
HAEMATE P 2400/1000 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVEL OU PARA PERFUSÃO

Pergunte a um médico sobre a prescrição de HAEMATE P 2400/1000 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVEL OU PARA PERFUSÃO

Como usar HAEMATE P 2400/1000 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVEL OU PARA PERFUSÃO
Introdução
PROSPECTO: INFORMAÇÃO PARA O UTILIZADOR
Haemate P 2400UI FVW/1000 UIFVIII
Pó e dissolvente para solução injetável e para perfusão
Fator von Willebrand humano (FVW)
Fator de coagulação VIII humano (FVIII)
Leia todo o prospecto detenidamente antes de começar a usar este medicamento,porque contém informações importantes para si.
- Conserva este prospecto, porque pode ter que voltar a lê-lo.
- Se tiver alguma dúvida, consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico.
- Este medicamento foi-lhe prescrito apenas para si, e não deve dá-lo a outras pessoas, mesmo que tenham os mesmos sintomas que si, porque pode prejudicá-las.
- Se experimentar efeitos adversos, consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico, mesmo que se trate de efeitos adversos que não aparecem neste prospecto. Ver seção 4.
Conteúdo do prospecto
- O que é Haemate P e para que é utilizado
- O que precisa saber antes de começar a usar Haemate P
- Como usar Haemate P
- Posíveis efeitos adversos
- Conservação de Haemate P
- Conteúdo do envase e informações adicionais
1. O que é Haemate P e para que é utilizado
O que é Haemate P?
Haemate P apresenta-se como pó acompanhado do dissolvente. A solução obtida é administrada por injeção ou perfusão na veia. Haemate P pertence a um tipo de medicamentos chamados antihemorrágicos.
Haemate P é fabricado a partir de plasma humano (a parte líquida do sangue) e contém fator von Willebrand humano (FVW) e fator de coagulação VIII humano (FVIII).
Para que é utilizadoHaemate P?
Como Haemate P contém tanto FVIII como FVW, é importante saber que fator precisa mais. Se tem hemofilia A, o seu médico prescrever-lhe-á Haemate P com o número de unidades de FVIII especificado. Se tem a doença de von Willebrand, o seu médico prescrever-lhe-á Haemate P com o número de unidades de FVW especificado.
Doença de von Willebrand
Profilaxia e tratamento de hemorragias ou sangramentos quirúrgicos na doença de von Willebrand, quando o tratamento apenas com desmopressina é ineficaz ou está contraindicado.
Hemofilia A (deficiência congénita de fator VIII)
Tratamento e profilaxia de hemorragias em pacientes com hemofilia A.
Este produto pode ser útil no manejo da deficiência adquirida de fator VIII.
2. O que precisa saber antes de começar a usar Haemate P
As secções seguintes contêm informações que o seu médico deve ter em conta antes de prescrever-lhe Haemate P.
Não use Haemate P:
- Se é alérgico (hipersensível) ao fator von Willebrand humano, ao fator de coagulação VIII humano, ou a algum dos outros componentes deste medicamento (incluídos na seção 6).
Informa o seu médico se é alérgico a qualquer medicamento ou alimento.
Advertências e precauções:
Traçabilidade
Recomenda-se encarecidamente que cada vez que se administre Haemate P, o seu médico deixe constância da data de administração, do número do lote do medicamento para manter um registo dos lotes utilizados.
Consulte com o seu médico ou farmacêutico antes de começar a usar Haemate P:
- Em caso de que apareçam reações alérgicas ou anafilácticas(reações alérgicas graves que produzem graves dificuldades respiratórias ou mareios). É possível que se produzam reações de hipersensibilidade de tipo alérgico. O seu médico deve informá-lo dos primeiros sintomas das reações de hipersensibilidade. Entre eles incluem-se erupções, sarpullido generalizado, pressão no peito, dificuldade na respiração, queda da pressão sanguínea e anafilaxia (reações alérgicas graves que produzem graves dificuldades respiratórias ou mareios). Se se produzirem esses sintomas, deixe de usar o produto de imediato e entre em contacto com o seu médico.
- A formação de inibidores (anticorpos), é uma complicação conhecida que pode produzir-se durante o tratamento com todos os medicamentos compostos por fator VIII. Esses inibidores, especialmente em grandes quantidades, impedem que o tratamento funcione corretamente, por isso se lhe supervisionará cuidadosamente a si e ao seu filho por si desenvolverem ditos inibidores. Se a sua hemorragia ou a do seu filho não se está a controlar com Haemate P, consulte o seu médico imediatamente.
- Se padece uma doença cardíaca ou tem risco de padecer, informe o seu médico ou farmacêutico.
- Se para a administração de Haemate P se necessita de um dispositivo de acesso venoso central (DAVC), o seu médico deverá considerar o risco de complicações relacionadas com o catéter, incluindo as infecções locais, bactérias no sangue (bacteriemia) e a formação de coágulos de sangue (trombose) no local de inserção do catéter.
Doença de von Willebrand
- Em caso de que exista o risco de formação de coágulos de sangue (efeitos trombóticos, incluindo coágulos de sangue no pulmão), particularmente no caso de que o paciente apresente fatores de risco clínicos ou de laboratório (por exemplo, em períodos perioperatórios sem receber profilaxia de trombose, mobilização tardia, obesidade, sobredosagem, cancro), o paciente deverá ser controlado acerca dos primeiros sintomas de trombose. Deve estabelecer-se a prevenção da trombose venosa de acordo com as recomendações atuais. Os pacientes com doença de von Willebrand, especialmente os pacientes com o tipo 3 desta doença, podem desenvolver anticorpos neutralizantes (inibidores) contra o fator de von Willebrand. O seu médico far-lhe-á os testes necessários para detectar a sua presença e considerará se seguir ou não com esta terapia.
O seu médico terá que considerar cuidadosamente os benefícios do tratamento com Haemate P em comparação com os riscos dessas complicações.
Segurança viral
Quando se administram medicamentos derivados do plasma ou sangue humanos, não se pode excluir totalmente a ocorrência de doenças devidas à transmissão de agentes infecciosos. Isso também se refere à possível transmissão de patógenos de natureza desconhecida ou emergente ou a outros tipos de infecções. No entanto, o risco de transmissão de agentes infecciosos reduz-se por:
- a seleção cuidadosa dos doadores de sangue e plasma para garantir que se exclua os possíveis portadores de infecções;
- análise de cada doação e mistura de plasmas para detectar sinais de vírus/infecções;
- inclusão de etapas no processo de fabricação do sangue ou plasma para inativar ou eliminar os vírus.
Estes procedimentos consideram-se eficazes para vírus envoltos como o vírus da imunodeficiência humana (VIH, o vírus da SIDA), o vírus da hepatite B e o vírus da hepatite C (que causam a inflamação do fígado) e para vírus não envoltos como o vírus da hepatite A (inflamação do fígado).
Os procedimentos de inativação/eliminação podem ter um valor limitado para vírus não envoltos como o parvovirus B19.
A infecção por parvovirus B19 pode ser grave para uma mulher grávida (infecção fetal) e para sujeitos com imunodeficiência ou com uma produção aumentada de hematíes (por exemplo, com anemia hemolítica).
É possível que o seu médico lhe recomende vacinar-se contra a hepatite A e B se receber de forma regular ou repetida concentrados de fator von Willebrand e fator de coagulação VIII humano.
Uso de Haemate P com outros medicamentos
- Informa o seu médico ou farmacêutico se está a utilizar ou utilizou recentemente ou pudesse ter que utilizar qualquer outro medicamento.
- Este medicamento não deve ser misturado com outros medicamentos, dissolventes e diluentes.
Gravidez, lactação e fertilidade
- Se está grávida ou em período de lactação, acredita que possa estar grávida ou tem intenção de engravidar, consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico antes de utilizar este medicamento.
- Devido a que a hemofilia A é rara nas mulheres, não se dispõe de experiência relativa ao uso de fator VIII durante a gravidez e a lactação.
- No caso da doença de von Willebrand, as mulheres são mesmo mais afetadas do que os homens. De acordo com a experiência acumulada após a comercialização, pode recomendar-se a substituição do FVW na prevenção e no tratamento de hemorragias agudas. Não há estudos clínicos disponíveis sobre a terapia substitutiva com o FVW em mulheres durante a gravidez e a lactação.
- Durante a gravidez e a lactação, Haemate P apenas deve ser administrado se estiver claramente indicado.
Condução e uso de máquinas
Haemate P não afeta a capacidade para conduzir veículos e usar máquinas.
Haemate P contém sódio
Haemate P 2400 UI VWF/1000 UI FVIII contém 52,5 mg de sódio (componente principal do sal de mesa/para cozinhar) em cada frasco. Isso equivale a 2,6% da ingestão diária máxima recomendada para um adulto.
3. Como usar Haemate P
O tratamento deve ser iniciado e supervisionado por um médico com experiência no tratamento de distúrbios de coagulação do sangue.
Dosagem
A quantidade de fator von Willebrand e fator VIII que precisa e a duração do tratamento dependem de vários fatores, como o seu peso, a gravidade da doença, o local e intensidade da hemorragia ou a necessidade de evitá-la durante uma operação ou investigação (ver a seção "Esta informação está destinada apenas a profissionais do setor sanitário").
Se lhe foi prescrito Haemate P para usar em casa, o médico deverá assegurar-se de que sabe como se injeta e a quantidade que deve utilizar.
Siga exatamente as instruções de administração de Haemate P indicadas pelo seu médico ou pelo pessoal sanitário do centro de hemofilia.
Se usar mais Haemate P do que deve
Não se comunicaram sintomas de sobredosagem com FVW e FVIII. No entanto, não se pode excluir o risco de desenvolver coágulos de sangue (trombose) em caso de uma dose extremamente alta, especialmente de produtos com FVW que tenham um elevado conteúdo de FVIII.
Reconstituição e administração
Certifique-se de que trabalha em condições estéreis em todas as etapas do processo.
Instruções gerais
- O pó liofilizado deve ser misturado (reconstituído) com o dissolvente (líquido) e extraído do frasco em condições assépticas.
- A solução deve ser transparente ou ligeiramente opalescente. Depois do filtrado/transvasamento (consulte mais adiante e antes de administrar ao paciente), a solução obtida deve ser examinada visualmente para comprovar que não contém partículas nem apresenta decoloração. Embora se sigam com precisão as recomendações para a preparação da solução (reconstituição), não é raro que fiquem alguns resíduos ou partículas. O filtro incluído no dispositivo Mix2Vial elimina essas partículas por completo. A filtragem não influencia nos cálculos de dosagem.
- Não use soluções visivelmente turvas nem soluções que ainda contenham partículas ou resíduos após a filtragem.
- Após a administração, a quantidade de medicamento que não se utilizou e o material residual devem ser eliminados de acordo com a normativa local e seguindo as instruções do seu médico.
Reconstituição:
Antes de abrir qualquer um dos frascos, tempere o pó de Haemate P e o dissolvente acompanhante até que estejam à temperatura ambiente. Para consegui-lo, pode deixar os frascos à temperatura ambiente durante aproximadamente uma hora ou bem pode tê-los nas mãos fechadas durante alguns minutos. Não exponha os frascos ao calor direto. Os frascos não devem ser aquecidos a uma temperatura superior à do corpo (37 °C).
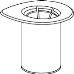
Retire com cuidado as cápsulas protectoras do frasco do dissolvente e do frasco de Haemate P. Limpe a parte exterior dos tapões de borracha de ambos os frascos com uma toalhita impregnada em álcool e deixe-os secar. Agora pode transferir o dissolvente para o frasco do pó com o sistema de administração incluído (Mix2Vial). Por favor, siga as instruções seguintes:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Transvasamento da solução preparada para a seringa e administração | |
|
|
|
|
Administração
Uma vez transferido o produto para a seringa, deve ser utilizado de imediato.
Para a injeção de Haemate P recomenda-se o uso de seringas descartáveis de plástico, pois a superfície de vidro esmerilado das seringas que são totalmente de vidro tende a pegar-se com soluções deste tipo.
A solução reconstituída deve ser administrada lentamente por via intravenosa a uma velocidade não superior a 4 ml por minuto. Tenha cuidado de que não entre sangue na seringa cheia de produto.
Se têm que ser administradas doses mais elevadas, também pode ser feito por perfusão. Com esse propósito, transfira o produto reconstituído para um sistema de perfusão aprovado. A perfusão deve ser feita seguindo as instruções do médico.
Observe se apresenta alguma reação imediata. Se se produzir alguma reação que possa estar relacionada com a administração de Haemate P, deve interromper-se imediatamente a injeção ou perfusão (ver também a seção 2).
Se usar mais Haemate P do que devia
Não se comunicaram sintomas de sobredosagem com FVW e FVIII. No entanto, não se pode excluir o risco de desenvolver coágulos de sangue (trombose) em caso de uma dose extremamente alta, especialmente de produtos com FVW que tenham um elevado conteúdo de FVIII.
Se tiver alguma outra dúvida sobre o uso do produto, pergunte ao seu médico ou farmacêutico.
4. Efeitos adversos possíveis
Tal como todos os medicamentos, este medicamento pode produzir efeitos adversos, embora nem todas as pessoas os sofram.
Os efeitos adversos seguintes foram observados muito raramente (em menos de 1 de cada 10.000 pacientes):
- Uma reação alérgica súbita (como angioedema, queimadura ou picadura no ponto de perfusão, arrepios, sofocos, urticária generalizada, dor de cabeça, erupções, hipotensão, letargia, náuseas, inquietude, taquicardia, pressão no peito, sensação de formigamento, vômito ou respiração difícil) e, em alguns casos, pode progredir para anafilaxia grave (incluindo choque).
- Aumento da temperatura corporal (febre).
Doença de von Willebrand
- Muito raramente, há risco de eventos trombóticos ou tromboembólicos, incluindo coágulos de sangue nos pulmões (risco de formação e migração de coágulos de sangue no sistema vascular, formado pelas artérias e veias, com um impacto potencial nos órgãos).
- Em pacientes que recebem produtos com FVW, níveis plasmáticos excessivos de FVIII:C de forma sustentada podem aumentar o risco de formação de coágulos sanguíneos (consulte também a seção 2).
- Os pacientes com doença de von Willebrand podem desenvolver muito raramente inibidores (anticorpos neutralizadores) do FVW. Se aparecerem tais inibidores, manifesta-se uma ausência de resposta clínica que leva a um sangramento contínuo. Isso ocorre especialmente em pacientes com uma forma específica da doença de von Willebrand, chamada de tipo 3. Esses anticorpos precipitam e podem aparecer ao mesmo tempo que as reações anafiláticas. Portanto, deve-se avaliar a presença de um inibidor nos pacientes que experimentam reação anafiláctica. Nesses casos, recomenda-se entrar em contato com um centro especializado em hemofilia.
Hemofilia A
- Nas crianças que não receberam tratamento prévio com medicamentos compostos por fator VIII, podem produzir-se anticorpos inibidores (ver seção 2) muito frequentemente (mais de 1 de cada 10 pacientes); no entanto, nos pacientes que receberam tratamento prévio com fator VIII (mais de 150 dias de tratamento), o risco é pouco frequente (menos de 1 de cada 100 pacientes). Se isso acontecer, os medicamentos que você ou seu filho tomam podem deixar de funcionar corretamente e você ou seu filho podem sofrer uma hemorragia persistente. Nesse caso, entre em contato com seu médico imediatamente.
Outros efeitos adversos em crianças e adolescentes
Espera-se que a frequência, o tipo e a gravidade dos efeitos adversos em crianças sejam os mesmos que em adultos.
Comunicação de efeitos adversos
Se você experimentar qualquer tipo de efeito adverso, consulte seu médico ou farmacêutico, mesmo que se trate de possíveis efeitos adversos que não aparecem neste prospecto. Você também pode comunicá-los diretamente através do Sistema Espanhol de Farmacovigilância de Medicamentos de Uso Humano: www.notificaRAM.es.
Para informações sobre a segurança viral, ver “Advertências e precauções” (seção 2).
5. Conservação de Haemate P
- Mantenha este medicamento fora da vista e do alcance das crianças
- Não utilize este medicamento após a data de validade que aparece na etiqueta e na caixa após EXP. A data de validade é o último dia do mês que se indica.
- Conservar abaixo de 25 °C.
- Não congelar.
- Mantenha o frasco no embalagem exterior para protegê-lo da luz.
- Haemate P não contém conservantes, portanto, a solução preparada deve ser usada imediatamente.
- Se a solução preparada não for administrada imediatamente, deve ser usada em um período de 3 horas.
- Uma vez transferido o produto para a seringa, deve ser utilizado de imediato.
Os medicamentos não devem ser jogados nos deságues, nem na lixeira. Pergunte ao seu farmacêutico como se livrar dos envases e dos medicamentos que não precisa. Dessa forma, você ajudará a proteger o meio ambiente.
6. Conteúdo do envase e informações adicionais
Composição de Haemate P
Os princípios ativos são: Fator von Willebrand humano e fator de coagulação VIII humano.
Os demais componentes são: Albúmina humana, glicina, cloreto de sódio, citrato de sódio, hidróxido de sódio ou ácido clorídrico (em pequenas quantidades para ajustar o pH).
Veículo :água para preparações injetáveis.
Aspecto do produto e conteúdo do envase
Haemate P é apresentado como um pó branco ou amarelo pálido ou sólido friável e é fornecido com água para preparações injetáveis como veículo. A solução preparada deve ser transparente ou ligeiramente opalescente, ou seja, poderia brilhar ao colocá-la contra a luz, mas não deve conter nenhum tipo de partículas detectáveis.
Apresentação
Caixa que contém:
1 frasco com pó
1 frasco com 15 ml de água para preparações injetáveis
1 dispositivo de transferência com filtro 20/20
Equipamento de administração (caixa interior):
1 seringa de 20 ml de uso único
1 equipamento de punção venosa
2 compressas com álcool
1 curativo adesivo não estéril
Título da autorização de comercialização e responsável pela fabricação
CSL Behring, S.A.
rua Tarragona 157, andar 18
08014 Barcelona (Espanha)
Responsável pela fabricação
CSL Behring, GmbH
Emil-von-Behring-Str. 76
35041 Marburg (Alemanha)
Data da última revisão deste prospecto:Julho 2023
A informação detalhada e atualizada deste medicamento está disponível na página web da Agência Espanhola de Medicamentos e Produtos Sanitários (AEMPS) (http://www.aemps.gob.es/)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Esta informação está destinada apenas a profissionais do setor sanitário:
Posologia
Doença de von Willebrand
É importante calcular a dose utilizando o número de UI de FVW:RCo especificado.
Em geral, a administração de 1 UI de FVW:RCo/kg de peso corporal aumenta os níveis circulantes de VWF:RCo em 0,02 UI/ml, o que representa um aumento de 2%.
Devem ser alcançados níveis superiores a 0,6 UI de FVW:RCo/ml (60%) e níveis superiores a 0,4 UI de FVIII:C/ml (40%).
As doses recomendadas para conseguir a hemostasia são 40 - 80 UI de FVW:RCo/kg de peso e 20 - 40 UI de FVIII:C/kg de peso.
Em certos casos pode ser necessária uma dose inicial de 80 UI de fator de von Willebrand, especialmente naqueles pacientes com uma doença de von Willebrand Tipo 3, nos quais a terapia de manutenção de níveis adequados pode requerer doses superiores às que demandam os outros tipos de doença de von Willebrand.
Prevenção de hemorragias em casos de cirurgia ou lesões graves:
Para prevenir sangramentos profusos durante ou após a cirurgia, a administração do produto deve ser iniciada de 1 a 2 horas antes de começar a cirurgia.
Uma dose adequada deve ser repetida a intervalos de 12 a 24 horas. A dose e a duração do tratamento dependem do estado clínico do paciente, do tipo e gravidade do sangramento e dos níveis de FVW:RCo e FVIII:C.
Quando se administram produtos que contêm fator VIII e fator de von Willebrand, o médico responsável pelo tratamento deve ter em conta que o tratamento contínuo pode ocasionar um aumento excessivo do FVIII:C. Após um tratamento de 24 - 48 horas, e a fim de evitar um aumento indesejável do FVIII:C, deve-se considerar uma redução das doses e/ou um aumento dos intervalos entre administrações, ou o uso de produtos de fator de von Willebrand que contenham baixos níveis de fator VIII.
População pediátrica
A posologia em pediatria baseia-se no peso corporal e, portanto, segue, em geral, as mesmas diretrizes que se usam para os adultos. A frequência de administração deve estar sempre orientada a conseguir a eficácia clínica em cada caso particular.
Hemofilia A
Monitorização do tratamento
Durante o curso do tratamento, recomenda-se controlar adequadamente os níveis de fator VIII para determinar a dose a administrar e a frequência das perfusões repetidas. A resposta individual dos pacientes à terapia com fator VIII pode variar, alcançando-se diferentes níveis de recuperação in vivoe demonstrando diferentes meias-vidas. A dose baseada no peso corporal pode requerer um ajuste em pacientes com baixo peso ou sobrepeso .No caso de intervenções de cirurgia maior, é indispensável monitorizar com precisão a terapia de substituição mediante testes de coagulação (atividade plasmática do fator VIII).
Deve-se monitorizar nos pacientes o desenvolvimento de inibidores do fator VIII. Ver também seção 2.
A dose e a duração do tratamento dependem do grau da deficiência de fator VIII, da localização e gravidade da hemorragia e do estado clínico do paciente.
É importante calcular a dose utilizando o número de UI de FVIII:C especificado.
O número de unidades de fator VIII administradas é expresso em Unidades Internacionais (UI), em relação ao padrão atual da Organização Mundial da Saúde (OMS) vigente para concentrados de fator VIII. A atividade plasmática de fator VIII é expressa como um percentual (em relação ao plasma humano normal) ou preferivelmente em Unidades Internacionais (em relação a um padrão internacional para fator VIII no plasma).
A atividade de uma unidade internacional de fator VIII é equivalente à quantidade do fator VIII contida em um ml de plasma humano normal.
Tratamento a demanda
O cálculo da dose necessária de fator VIII baseia-se na observação empírica de que 1 UI de fator VIII por kg de peso corporal eleva a atividade plasmática de fator VIII em aproximadamente 2% (2 UI/dl). A dose necessária é determinada mediante a fórmula seguinte:
Unidades necessárias = peso corporal (kg) x aumento desejado de fator VIII (% ou UI/dl) x 0,5
A dose e a frequência da administração devem ser estabelecidas sempre em função da eficácia clínica observada em cada caso.
No caso de episódios hemorrágicos como os detalhados a seguir, a atividade de fator VIII não deve ser inferior ao nível plasmático de atividade estabelecido (em % de plasma normal ou UI/dl) no período correspondente. Pode-se empregar a seguinte tabela como guia de dosificação em episódios hemorrágicos e cirurgia:
Grau de hemorragia/tipo de cirurgia | Nível de fator VIII requerido (% ou UI/dl) | Frequência de dose (horas)/duração da terapia (dias) |
Hemorragia | ||
Hemartrose precoce, sangramento muscular ou da cavidade bucal | 20 - 40 | Repetir a cada 12 - 24 horas. Pelo menos 1 dia, até que a hemorragia se tenha resolvido, em função da dor, ou até a cicatrização adequada da ferida. |
Hemartrose mais extensa, sangramento muscular ou hematoma | 30 - 60 | Repetir a perfusão a cada 12 - 24 horas, durante 3 - 4 dias ou mais até que o dolor e a discapacidade aguda se tenham resolvido. |
Hemorragias com risco vital | 60 - 100 | Repetir a perfusão a cada 8 - 24 horas até que desapareça o risco. |
Cirurgia | ||
Menor - incluindo a extração dental | 30 - 60 | A cada 24 horas, pelo menos 1 dia, até a cicatrização da ferida. |
Maior | 80 - 100 (pré e pós-operatório) | Repetir a perfusão a cada 8 - 24 horas até a adequada cicatrização da ferida, e luego terapia durante um mínimo de 7 dias para manter uma atividade de fator VIII de 30% - 60% (UI/dl). |
Profilaxia
Para a profilaxia a longo prazo em pacientes com hemofilia A grave, as doses usuais são de 20 a 40 UI de fator VIII por kg de peso corporal, a intervalos de 2 ou 3 dias. Em certos casos, especialmente em pacientes jovens, pode ser necessário acortar os intervalos entre administrações ou utilizar doses mais elevadas.
População pediátrica
Não se dispõe de experiência clínica no tratamento de crianças com Haemate P.
Advertências e precauções especiais de uso
Quando se utiliza um produto que contém o fator de von Willebrand, o médico responsável pelo tratamento deve ter em conta que um tratamento contínuo pode causar um aumento excessivo de FVIII:C. Em pacientes que recebem produtos com FVW que contêm FVIII, é necessário supervisionar os níveis plasmáticos de FVIII:C para evitar níveis plasmáticos excessivos de forma sustentada, o que poderia aumentar o risco de efeitos trombóticos, e é necessário avaliar medidas antitrombóticas.
Reações adversas
Quando se necessitam doses muito grandes ou frequentemente repetidas, quando há presença de inibidores ou quando há envolvidos cuidados pré ou pós-quirúrgicos, deve-se supervisionar a aparência de sintomas de hipervolemia em todos os pacientes. Além disso, em pacientes com grupos sanguíneos A, B e AB deve-se controlar se há sintomas de hemólise intravascular e/ou diminuição dos valores de hematocrito.
- País de registo
- Substância ativa
- Requer receita médicaSim
- Fabricante
- Esta informação é apenas para referência e não constitui aconselhamento médico. Consulte sempre um médico antes de tomar qualquer medicamento. A Oladoctor não se responsabiliza por decisões médicas baseadas neste conteúdo.
- Alternativas a HAEMATE P 2400/1000 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVEL OU PARA PERFUSÃOForma farmacêutica: INJETÁVEL, 100 UI FVIII/ 120 UI FVW por mlSubstância ativa: von Willebrand factor and coagulation factor VIII in combinationFabricante: Instituto Grifols S.A.Requer receita médicaForma farmacêutica: INJETÁVEL, 25 UI FVIII/ 30 UI FVW por mlSubstância ativa: von Willebrand factor and coagulation factor VIII in combinationFabricante: Instituto Grifols S.A.Requer receita médicaForma farmacêutica: INJETÁVEL, 50 UI FVIII/60 UI FvW por mlSubstância ativa: von Willebrand factor and coagulation factor VIII in combinationFabricante: Instituto Grifols S.A.Requer receita médica
Alternativas a HAEMATE P 2400/1000 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVEL OU PARA PERFUSÃO noutros países
As melhores alternativas com o mesmo princípio ativo e efeito terapêutico.
Alternativa a HAEMATE P 2400/1000 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVEL OU PARA PERFUSÃO em Polónia
Alternativa a HAEMATE P 2400/1000 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVEL OU PARA PERFUSÃO em Ukraine
Médicos online para HAEMATE P 2400/1000 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVEL OU PARA PERFUSÃO
Avaliação de posologia, efeitos secundários, interações, contraindicações e renovação da receita de HAEMATE P 2400/1000 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVEL OU PARA PERFUSÃO – sujeita a avaliação médica e regras locais.




 1
1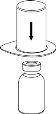 2
2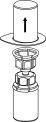 3
3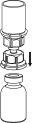 4
4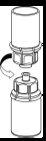 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8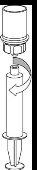 9
9









