

Leuprostin

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Leuprostin

How to use Leuprostin
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Leuprostin, 5 mg, Implant
Leuprorelin
Read the package leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
In case of any doubts, consult a doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
This medicine has been prescribed to you by a doctor and should not be given to others.
The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
If the patient experiences any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Leaflet:
- 1. What is Leuprostin and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Leuprostin
- 3. How to use Leuprostin
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Leuprostin
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Leuprostin and what is it used for
The active substance of Leuprostin (leuprorelin acetate) belongs to a group of inhibitors of certain sex hormones.
Leuprostin acts on the pituitary gland, initially stimulating and then inhibiting the production of hormones that regulate the production of male sex hormones in the testes.
This means that the concentration of sex hormones decreases and remains at the same level during treatment. After stopping the use of Leuprostin, the concentrations of hormones secreted by the pituitary gland and sex hormones return to normal values.
Leuprostin is used for the symptomatic treatment of advanced prostate cancer that is dependent on hormone activity.
Leuprostin is also used for the treatment of locally advanced prostate cancer and prostate cancer limited to the prostate, which are dependent on hormone activity, during or after radiotherapy.
2. Important information before using Leuprostin
When not to use Leuprostin
if the patient is allergic to leuprorelin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
if the patient is allergic to substances similar to leuprorelin, such as goserelin or buserelin;
if the cancer diagnosed in the patient is not dependent on hormone activity;
in women and children.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Leuprostin, the patient should discuss it with their doctor or nurse:
if the patient has high blood pressure. In this case, the doctor will closely monitor the patient's condition.
if the patient has undergone surgery to remove both testes. In this case, Leuprostin will not cause further reduction in the concentration of male sex hormone in the blood.
if the patient still has neurological symptoms (spinal cord compression, metastases to the spine) or experiences discomfort while urinating due to changes in the urinary tract before starting treatment. The patient should immediately inform their doctor, who will closely monitor their condition in the first weeks of treatment in a hospital setting, if possible.
if the symptoms of the disease recur (i.e., pain, difficulty urinating, or weakness in the legs during long-term use of Leuprostin). In this case, the doctor will regularly check the effectiveness of the treatment by performing appropriate tests (digital rectal examination, imaging tests) and monitoring blood parameters (phosphatase activity and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and testosterone levels).
if the patient is at risk of developing osteoporosis. If possible, the doctor may recommend additional medication to prevent bone loss.
if the patient has diabetes. In this case, the doctor will closely monitor the patient's condition.
if the patient has fatty liver disease (a condition in which excess fat accumulates in the liver)
If the patient experiences severe or recurring headaches, vision problems, or ringing in the ears, they should immediately consult their doctor.
Depression (which can be severe) has been reported in patients using Leuprostin. If the patient experiences depressive mood during treatment with Leuprostin, they should inform their doctor.
The patient should inform their doctor about any heart or blood vessel diseases, including arrhythmias or medications taken for this purpose. During treatment with Leuprostin, the risk of arrhythmias may increase.
Severe skin reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN), have been reported with the use of leuprorelin. If the patient experiences any symptoms of severe skin reactions, they should immediately consult their doctor.
Leuprostin and other medicines
The patient should inform their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take.
Leuprostin may interact with certain medicines used to treat arrhythmias (such as quinidine, procainamide, amiodarone, and sotalol) or increase the risk of arrhythmias when used with other medicines [such as methadone (used as a pain reliever and in detoxification of drug addicts), moxifloxacin (an antibiotic), and antipsychotic medicines (used to treat severe mental disorders)].
Children and adolescents
Leuprostin is intended for use in adult patients only.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Leuprostin is intended for use in men only.
Driving and using machines
Both the medicine and the underlying cancer can cause fatigue. This is more likely if the patient consumes alcoholic beverages. If this applies to the patient, they should not drive or operate machinerywithout consulting their doctor.
3. How to use Leuprostin
Administration of Leuprostin
The injection site should be cleaned.
A local anesthetic may be used to alleviate pain during injection of the implant.
Leuprostin is administered subcutaneously into the patient's abdominal wall.
Leuprostin should only be administered by a doctor or nurse who will also prepare the medicine.
Dosage
The recommended doseis 1 implantcontaining 5 mg of leuprorelin, administered every 3 months.
The patient should strictly follow the doctor's instructions regarding the timing of administration and intervals between injections.
Leuprostin is administered every 3 months. If the next injection is delayed by up to 4 weeks, the effectiveness of the treatment usually remains unchanged.
An implant contained in one ampoule-syringe is injected.
The ampoule-syringe contains one implant containing 5 mg of leuprorelin.
Blood tests
The doctor will order regular blood tests to check the effectiveness of the medicine.
After 3 months of therapy, the doctor usually evaluates whether Leuprostin is effective in treating prostate cancer in the patient. To do this, it is necessary to check the level of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) and testosterone in the blood.
Duration of treatment
The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. Treatment should be continued even if the symptoms of the disease have disappeared or the progression of the disease has slowed down.
Prostate cancer can be treated with Leuprostin for several years. Therefore, it can be used continuously if it is effective and well tolerated by the patient. The doctor will order tests at regular intervals to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment, especially in case of recurrence:
- pain
- difficulty urinating
- weakness in the legs.
More frequent administration of Leuprostin than recommended
It is unlikely that the doctor or nurse will administer an overdose of the medicine.
In case of accidental administration of a larger amount of medicine, the doctor will monitor the patient and, if necessary, provide appropriate treatment.
Missing a dose of Leuprostin
If the patient suspects that they have not received their dose of medicine after 3 months, they should consult their doctor.
Stopping treatment with Leuprostin
If treatment is stopped without the doctor's recommendation, the symptoms associated with the disease may worsen.
Therefore, treatment should not be stopped prematurely without consulting a doctor.
In case of any further doubts about the use of this medicine, the patient should consult their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Leuprostin can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If the patient experiences any of the following serious side effects, they should immediately consult their doctor or go to the emergency department of the nearest hospital:
Allergic reactions(anaphylactic reactions) with sudden onset of symptoms such as:
- hot flashes, rash, itching, or hives on the skin and (or) mucous membranes
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or other parts of the body
- shortness of breath, wheezing, or difficulty breathing
- decreased blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, seizures, and, in severe cases, life-threatening circulatory failure. Swelling and pain in some parts of the bodycaused by the formation of a blood clot in a vein. Difficulty breathing, chest pain, fainting, rapid heartbeat, bluish discoloration of the skin, and changes in skin colordue to the presence of a blood clot in the lungs.
These are rare side effects (may occur in less than 1 in 1000 people).
A common phenomenon is the initial short-term increase in blood testosterone levels. This may cause a transient worsening of symptoms associated with the disease, such as:
bone pain
difficulty urinating due to narrowing of the urinary tract
spinal cord compression
weakness in the legs
swelling of tissues due to fluid accumulation (lymphedema)
These symptoms usually resolve on their own without the need to stop using Leuprostin.
At the beginning of treatment, the doctor may recommend taking an appropriate hormone antagonist (so-called anti-androgen) to alleviate possible disorders associated with the initial increase in testosterone levels.
During treatment, testosterone levels decrease to very low values. As a result, some patients may experience the following side effects:
Very common(may occur in more than 1 in 10 people):
hot flashes
increased sweating
bone pain
decreased or lost sexual desire and potency
decreased testicle size
weight gain
reactions at the injection site, such as redness or hardening, pain, swelling, and itching, which usually resolve even if treatment is continued; in single cases, ulceration
Common(may occur in less than 1 in 10 people):
breast enlargement in men
decreased appetite
increased appetite
depression, mood changes
sleep disorders
headache
abnormal sensations, such as tingling and (or) numbness
nausea and (or) vomiting
joint or back pain
muscle weakness
increased need to urinate at night
increased need to urinate during the day
difficult and painful urination
feeling of fatigue
swelling of the ankles, feet, or toes (peripheral edema)
weight loss
increased activity of liver enzymes (ALT, AST, gamma-GT) and other enzymes (LDH, alkaline phosphatase)
Uncommon(may occur in less than 1 in 100 people):
generalized allergic reactions, such as fever, itching, increased eosinophil count, rash
diarrhea
dryness of the skin or mucous membranes
testicular pain
inability to completely empty the bladder
increased sweating at night
Rare(may occur in less than 1 in 1000 people):
decreased or increased blood sugar levels
dizziness
transient changes in taste
decreased or increased blood pressure
hair loss
Very rare(may occur in less than 1 in 10,000 people):
pituitary apoplexy after the first administration in patients with pituitary adenoma (as with other medicines in this class)
Frequency not known(frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
non-inflammatory lung disease (interstitial lung disease), mainly reported in Japan
pneumonia, lung disease
single cases of ulceration at the injection site
changes in ECG (QT interval prolongation)
seizures
idiopathic intracranial hypertension (increased intracranial pressure around the brain, characterized by headache, double vision, and other vision problems, as well as ringing in one or both ears)
red, flat, round, or oval patches on the torso, often with blisters in the center, peeling skin, ulcers in the mouth, throat, nose, genitals, and eyes.
These severe skin reactions may be preceded by fever and flu-like symptoms (Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis).
redness and itching rash. (toxic skin eruptions)
skin reaction causing the appearance of red dots or patches on the skin, which may look like a target with a dark red center surrounded by lighter red rings (erythema multiforme).
Special information
The effectiveness of Leuprostin can be monitored by measuring testosterone and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels in the blood, as well as phosphatase activity. Testosterone levels increase at the beginning of treatment and decrease within the next 2 weeks. After 2 to 4 weeks, testosterone levels reach values observed in patients after removal of both testes and remain at this level throughout the treatment period.
At the beginning of treatment, a transient increase in phosphatase activity in the blood is possible. After a few weeks, this activity returns to normal or near-normal values.
The decrease in testosterone levels that occurs after removal of the testes or as a result of taking medicines that suppress sex hormones (such as Leuprostin) may cause a decrease in bone density with a higher risk of fractures (see "Warnings and precautions").
The decrease in bone density is more pronounced after removal of the testes than after administration of Leuprostin. The doctor may recommend taking additional medication that regulates calcium metabolism (from the group of so-called bisphosphonates).
Reporting side effects
If the patient experiences any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products: Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw
tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Leuprostin
This medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
The medicine should not be used after the expiry date stated on the carton, blister, and syringe label after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Do not store above 30°C.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Leuprostin contains
The active substance is leuprorelin (in the form of leuprorelin acetate).
Each implant contains 5 mg of leuprorelin (in the form of leuprorelin acetate).
The other ingredient is: polylactic acid.
What Leuprostin looks like and contents of the pack
Ampoule-syringe made of polycarbonate (PC) with a plunger made of acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer (ABS) and a needle, placed in a bag made of PET/Aluminum/PE film, in a cardboard box.
Packs contain:
1 ampoule-syringe with 1 implant
2 ampoule-syringes, each with 1 implant
3 ampoule-syringes, each with 1 implant
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Sandoz GmbH
Biochemiestrasse 10
6250 Kundl, Austria
Manufacturer
EVER Pharma Jena GmbH
Otto-Schott-Strasse 15
07745 Jena, Germany
Sandoz GmbH
Biochemiestrasse 10
6250 Kundl, Austria
EVER Pharma Jena GmbH
Brüsseler Strasse 18
07747 Jena, Germany
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European
Economic Area under the following names:
Austria:
Leuprorelin Sandoz 5 mg - Implantat für 3 Monate
Denmark:
Leuprorelin „Sandoz“
Germany:
Leuprorelin HEXAL 5 mg
Greece:
PROSTAPLANT 5 mg εμφύτευμα
Hungary:
Leuprorelin -Sandoz 5mg implantátum
Ireland:
Leuprex 3, 5 mg Implant
Italy:
LEPTOPROL
Norway:
Leuprorelin Sandoz 5 mg implantat
Poland:
Leuprostin
Sweden:
Leuprorelin Sandoz 5 mg implantat
Slovakia:
Leuprorelin Sandoz 5 mg implantát
For more information about this medicine, please contact:
Sandoz Polska Sp. z o.o.
ul. Domaniewska 50 C
02-672 Warszawa
tel. 22 209 70 00
Date of last revision of the leaflet:12/2024
Sandoz logo
Information intended for healthcare professionals only
The user should carefully read the instructions, as the applicator for this medicinal product may differ from others used previously.
Instructions for use
- 1. Clean the injection site located on the anterior abdominal wall below the navel.
- 2. Remove the applicator from the sterile packaging and check if the implant is visible inside (see figure in the frame). For certainty, the applicator should be examined under light or gently shaken.
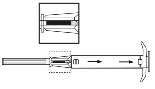
- 3. Pull the applicator plunger completely backuntil a full line appears in the second notch.
Caution:The plunger can only be moved forward to inject the implant if it has been completely pulled back!
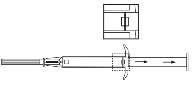
- 4. Remove the protective cap from the needle.
- 5. Hold the applicator body with one hand. With the other hand, pinch the skin of the patient's abdominal wall below the navel. See figure. Holding the beveled needle tip upwards, insert the entire needleinto the subcutaneous tissue at a slight angle, almost parallel to the skin surface.
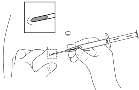
- 6. Carefully withdrawthe applicator about 1 cm backto create a puncture channel for the implant.
- 7. Inject the implant into the puncture channel by completelydepressing the plunger until it clicks into place with an audible click.

- 8. Remove the needle. To ensure that the implant has been injected correctly, check if the light blue plunger tip is visible in the needle hub.
Information on dosing can be found in section 3 "How to use Leuprostin".
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterEVER Pharma Jena GmbH EVER Pharma Jena GmbH Sandoz GmbH
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to LeuprostinDosage form: Powder, 22.5 mgActive substance: leuprorelinPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 45 mgActive substance: leuprorelinPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 7.5 mgActive substance: leuprorelinPrescription required
Alternatives to Leuprostin in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Leuprostin in Spain
Alternative to Leuprostin in Ukraine
Online doctors for Leuprostin
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Leuprostin – subject to medical assessment and local rules.











