
How to use Levosert
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: information for the user
Levosert, 52 mg (20 micrograms/24 hours), intrauterine therapeutic system
Levonorgestrel
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Levosert and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Levosert
- 3. How to use Levosert
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Levosert
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Levosert and what is it used for
Levosert is an intrauterine therapeutic system for use in the uterus, where it gradually releases a hormone called levonorgestrel.
It can be used in the following cases:
Contraception method (prevention of pregnancy)
The Levosert system is an effective, long-term, and temporary (reversible) method of contraception.
The Levosert system prevents pregnancy by inhibiting the growth of the endometrium,
thickening of cervical mucus (in the cervical canal), which prevents sperm from entering the egg and inhibiting ovulation in some women. It may also have a local effect on the endometrium caused by the presence of the intrauterine therapeutic system in the shape of the letter T.
Treatment of excessive menstrual bleeding
The Levosert system is also used to reduce the heaviness of menstrual bleeding and may be used to treat heavy menstrual bleeding (periods), known as menorrhagia. The hormone contained in the Levosert system acts to inhibit the monthly development of the endometrium, so there is less bleeding every month.
The Levosert system is effective for eight years as a contraceptive method (prevention of pregnancy) and for five years in the indication for excessive menstrual bleeding. In order to ensure contraception, the Levosert system should be removed before the end of the eighth year and immediately replaced with a new Levosert system if further use is necessary. In the case of immediate insertion of the system, no additional protection is required. In the case of the indication for excessive menstrual bleeding, the Levosert system should be replaced before the end of the fifth year. If symptoms have not returned by the end of the fifth year of use, further use after five years may be considered. The system should be removed or replaced no later than after 8 years.
Children and adolescents
The Levosert system is not indicated for use before the first menstrual period (menarche).
2. Important information before using Levosert
Before inserting the Levosert system, the doctor or nurse may order several tests to ensure that the Levosert therapeutic system is suitable for the patient.
This includes a pelvic exam, but other tests may also be performed, such as a breast exam, if the doctor or nurse considers it appropriate.
Before inserting the Levosert system, patients must be effectively cured of genital infections.
The doctor or nurse should be informed if the patient has epilepsy, as a seizure may occur, although rarely, during the insertion of the Levosert system.
Some women may feel weak after the procedure. This is a normal condition, and the doctor or nurse will inform the patient to rest for a while.
Not all women can use the intrauterine therapeutic system Levosert.
The Levosert intrauterine therapeutic system should not be used if the patient:
- is pregnant or suspects pregnancy;
- has or has had inflammatory conditions of the pelvic organs;
- has abnormal or unpleasant vaginal discharge or vaginal itching, which may indicate an infection;
- has or has had endometritis after childbirth;
- has or has had uterine infections after childbirth or miscarriage within the last 3 months;
- has or has had cervical inflammation;
- has or has had abnormal cervical cytology test results (changes in the cervix);
- has or has had liver disorders;
- has uterine abnormalities, including uterine fibroids, especially if they deform the uterine cavity;
- has abnormal vaginal bleeding;
- has any disease that makes the patient prone to infections. The doctor will inform the patient if this situation applies to them;
- has or has had a hormone-dependent tumor, such as breast cancer;
- has or has had any type of tumor or suspected tumor, including blood cancer (leukemia), cervical or uterine cancer, unless it is in remission;
- has or has had trophoblastic diseases (trophoblast provides nutrients to the fetus). The doctor will inform the patient if this situation applies to them;
- is allergic to levonorgestrel or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions
The Levosert system, like other hormonal contraceptives, does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) or other sexually transmitted diseases (such as chlamydia, genital herpes, genital warts, gonorrhea, hepatitis B virus, and syphilis). Only the use of condoms can provide protection against these diseases.
The Levosert system should not be used as emergency contraception (after unprotected sex).
Before starting to use the Levosert intrauterine therapeutic system, the patient should discuss it with their doctor if:
- -the patient has migraines, dizziness, vision disturbances, exceptionally severe headaches, or more frequent headaches than usual;
- the patient has jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes);
- the patient has diabetes (high blood sugar levels), high blood pressure, or abnormal blood lipid levels;
- the patient has blood cancer (including leukemia) that is currently in remission;
- the patient is taking long-term steroid therapy;
- the patient has ever had an ectopic pregnancy (fetal development outside the uterus) or ovarian cysts;
- the patient has or has had severe arterial disease, such as a heart attack or stroke;
- the patient has had blood clots (thrombosis) in the past;
- the patient is taking any other medicines, as some medicines may inhibit the action of the Levosert system;
- the patient has irregular bleeding;
- the patient has seizures (epilepsy).
If any of the above conditions occur or have occurred, the doctor will decide whether the Levosert system can be used.
If the patient is using the Levosert system and any of the above conditions occur for the first time, the doctor should also be informed.
The following subjective and objective symptoms may indicate an ectopic pregnancy (pregnancy developing outside the uterus) and, in such a case, the patient should immediately consult a doctor (see also "Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility"):
- Menstrual bleeding has stopped, and then persistent bleeding or pain has occurred.
- Severe or persistent abdominal pain has occurred.
- The patient has experienced normal pregnancy symptoms, but also bleeding and dizziness.
- A pregnancy test is positive.
If the patient experiences painful swelling of the leg, sudden chest pain, or difficulty breathing, they should see a doctor or nurse as soon as possible, as these may be symptoms of a blood clot. It is essential that any blood clots are treated as soon as possible.
The patient should also immediately consult a doctor if they experience persistent abdominal pain, fever, pain during sex, or unusual bleeding. If the patient experiences severe pain or fever shortly after inserting the Levosert system, it may mean that a severe infection has developed, which must be treated immediately.
Expulsion
Uterine contractions during menstrual bleeding may sometimes cause the system to move or be expelled. This is more likely if the woman is overweight at the time of insertion or if she has had heavy menstrual bleeding in the past. If the system is not in place, it may not work as intended, and the risk of pregnancy increases. Expulsion of the system results in loss of protection against pregnancy.
Possible symptoms of expulsion include vaginal bleeding or abdominal pain, but the Levosert system can also be expelled without being noticed. Since the Levosert system reduces menstrual bleeding, the intensity of these bleedings may be a sign of expulsion or displacement of the system.
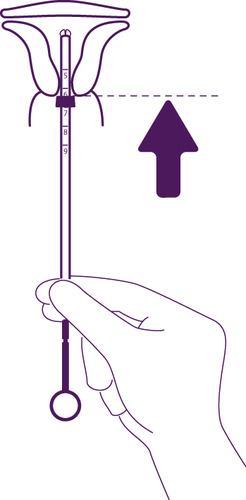
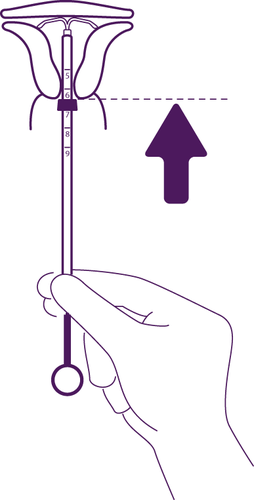
It is recommended to check with your fingers (e.g., during bathing) whether the threads are in the correct position. See also section 3 "How to use Levosert - Self-checking of the correct position of the Levosert system". If symptoms suggesting expulsion of the system occur or the threads cannot be felt in the cervical canal area, the patient should use other contraceptive methods (such as condoms) and consult a doctor.
Psychiatric disorders
Some women using hormonal contraceptives, including Levosert, have reported depression or low mood. Depression can be severe and sometimes lead to suicidal thoughts. If mood changes and symptoms of depression occur, the patient should consult a doctor as soon as possible for further medical advice.
Levosert and smoking
Women should quit smoking. Smoking increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, or blood clots.
Using tampons and menstrual cups
It is recommended to use sanitary pads. If tampons or menstrual cups are used, they should be changed carefully to avoid pulling on the Levosert system threads.
Levosert and other medicines
Since the mechanism of action of the Levosert system is primarily local, taking other medicines should not increase the risk of pregnancy during the use of the Levosert system.
However, it is recommended that the patient tells their doctor about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take, including those available without a prescription. This includes:
- medicines used to treat epilepsy (such as lamotrigine, barbiturates, phenytoin, primidone, carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, felbamate)
- medicines used to treat tuberculosis (such as rifampicin, rifabutin)
- medicines used to treat HIV and hepatitis C virus infections (such as nevirapine, efavirenz, ritonavir, nelfinavir)
- medicines used to treat fungal infections (such as griseofulvin, itraconazole, ketoconazole)
- medicines used to treat bacterial infections (such as clarithromycin, erythromycin)
- medicines used to treat certain heart conditions, high blood pressure (such as verapamil, diltiazem)
- herbal medicines containing St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum)
- grapefruit juice
The Levosert system should not be used at the same time as other hormonal contraceptive methods.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
The Levosert system should not be used during pregnancy or if pregnancy is suspected.
Can the patient become pregnant while using the Levosert system?
Women using the Levosert system very rarely become pregnant.
Lack of menstrual bleeding does not necessarily mean that the woman is pregnant. In some women, menstrual bleeding may not occur during the use of the intrauterine system.
If menstrual bleeding does not occur for 6 weeks, a pregnancy test should be considered. If the result is negative, there is no need to perform another test unless other symptoms suggesting pregnancy occur, such as nausea, fatigue, and breast tenderness.
If the woman becomes pregnant with the Levosert system in place, she should immediately consult a doctor to have the Levosert system removed. Removal may cause a miscarriage. However, leaving the Levosert system in place during pregnancy may increase not only the risk of miscarriage but also the risk of preterm birth. If the Levosert system cannot be removed, the patient should discuss the benefits and risks of continuing the pregnancy with their doctor. If the pregnancy is continued, it should be monitored closely by the doctor, and the patient should immediately inform their doctor if symptoms such as abdominal cramps, abdominal pain, or fever occur.
Levosert contains a hormone called levonorgestrel, and there have been single reports of its effect on the genital organs of girls exposed to levonorgestrel released from an intrauterine device left in the uterus.
What should the patient do if they want to have a child?
If the patient wants to become pregnant and have a child, they should ask their doctor to remove the Levosert system. After removal of the system, natural fertility returns soon.
Can the patient breastfeed while using the Levosert system?
Very small amounts of the hormone in the Levosert system have been detected in breast milk, but its concentration is lower than with any other hormonal contraceptive method. There is no need to worry about the risk to the newborn. If the woman wants to breastfeed, she should discuss it with her doctor.
Driving and using machines
The effect on the ability to drive and use machines is not known.
Levosert contains barium sulfate.
The Levosert system's T-shaped frame contains barium sulfate, so it may be visible during X-ray examination.
3. How to use Levosert
The system should only be inserted by a doctor or a specially trained nurse (see the special instruction for insertion included in the packaging).
These individuals will explain the insertion procedure and any risks associated with its use.
Before inserting the Levosert system, the patient will be examined by a doctor or nurse. If the patient has any concerns about using the system, they should discuss them with their doctor or nurse.
During the insertion procedure, the patient may experience some discomfort. The patient should inform their doctor about any pain they feel.
Starting to use the Levosert system
- Before inserting the Levosert system, it should be ensured that the patient is not pregnant.
- The Levosert system should be inserted within 7 days of the start of menstruation. If the Levosert system is inserted during these days, the medicine will start working immediately and prevent pregnancy.
- If the Levosert system cannot be inserted within 7 days of the start of menstruation or if menstruation occurs at an unpredictable time, the Levosert system can be inserted on any other day. In this case, the patient should not have unprotected sex and should have a negative pregnancy test before insertion. Additionally, the Levosert system may not prevent pregnancy immediately. Therefore, the patient should use a mechanical contraceptive method (e.g., condoms) or abstain from sex for 7 days after insertion.
- The Levosert system is not intended for use as emergency contraception (after unprotected sex).
Starting to use the Levosert system after childbirth
- The Levosert system can be inserted after childbirth, when the uterus has returned to its normal size, but not earlier than 6 weeks after childbirth (see section 4 "Possible side effects - Perforation").
- More information on the timing of insertion can be found in the "Starting to use Levosert" section above.
Starting to use the Levosert system after a miscarriage
The Levosert system can be inserted immediately after a miscarriage, if the pregnancy lasted less than 3 months, provided that there are no genital infections. The Levosert system will then start working immediately.
Replacing the Levosert system
The Levosert system can be replaced with a new Levosert system at any time during the menstrual cycle. The Levosert system will then start working immediately.
Switching from another contraceptive method (such as combined hormonal contraceptives, implant)
- The Levosert system can be inserted immediately if there is sufficient certainty that the patient is not pregnant.
- If more than 7 days have passed since the last menstrual bleeding, the patient should abstain from sex or use additional contraceptive protection for the next 7 days.
Inserting the Levosert system
The examination by a healthcare professional before inserting the system may include:
- a cervical smear (cytological smear)
- a breast exam
- if necessary, other tests, such as tests for infections, including sexually transmitted diseases, pregnancy test. The healthcare professional will also perform a gynecological examination to determine the position and size of the uterus.
After the gynecological examination
- A device called a speculum is inserted into the vagina, and the cervix may be cleaned with an antiseptic solution. Then, the Levosert system is inserted into the uterus using a thin, flexible plastic tube (insertion tube). Before inserting the tube into the cervix, local anesthesia may be applied.
- Some women may feel dizzy or faint during or after the insertion of the Levosert system, or after its removal.
- Pain and bleeding may occur during or immediately after the insertion.
After the Levosert system has been inserted, the patient should receive a reminder card for follow-up examinations from their doctor. The patient should bring this card with them to each scheduled visit.
How soon will the Levosert system start working?
Contraception
If the Levosert system is inserted during menstruation or within 7 days of the start of menstruation, or if the patient already has a system in place and it is time to replace it, or if the patient has just had a miscarriage, the patient is protected against pregnancy from the moment the intrauterine system is inserted. The likelihood of pregnancy is about 2 cases per 1000 women in the first year of using the system. The risk of pregnancy may increase if the Levosert system is expelled or if there is a perforation.
Excessive menstrual bleeding
After using the Levosert system, menstrual bleeding usually decreases significantly within 3 to 6 months of therapy.
How often should the system be checked?
The Levosert system should be checked 4 to 6 weeks after insertion, and then regularly, at least once a year, until it is removed. The doctor may determine how often and what kind of checks are required in each case. The patient should bring the reminder card they received from their doctor to each scheduled follow-up visit. Additionally, the patient should consult their doctor if any of the symptoms described in section 2 "Warnings and precautions" occur.
Furthermore, the patient should see their doctor as soon as possible if they experience:
- painful swelling of the leg,
- sudden chest pain,
- difficulty breathing, as these may be symptoms of a blood clot.
How can it be determined if the system is in place?
After each menstrual bleeding, the woman can check for the presence of two threads attached to the lower edge of the system. The doctor will show them how to do this.
Do not pullon the threads, as this can cause the system to be accidentally removed. If the woman cannot find the threads, they should see their doctor or nurse as soon as possible and, in the meantime, not have unprotected sex or use barrier contraception (such as condoms). The threads may have moved up into the uterus or cervix. If the threads are still not found by the doctor or nurse, they may have broken off, or the Levosert system may have been expelled, and in rare cases, it may have perforated the uterine wall (uterine perforation, see section 4).
What happens if the system is expelled?
If the system is expelled, either completely or partially, it will not provide protection against pregnancy.
Expulsion of the system is rare and may occur during menstruation without the patient noticing, but it is possible. A symptom may be an unusual increase in menstrual bleeding.
The patient should inform their doctor or clinic staff if they experience any unexpected changes in their bleeding pattern.
Removing the Levosert system
The Levosert system should be removed or replaced after 8 years of use to ensure contraception and after 5 years of use in the case of heavy menstrual bleeding or earlier if heavy or bothersome menstrual bleeding returns. If symptoms have not returned by the end of the fifth year of use, further use after five years may be considered. The system should be removed or replaced no later than after 8 years. The doctor can easily remove the system at any time, after which the patient can become pregnant. Some women may feel dizzy or faint during or after the removal of the Levosert system. Pain and bleeding may occur during the removal of the Levosert system.
Continuing contraception after removal of the system
If the patient does not plan to become pregnant, the Levosert system should not be removed after the seventh day of the menstrual cycle (menstruation), unless the patient is using other contraceptive methods (e.g., condoms) for at least 7 days before removal.
In the case of irregular periods or amenorrhea, the patient should use mechanical contraception for 7 days before removal.
A new Levosert system can also be inserted immediately after removal of the previous one, in which case additional protection is not necessary. If the patient does not want to continue using the same method, they should ask their doctor for advice on other effective contraceptive methods.
How does the Levosert system affect menstrual bleeding?
For all patients using the Levosert system
Many women experience spotting (small amounts of blood) in the first 3-6 months after insertion of the system. Some women may have prolonged or heavier menstrual bleeding.
The patient may experience heavier bleeding, usually within the first 2 to 3 months, before the reduction in blood loss. It is possible that the number of days of bleeding and the amount of blood lost each month will decrease gradually. This is due to the effect of the hormone (levonorgestrel) on the endometrium.
If the patient has the Levosert system inserted to reduce excessive menstrual bleeding
Levosert usually significantly reduces the heaviness of menstrual bleeding within 3 to 6 months of treatment. However, before the heaviness of bleeding is reduced, menstrual bleeding may be heavier during the first 2 to 3 months of treatment. If there is no significant reduction in bleeding after 3 to 6 months, other treatment methods should be considered.
If the Levosert system has been in place for some time and there are changes in bleeding patterns, the patient should consult their doctor or other healthcare professional.
If the patient has any questions about using this medicine, they should consult their doctor.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The most common side effects of the Levosert system occur within the first few months after insertion of the system and decrease over time.
If any of the following serious side effects occur, the patient should immediately consult their doctor or nurse:
- Severe pain or fever occurring soon after insertion of the systemmay indicate that the patient has developed a severe infection, which must be treated immediately. In rare cases, a very severe infection (sepsis) may occur.
- Severe pain and persistent bleeding, as this may be a sign of uterine perforation. Perforation is not very common but usually occurs during the insertion of the Levosert system, although it may only be diagnosed later. If this happens, the Levosert system will be removed; very rarely, this condition may require surgery. The risk of perforation is low, but it increases in breastfeeding women and in women who have given birth to a child less than 36 weeks before insertion of the system, and the risk may also be increased in women with a permanently retroverted uterus (retroversion of the uterus). If uterine perforation is suspected, the patient should consult their doctor and inform them that they have a Levosert system, especially if it is not the doctor who inserted the system. Possible objective and subjective symptoms of perforation may include:
- severe pain (resembling menstrual cramps) or more severe pain than expected,
- increased bleeding (occurring after insertion of the system),
- pain or bleeding lasting longer than a few weeks,
- sudden changes in menstrual bleeding,
- pain during sex,
- the patient cannot find the Levosert system threads (see section 3 "How to use Levosert - How to check if the system is in place?").
- Abdominal pain, especially if the patient has a fever or has not had menstrual bleeding or has had unexpected bleeding, as this may indicate an ectopic pregnancy. The overall risk of ectopic pregnancy in women using the Levosert system is low. However, if a woman becomes pregnant while using the Levosert system, the relative likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy increases.
Very common(may occur in more than 1 in 10 women) side effects:
- changes in menstrual bleeding. Spotting, shorter or longer menstrual bleeding, painful menstruation may occur. Although the Levosert system usually results in a significant reduction in menstrual bleeding within 3 to 6 months of treatment, in the first 2 to 3 months, menstrual bleeding may be heavier before the reduction in blood loss. Menstrual bleeding may completely stop. If there is no significant reduction in blood loss within 3 to 6 months, other treatment methods should be considered;
- ovarian cysts. These are fluid-filled blisters in the ovary;
- bacterial or fungal infections of the vagina or external genitalia (vulva);
- acne (pimples);
- pain or bleeding during insertion of the system.
Common(may occur in up to 1 in 10 women) side effects:
- depression, nervousness, or other mood changes;
- decreased libido;
- headaches;
- migraines;
- feeling weak (pre-syncope);
- dizziness;
- abdominal, pelvic, or back pain;
- discomfort in the abdominal cavity;
- nausea;
- bloating;
- vomiting;
- painful menstruation;
- excessive vaginal discharge;
- vulvovaginitis
- breast tenderness, breast pain;
- pain during sex;
- uterine contractions;
- expulsion of the intrauterine therapeutic system Levosert;
- weight gain.
Uncommon(may occur in up to 1 in 100 women) side effects:
- genital infections, which may cause: vaginal itching, pain when urinating, or abdominal pain (abdominal cramps) associated with inflammation of the uterus, ovaries, or fallopian tubes;
- fainting;
- acne;
- cervicitis;
- swelling or edema of the legs or ankles;
- increased hair growth on the face and body;
- hair loss;
- skin itching (pruritus);
- skin discoloration or increased pigmentation, especially on the face (chloasma);
- ectopic pregnancy;
- perforation (puncture) of the uterine wall (see above "serious side effects").
Rare(may occur in up to 1 in 1000 women) side effects:
- rash, itching.
Severe pain or fever occurring soon after insertion of the system may indicate that the patient has developed a severe infection, which must be treated immediately. In rare cases, a very severe infection (sepsis) may occur.
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, the patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Levosert
Store in the original packaging. Store the sachet in the outer carton to protect it from light. The sachet should be stored tightly closed. The packaging should only be opened by a doctor or a person from the clinic.
The medicine should be stored out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the sachet and outer packaging after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
The batch number is stated on the packaging after the abbreviation "Lot".
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Levosert contains
- The active substance of the medicine is 52 mg of levonorgestrel. The hormone is placed in a substance called polydimethylsiloxane. It is also coated with a membrane (coating) made of polydimethylsiloxane.
What Levosert looks like and what the packaging contains
- The Levosert system consists of a small T-shaped frame made of a plastic material called polypropylene. This design of the system allows for the gradual release of the hormone into the uterus.
- The system also contains two thin threads made of polypropylene, dyed with copper phthalocyanine, blue. The threads are attached to the lower part of the frame. They allow the doctor to easily remove the system and the patient to check that the system is in place.
Levosert intrauterine therapeutic system with an insertion device is packaged individually in a sachet consisting of 2 sheets: a transparent polyester film and a removable HDPE lid.
Each packaging contains one intrauterine therapeutic system in a tearable sachet, which is individually packaged in a cardboard box with a patient information leaflet and a patient reminder card.
Marketing authorization holder
GEDEON RICHTER POLSKA Sp. z o.o.
ul. Ks. J. Poniatowskiego 5
05-825 Grodzisk Mazowiecki
Manufacturer
Gedeon Richter Plc.
Gyömrői út 19-21
1103 Budapest
Hungary
Odyssea Pharma SRL
Rue du Travail 16
4460 Grâce Hollogne
Belgium
To obtain more detailed information about the medicine and its names in other EU member states, the patient should contact:
GEDEON RICHTER POLSKA Sp. z o.o.
Medical Department
ul. ks. J. Poniatowskiego 5
05-825 Grodzisk Mazowiecki
phone: +48 (22)755 96 48
[email protected]
Date of last revision of the leaflet: November 2024 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following information is intended for healthcare professionals only
See: special instruction included in the packaging
Instructions for use and storage
Levosert, 52 mg (20 micrograms/24 hours), intrauterine therapeutic system
Levonorgestrel
Checklist for the prescribing doctor:
Before prescribing and/or inserting the Levosert system, the doctor should ensure that:
- The patient meets all the indications for adjusting contraception or has excessive menstrual bleeding and meets the criteria for the duration of treatment, which is up to eight or five years.
- The patient card included in the packaging has been completed and given to the patient (each case of using the system for longer than eight years for contraception and/or for the treatment of excessive menstrual bleeding should be reported as off-label use).
Instructions for inserting the system
The doctor should carefully read the following instructions, as there may be differences in the type of system compared to other intrauterine devices used previously.
For insertion by a healthcare professional using an aseptic method.
The Levosert system should only be inserted by healthcare professionals with experience in inserting intrauterine therapeutic systems (IUS) and/or who have received appropriate training in inserting the Levosert system and have carefully read this instruction before inserting the Levosert system.
The Levosert system is supplied in a sterile package, which should not be opened until the time of use. It should not be re-sterilized. The system can only be used once.
The unpackaged system should be inserted under aseptic conditions. If the sterile packaging is damaged, the system should be discarded (see section 6.6 of the Summary of Product Characteristics). The system should not be used if the inner packaging is damaged or open. The system should not be used after the expiry date stated on the box and sachet after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
More information on the timing of insertion can be found in the Summary of Product Characteristics, section 4.2.
The Levosert system is supplied with a patient reminder card included in the outer packaging. The patient reminder card should be completed and given to the patient after insertion of the system.
Preparation for insertion
- The patient should be examined to rule out contraindications to the insertion of the Levosert system (see sections 4.3 and 4.4 in the "Medical examination" section).
- A speculum should be inserted, the cervix visualized, and then the cervix and vagina cleaned with an appropriate antiseptic solution.
- If necessary, the assistance of an assistant may be required.
- The anterior lip of the cervix should be grasped with a surgical hook or other forceps to stabilize the uterus. If the uterus is retroverted, it may be more appropriate to grasp the posterior lip of the cervix. To straighten the cervical canal, the cervix can be gently pulled with the forceps. The forceps should remain in place, and gentle traction on the cervix should be maintained throughout the insertion procedure.
- A sound should be inserted through the cervical canal to the uterine fundus to measure the depth. If the uterine depth is less than 5.5 cm, the insertion should be stopped. The position of the uterine cavity and any intrauterine abnormalities (e.g., septum, submucous fibroids) or a previously inserted intrauterine contraceptive that has not been removed should be confirmed. If difficulties are encountered, consideration should be given to dilating the cervix. If cervical dilation is necessary, consideration should be given to using analgesics and/or a cervical block.
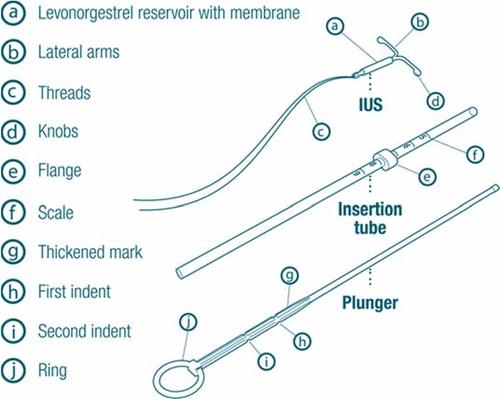
Description
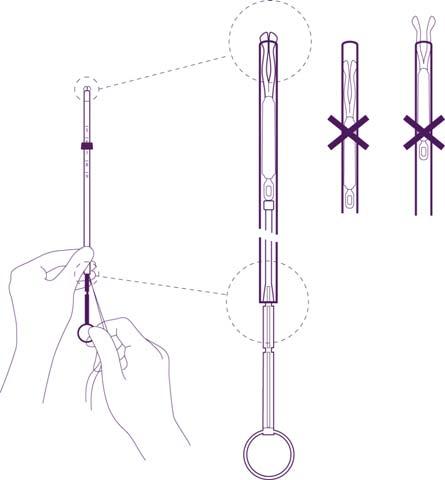
Figure 1
- a- levonorgestrel reservoir with membrane
- b- arms
- c- threads
- d- bulge
- e- collar
- f- scale
- g- thickened section with marking
- h- first narrowing
- i- second narrowing
- j- IUS ring - intrauterine system Insertion tube– introduction tube Plunger- piston
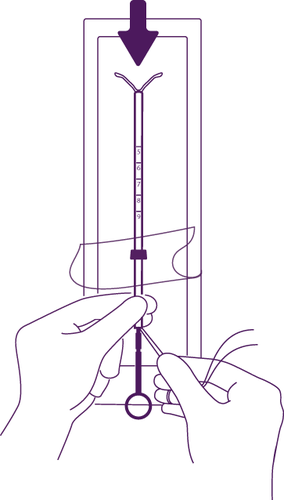
Preparations for system insertion
Figure 2
Figure 3
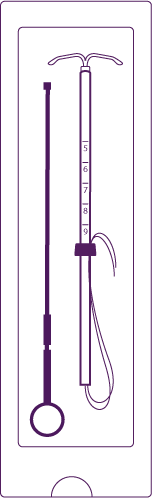
Load the piston and intrauterine system
into the introduction tube
Open the sachet partially (to about 1/3
of the length from the bottom) and insert the piston into the introduction tube.
Release the threads from under
the collar, so that they hang freely.
Pull the thread and load the intrauterine system
into the introduction tube. The arms of the intrauterine system
must be in one plane with the flat
surface of the collar.
Figure 4
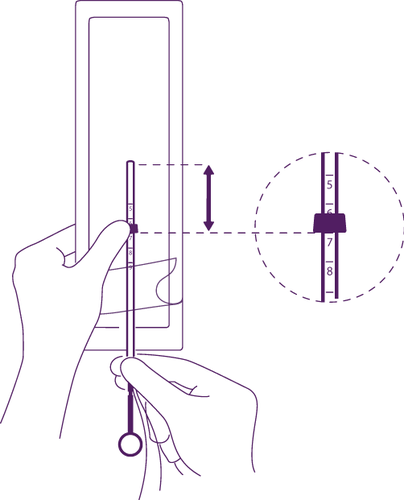
Set the lower edge of the collar to
the depth measured during uterine sounding
of the uterus
Set the blue collar so that its
lower edge indicates the measured
uterus depth. The flat surfaces
of the collar must always remain
in a parallel position to the arms.
This will allow the correct opening of the arms
inside the uterine cavity.
Set the intrauterine system
in the correct position in the introduction tube
Hold the piston firmly, pull the threads
and move the tube so that the intrauterine system
is set in the correct position.
The bulges on the transverse arms must
touch each other, slightly above
the upper edge of the introduction tube
(enlargement 1), while the lower edge
of the tube should be aligned with the first
narrowing on the piston (enlargement 2).
If the tube is not aligned with the first
narrowing on the piston, you should pull the threads more firmly.
Figure 5
Application
Figure 6
Insert the applicator with the intrauterine system
into the cervical canal of the uterus, until the blue
collar comes into contact with the cervix
Remove the applicator with the intrauterine system
completely from the sachet, holding the piston
firmly with the introduction tube, set in the correct position.
Insert the set into the cervical canal
of the uterus, until the blue collar comes into contact with the cervix.
Release the arms of the intrauterine system
Figure 7
Hold the piston, release the threads
and pull the introduction tube, until its lower edge is aligned with the second
narrowing on the piston.
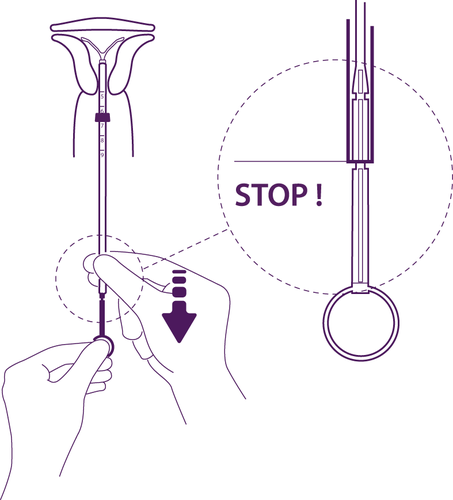
Figure 8
Move the intrauterine system to the bottom
of the uterus
To place the intrauterine system
in the correct position in the uterine cavity,
you should move the introduction tube
simultaneously with the piston, until the blue
collar comes into contact with the cervix again.
Following the instructions allows for proper placement of the Levosert system in the uterine cavity.
Figure 9
Release the intrauterine system from the introduction tube
into the uterine cavity
Holding the piston still, pull the introduction tube
down to the ring at the end of the piston.
The movement of the thickened section of the piston
will be accompanied by slight resistance. Nevertheless,
the tube should be pulled down to the ring at the end of the piston.
Following the instructions allows for complete release of the Levosert system from the introduction tube.
Figure 10
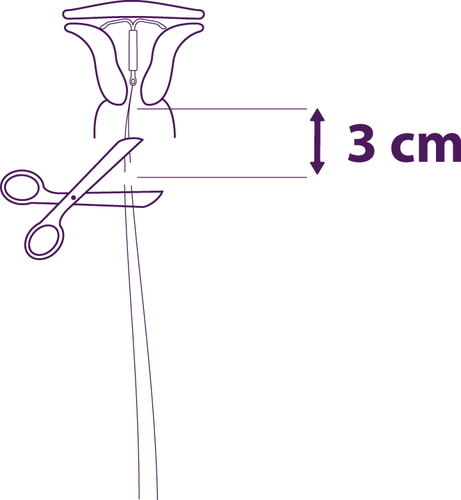
Remove the applicator elements one by one
and cut the threads
Remove the piston first, then the introduction tube.
Cut the threads at a distance of about 3 cm from
the cervix.
The insertion of the Levosert system has been completed.
Important information to consider during or after insertion of the intrauterine device:
- In case of suspicion that the intrauterine device is not in the correct position:
- The inserted device should be checked using an ultrasound examination or another appropriate radiological examination.
- If incorrect insertion of the device is suspected, the Levosert system should be removed. After removal, the same intrauterine device Levosert should not be re-inserted.
IMPORTANT!
In case of difficulties during insertion and (or) severe pain or bleeding during or after
insertion of the system, the possibility of perforation should be considered and appropriate steps should be taken, such as physical and ultrasound examination. If necessary, the system should be removed and a new, sterile one should be inserted.
After insertion of the system, patients should be re-examined after 4 to 6 weeks to check the threads and ensure that the system is in the correct position. A physical examination alone (including thread checking) may not be sufficient to rule out partial perforation.
All cases of uterine perforation or difficulties with system insertion should be reported to the pharmacotherapy safety monitoring unit:
Medical Department
GEDEON RICHTER POLSKA Sp. z o.o.
ul. ks. J. Poniatowskiego 5
05-825 Grodzisk Mazowiecki
Tel.: (22) 755 96 48,
e-mail [email protected]
Removal/Replacement
To remove the Levosert system, gently pull the threads with forceps. If the threads are not visible and the system has been detected in the uterine cavity during an ultrasound examination, narrow forceps can be used. This method may require dilation of the cervical canal or surgical intervention. After removal of the Levosert system, check if the system has been damaged.
In cases of particularly difficult removal procedures, single cases of displacement of the hormone-containing cylinder above the horizontal arms and their hiding together inside the cylinder have been reported. This situation does not require further intervention, as long as the intrauterine therapeutic system (IUS) remains complete. The bulges of the horizontal arms usually prevent the complete separation of the cylinder from the "T"-shaped scaffold of the intrauterine device.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterGedeon Richter Plc. Odyssea Pharma SA
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to LevosertDosage form: System, 19.5 mg/systemActive substance: plastic IUD with progestogenManufacturer: BAYER OyPrescription requiredDosage form: System, 52 mg (20 mcg/24h)Active substance: plastic IUD with progestogenPrescription requiredDosage form: System, 52 mgActive substance: plastic IUD with progestogenManufacturer: BAYER OyPrescription required
Alternatives to Levosert in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Levosert in Ukraine
Alternative to Levosert in Spain
Online doctors for Levosert
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Levosert – subject to medical assessment and local rules.






