FEIBA 100 U/mL POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR SOLUTION FOR INFUSION


How to use FEIBA 100 U/mL POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
FEIBA 100U/ml powder and solvent for solution for infusion
anti-inhibitor coagulant complex
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is FEIBA and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use FEIBA
- How to use FEIBA
- Possible side effects
- Storage of FEIBA
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is FEIBA and what is it used for
FEIBA is a preparation made from human plasma, which allows for hemostasis, even when the amount of specific coagulation factors is reduced or absent.
FEIBA is used for the treatment and prophylaxis of bleeding in patients with hemophilia A with inhibitors.
FEIBA is used for the treatment of bleeding in patients with hemophilia B with inhibitors.
FEIBA may be used for the treatment and prophylaxis of bleeding in non-hemophilic patients with acquired factor VIII inhibitors.
In addition, FEIBA is used for prophylaxis during surgical interventions in patients with hemophilia A with inhibitors.
FEIBA can be used in all age groups.
2. What you need to know before you use FEIBA
Tell your doctor if you have any known allergies.
Tell your doctor if you are on a low-sodium diet.
Do not use FEIBA
FEIBA should only be used in the following circumstances if, for example, due to a very high level of inhibitors, no response to treatment with the appropriate coagulation factor concentrate is expected:
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor before starting to use FEIBA because hypersensitivity reactions can occur, as with all plasma-derived products administered intravenously. To recognize an allergic reaction as early as possible, you should know that the first potential symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction may be:
- erythema (redness of the skin)
- rash
- appearance of hives on the skin (urticaria)
- itching all over the body
- swelling of the lips and tongue
- difficulty breathing/dyspnea
- chest tightness
- general discomfort
- dizziness
- drop in blood pressure
Other symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions to plasma-derived products include lethargy and fatigue.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should stop administration immediately and contact your doctor immediately. The described symptoms may indicate anaphylactic shock. Severe symptoms require early emergency treatment.
Your doctor will only reuse FEIBA in patients with suspected hypersensitivity to the product or to any of its components after carefully weighing the expected benefit and the risk of re-exposure and/or not expecting any response with other preventive treatment or alternative therapy.
- If you experience significant changes in blood pressure or pulse rate, difficulty breathing, coughing, or chest pain, you should stop administration immediately and contact your doctor. Your doctor will initiate appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic measures.
- In patients with hemophilia with inhibitors or with acquired inhibitors to coagulation factors. During treatment with FEIBA, these patients may have an increased tendency to develop bleeding and an increased risk of thrombosis at the same time.
During treatment with FEIBA, thrombotic and thromboembolic events, including disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, and stroke, have occurred. It is likely that concomitant use with recombinant factor VIIa increases the risk of developing a thromboembolic event. Some of the thromboembolic events occurred with high-dose treatment with FEIBA.
In a trial conducted by another company to evaluate emicizumab (a medicine to prevent bleeding in patients with hemophilia A), some patients who experienced intercurrent bleeding were treated with FEIBA to control the bleeding, and some of these patients developed thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA). TMA is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition. When this condition occurs, the vascular wall can be damaged and blood clots can develop in small blood vessels. In some cases, this can cause kidney damage and damage to other organs. In case of intercurrent bleeding while on prophylaxis with emicizumab, contact your hematologist or Hemophilia Treatment Center immediately.
When administering medicines derived from human plasma or blood, certain measures must be taken to prevent infections from being passed on to patients. Such measures include careful selection of donors to exclude those at risk of carrying infectious diseases, testing for specific infection markers in individual donations and plasma pools, as well as inclusion of stages in the manufacturing process to eliminate/inactivate viruses. Despite this, when administering medicines derived from human blood or plasma, the possibility of transmitting infectious agents cannot be completely excluded. This also applies to emerging or unknown viruses or other types of infections.
These measures are considered effective for enveloped viruses such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C virus, and for non-enveloped viruses such as hepatitis A virus. The measures taken may have limited value for non-enveloped viruses such as parvovirus B19. Parvovirus B19 infection can be severe for a pregnant woman (fetal infection) and for individuals with impaired immune systems or for patients with certain types of anemia (e.g., sickle cell disease or hemolytic anemia).
It is possible that your doctor may recommend that you be vaccinated against hepatitis A and hepatitis B if you are regularly or repeatedly administered plasma-derived products for factor VIII inhibitors.
After administration of high doses of FEIBA, the transient increase in passively transferred hepatitis B surface antibodies may lead to misinterpretation of positive serological test results.
FEIBA is a plasma-derived product and may contain substances that react when infused into patients, causing the presence of isohemagglutinins (antibodies that cause the agglutination of other people's red blood cells). This process can lead to misinterpretation of blood test results.
It is strongly recommended that each time a dose of FEIBA is administered, a record be kept of the name of the medicine and batch number administered in order to maintain a record of the batches used.
Children
Experience in children under 6 years is limited; the same dosage regimen as in adults should be adapted for the child's clinical condition.
Other medicines and FEIBA
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
No adequate and well-controlled studies have been conducted on the combined or sequential use of FEIBA and recombinant factor VIIa, antifibrinolytics, or emicizumab. When using systemic antifibrinolytics such as tranexamic acid and aminocaproic acid during treatment with FEIBA, the possibility of thromboembolic events should be considered. Therefore, antifibrinolytics should not be used until approximately 6 to 12 hours after administration of FEIBA.
According to available in vitro data and clinical observations, a potential drug interaction with concomitant use with recombinant factor VIIa cannot be excluded, which may potentially produce a thromboembolic event. Tell your doctor if you are to be treated with FEIBA after having received emicizumab (a medicine to prevent bleeding in patients with hemophilia A), as specific warnings and precautions need to be considered. Your doctor will need to closely monitor you.
As with all products used for blood coagulation, FEIBA should not be mixed with other medicines before administration, as this may impair the efficacy and tolerance of the product. It is advisable to flush the venous line with isotonic saline solution before and after administration of FEIBA.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Your doctor will decide whether FEIBA can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Due to the increased risk of thrombosis during pregnancy, FEIBA should only be administered under close medical supervision and only if clearly indicated. For information on the risk of parvovirus B19 infection, see section warnings and precautions.
Driving and using machines
There is no indication that FEIBA can affect the ability to drive and use machines.
FEIBA contains sodium
500 U
This medicine contains approximately 40 mg of sodium (main component of table/cooking salt) per vial. This is equivalent to 2% of the maximum recommended daily sodium intake for an adult.
1,000 U
This medicine contains approximately 80 mg of sodium (main component of table/cooking salt) per vial. This is equivalent to 4% of the maximum recommended daily sodium intake for an adult.
2,500 U
This medicine contains approximately 200 mg of sodium (main component of table/cooking salt) per vial. This is equivalent to 10% of the maximum recommended daily sodium intake for an adult.
3. How to use FEIBA
Reconstitute the FEIBA lyophilized powder with the included solvent and administer the solution intravenously.
Follow exactly the administration instructions for this medicine as indicated by your doctor. If in doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
Your doctor will determine the frequency and dose required for you personally, taking into account the severity of the blood coagulation disorder, the location and magnitude of the bleeding, and your clinical condition and response to the preparation. Do not change the dosage established by your doctor and do not discontinue administration of the preparation.
If you feel that the effect of FEIBA is too strong or too weak, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Warm the product to room temperature or body temperature before administration, if necessary.
FEIBA should be reconstituted immediately before administration. The solution should be used immediately (since the preparation does not contain preservatives).
Gently swirl until all the product is dissolved. Ensure that FEIBA is completely dissolved, otherwise less FEIBA units will pass through the filter of the equipment.
Solutions that appear turbid or contain deposits should be discarded.
Do not reuse opened vials.
Use only the water for injections and the equipment for reconstitution included in the pack.
If other equipment is used, ensure that a filter with a pore size of at least 149 micrometers is used.
Do not use the product if the sterility barrier system or the vial is damaged or shows any sign of deterioration.
Do not refrigerate after reconstitution.
After complete reconstitution of FEIBA, the injection or infusion should begin immediately and should be completed within 3 hours of reconstitution.
Disposal of unused medicine and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
Reconstitution of powder for preparation of a solution for infusion with the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device:
- Warm the unopened vial of solvent (water for injections) to room temperature or up to 37°C, if necessary, for example, by using a water bath for several minutes.
- Remove the protective caps from the vial of powder and the vial of solvent, and disinfect the rubber stoppers of both vials. Place the vials on a flat surface.
- Open the packaging of the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device by removing the protective foil without touching the contents of the package (Figure a). Do not remove the device from the packaging.
- Turn the packaging over and insert the transparent plastic tip through the rubber stopper of the vial of solvent (Figure b). Now remove the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device from its packaging (Figure c). Do not remove the blue protective cap from the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device.
- With the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device attached to the vial of solvent, turn the system over so that the vial of solvent is on top of the device. Insert the purple plastic tip of the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device through the stopper of the vial of FEIBA. The vacuum will cause the solvent to flow into the vial of FEIBA (Figure d).
- Gently swirl, without shaking, the entire system until all the powder is dissolved. Ensure that FEIBA is completely dissolved, otherwise the active material may be retained in the filter of the device.
Figure a | Figure b | Figure c |
|
|
|
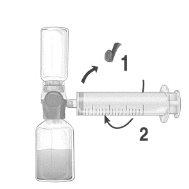
Infusion
Use aseptic technique throughout the procedure!
- Remove the blue protective cap from the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device. Firmly connect the syringe to the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device. DO NOT INTRODUCE AIR INTO THE SYRINGE. (Figure e). It is strongly recommended to use a Luer Lock syringe to ensure a firm connection between the syringe and the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device (turn the syringe clockwise until it stops when it reaches the top).
- Turn the system over so that the dissolved product is at the top. Introduce the dissolved product into the syringe by slowly pulling back the plunger and ensuring that the firm connection between the BAXJECT II Hi-Flow device and the syringe is maintained throughout the process while pulling back the syringe plunger (Figure f).
- Disconnect the syringe.
- If foam forms inside the syringe, wait for the foam to settle. Administer the solution slowly intravenously using the provided infusion equipment.
Figure d | Figure e | Figure f |
|
|
|
Do not exceed an infusion rate of 10 U of FEIBA/kg per minute.
If you use more FEIBA than you should
Inform your doctor immediately. Overdose of FEIBA may increase the risk of side effects, such as thromboembolism (formation of a blood clot with redness in the blood vessels), disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), or myocardial infarction. Some of the thromboembolic events reported occurred with high-dose treatment with FEIBA or in patients with other risk factors for thromboembolic events. If signs or symptoms of a thromboembolic event are observed, the infusion should be interrupted immediately and necessary diagnostic and therapeutic measures should be taken.
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult your doctor or pharmacist immediately or call the Toxicology Information Service, phone 91 562 04 20, indicating the medicine and the amount ingested.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine may cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
Common Adverse Effects(may affect up to 1 in 10 patients)
Hypersensitivity, headache, dizziness, hypotension, skin rash, positive hepatitis B surface antibodies.
Adverse Effects with Unknown Frequency(cannot be estimated from available data)
Disorders of the Blood and Lymphatic System:disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), increased inhibitor titre.
Disorders of the Immune System:anaphylactic reactions, whole-body skin rash (urticaria).
Disorders of the Nervous System:numbness sensation in the limbs (hypoesthesia), abnormal or reduced sensitivity (paresthesia), stroke (thrombotic or embolic accident), somnolence, altered taste sensation (dysgeusia).
Cardiac Disorders:heart attack (myocardial infarction), heart palpitations (tachycardia).
Vascular Disorders:formation of blood clots with reddening of blood vessels (thromboembolic events, venous and arterial thrombosis), increased blood pressure (hypertension), flushing.
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders:pulmonary artery obstruction (pulmonary embolism), airway obstruction (bronchospasm), wheezing, cough, difficulty breathing (dyspnea).
Gastrointestinal Disorders:vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, feeling of sickness (nausea).
Disorders of the Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue:numbness sensation in the face, facial swelling, tongue, and lip swelling (angioedema), whole-body skin rash (urticaria), itching (pruritus).
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions:pain at the injection site, general discomfort, feeling of heat, chills, fever, chest pain, chest discomfort.
Investigations:decrease in blood pressure, increase in D-dimer fibrin level in blood.
Rapid intravenous perfusion may cause a stabbing pain and a numbness sensation in the face and limbs, as well as a decrease in blood pressure.
Cases of myocardial infarction have been reported after administration of doses higher than the maximum daily dose and/or with prolonged administration and/or presence of thromboembolic risk factors.
Reporting of Adverse Effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor, even if it is a possible adverse effect that does not appear in this prospectus. You can also report it directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: www.notificaram.es.
By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of FEIBA
Keep this medicine out of sight and reach of children.
Do not store above 25°C. Do not freeze.
Store in the original packaging to protect from light.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date shown on the label and packaging. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of packaging and medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Composition of FEIBA
Powder
- The active ingredient per vial is anti-inhibitor coagulant complex.
- 1 ml contains 100 U of anti-inhibitor coagulant complex.
- FEIBA 100 U/ml is available in three presentations:
- The 500 U presentation of FEIBA contains 500 U (units) of anti-inhibitor coagulant complex in 200 – 600 mg of human plasma protein.
- The 1,000 U presentation of FEIBA contains 1,000 U (units) of anti-inhibitor coagulant complex in 400 – 1,200 mg of human plasma protein.
- The 2,500 U presentation of FEIBA contains 2,500 U (units) of anti-inhibitor coagulant complex in 1,000 – 3,000 mg of human plasma protein.
FEIBA also contains factors II, IX, and X, mainly non-activated, as well as activated factor VII. The coagulant factor VIII antigen (FVIII C:Ag) as well as the factors of the kallikrein-kinin system are present only in trace amounts.
- The other components are sodium chloride and sodium citrate.
Solvent
- Water for injectable preparations.
Appearance of the Product and Container Contents
The product is presented as a lyophilized or friable solid, white to off-white or pale green in color. The reconstituted solution has a pH between 6.5 and 7.3.
The powder and solvent are supplied in closed glass vials with rubber stoppers.
Presentation:1 x 500 U
1 x 1,000 U
1 x 2,500 U
Only some package sizes may be marketed.
Container Contents:
- 1 vial with 500 U/1,000 U/2,500 U of FEIBA - powder for solution for infusion
- 1 vial with 5 ml/10 ml/25 ml of water for injectable preparations
- 1 BAXJECT II Hi-Flow reconstitution device
- 1 disposable syringe
- 1 butterfly needle
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder:
Baxalta Innovations GmbH
Industriestrasse, 67
1221 Vienna, Austria
Manufacturer:
Takeda Manufacturing Austria AG
Industriestrasse, 67
1221 Vienna, Austria
Local Representative of the Marketing Authorization Holder
Takeda Farmacéutica España, S.A.
Calle Albacete, 5, 9th floor,
Edificio Los Cubos
28027 Madrid
Spain
Tel: +34 91 790 42 22
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Austria:
FEIBA 100 E./ml Pulver und Lösungsmittel zur Herstellung einer Infusionslösung
Bulgaria:
FEIBA 100 U/ml powder and solvent for solution for infusion
Croatia:
FEIBA 100 U/ml prašak i otapalo za otopinu za infuziju
Cyprus:
FEIBA 100 U/ml κ?νις και διαλ?της για δι?λυμα προς ?γχυση
Czech Republic:
FEIBA
Denmark:
Feiba
Estonia:
FEIBA 100 Ü/ML
Finland:
Feiba
Germany:
FEIBA 500 E konzentriert
FEIBA 1000 E konzentriert
FEIBA 2500 E konzentriert
Greece:
FEIBA 100 U/ml κ?νις και διαλ?της για δι?λυμα προς ?γχυση
Ireland:
FEIBA 100 U/ml powder and solvent for solution for infusion
Latvia:
Feiba 100 V/ml pulveris un škidinatajs infuziju škiduma pagatavošanai
Lithuania:
Feiba 100 V/ml milteliai ir tirpiklis infuziniam tirpalui
Malta:
FEIBA 100 U/ml powder and solvent for solution for infusion
Netherlands:
FEIBA 100 E/ML, poeder en oplosmidel voor oplossing voor injectie
Norway:
Feiba
Romania:
FEIBA 100 U/ml pulbere si solvent pentru solutie injectabila
Slovakia:
FEIBA 100 U/ml prášok a rozpúšt’adlo na infúzny roztok
Slovenia:
FEIBA 100 e./ml prašek in vehikel za raztopino za infundiranje
Spain:
FEIBA 100 U/ml polvo y disolvente para solución para perfusión
Sweden:
Feiba 100 enheter/ml pulver och vätska till infusionsvätska, lösning
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet:08/2024
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
Treatment should be initiated and monitored under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of coagulation disorders.
Posology
The dose and duration of therapy depend on the severity of the hemostatic function disorder, the location and severity of the hemorrhage, and the patient's clinical condition.
The dose and frequency of administration should always be determined based on clinical efficacy in each case.
As a general guideline, doses of 50 – 100 U/kg of FEIBA are recommended; a single dose of 100 U/kg should not be exceeded, nor a maximum daily dose of 200 U/kg, unless the severity of the hemorrhage requires and justifies the use of higher doses.
Due to specific patient factors, the response to a bypassing agent may vary, and in a given hemorrhagic situation, patients with an insufficient response to one agent may respond to another agent. In case of insufficient response to a bypassing agent, the use of another agent should be considered.
Pediatric Population
Experience in children under 6 years is limited; the same dosing regimen as in adults should be adapted for the child's clinical condition.
- Spontaneous Hemorrhage
Hemorrhages in Joints, Muscles, and Soft Tissue
For mild to moderate hemorrhages, a dose of 50 – 75 U/kg is recommended every 12 hours. Treatment should continue until clear signs of clinical improvement appear, such as decreased pain, reduced swelling, or increased joint mobility.
For severe hemorrhages in muscles and soft tissue, e.g., retroperitoneal hemorrhage, a dose of 100 U/kg every 12 hours is recommended.
Hemorrhages in Mucous Membranes
A dose of 50 U/kg every 6 hours is recommended, under strict patient surveillance (visual control of bleeding, repeat hematocrit). If bleeding does not stop, the dose can be increased to 100 U/kg; however, a dose of 200 U/kg should not be exceeded.
Other Severe Hemorrhages
In severe hemorrhage, such as CNS hemorrhage, a dose of 100 U/kg every 12 hours is recommended. In particular cases, FEIBA can be administered every 6 hours until clear signs of clinical improvement appear (the maximum daily dose of 200 U/kg should not be exceeded).
- Surgery
In surgical interventions, an initial dose of 100 U/kg can be administered before surgery, and 6 to 12 hours later, another dose of 50 – 100 U/kg can be administered. As postoperative maintenance doses, 50 – 100 U/kg can be administered every 6 – 12 hours; the dose, dosing intervals, and duration of peri- and postoperative treatment depend on the surgical intervention, the patient's general condition, and clinical efficacy in each particular case (the maximum daily dose of 200 U/kg should not be exceeded).
- Prophylaxis in Patients with Hemophilia A with Inhibitor
- Prophylaxis of Hemorrhages in Patients with High Inhibitor Titers and Frequent Hemorrhages, after Failed Immune Tolerance Induction (ITI) or when ITI is not Considered:
A dose of 70 – 100 U/kg every other day is recommended. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 100 U/kg per day or gradually reduced.
- Prophylaxis of Hemorrhages in Patients with High Inhibitor Titers during Immune Tolerance Induction (ITI):
FEIBA can be administered in combination with factor VIII, at a dosing interval of 50 – 100 U/kg, twice daily, until the factor VIII inhibitor titer has decreased to <2 u.b.*< p>
*1 Bethesda Unit is defined as the amount of antibodies that inhibits 50% of factor VIII activity in plasma incubated (2 hours at 37°C).
- Use of FEIBA in Special Patient Groups
FEIBA has also been used in combination with a factor VIII concentrate as long-term treatment for the complete and permanent elimination of factor VIII inhibitors.
Monitoring
In case of an inadequate response to treatment with the product, a platelet count is recommended, as a sufficient number of functionally intact platelets is considered necessary for the treatment with the product to be effective.
Due to the complex mechanism of action, there is no direct monitoring of the active ingredients. Coagulation tests such as whole blood coagulation time (TCT), thromboelastogram (TEG, r value), and activated partial thromboplastin time (TTPa) generally show only minor shortenings, which do not necessarily correlate with clinical improvement. For these reasons, the usefulness of these tests for monitoring treatment with FEIBA is very limited.
Method of Administration
FEIBA should be administered slowly, by intravenous route. FEIBA should be infused at an infusion rate of 2 U/kg/min. In patients who have tolerated the infusion rate of 2 U/kg/min well, the infusion rate can be increased up to a maximum of 10 U/kg/min.
FEIBA should be reconstituted immediately before administration. The solution should be used immediately (since the preparation does not contain preservatives). Do not use cloudy solutions or those containing deposits. The disposal of unused medicinal products and all materials that have come into contact with them should be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
Therapy Monitoring
Individual doses of 100 U/kg and daily doses of 200 U/kg should not be exceeded. Patients receiving more than 100 U/kg should be monitored for the development of DIC and/or acute coronary ischemia and for symptoms of thrombotic or thromboembolic events. High doses of FEIBA should only be administered for the time strictly necessary to stop a hemorrhage.
If clinically significant changes in blood pressure or pulse rate, respiratory difficulty, cough, or chest pain occur, the infusion should be interrupted immediately, and the necessary diagnostic and therapeutic measures should be taken. The characteristic laboratory parameters of DIC are a decrease in fibrinogen, a decrease in platelet count, and/or the presence of fibrin or fibrinogen degradation products (PDF). Other parameters for the development of DIC are a marked prolongation of thrombin time, prothrombin time, or activated partial thromboplastin time (TTPa). In patients with hemophilia with inhibitors or with acquired inhibitors of factors VIII, IX, and/or XI, the TTPa is prolonged due to the underlying disease.
The administration of FEIBA in patients with inhibitors may produce an initial "anamnestic" increase in inhibitor levels. During continued administration of FEIBA, inhibitor levels may decrease over time. Both clinical data and published data suggest that the efficacy of FEIBA is not reduced.
Patients with hemophilia with inhibitors or with acquired inhibitors of coagulation factors who receive treatment with FEIBA may be more prone to bleeding while the risk of thrombosis may increase.
Laboratory Tests and Clinical Efficacy
In vitro tests to control efficacy, such as TTPa, whole blood coagulation time (TCT), and thromboelastogram (TEG), do not necessarily correlate with clinical improvement. For this reason, it is not recommended to seek the normalization of these values by increasing the dose of FEIBA, and it is even strongly discouraged due to the possible risk of DIC due to overdose.
Importance of Platelet Count
In case of an inadequate response to treatment with FEIBA, a platelet count is recommended, as a sufficient number of functionally intact platelets is considered necessary for the treatment with FEIBA to be effective.
Treatment of Patients with Hemophilia B with Inhibitor
Experience in patients with hemophilia B with factor IX inhibitors is limited due to the rarity of the disease. Five patients with hemophilia B with inhibitors were treated with FEIBA during clinical trials, either with on-demand treatment or prophylactic treatment or for surgical interventions:
In a prospective, open, randomized, and parallel study in patients with hemophilia A or B with constantly elevated inhibitor titers (090701, PROOF), 36 patients were randomized to receive prophylactic treatment or on-demand treatment for 12 months ± 14 days. The 17 patients in the prophylactic treatment group received 85 ± 15 U/kg of FEIBA, administered every other day, and the 19 patients in the on-demand treatment group received individualized treatment, determined by the physician. Two patients with hemophilia B with inhibitors received on-demand treatment, and one patient with hemophilia B received prophylactic treatment. The median Annualized Hemorrhage Rate (AHR) for all types of hemorrhagic episodes in the patients in the prophylactic treatment group (median AHR = 7.9) was lower than that in the patients in the on-demand treatment group (median AHR = 28.7), which represents a 72.5% decrease in the median AHR between the treatment groups.
In another completed, prospective, observational, or non-interventional study of the perioperative use of FEIBA (PASS-INT-003, SURF), a total of 34 surgical interventions were performed in 23 patients. Most patients (18) had congenital hemophilia A with inhibitors, two were patients with hemophilia B with inhibitors, and three were patients with acquired hemophilia A with inhibitors. The exposure time to FEIBA ranged from 1 to 28 days, with a mean of 9 days and a median of 8 days. The mean cumulative dose was 88,347 U, and the median dose was 59,000 U. In patients with hemophilia B with inhibitors, the longest exposure to FEIBA was 21 days, and the maximum dose administered was 7,324 U.
Additionally, there are isolated reports of the use of FEIBA in the treatment of patients with acquired inhibitors against factors IX, X, XI, and XIII.
In rare cases, FEIBA has also been used in patients with the presence of von Willebrand factor inhibitors.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to FEIBA 100 U/mL POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR SOLUTION FOR INFUSIONDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 50 U/mlActive substance: factor VIII inhibitor bypassing activityManufacturer: Baxalta Innovations GmbhPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 1,000 IUActive substance: coagulation factor VIIIManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AgPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 1500 IUActive substance: coagulation factor VIIIManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AgPrescription required
Online doctors for FEIBA 100 U/mL POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Discuss questions about FEIBA 100 U/mL POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR SOLUTION FOR INFUSION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions