WILATE 1000 IU FvW/1000 IU FVIII, POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION

How to use WILATE 1000 IU FvW/1000 IU FVIII, POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
WILATE,500 UI FvW and 500 UI FVIII, powder and solvent for solution for injection.
WILATE,1000 UI FvW and 1000 UI FVIII, powder and solvent for solution for injection.
Human von Willebrand factor and human coagulation factor VIII.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack and other information:
- What Wilate is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use Wilate
- How to use Wilate
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Wilate
- Contents of the pack and further information
1. What Wilate is and what it is used for
Wilate belongs to a group of medicines called coagulation factors, containing human von Willebrand factor (FvW) and human coagulation factor VIII.
These two proteins together play a role in blood coagulation.
Von Willebrand disease
Wilate is used to treat and prevent bleeding in patients with von Willebrand disease (VWD), which is a group of related diseases. VWD is a blood clotting disorder where bleeding can last longer than expected. This can be due to a lack of FvW in the blood or because FvW does not work as it should.
Hemophilia A
Wilate is used to treat and prevent bleeding in patients with hemophilia A. This is a disease where bleeding can last longer than expected. It is due to an innate lack of factor VIII in the blood.
2. What you need to know before you use Wilate
Do not use Wilate
- If you are allergic (hypersensitive) to human von Willebrand factor, human coagulation factor VIII or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting treatment with Wilate
- Any medicine, such as Wilate, that is prepared from human blood (containing proteins) and is injected into a vein (administered intravenously) can cause allergic reactions. Pay attention to the first signs of allergic reactions (hypersensitivity), such as hives, skin rash, chest tightness, difficulty breathing, low blood pressure, or anaphylaxis (when any of the above symptoms or all of them develop rapidly and are intense).
If you experience these symptoms, you should immediately stop the injection and contact your doctor.
- When administering medicines derived from plasma or human blood, certain measures must be taken to prevent infections from being transmitted to patients. Such measures include careful selection of blood and plasma donors to ensure the exclusion of those at risk of being carriers of infections, analysis of virus/infection signs in individual donations and plasma pools, as well as inclusion of processing stages capable of inactivating or removing viruses. Despite these measures, when administering medicines prepared from human blood or plasma, the possibility of transmitting an infection cannot be entirely excluded. This also applies to all unknown or emerging viruses or other types of infections.
The measures taken are considered effective against enveloped viruses such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C virus, and against the non-enveloped virus, hepatitis A virus. The measures taken may have limited value against non-enveloped viruses, such as parvovirus B19.
Parvovirus B19 infection can be severe for a pregnant woman (infection in the baby) and for individuals with a weakened immune system or who have a certain type of anemia (e.g., sickle cell disease or abnormal destruction of red blood cells).
- It is strongly recommended that each time you receive a dose of Wilate, you note the name and batch number of the product in order to maintain a record of the batches used.
It is possible that your doctor may recommend that you be vaccinated against hepatitis A and B if you are regularly administered human plasma-derived FvW/factor VIII products.
Von Willebrand disease (VWD)
- See section 4 (Von Willebrand disease (VWD)) for side effects related to VWD treatment.
Hemophilia A
The formation of inhibitors (antibodies) is a known complication that can occur during treatment with all factor VIII medicines. These inhibitors, especially in large quantities, can prevent the treatment from working properly, so you and your child will be carefully monitored for the development of these inhibitors. If your bleeding or your child's bleeding is not being controlled with Wilate, consult your doctor immediately.
- See section 4 (Hemophilia A) for side effects related to hemophilia A treatment.
Using Wilate with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
Although no interactions of Wilate with other medicines are known, inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are using or have recently used other medicines, even those purchased without a prescription.
Do not mix Wilate with other medicines during injection.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before using any medicine.
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
Wilate contains sodium
This medicine contains up to 58.7 mg of sodium (the main component of table/cooking salt) in each vial of 500 UI FvW and FVIII and up to 117.3 mg in each vial of 1000 UI FvW and FVIII. This is equivalent to 2.94% and 5.87%, respectively, of the maximum recommended daily sodium intake for an adult.
3. How to use Wilate
Wilate must be injected into a vein (administered intravenously) after reconstitution with the provided solvent. Treatment should be initiated under medical supervision.
Dose
Your doctor will recommend your individual dose and how often you should use Wilate. Follow your doctor's instructions for administering Wilate exactly. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
If you use more Wilate than you should
No symptoms of overdose with FvW or human factor VIII have been described. However, do not exceed the recommended dose.
If you forget to use Wilate
Do not administer a double dose to make up for forgotten doses.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Wilate can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
- Although rarely, allergic or hypersensitivity reactions have been observed. These reactions can include:
irritation and itching at the injection site, chills, flushing, headache, rashes (hives), low blood pressure (hypotension), fatigue (lethargy), nausea (dizziness), restlessness, increased heart rate (tachycardia), chest tightness, tingling, vomiting, difficulty breathing, sudden swelling in several parts of the body (angioedema).
If you experience any of these symptoms, inform your doctor.
You should stop using Wilate and see your doctor immediately if you experience symptoms of angioedema, such as:
- swelling of the face, tongue, or throat
- difficulty swallowing
- hives and difficulty breathing
- Although rarely, fever has also been observed.
- Pain in the abdomen, back, chest, cough, and dizziness may also occur, but the frequency of these adverse reactions is unknown.
- In very rarecases, hypersensitivity can lead to a severe allergic reaction called anaphylaxis (when any of the above symptoms or all of them develop rapidly and are intense), which can include shock. In case of anaphylactic shock, treatment using current medical recommendations for shock is essential.
Von Willebrand disease (VWD)
- When using a FvW product containing factor VIII to treat VWD, continued treatment may cause an excessive increase in factor VIII in the blood. This can increase the risk of altered blood flow (thrombosis).
If you are a patient with known clinical or laboratory risk factors, you should be monitored for the first signs of thrombosis. Your doctor should establish prevention (prophylaxis) of thrombotic episodes according to current recommendations.
- Patient with VWD (especially type 3 patients) may develop inhibitors (neutralizing antibodies) of FvW during treatment with FvW. In these very rarecases, the inhibitors can interrupt the proper functioning of Wilate.
In case your bleeding continues, the presence of these inhibitors in your blood should be analyzed.
The inhibitors can increase the risk of severe allergic reactions (anaphylactic shock). If you experience an allergic reaction, the presence of inhibitors should be analyzed.
Once inhibitors have been detected in your blood, contact a doctor with experience in treating patients with bleeding disorders. In patients with high levels of inhibitors, another type of treatment may be useful and should be considered.
Hemophilia A
- In children who have not received prior treatment with factor VIII medicines, inhibitor antibodies (see section 2) may occur very frequently (more than 1 in 10 patients); however, in patients who have received prior treatment with factor VIII (more than 150 days of treatment), the risk is rare (less than 1 in 100 patients). If this happens, the medicines you or your child are taking may stop working properly, and you or your child may experience persistent bleeding. In this case, contact your doctor immediately.
The inhibitors can increase the risk of severe allergic reactions (anaphylactic shock). If you experience an allergic reaction, the presence of inhibitors should be analyzed.
Uncommon:may affect up to 1 in 100 patients. Rare:may affect up to 1 in 1,000 patients. Very rare:may affect up to 1 in 10,000 patients. |
There is not enough data to recommend the use of Wilate in previously untreated patients.
Experience with Wilate treatment in children under 6 years of age is limited.
For information on viral safety, see section 2 (Warnings and precautions).
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Wilate
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Store the powder and solvent vial in the refrigerator (2°C - 8°C).
Do not freeze.
Keep the vials in the outer packaging to protect them from light.
Do not use Wilate after the expiry date stated on the carton after EXP: The expiry date is the last day of the month stated.
Wilate can be stored at a temperature below 25°C for 2 months. In this case, the validity period is 2 months after the product is first removed from the refrigerator. You should note the new validity period on the carton.
The powder should only be dissolved immediately before injection. The solution has been shown to be stable for 4 hours at a temperature below 25°C. However, to avoid contamination, the solution should be used immediately and only once. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Wilate
- The active substance is human von Willebrand factor and human coagulation factor VIII.
- The other components are sodium chloride, glycine, sucrose, sodium citrate, calcium chloride. Solvent: water for injectable preparations with 0.1% polysorbate 80.
Appearance of the Product and Container Contents
Lyophilized powder: white or pale yellow powder or pulverized solid.
Reconstituted solution: must be transparent or slightly opalescent.
Wilate is supplied as a powder and solvent for solution for injection. It is presented in 2 container sizes:
- Wilate, 500 IU FvW and 500 IU FVIII, powder and solvent for solution for injection, nominally contains 500 IU of human von Willebrand factor and 500 IU of human coagulation factor VIII per vial. The product contains approximately 100 IU/ml of human von Willebrand factor and 100 IU/ml of human coagulation factor VIII when reconstituted with 5 ml of water for injectable preparations with 0.1% polysorbate 80 (solvent).
- Wilate, 1000 IU FvW and 1000 IU FVIII, powder and solvent for solution for injection, nominally contains 1000 IU of human von Willebrand factor and 1000 IU of human coagulation factor VIII per vial. The product contains approximately 100 IU/ml of human von Willebrand factor and 100 IU/ml of human coagulation factor VIII when reconstituted with 10 ml of water for injectable preparations with 0.1% polysorbate 80 (solvent).
Container Contents
1 vial of lyophilized powder
1 vial of solvent
1 box with equipment for intravenous injection (1 transfer device, 1 infusion set, 1 disposable syringe)
2 alcohol swabs
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Octapharma S.A.
Avda. Castilla, 2. (P.E. San Fernando)
Ed. Dublin – 2ª Planta, 28830 San Fernando de Henares
Madrid
Manufacturer:
Octapharma Dessau GmbH
Otto-Reuter-Str. 3
D-06847 Dessau-Roßlau
Germany
or
Octapharma Pharmazeutika Produktionsges.m.b.H.
Oberlaaerstr. 235
A-1100 Vienna
Austria
or
Octapharma GmbH
Elisabeth-Selberst-Str. 11
40764 Langenfeld
Germany
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet: 02/2021
This Medicinal Product is Authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the Following Names:
Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Estonia, Germany, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovenia, Slovakia, Spain, United Kingdom: Wilate 500/Wilate 1000
Finland, Norway, Sweden: Wilate
Denmark: Wilnativ
France: Eqwilate 500/ Eqwilate 1000
Instructions for Ambulatory Treatment
- Read all instructions and follow them carefully.
- Do not use Wilate after the expiration date stated on the container.
- During the procedure described below, sterility must be maintained.
- The reconstituted medicinal product must be inspected visually for particles or color changes before administration.
- The solution must be clear or slightly opalescent. Do not use cloudy solutions or those containing sediment.
- Use the prepared solution immediately to avoid microbial contamination.
- Use only the equipment provided. The use of other injection/infusion equipment may cause additional risk and treatment failure.
Instructions for Preparing the Solution:
- Do not use the product directly from the refrigerator. Leave the solvent and powder in the closed vials until they reach room temperature.
- Remove the flip-off caps from the vials and clean the rubber stoppers with one of the included alcohol swabs.
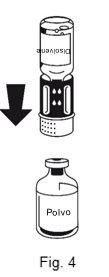
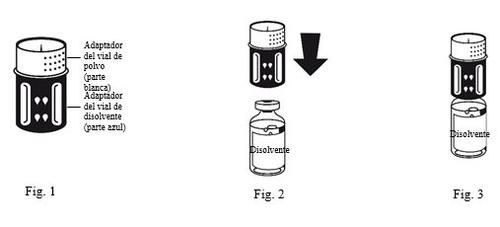
- The transfer device is shown in Fig. 1. Place the solvent vial on a flat surface and hold it firmly. Take the transfer device and turn it over. Place the blue part of the transfer device over the top of the solvent vial and press firmly until you hear a click (Fig. 2 + 3). Do not twist it when attaching.
|
|
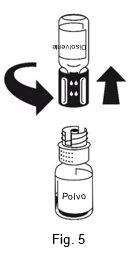
The dissolution is complete in less than 10 minutes at room temperature. A slight foam may appear during preparation. Unscrew the two parts of the transfer device (Fig. 5). The foam will disappear. Discard the empty solvent vial along with the blue part of the transfer device. |
|
Instructions for Injection:
As a precaution, the pulse rate should be measured before and during injection. If the pulse rate increases significantly, reduce the injection rate or interrupt administration for a brief period.
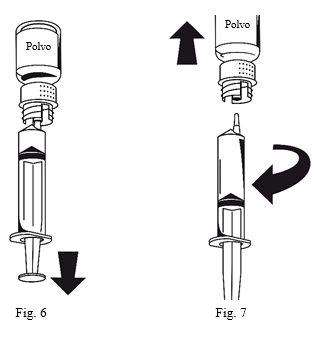
- Attach the syringe to the white part of the transfer device. Turn the vial over and withdraw the solution into the syringe (Fig. 6). The solution must be clear or slightly opalescent. Once the solution has been transferred, hold the syringe plunger firmly (keeping it down) and withdraw the syringe from the transfer device (Fig. 7). Discard the empty vial along with the white part of the transfer device.
- Clean the injection site with one of the included alcohol swabs.
- Attach the included infusion set to the syringe.
- Insert the injection needle into the chosen vein. If a tourniquet has been used to make the vein more visible, this tourniquet must be released before starting the injection of Wilate.
There should be no blood flow into the syringe due to the risk of fibrin clot formation.
- Inject the solution into the vein at a slow rate, not exceeding 2-3 ml per minute.
If more than one vial of Wilate powder is used for a treatment, the same injection needle and syringe may be used. The transfer device is for single use.
Disposal of unused medicinal product and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
Wilate must not be mixed or injected (with the same infusion set) with other medicinal products. Use only the infusion set provided. The use of other injection/infusion equipment may cause additional risks and treatment failure (adsorption of FvW/factor VIII onto the inner surfaces of some infusion equipment).
Detailed and up-to-date information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to WILATE 1000 IU FvW/1000 IU FVIII, POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 100 IU FVIII/ 120 IU FVW per mlActive substance: von Willebrand factor and coagulation factor VIII in combinationManufacturer: Instituto Grifols S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 25 IU FVIII/ 30 IU FVW per mlActive substance: von Willebrand factor and coagulation factor VIII in combinationManufacturer: Instituto Grifols S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 50 IU FVIII/60 IU vWF per mlActive substance: von Willebrand factor and coagulation factor VIII in combinationManufacturer: Instituto Grifols S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for WILATE 1000 IU FvW/1000 IU FVIII, POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Discuss questions about WILATE 1000 IU FvW/1000 IU FVIII, POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions