WILLFACT 1000 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION

How to use WILLFACT 1000 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Willfact 500UI powder and solvent for solution for injection
Willfact 1000UIpowder and solvent for solution for injection
Willfact 2000UIpowder and solvent for solution for injection
human von Willebrand factor
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine, because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, as you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack:
- What is Willfact and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Willfact
- How to use Willfact
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Willfact
- Contents of the pack and further information
1. What is Willfact and what is it used for
Willfact is obtained from human plasma (the liquid part of the blood) and is a medicine that contains the active substance called von Willebrand factor (VWF).
VWF is involved in blood clotting. The lack of this factor, as occurs in von Willebrand disease, means that the blood does not clot as quickly as it should, resulting in a greater tendency to bleed. Replacement of VWF with Willfact will temporarily repair the blood clotting mechanisms.
Willfact is indicated for the prevention and treatment of surgical or other haemorrhages in patients with von Willebrand disease when treatment with desmopressin (DDAVP) alone is not effective or is contraindicated.
Willfact can be used in all age groups.
Willfact must not be used as a treatment for Haemophilia A.
2. What you need to know before you use Willfact
Do not useWillfact
- if you are allergic to human von Willebrand factor or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- if you have Haemophilia A.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before starting treatment with Willfact.
Treatment with Willfact should always be supervised by a doctorexperienced in the treatment of haemostatic disorders.
If you have a severe haemorrhage and a blood test indicates that your factor VIII level is low, you will receive VWF preparation in addition to a factor VIII preparation in the first 12 hours.
Reactions to the medicine
Allergic reactions can occur with all human blood or plasma-derived proteins administered intravenously. During injection, you will be monitored for any early signs of hypersensitivity. This includes rash (hives or generalised urticaria), chest tightness, difficulty breathing, low blood pressure (hypotension), and severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis).
Your doctor will inform you of the warning signs of an allergic reaction.
If signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity occur, treatment should be discontinued and medical attention sought immediately.
Virus safety
When medicines are prepared from human blood or plasma, certain measures are taken to prevent the transmission of infections to patients. These include:
- careful selection of blood and plasma donors to exclude those at risk of carrying infections,
- testing of each donation and plasma pools for signs of viruses/infections,
- inclusion of steps in the processing of blood or plasma that can inactivate or remove viruses.
Despite these measures, when medicines prepared from human blood or plasma are administered, the possibility of transmitting infections cannot be totally excluded. This also applies to any unknown or emerging viruses or other types of infections.
The measures taken are considered effective against enveloped viruses such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C virus.
The measures taken may have limited value against non-enveloped viruses such as hepatitis A virus and parvovirus B19. Parvovirus B19 infection can be severe for pregnant women (since there is a risk of infection of the fetus) and for individuals whose immune system is depressed or who have certain types of anaemia (e.g. sickle cell anaemia or haemolytic anaemia).
Vaccinations
Your doctor may recommend that you consider vaccination against hepatitis A and B if you regularly receive human plasma-derived von Willebrand factor.
Batch number registration
It is strongly recommended that each time you receive a dose of Willfact, you record the name and batch number of the medicine to keep a record of the batches used.
Risk of thrombosis
Blood clots (thrombosis) can also block blood vessels. There is a risk, especially if your medical history or test results indicate that you have certain risk factors. In this case, you will be closely monitored for any early signs of thrombosis and will receive preventive treatment (prophylaxis) against blockage of the veins due to blood clots.
When using a von Willebrand factor product that contains factor VIII, your doctor will take into account that continued treatment may lead to an excessive increase in FVIII. If you receive a FVW product that contains FVIII, your doctor will periodically check your plasma FVIII levels. This ensures that there is no sustained excess of plasma FVIII levels, which could increase the risk of thrombotic events.
Limited efficacy
In patients with von Willebrand disease, especially those with Type 3, proteins that neutralise the effect of VWF may be formed. These proteins are called neutralising antibodies or inhibitors. If laboratory results show that your VWF levels are not being replaced or if bleeding is not stopped despite administration of an adequate dose of Willfact, your doctor will check if your body has developed inhibitors against VWF.
If these inhibitors are present in high concentrations, treatment with VWF may not be effective, and other treatment options should be considered. The new treatment will be administered by a doctor experienced in the treatment of haemostatic disorders.
Other medicines and Willfact
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Willfact must not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding unless clearly indicated.
The safety of Willfact during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been studied in controlled clinical trials. Animal studies are insufficient to establish safety with respect to fertility, pregnancy, and child development during pregnancy and after birth.
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
No effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been observed.
Willfact containssodium
A 5 ml vial (500 IU) of Willfact contains 0.15 mmol (3.4 mg) of sodium.
This is equivalent to 0.17% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium for an adult.
A 10 ml vial (1000 IU) of Willfact contains 0.3 mmol (6.9 mg) of sodium.
This is equivalent to 0.35% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium for an adult.
A 20 ml vial (2000 IU) of Willfact contains 0.6 mmol (13.8 mg) of sodium.
This is equivalent to 0.69% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium for an adult.
3. How to use Willfact
Your treatment should be started and monitored by a doctor experienced in the treatment of bleeding disorders.
If your doctor considers that administration can be carried out at home, they will provide you with appropriate instructions.
Dosage
Always use this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. If you are not sure, consult your doctor.
Willfact should preferably be administered by your doctor or nurse. However, if you have been prescribed Willfact for self-administration at home, your doctor will ensure that you are taught how to inject it and what dose to use. Follow the instructions given by your doctor and ask for help if you have problems handling the syringe; it should always be used by a trained person.
Your doctor will calculate your dose of Willfact (in international units or IU).
The dose you receive will depend on:
- body weight,
- site of bleeding,
- severity of bleeding,
- clinical condition,
- surgery required,
- levels of VWF activity in your blood after surgery,
- severity of your disease
This dose varies between 40 to 80 IU/kg.
Your doctor will recommend that you undergo blood tests during treatment to monitor
- factor VIII (FVIII:C) levels,
- von Willebrand factor (VWF:RCo) levels,
- the presence of inhibitors,
- early signs of clot formation if you are at risk of such complications.
Based on the results of these tests, your doctor may decide to adjust the dose and frequency of your injections.
In certain cases, it may be necessary to use a factor VIII preparation (another clotting protein) in addition to Willfact to treat or prevent bleeding more quickly (in emergency situations or acute bleeding).
Willfact can be administered as long-term prophylaxis; the dose level is also determined individually in this case. Doses of 40 to 60 IU/kg of Willfact, administered two or three times a week, reduce the number of bleeding episodes.
Use in children and adolescents
The dose for children and adolescents is based on body weight. In some cases, especially in younger patients (under 6 years), higher doses (up to 100 IU/kg) may be necessary.
Tell your doctor if you think the effect of Willfact is too strong or too weak.
Method of administration
Detailed instructions for reconstitution and administration of the medicine are given at the end of the leaflet.
If you use moreWillfactthan you should
No symptoms of overdose with Willfact have been reported.
However, the risk of thrombosis cannot be excluded in the case of significant overdosing.
If you forget to use Willfact
If you forget to take WILLFACT, consult your doctor.
Do not take a double dose to make up for the forgotten dose.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult your doctor or pharmacist or call the Toxicology Information Service, telephone 91 562 04 20, indicating the medicine and the amount taken.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Contact your doctor immediately if:
- You notice symptoms of hypersensitivity or allergic reactions (observed in less than 1 in 100 people).
In some cases, these reactions can evolve into a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis), including anaphylactic shock (observed with an unknown frequency).
The warning signs of allergic reactions are
- Difficulty breathing and swallowing
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
- Increased heart rate
- Decreased or falling blood pressure
- Fainting
- Extreme fatigue
- Restlessness, nervousness
- Headache
- Chills, feeling of cold
- Flushing, hot flushes
- Swelling in different parts of the body
- Rash, generalised urticaria
- Burning and itching at the infusion site
- Tingling
- Vomiting
- Nausea
If one of these effects occurs, stop treatment immediately and contact your doctorto initiate appropriate treatment according to the type and severity of the reaction. |
- You notice that the medicine is not working properly (bleeding is not controlled). This may be due to inhibition of von Willebrand factor (observed with an unknown frequency).
In patients with von Willebrand disease, especially those with Type 3, proteins that neutralise the effect of VWF may be formed. These proteins are called neutralising antibodies or inhibitors. Patients treated with VWF should be carefully monitored by their doctors to detect the development of inhibitors through clinical observations and appropriate laboratory tests. If such inhibitors occur, the condition may manifest as an inadequate clinical response or occur concurrently with severe allergic reactions.
- You notice any symptoms of impaired perfusion in the limbs (e.g. cold and pale limbs) or vital organs (e.g. severe chest pain). This may be due to the formation of blood clots in the blood vessels (observed with an unknown frequency).
There is a risk of blood clot formation (thrombosis), especially in patients with known risk factors. After correction of the von Willebrand factor deficiency, you should be monitored for early signs of thrombosis or disseminated intravascular coagulation and receive treatment to prevent thrombosis in situations that involve a higher risk of thrombosis (after surgery, during bed rest, in cases of deficiency of a coagulation inhibitor or a fibrinolytic enzyme).
If you receive factor VIII preparations that contain VWF, the risk of thrombosis may also increase due to persistently elevated plasma FVIII levels.
The following side effect has been observed frequently(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Infusion site reactions
The following side effects have been observed infrequently(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Dizziness
- Paresthesia, hypoesthesia
- Flushing
- Itching
- Feeling of oppression
- Chills, feeling of cold
The following side effect has been observed with an unknown frequency:
- Fever
Reporting of side effects:
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly through the Spanish Medicines Monitoring System for Human Use: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Willfact
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the vial label and carton.
Do not store above 25°C. Store in the original package to protect from light.
Do not freeze.
For reasons of sterility, the product should be used immediately after physical and chemical reconstitution. However, physicochemical stability has been demonstrated for 24 hours at +25°C.
Do not use this medicine if you notice that the solution is turbid or contains deposits.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist or nurse how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Content and Additional Information
Composition ofWillfact
- The active ingredientis: human von Willebrand factor (500 IU, 1000 IU, or 2000 IU), expressed in International Units (IU) of ristocetin cofactor activity (FVW:RCo).
After reconstitution with 5 ml (500 IU), 10 ml (1000 IU), or 20 ml (2000 IU) of water for injectable preparations, a vial contains approximately 100 IU/ml of human von Willebrand factor.
Before adding albumin, the specific activity is greater than or equal to 60 IU of FVW:RCo/mg of total protein.
- The other componentsare:
Powder: human albumin, arginine hydrochloride, glycine, sodium citrate, and calcium chloride dihydrate.
Solvent: water for injectable preparations.
Appearance of the Productand Container Content
Willfact is presented as a white or pale yellow powder or friable solid and a clear or colorless solvent for injectable solution after reconstitution with a transfer system.
Willfact is available in containers of 500 IU/5 ml, 1000 IU/10 ml, and 2000 IU/20 ml.
The reconstituted solution should be clear or slightly opalescent, colorless or slightly yellow.
Marketing Authorization Holder
LFB-BIOMEDICAMENTS
3, avenue des Tropiques,
ZA de Courtaboeuf,
91940 Les Ulis
FRANCE
Manufacturer
LFB BIOMEDICAMENTS
3, Avenue des Tropiques, BP 305 - Les Ulis, Courtaboeuf - F-91958 – France
or
LFB BIOMEDICAMENTS
59 Rue de Trevise. BP 2006 - Lille - F-59011 - France
For further information on this medicinal product, please contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
LFB BIOTERAPIAS HISPANIA,S.L.
C/ Diego de León 47
28006 Madrid
(Spain)
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Austria Willfact
Czech Republic WILLFACT
Denmark Willfact
Germany WILLFACT
Hungary Willfact
Norway Willfact
Poland Willfact
Slovak Republic Willfact
Spain Willfact
Sweden Willfact
United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) Willfact
Date of the last revision of this leaflet:March 2024
Detailed and up-to-date information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
_____________________________________________________________________________
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE:
Posology
Generally, the administration of 1 IU/kg of von Willebrand factor raises the circulating level of FvW:RCo by approximately 0.02 IU/mL (2%).
Levels of VWF:RCo of > 0.6 IU/mL (60%) and FVIII:C of > 0.4 IU/mL (40%) should be achieved.
Hemostasis cannot be guaranteed until the coagulant activity of factor VIII (FVIII:C) has reached 0.4 IU/ml (40%). The injection of von Willebrand factor alone does not induce a maximum increase in FVIII:C until at least 6 to 12 hours have passed. It cannot immediately correct the FVIII:C level. Therefore, if the patient's baseline FVIII:C levels are below this critical level, in all situations where rapid correction of hemostasis is required, such as treatment of a hemorrhage, severe trauma, or emergency surgery, factor VIII should be administered with the first injection of von Willebrand factor to achieve a hemostatic plasma level of FVIII:C.
However, if an immediate increase in FVIII:C is not necessary, such as in the case of scheduled surgery, or if the patient's baseline FVIII:C levels are sufficient to ensure hemostasis, the physician may decide to dispense with the co-administration of FVIII for the first injection of von Willebrand factor.
- Start of treatment:
The first dose of WILLFACT is 40 to 80 IU/kg for the treatment of hemorrhages or trauma, along with the necessary amount of factor VIII product, calculated based on the patient's baseline plasma level of FVIII:C, in order to achieve an adequate plasma level of FVIII:C immediately before the intervention or as soon as possible after the start of the hemorrhagic episode or severe trauma. In the case of surgery, the first injection should be administered 1 hour before the intervention.
A initial dose of 80 IU/kg of WILLFACT may be necessary, especially in patients with type 3 von Willebrand disease, in whom maintaining adequate levels may require higher doses than in other types of VWD.
In the case of elective surgery, the first injection of WILLFACT should be administered between 12 and 24 hours before the intervention, and the second before the intervention. In these cases, it is not necessary to administer factor VIII concurrently, as the endogenous FVIII:C usually reaches the critical level of 0.4 IU/mL (40%) before the intervention. However, this should be confirmed in each patient.
- Subsequent injections:
If necessary, treatment should be continued with 40 to 80 IU/kg of WILLFACT alone per day, in one or two daily injections for one or several days. The dose and frequency of injections should always be adapted to the type of surgical intervention, the patient's clinical and biological status (VWF:RCo and FVIII:C), and the type and severity of the hemorrhagic episode.
- Long-term prophylaxis:
WILLFACT can be administered as long-term prophylaxis, at doses adapted to each patient. Doses of WILLFACT of 40 to 60 IU/kg, administered 2 to 3 times a week, reduce the number of hemorrhagic episodes.
- Ambulatory treatment:
Home treatment can be initiated with the physician's approval, especially in cases of mild to moderate hemorrhages or during long-term prophylaxis to prevent hemorrhages.
- Pediatric population
For each indication, the dose is based on body weight. The dose and duration of treatment should be adjusted according to the patient's clinical status and plasma levels of FVIII:C and FVW:Rco.
- Start of treatment:
- For children under 6 years of age, the initial dose may be guided by the patient's incremental recovery (IR) or, if no IR data are available, an initial dose of 60 to 100 IU/kg may be necessary to raise FVW:Rco levels to 100 IU/dl.
- In the case of children over 6 years of age and adolescents, the posology is the same as for adult patients.
- Subsequent injections:
For children and adolescents, subsequent doses should be individualized according to the clinical status and FVW:Rco levels, and adjusted according to the clinical response.
In the case of scheduled surgery:
- In children under 6 years of age, after a first dose administered 12 to 24 hours before the intervention, a repeated dose may be administered 30 minutes before the intervention.
- In the case of children over 6 years of age and adolescents, the posology is the same as for adult patients.
- Prophylaxis:
For children and adolescents, the dose and frequency of subsequent administrations should be individualized according to the patient's incremental recovery and FVW:Rco levels, and adjusted according to the clinical response.
Route and Method of Administration
Intravenous administration
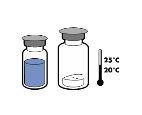
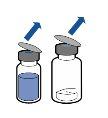
Reconstitution:
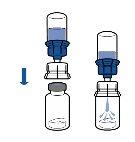
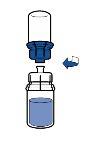
Current guidelines for aseptic procedures should be followed. The transfer system should only be used to reconstitute the medicinal product, as described below. It is not designed to administer the medicinal product to the patient.
|
|
The powder usually dissolves instantly and should dissolve in less than 10 minutes.
The solution should be clear or slightly opalescent, colorless or pale yellow. The reconstituted product should be visually inspected for particles and discoloration before administration.
Do not use solutions that are cloudy or contain sediment.
Do not mix with other medicinal products.
Do not dilute the reconstituted product.
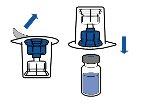
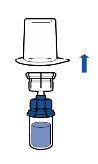
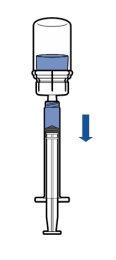
Administration:
|
|
Storage after Reconstitution
For reasons of sterility, the product should be used immediately after reconstitution. However, its physical and chemical stability has been demonstrated after 24 hours at +25°C.
Disposal of unused products or containers should be carried out in accordance with local requirements.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to WILLFACT 1000 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 100 IU/mlActive substance: von Willebrand factorManufacturer: Lfb BiomedicamentsPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 100 IU/mlActive substance: von Willebrand factorManufacturer: Lfb BiomedicamentsPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 1,000 IUActive substance: coagulation factor VIIIManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AgPrescription required
Online doctors for WILLFACT 1000 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Discuss questions about WILLFACT 1000 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions