

Feiba Nf

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Feiba Nf

How to use Feiba Nf
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
FEIBA NF, 500 IU, powder and solvent for solution for injection
Anti-inhibitor Coagulant Complex
Read the package leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this package leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this package leaflet, inform your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Package Leaflet
- 1. What is FEIBA NF and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using FEIBA NF
- 3. How to use FEIBA NF
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store FEIBA NF
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is FEIBA NF and what is it used for
FEIBA NF is a medicine obtained from human plasma, which enables blood clotting in case of deficiency or lack of certain clotting factors. FEIBA NF is used to treat bleeding and prevent bleeding in patients with hemophilia A and hemophilia B complicated by the presence of clotting factor inhibitors. Additionally, FEIBA NF may be used to treat and prevent bleeding in non-hemophilic patients with acquired inhibitors of clotting factors VIII, IX, and XI. There are single reports of the use of FEIBA NF in the treatment of patients with acquired inhibitors of clotting factors X and XIII. FEIBA NF is also used in combination with factor VIII concentrate during long-term treatment aimed at complete and permanent elimination of factor VIII inhibitors, to enable regular treatment with factor VIII concentrate, as in patients without inhibitors.
2. Important information before using FEIBA NF
Inform your doctor if you have any allergies. Inform your doctor if you are on a low-sodium diet.
When not to use FEIBA NF
In the situations listed below, FEIBA NF should only be used when it is not possible to expect results from other suitable clotting factor concentrates, e.g., due to a very high inhibitor titer and life-threatening bleeding or risk of bleeding (post-traumatic, post-operative).
- If you have been diagnosed with an allergy (hypersensitivity) to the anti-inhibitor coagulant complex or to any other component of FEIBA NF.
- If you have disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC, consumption coagulopathy, a life-threatening condition associated with massive blood clotting and the formation of blood clots in blood vessels, leading to a general consumption of clotting factors).
- In case of coronary heart disease, acute thrombosis, and/or embolism: FEIBA NF should only be used in life-threatening bleeding episodes.
Warnings and precautions
Before using FEIBA NF, contact your doctor, as it is possible to experience allergic reactions, as with other plasma products administered intravenously. The patient should be able to recognize early signs of an allergic reaction, such as: redness, skin rash, itching rash (hives), itching, swelling of the lips and tongue, wheezing, feeling of pressure in the chest, malaise, dizziness, and sudden drop in blood pressure to recognize an allergic reaction as soon as possible.
- redness
- skin rash
- itching rash (hives)
- itching
- swelling of the lips and tongue
- wheezing
- feeling of pressure in the chest
- malaise
- dizziness
- sudden drop in blood pressure
Other symptoms of allergic reactions to plasma-derived medicines include coma and restlessness. If one or more of these symptoms occur, discontinue the use of the medicine and contact your doctor. These symptoms may be early signs of anaphylactic shock. Severe allergic reactions require immediate emergency treatment. In the case of patients suspected of being allergic to the medicine or any of its components, the doctor will decide to re-administer FEIBA NF only after careful consideration of the risk and expected benefits and/or when it is not possible to expect results from other preventive therapy or alternative treatments.
- If you experience significant changes in blood pressure or heart rate, difficulty breathing, coughing, or chest pain. Discontinue the infusion and contact your doctor. The doctor will take appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic measures.
- In patients with hemophilia and the presence of an inhibitor or acquired inhibitors of clotting factors. During treatment with FEIBA NF in these patients, there may be an increased tendency to bleeding and an increased risk of thrombosis.
During treatment with FEIBA NF, thromboembolic events, including disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, and stroke, have occurred. Some thromboembolic events occurred with the use of high doses of FEIBA NF. Concomitant use of recombinant factor VIIa may increase the risk of thromboembolic events. Cases of thrombotic microangiopathy have been reported in a clinical study of emicizumab, in which patients received FEIBA NF as part of the breakthrough bleeding treatment regimen. For medicines produced from human blood or plasma, certain measures are taken to prevent infections in patients. These measures include careful selection of blood and plasma donors to ensure that those at risk of transmitting infections are excluded, as well as testing individual donations and plasma pools for viruses/infections. Manufacturers of these products also include steps in the processing of blood and plasma that aim to inactivate or remove viruses. Despite these measures, it is not possible to completely exclude the possibility of transmitting an infection when administering medicines produced from human blood or plasma. This applies to both known and newly discovered viruses or other types of infections. The measures taken are considered effective against enveloped viruses, such as HIV (which causes AIDS), hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C virus, as well as the non-enveloped hepatitis A virus. The measures taken may have limited value against non-enveloped viruses, such as parvovirus B19. Parvovirus B19 infection can be serious in pregnant women (fetal infection) and for individuals with impaired immunity or increased erythropoiesis (e.g., hemolytic anemia). For patients receiving regular or repeated factor VIII from human plasma, it is recommended to consider appropriate vaccinations (against hepatitis A and B). After administration of high doses of FEIBA NF, a transient increase in passively transferred antibodies against the hepatitis B surface antigen may result in false-positive serological test results. The medicine contains isoagglutinins, antibodies against red blood cells, which, when passively transferred, can cause misleading serological test results. It is strongly recommended that, during each administration of a dose of FEIBA NF to a patient, the name and batch number of the medicine be recorded to maintain information about the batches used.
FEIBA NF and other medicines
Inform your doctor about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken, including those available without a prescription. No adequate and well-controlled studies have been conducted on the concomitant use of FEIBA NF and recombinant factor VIIa, antifibrinolytic agents, or emicizumab. Consider the possibility of thromboembolic events when using systemic antifibrinolytic agents, such as tranexamic acid and aminocaproic acid, in combination with FEIBA NF. Therefore, antifibrinolytic agents should not be used for approximately 6 to 12 hours after administration of FEIBA NF. Regarding available in vitro data and clinical observations, in cases of concomitant use of recombinant factor VIIa, it is not possible to exclude the possibility of a potential drug interaction that may result in a thromboembolic event. If treatment with FEIBA NF is considered after the patient has received emicizumab, the patient must be closely monitored by the attending physician. As with all medicinal products of clotting factors, FEIBA NF should not be mixed with other medicines before administration; this may adversely affect the efficacy and safety of the medicine. It is recommended to flush the intravenous access with isotonic sodium chloride solution before and after administration of FEIBA NF.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
The doctor will decide whether to use FEIBA NF during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Due to the increased risk of thrombosis during pregnancy, FEIBA NF should only be used under close medical supervision and when clearly indicated.
Driving and using machines
No effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been observed.
FEIBA NF contains sodium
The medicine contains 80 mg of sodium (the main component of common salt) per vial, which corresponds to 4% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
3. How to use FEIBA NF
FEIBA NF lyophilized powder is dissolved in the attached solvent and administered intravenously. FEIBA NF should be used strictly according to the doctor's recommendation. In case of doubts, consult your doctor or pharmacist. The doctor determines the appropriate dose and frequency of administration individually for each patient, taking into account the severity of the bleeding disorder, the location and extent of the bleeding, and the patient's overall condition and response to the medicine. Do not change the dosage of the medicine on your own or discontinue its use. If you feel that the medicine is working too strongly or too weakly, contact your doctor or pharmacist. Before administration, warm the medicine to room temperature or body temperature if necessary. FEIBA NF should be prepared immediately before administration. The prepared solution should be used immediately (the medicine does not contain preservatives). Gently mix by rotating until the powder is dissolved. Ensure that FEIBA NF has been completely dissolved; otherwise, fewer units of FEIBA will pass through the filter of the device. Do not use a solution that is cloudy or contains sediment. Do not use a solution from previously opened vials. Use only the provided solvent (sterile water for injections) and the set for preparing the solution. If a different set is used for preparation and administration than the one attached to the FEIBA NF package, ensure that a filter with a pore size of at least 149 µm is used. Do not use if the sterility system or packaging of the medicine is damaged or broken. Record the administration of the medicine on the attached self-adhesive label. Dispose of any unused medicine or waste in accordance with local regulations.
Administration using needles:
Follow aseptic procedures throughout the entire procedure.
- 1. Warm the closed vial containing the solvent (sterile water for injections) to room temperature if necessary, e.g., using a water bath for a few minutes (max. 37°C).
- 2. Remove the protective caps from the vials with the powder and solvent and disinfect the rubber stoppers of both vials.
- 3. By twisting and pulling, remove the protective cover from one end of the attached double-ended needle (Fig. A). Insert the exposed needle into the rubber stopper of the vial with the solvent (Fig. B).
- 4. Remove the protective cover from the other end of the double-ended needle, taking care not to touch the exposed part.
- 5. Invert the vial with the solvent and place it over the vial with the powder, and insert the free end of the double-ended needle into the rubber stopper of the vial with the powder (Fig. D). The solvent will be drawn into the vial with the powder by vacuum.
- 6. Separate the two vials by pulling out the needle from the vial with the powder (Fig. E). Gently shake or rotate the vial with the powder to accelerate the dissolution process.
- 7. After the powder has dissolved, insert the needle with the air vent (Fig. F), and the formed foam will disappear. Remove the needle with the air vent.
Injection/infusion:
Follow aseptic procedures throughout the entire procedure.
- 1. Remove the protective cover from the attached needle with a filter by twisting and pulling, and attach the needle to a sterile single-use syringe. Draw the solution into the syringe (Fig. G).
- 2. Detach the needle with the filter from the syringe and, after attaching the provided infusion set with a butterfly needle (or a single-use injection needle), slowly inject the solution intravenously. A syringe pump can be used to control the infusion rate.
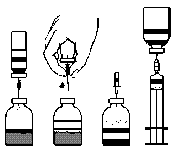
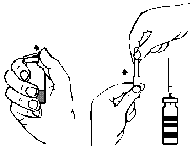
Fig. A Fig. B Fig. C Fig. D Fig. E Fig. F Fig. G
Administration using BAXJECT II Hi-Flow
Preparing the solution for injection
Follow aseptic procedures throughout the entire procedure.
- 1. Bring the vial with the solvent (sterile water for injections) to room temperature if necessary, e.g., using a water bath for a few minutes (max. 37°C).
- 2. Remove the protective caps from the vials with the powder and solvent and disinfect the rubber stoppers of both vials. Place the vials on a flat surface.
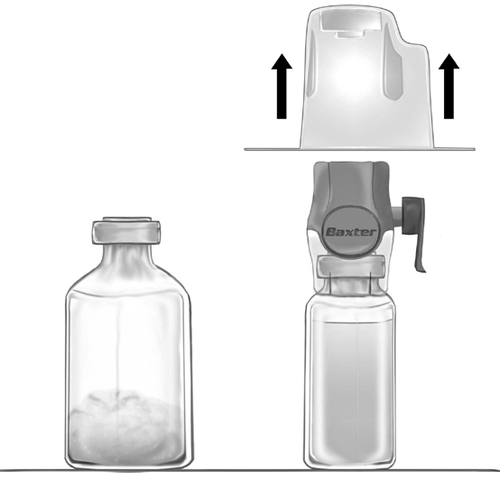
- 3. Open the packaging of the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device by tearing off the paper lid, without touching the inside (Fig. a). Do not remove the device from the packaging.
- 4. Invert the packaging and puncture the transparent plastic spike through the stopper of the solvent vial (Fig. b). Holding the packaging by the edges, remove it from the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device (Fig. c). Do not remove the blue cap from the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device.
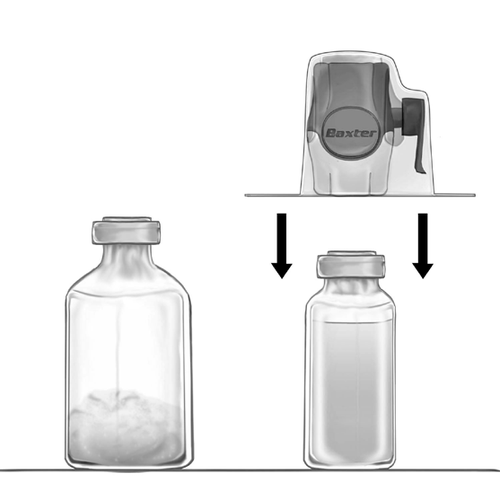
- 5. The BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device connected to the solvent vial should be inverted so that the solvent vial is above the device. Puncture the white plastic spike through the stopper of the vial with FEIBA NF powder. Under the influence of vacuum, the solvent will be drawn into the vial with FEIBA NF powder (Fig. d).
- 6. Mix gently, with a rotary motion, but without shaking, until the product is completely dissolved. Ensure that FEIBA NF has been completely dissolved – otherwise, the active substance will not pass through the filter of the device.
Fig. a
Fig. b
Fig. c
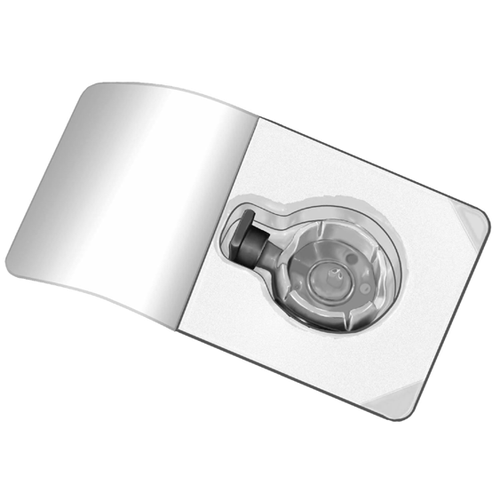

Injection/infusion
Follow aseptic procedures throughout the entire procedure.
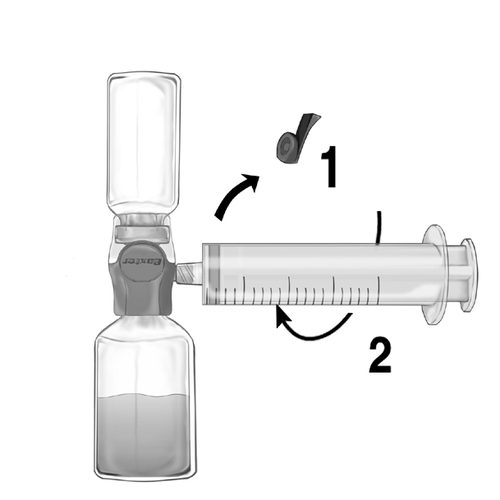
- 1. Remove the blue cap from the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device. Tightly connect the syringe to the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device (DO NOT DRAW AIR INTO THE SYRINGE). To ensure a secure connection between the syringe and the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device, it is particularly recommended to use a syringe with a luer-type tip (by screwing the syringe, rotate it clockwise until it stops) (Fig. e).
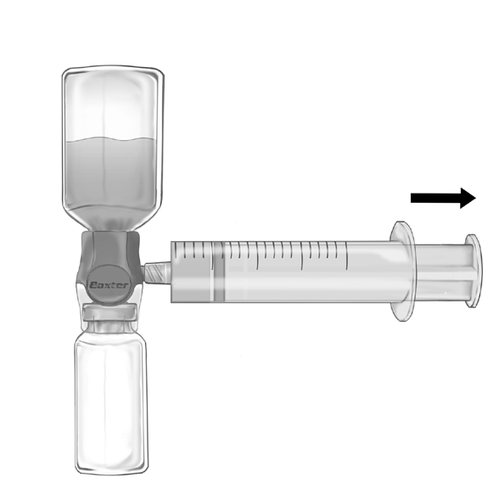
- 2. Invert the set so that the solution is at the top. Draw the solution into the syringe, SLOWLY pulling the plunger back and ensuring that the connection between the syringe and the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device is secure and the syringe is attached throughout the solution drawing process (Fig. f).
- 3. Detach the syringe.
- 4. If a foamy solution appears in the syringe, wait until the foam disappears. Slowly administer the solution intravenously using the infusion set (or a single-use injection needle). A syringe pump can be used to control the infusion rate.
Fig. d
Fig. e
Fig. f
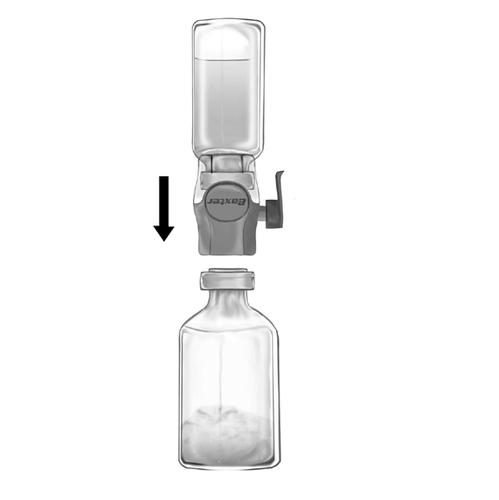

Do not exceed the infusion rate of 2 FEIBA units per kg body weight per minute.
In case of overdose:
Inform your doctor immediately. Overdose of FEIBA NF may increase the risk of side effects, such as thromboembolic events (formation of blood clots that move in blood vessels), consumption coagulopathy (DIC), or myocardial infarction.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, FEIBA NF can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this package leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
The following frequencies have been used to assess side effects: Very common: may affect more than 1 in 10 people Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people Uncommon: may affect up to 1 in 100 people Rare: may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people Very rare: may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people Unknown: frequency cannot be estimated from the available data In clinical trials, the following side effects were reported as common: Allergic reactions, headache, dizziness, hypotension, rash, positive test result for antibodies against the hepatitis B surface antigen. In post-marketing studies, the following side effects were reported with an unknown frequency: Blood and lymphatic system disorders: disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), increase in inhibitor titer Immunological disorders: allergic reactions, itching rash (hives) Nervous system disorders: numbness (paresthesia), abnormal or decreased sensation (hypoesthesia), stroke (thromboembolic or hemorrhagic), drowsiness, taste disorders Cardiac disorders: myocardial infarction (heart attack), palpitations (tachycardia) Vascular disorders: formation of blood clots that move in blood vessels (thromboembolic events), increased blood pressure (hypertension), sudden flushing Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders: pulmonary embolism (pulmonary thromboembolism), bronchospasm (bronchial constriction), wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath (dyspnea) Gastrointestinal disorders: vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, nausea Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: numbness of the face, facial swelling, swelling of the lips and tongue (angioedema), itching rash (hives), itching (pruritus) General disorders and administration site conditions: pain at the injection site, general malaise, feeling of heat, chills, fever, chest pain, chest discomfort Laboratory tests: decrease in blood pressure
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this package leaflet, inform your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, Fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl. Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store FEIBA NF
Store in a place invisible and inaccessible to children. Do not store above 25°C. Do not freeze. Store the medicine in its original packaging to protect it from light. Do not use FEIBA NF after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the given month. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What FEIBA NF contains
Powder
- The active substance is factor VIII with bypassing activity. One vial contains 500 IU of factor VIII with bypassing activity in 200-600 mg of human plasma protein.
- FEIBA NF also contains factors II, IX, and X, mainly in the form of non-activated factors, as well as activated factor VII. Antigenic factor VIII (F VIII C:Ag) and factors of the kallikrein-kinin system are present only in trace amounts or not at all.
- Other components of the medicine are sodium chloride and sodium citrate.
Solvent
- water for injections
What FEIBA NF looks like and contents of the pack
The medicine is a lyophilized powder or a fine solid substance with a white or pale green color. The powder and solvent are provided in glass vials sealed with rubber stoppers. The pH value of the solution after reconstitution is between 6.8 and 7.6. Package size: 1 set Contents of the package (with needles): 1 vial with 500 IU FEIBA NF, sealed with a rubber stopper 1 vial with 20 ml water for injections, sealed with a rubber stopper 1 double-ended needle 1 needle with an air vent 1 single-use syringe 1 injection needle 1 needle with a filter 1 butterfly needle (infusion set with butterfly needle) Contents of the package (with BAXJECT II Hi-Flow): 1 vial with 500 IU FEIBA NF, sealed with a rubber stopper 1 vial with 20 ml water for injections, sealed with a rubber stopper 1 BAXJECT II Hi-Flow - a needleless transfer device for transferring and mixing medicines contained in two vials 1 single-use syringe 1 injection needle 1 butterfly needle (infusion set with butterfly needle)
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer:
Marketing authorization holder:
Takeda Pharma Sp. z o.o., ul. Prosta 68, 00-838 Warsaw
Manufacturer:
Baxter AG, Industriestrasse 67, A-1220 Vienna, Austria Takeda Manufacturing Austria AG, Industriestrasse 67, 1221 Vienna, Austria
Date of last revision of the package leaflet:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Treatment should be initiated and supervised by a doctor with experience in the treatment of hemophilia.
Dosage
Dosage and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the bleeding disorder, the location and extent of the bleeding, and the patient's clinical condition. The dose, as well as the frequency of administration, should always be aimed at clinical efficacy in the given case. Generally, a dose of 50-100 IU FEIBA per kg body weight is recommended; however, the single dose should not exceed 100 IU/kg body weight, and the maximum daily dose should not exceed 200 IU/kg body weight, unless the severity of the bleeding justifies and necessitates the use of higher doses. Due to specific factors for the individual patient, the response to the anti-inhibitor coagulant complex may vary, and in a given case of bleeding in a patient who has an inadequate response to one of the factors, it is recommended to consider the use of another factor.
Bleeding episodes
Bleeding into joints, muscles, and soft tissues
In cases of minor or moderate bleeding, a dose of 50-75 IU/kg is recommended at 12-hour intervals. Treatment should be continued until clear signs of clinical improvement are achieved, such as relief of pain, reduction of swelling, or mobilization of the joint. In cases of major bleeding into muscles and soft tissues, such as bleeding into the retroperitoneal space, doses of 100 IU/kg are recommended at 12-hour intervals.
Bleeding from mucous membranes
A dose of 50 IU/kg is recommended every 6 hours, with close monitoring of the patient (observation of the bleeding surface, repeated hematocrit measurements in the patient). If the bleeding does not stop, the dose can be increased to 100 IU/kg. Do not exceed the maximum daily dose of 200 IU/kg.
Other severe bleeding episodes
In severe bleeding episodes, such as bleeding into the central nervous system, a dose of 100 IU/kg is recommended at 12-hour intervals. In individual cases, FEIBA NF can be administered at 6-hour intervals until clear clinical improvement is achieved. Do not exceed the maximum daily dose of 200 IU/kg!
Monitoring
Due to the complex mechanism of action, there is no direct method for monitoring the active substances. Tests of the coagulation system, such as whole blood clotting time (WBCT), thromboelastogram (TEG, r-value), and aPTT, usually show small changes and may not reflect clinical improvement. Therefore, these tests have very limited value in monitoring treatment with FEIBA NF.
Method of administration
FEIBA NF should be administered slowly intravenously (no faster than 2 IU/kg body weight per minute). FEIBA NF should be prepared immediately before administration. The solution should be used immediately (it does not contain preservatives). Do not use a solution that is cloudy or contains sediment. Unused solution residues should be disposed of in accordance with the applicable procedure.
Monitoring of treatment
Do not exceed single doses of 100 IU/kg body weight and a daily dose of 200 IU/kg body weight. Patients receiving more than 100 IU/kg body weight should be monitored for the occurrence of DIC and/or acute coronary syndrome. High doses of FEIBA NF should only be administered for the period necessary to stop the bleeding. In case of significant changes in blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory disorders, coughing, or chest pain, discontinue the infusion and contact your doctor. The doctor will take appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic measures. Laboratory test results indicating DIC are: decreased fibrinogen levels, decreased platelet count, and the presence of fibrin/fibrinogen degradation products (FDP). Further signs of DIC are significant prolongation of thrombin time, prothrombin time, or aPTT. In patients with hemophilia complicated by the presence of an inhibitor or in patients with acquired inhibitors of clotting factors VIII, IX, X, and XI, aPTT may be prolonged due to the bleeding disorder itself. Administration of FEIBA NF to patients with inhibitors may result in an initial anamnestic increase in inhibitor levels. Under the influence of further administration of FEIBA NF, the inhibitor level may decrease over time. Clinical and literature data indicate that the efficacy of FEIBA NF is not reduced. During administration of FEIBA NF, patients with hemophilia complicated by the presence of an inhibitor or patients with acquired inhibitors of clotting factors may experience a simultaneous tendency to bleeding and an increased risk of thrombosis.
Laboratory tests and clinical efficacy
Results of in vitro laboratory tests to assess treatment efficacy, such as aPTT, whole blood clotting time, and thromboelastogram (TEG), may not reflect clinical improvement. Therefore, attempts to restore normal values of these parameters by increasing FEIBA NF doses may be misleading and should be avoided due to the possibility of DIC caused by overdose.
Importance of platelet count
In case of inadequate response to treatment with FEIBA NF, it is recommended to determine the platelet count, as a sufficient number of functionally active platelets is necessary for the efficacy of FEIBA NF.
Additional information about the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device:
- The device is sterilized by gamma radiation.
- For single use only.
- Does not contain latex.

Do not use in case of damaged packaging. BAXJECT and FEIBA are registered trademarks of Baxalta Incorporated.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterTakeda Manufacturing Austria AG
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Feiba NfDosage form: Powder, 1000 IU (1000 IU FEIBA), 50 IU/mlActive substance: factor VIII inhibitor bypassing activityManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AGPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 500 IU (500 IU FEIBA), 50 IU/mlActive substance: factor VIII inhibitor bypassing activityManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AGPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 2500 IU (2500 IU FEIBA), 50 IU/mlActive substance: factor VIII inhibitor bypassing activityManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AGPrescription required
Alternatives to Feiba Nf in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Feiba Nf in Spain
Online doctors for Feiba Nf
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Feiba Nf – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














