зменшувати (див. розділ 3, "Якщо ви припините лікування Дапароксом").
Якщо ви прийняли більше Дапароксу, ніж потрібно
У разі передозування або випадкового прийняття лікарського засобу зверніться негайно до вашого лікаря або фармацевта або телефонуйте до служби токсикологічної інформації, телефон: 91 562 04 20 (зазначаючи лікарський засіб і кількість, прийняту). Окрім відомих побічних ефектів (див. розділ 4, "Можливі побічні ефекти"), ви можете відчувати такі симптоми: гарячка і мимовільні скорочення м'язів.
Якщо ви забули прийняти Дапарокс
Не приймайте подвійну дозу для компенсації пропущених доз. Пропустіть пропущену дозу і приймайте наступну, коли це необхідно. Якщо у вас виникли питання, зверніться до вашого лікаря.
Якщо ви припините лікування Дапароксом
Не припиняйте лікування Дапароксом без консультації з вашим лікарем, і ніколи не припиняйте лікування раптово, оскільки це може спричинити симптоми відміни.
Ефекти, які ви можете відчувати, якщо припините приймати пароксетин, включають: головокружіння, порушення чуття (поколювання або відчуття печіння, відчуття електричних розрядів, звуки вух, свист, шум у вухах), тривогу, порушення сну (як яскраві сни або кошмари) і головний біль. Менше поширені ефекти включають: збудження, нудоту, тремор, сплутаність, потіння, емоційну нестабільність, порушення зору, сильні серцеві удари (аритмія), діарею та раздражливість (див. розділ 4, Можливі побічні ефекти).
Ці симптоми зазвичай починаються в перші дні після припинення лікування, але також можуть виникнути у пацієнтів, які забули прийняти дозу. Зазвичай, ефекти відміни зникають за два тижні. У деяких пацієнтів вони можуть бути більш серйозними або можуть тривати довше (2-3 місяці або більше). Якщо ви та ваш лікар вирішите припинити лікування пароксетином, добову дозу слід поступово зменшувати протягом кількох тижнів або місяців (починаючи з дози 10 мг на тиждень). Ви повинні завжди консультуватися з вашим лікарем перед зменшенням дози.
Якщо у вас є будь-які інші питання щодо застосування цього лікарського засобу, зверніться до вашого лікаря або фармацевта.
4. Можливі побічні ефекти
Як і всі лікарські засоби, цей лікарський засіб може спричиняти побічні ефекти, хоча не всі люди їх відчувають.
Зверніться до вашого лікаря або до лікарні негайно, якщо ви відчуваєте будь-який з наступних побічних ефектів під час лікування.
Побічні ефекти рідко трапляються(можуть впливати до 1 особи з 100)
- аномальна кровотеча, переважно гематоми на шкірі (екхімози) та гінекологічне кровотеча.
Побічні ефекти дуже рідко трапляються(можуть впливати до 1 особи з 1000)
- напади та судоми
- відчуття неспокою та гіперактивності з нездатністю сідати або залишатися на місці (акатизія)
- низькі концентрації натрію в крові (гіпонатріємія), переважно у пацієнтів похилого віку.
Побічні ефекти дуже рідко трапляються(можуть впливати до 1 особи з 10 000)
- алергічні реакції, які можуть бути серйознимиз пароксетином, включаючи свербіж і болючу еритему (уртикарію) або серйозні реакції, які спричиняють набухання шкіри, горла або язика, труднощі з диханням і/або свербіж (ангіоневротичний набухання). Якщо ви розвиваєте червоний висип з бугорками, набухання повік, обличчя, губ, рота або язика, починаєте відчувати свербіж або маєте труднощі з диханням (брак повітря) або ковтанням, і відчуваєте слабкість або головокружіння і, як наслідок, падаєте або втрачаєте свідомість, зверніться до вашого лікаря або до лікарні негайно.
- серотоніновий синдром (симптоми можуть включати збудження, сплутаність, потіння, галюцинації, гіперрефлексію, мимовільні скорочення м'язів (міоклонус), тремор та збільшення частоти серцевих скорочень (тахікардія).
- раптове збільшення тиску в оці (глаукома)
Побічні ефекти з невідомою частотою(не можуть бути оцінені на основі доступних даних)
- агресія, випадки думок/поведінки самоліквідації або суїциду були повідомлені під час лікування пароксетином або негайно після припинення лікування. Однак, ці симптоми також можуть бути спричинені основною хворобою.
- сильне вагінальне кровотеча незабаром після пологів (постнатальне кровотеча), див. "Вагітність, лактація та фертильність" у розділі 2 для більшої інформації.
Інші побічні ефекти
Побічні ефекти дуже часто трапляються(можуть впливати більше 1 особи з 10)
- нудота
- порушення статевої функції, такі як проблеми з еякуляцією, зниження статевого потягу, імпотенція у чоловіків та нездатність досягти оргазму.
Побічні ефекти часто трапляються(можуть впливати до 1 особи з 10)
- збільшення рівня холестерину в крові, зниження апетиту.
- сонливість, нездатність заснути (безсоння), збудження, яскраві сни (включно з кошмарами).
- головокружіння, тремор, головний біль, порушення концентрації (зниження концентрації)
- розмитість зору
- зевання
- запор, діарея, блювота, сухість у роті
- потіння
- збільшення ваги, відчуття загальної слабкості з втратою м'язової сили (астенія).
Побічні ефекти рідко трапляються(можуть впливати до 1 особи з 100)
- зниження кількості білих кров'яних тілець
- якщо ви пацієнт з цукровим діабетом, ви можете спостерігати втрату контролю над рівнями цукру в крові під час прийому пароксетину. Зверніться до вашого лікаря щодо корекції дози інсуліну або лікарських засобів для лікування цукрового діабету.
- сплутаність, уява речей, які насправді не існують (галюцинації)
- мимовільні рухи тіла або обличчя (екстрапірамідні розлади)
- розширення зіниці (мідріаз)
- швидкий серцевий ритм (синусова тахікардія)
- відчуття слабкості або головокружіння при раптовому піднятті (ортостатична гіпотонія)
- свербіж шкіри, свербіж (прурит)
- проблеми з опорожненням сечового міхура (уретральна стриктура) та нетримання сечі
Побічні ефекти дуже рідко трапляються(можуть впливати до 1 особи з 1000)
- ейфорія або надмірне збудження, яке спричиняє аномальне поведіння (манія, маніакальні періоди), тривогу, панічні атаки, втрату особистості
- нездоланна потреба рухати ногами (синдром неспокійних ніг)
- повільний серцевий ритм (брадикардія)
- підвищення рівня печінкових ферментів
- м'язовий біль (міалгія), суглобовий біль (артралгія)
- підвищення рівня пролактину в крові (гіперпролактинемія), яке може спричинити аномальне вироблення молока грудьми у чоловіків і жінок (галакторея) та порушення менструального циклу (включно з сильними або нерегулярними менструаціями, кровотечами між менструаціями та відсутністю або затримкою менструації).
Побічні ефекти дуже рідко трапляються(можуть впливати до 1 особи з 10 000)
- зниження кількості тромбоцитів у крові, з підвищенням ризику кровотечі або утворення гематом (тромбоцитопенія)
- затримання рідини та низькі концентрації натрію в крові внаслідок синдрому недостатньої секреції антидіуретичного гормону (СНДГ)
- шлунково-кишкова кровотеча
- печінкові розлади, такі як запалення (гепатит), іноді пов'язане з жовтяницею та/або печінковою недостатністю
- серйозні шкірні побічні ефекти (включно з еритемою мультиформою, синдромом Стівенса-Джонсона та токсичною епідермальною некролізом), кропив'янка, чутливість до сонячного світла.
- біль при ерекції (приапізм)
- набухання рук і/або ніг (периферичний едема)
Побічні ефекти з невідомою частотою(не можуть бути оцінені на основі доступних даних)
- скреготіння зубів
- звуки вух, свист, шум у вухах (тинітус)
- запалення товстої кишки (що спричиняє діарею)
Пацієнти, які приймають цей лікарський засіб, мають більший ризик переломів кісток.
Симптоми відміни, спостережені при припиненні лікування пароксетином
Часто: головокружіння, порушення чуття, порушення сну, тривога та головний біль.
Рідко: збудження, нудота, потіння, тремор, сплутаність, емоційна нестабільність, порушення зору, сильні серцеві удари, діарея та раздражливість.
Ці симптоми зазвичай є легкими або помірними та зникають самі собою. Не припиняйте лікування пароксетином без консультації з вашим лікарем, і ніколи не припиняйте лікування раптово, оскільки це може спричинити симптоми відміни (див. розділ 3, "Якщо ви припините лікування Дапароксом").
Додаткові побічні ефекти у дітей і підлітків
Коли діти та підлітки молодше 18 років приймали пароксетин, принаймні 1 з 100, але менше 1 з 10 дітей/підлітків відчували один з наступних побічних ефектів: емоційні зміни (плакання та зміни настрою), самоліквідація, думки про самогубство, ворожнє та не дружнє поведіння, втрату апетиту, тремор, потіння, гіперактивність, збудження, нудоту, біль у животі та нервозність.
Звіт про побічні ефекти
Якщо ви відчуваєте будь-який побічний ефект, зверніться до вашого лікаря або фармацевта, навіть якщо це можливі побічні ефекти, які не перелічені в цьому листку. Ви також можете повідомити про них безпосередньо через Іспанську систему моніторингу лікарських засобів для людини https://www.notificaram.es. Надсилаючи повідомлення про побічні ефекти, ви можете допомогти надати більше інформації про безпеку цього лікарського засобу.
5. Зберігання Дапароксу 33 мг/мл крапель для прийому всередину у вигляді розчину
Тримайте цей лікарський засіб поза зоною досяжності дітей.
Не використовувати цей лікарський засіб після закінчення терміну придатності, вказаного на упаковці після "CAD". Термін придатності - останній день місяця, який вказано.
Цьому лікарському засобу не потрібні особливі умови зберігання.
Після відкриття розчин повинен бути використаний протягом 56 днів.
Лікарські засоби не повинні бути викинуті у водопровід або сміття. Відкладайте упаковки та лікарські засоби, які вам не потрібні, у пункт збору SIGRE в аптеці. У разі сумнівів зверніться до вашого фармацевта щодо того, як позбутися упаковок та лікарських засобів, які вам не потрібні. Таким чином, ви допоможете захистити навколишнє середовище.
6. Зміст упаковки та додаткова інформація
Склад Дапароксу 33 мг/мл крапель для прийому всередину у вигляді розчину
- Активний інгредієнт - пароксетин (у вигляді месилату).
1 мл Дапароксу містить 33,1 мг пароксетину (у вигляді месилату).
Одна крапля містить 1 мг пароксетину (у вигляді месилату).
- Інші компоненти (експіцієнти) такі:
Содій сакхарин (Е954)
Ацесульфам К (Е950)
Аромат перцевої м'яти (есенційна олія перцевої м'яти, ментол, евкаліптове масло, етанол, вода)
Полісорбат 80 (Е433)
Етанол (111 мг/мл)
Пропіленгліколь (Е1520).
Вигляд Дапароксу та вміст упаковки
Дапарокс - прозора рожева або коричнева рідина, упакована у скляний флакон об'ємом 20 мл, який містить не менше 18,5 мл розчину.
Флакон упакований у паперову коробку та містить дозатор-крапельницю та кришку, захищену від дітей. До складу упаковки також може входити шприц для перорального застосування.
Можливо, що тільки деякі розміри упаковок будуть випускатися.
Власник авторизації на розміщення лікарського засобу на ринку та відповідальна особа за виробництво
Власник:
ANGELINI PHARMA ESPAÑA, S.L.
c/ Антоніо Мачадо, 78-80.
3-ій поверх, модуль А-будівля Австралія
08840 Віладеканс, Барселона (Іспанія)
Телефон: 932 534 500
Відповідальна особа за виробництво:
Synthon BV
Microweg 22
6545 CM Неймеген
Нідерланди
Synthon Hispania, S.L.
- Кастельйо, 1
Промислова зона Лас-Салінас
08830 Сант-Бой-де-Льобрегат (Барселона) - Іспанія
Hormosan Pharma GmbH
Ханавер-Ландштрасе 139 - 143
60314 Франкфурт-на-Майні - Німеччина
Цей лікарський засіб авторизований у державах-членах Європейського економічного простору під наступними назвами
Австрія: Еннос 33,1 мг/мл, розчин для перорального прийому
Німеччина: Пароксетин-Гормозан 33,1 мг/мл.
Італія: Дапагут 33,1 мг/мл, пероральні краплі, розчин
Нідерланди: Парміт
Іспанія: Дапарокс 33 мг/мл краплі для прийому всередину у вигляді розчину
Дата останнього перегляду цього листка: Грудень 2023
Детальна та актуальна інформація про цей лікарський засіб доступна на сайті Іспанського агентства лікарських засобів та медичних продуктів (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es

Скільки коштує ДАПАРОКС 33 мг/мл ОРАЛЬНИЙ РОЗЧИН У КРАПЛЯХ в Іспанії у 2026 році?
ДАПАРОКС 33 мг/мл ОРАЛЬНИЙ РОЗЧИН У КРАПЛЯХ коштує в середньому 7.18 євро у січень, 2026 році. Ціна може змінюватися залежно від регіону, аптеки та наявності рецепта. Рекомендуємо перевіряти актуальну вартість у місцевих аптеках або через онлайн-сервіси.
- Країна реєстрації
- Середня ціна в аптеках7.18 EUR
- Діючі речовини
- Потрібен рецептТак
- Виробник
- Інформація є довідковою і не є медичною порадою. Перед прийомом будь-яких препаратів обов'язково проконсультуйтеся з лікарем. Oladoctor не несе відповідальності за медичні рішення, прийняті на основі цього контенту.
- Альтернативи до ДАПАРОКС 33 мг/мл ОРАЛЬНИЙ РОЗЧИН У КРАПЛЯХФорма випуску: ТАБЛЕТКА, 20 мгДіючі речовини: paroxetineВиробник: Angelini Pharma Espana S.L.Потрібен рецептФорма випуску: ТАБЛЕТКА, 20 мгДіючі речовини: paroxetineВиробник: Glaxosmithkline S.A.Потрібен рецептФорма випуску: ТАБЛЕТКА, 20 мг пароксетину гідрохлоридуДіючі речовини: paroxetineВиробник: Glaxosmithkline S.A.Потрібен рецепт
Аналоги ДАПАРОКС 33 мг/мл ОРАЛЬНИЙ РОЗЧИН У КРАПЛЯХ в інших країнах
Найкращі аналоги з тією самою діючою речовиною та терапевтичним ефектом.
Аналог ДАПАРОКС 33 мг/мл ОРАЛЬНИЙ РОЗЧИН У КРАПЛЯХ у Poland
Аналог ДАПАРОКС 33 мг/мл ОРАЛЬНИЙ РОЗЧИН У КРАПЛЯХ у Ukraine
Лікарі онлайн щодо ДАПАРОКС 33 мг/мл ОРАЛЬНИЙ РОЗЧИН У КРАПЛЯХ
Консультація щодо дозування, побічних ефектів, взаємодій, протипоказань та поновлення рецепта на ДАПАРОКС 33 мг/мл ОРАЛЬНИЙ РОЗЧИН У КРАПЛЯХ – за рішенням лікаря та згідно з місцевими правилами.










