
Zafiron
Ask a doctor about a prescription for Zafiron

How to use Zafiron
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
ZAFIRON, 12 μg/inhalation dose, powder for inhalation in hard capsules
Formoterol fumarate
Read the package leaflet carefully before taking the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Leaflet:
- 1. What is Zafiron and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking Zafiron
- 3. How to take Zafiron
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Zafiron
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Zafiron and what is it used for
The active substance of Zafiron is formoterol fumarate. It is a bronchodilator. Its action is based on the relaxation of smooth muscles in the bronchi, which makes breathing easier. This effect occurs quickly (within 1 to 3 minutes) and lasts for 12 hours after inhalation. Each hard capsule contains 12 micrograms of formoterol fumarate dihydrate and is intended for use with an inhaler.
Zafiron is indicated for use in:
- preventing and treating bronchial constriction in patients with asthma, as an adjunct to inhaled glucocorticosteroid therapy,
- preventing bronchial constriction caused by inhaled allergens, cold air, or physical exertion;
- preventing and treating bronchial constriction in patients with reversible or irreversible chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Zafiron improves the quality of life in patients with COPD.
The bronchodilatory effect lasts for 12 hours after Zafiron inhalation. Therefore, maintenance therapy, involving the use of Zafiron twice a day, in most cases leads to the relief of bronchial constriction associated with chronic conditions, both during the day and at night.
2. Important information before taking Zafiron
When not to take Zafiron:
- if the patient is allergic to the active substance or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions
Before taking Zafiron, the patient should inform the doctor about any history of hypersensitivity to formoterol or any other substance. Before starting Zafiron, the patient should discuss with the doctor:
- if the patient has heart disease, including arrhythmias;
- if the patient has accelerated heart rate;
- if the patient has severe heart failure;
- if the patient has high blood pressure;
- if the patient has diabetes;
- if the patient has hyperthyroidism;
- if the patient has an aneurysm (bulging of the artery wall due to its weakening);
- if the patient has a heart condition related to an abnormal electrical impulse, called "QT interval prolongation";
- if the patient has a pheochromocytoma (a tumor of the adrenal gland that can affect blood pressure).
If the doctor has prescribed regular use of other medicines for respiratory diseases, it is essential to continue their regular use. DO NOT STOP taking the medicine or reduce the dose without consulting a doctor, even if there is a significant improvement in health. If, however, symptoms related to bronchial constriction (e.g., wheezing, shortness of breath) do not subside or worsen, or if the improvement is not as significant or does not last as long as usual, the patient should contact the doctor as soon as possible, as this may indicate a worsening of the disease and a change in treatment may be necessary. In patients with diabetes, the doctor may recommend monitoring blood glucose levels. In patients with asthma, Zafiron should not be used as the only asthma control medicine. Zafiron should always be used in combination with an inhaled corticosteroid. During Zafiron treatment, other products containing long-acting beta2-adrenergic receptor agonists, such as salmeterol, should not be used.
Do not take Zafiron when:
- the patient's condition is well-controlled with an inhaled corticosteroid,
- the patient only needs a short-acting beta2-adrenergic receptor agonist occasionally.
In clinical trials with Zafiron, severe asthma attacks (see section 4 "Possible side effects") have been observed. Zafiron should not be started or the dose increased during an asthma attack. The patient should not change or stop taking any medicines for controlling or treating breathing problems, including inhaled corticosteroids. For asthma, Zafiron should not be used to relieve sudden wheezing. A short-acting, inhaled bronchodilator (e.g., salbutamol) should always be used to treat sudden asthma symptoms. Treatment with Zafiron may lead to a decrease in blood potassium levels, increasing the patient's susceptibility to heart rhythm disorders. Therefore, especially in severe asthma, the doctor may recommend monitoring blood potassium levels.
Paradoxical bronchospasm
As with other inhaled medicines, paradoxical bronchospasm may occur after taking Zafiron. In such cases, the medicine should be stopped immediately, and the doctor should be consulted, who may prescribe alternative treatment.
Children and adolescents
Zafiron should not be used in children under 6 years of age.
Use in elderly patients
In elderly patients, the same dose of Zafiron can be used as in adult patients.
Important information about a similar product
Zafiron belongs to a group of medicines called long-acting beta2-adrenergic receptor agonists. A large clinical trial with another long-acting beta2-adrenergic receptor agonist showed an increased risk of asthma-related death. It is not known whether Zafiron has a similar effect. The patient should discuss the benefits and risks of asthma treatment with Zafiron with their doctor.
Zafiron and other medicines
The patient should tell the doctor about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take. It may be necessary to change the dosage or, in some cases, stop taking one of the medicines. This applies to both prescription and over-the-counter medicines, especially:
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or tricyclic antidepressants (medicines used to treat depression and mood changes);
- sympathomimetic medicines (medicines similar to adrenaline used to treat asthma or reduce nasal congestion);
- antihistamines (anti-allergic medicines used to prevent or treat allergic reaction symptoms);
- steroids (medicines often used to treat asthma and other inflammatory diseases);
- diuretics (medicines used to treat swelling caused by fluid retention, heart failure, and high blood pressure);
- beta-adrenergic receptor blockers (medicines used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, angina, anxiety, and heart rhythm disorders. Some eye drops used to treat glaucoma may contain beta-adrenergic receptor blockers);
- quinidine, disopyramide, procainamide (medicines used to treat heart rhythm disorders);
- phenothiazine derivatives (medicines used to treat mental disorders, such as schizophrenia, manic excitement, psychotic reactions, and anxiety);
- digitalis glycosides (medicines used to treat heart failure and heart rhythm disorders);
- xanthine derivatives (medicines used to treat asthma or other chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases);
- macrolides (e.g., erythromycin, azithromycin) used to treat bacterial infections;
- general anesthetics, such as halogenated hydrocarbons (e.g., halothane). These medicines are used for anesthesia during surgery. The patient should inform the doctor about Zafiron use if they are scheduled for surgery under general anesthesia;
- anticholinergic medicines (e.g., ipratropium bromide) used to treat gastrointestinal, urinary, or other disorders.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a baby, they should consult their doctor before taking this medicine. Pregnancy Zafiron should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly prescribed by a doctor. The doctor will inform the patient about the potential risks associated with Zafiron use during pregnancy. Breastfeeding Zafiron should not be used during breastfeeding.
Driving and using machines
If dizziness or other similar side effects occur, the patient should not drive or operate machinery.
Zafiron contains lactose.
If the patient has previously been diagnosed with intolerance to some sugars, they should consult their doctor before taking Zafiron. The excipient lactose contains a small amount of milk proteins, which may cause allergic reactions.
3. How to take Zafiron
This medicine should always be taken as directed by the doctor. If the patient has any doubts, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
The medicine is for inhalation use only. Do not swallow the capsules.
The doctor will adjust the dose individually for each patient.
Do not take a higher dose than recommended. Use in adults
Asthma
In asthma treatment, Zafiron should always be taken as an add-on therapy with an inhaled corticosteroid. Maintenance treatment: inhalation of the contents of 1 to 2 inhalation capsules (12 to 24 micrograms) twice a day. The maximum recommended maintenance dose is 4 capsules (48 micrograms) per day. If necessary, the doctor may recommend an additional 1 to 2 capsules per day to reduce symptoms, provided that the maximum recommended daily dose of 48 micrograms is not exceeded. If the need for additional doses occurs frequently (e.g., more than two days a week), the patient should inform their doctor as soon as possible, as this may indicate a worsening of asthma. In case of a sudden asthma attack, a short-acting bronchodilator (e.g., salbutamol) should be used.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Maintenance treatment: inhalation of the contents of 1 to 2 inhalation capsules (12 to 24 micrograms) twice a day.
Prevention of bronchial constriction caused by physical exertion or allergens
Inhalation of the contents of one inhalation capsule (12 micrograms) at least 15 minutes before exercise or exposure to an allergen. In patients with a history of severe bronchial constriction, the use of 2 inhalation capsules (24 micrograms) may be necessary. In asthma treatment, inhaled corticosteroids are always used. Use in children and adolescents (over 6 years old)
Asthma
Maintenance treatment: inhalation of the contents of 1 inhalation capsule (12 μg) twice a day. The maximum recommended dose is 24 micrograms per day. In case of a sudden asthma attack, a short-acting bronchodilator (e.g., salbutamol) should be used.
Prevention of bronchial constriction caused by physical exertion or allergens
Inhalation of the contents of 1 inhalation capsule (12 micrograms) about 15 minutes before exercise or exposure to an allergen. Children over 6 years old can use Zafiron only if they can properly use the inhaler (see "Inhaler Instructions") and only with the help of an adult. Zafiron is not recommended for use in children under 6 years old.
Method of use and handling the inhaler
The capsule should be removed from the blister pack immediately before use. Do not swallow the capsules. The powder in the capsule is intended for inhalation only with the inhaler.
- 1. Remove the cap.
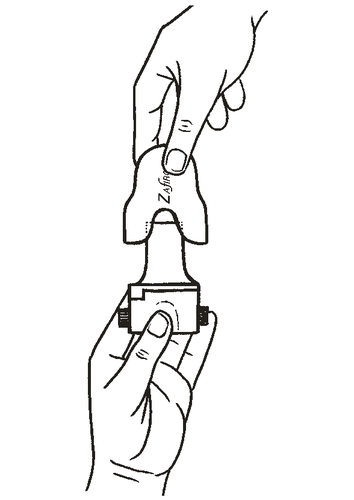
- 2. Hold the inhaler base firmly and open the mouthpiece by turning it in the direction of the arrow.
in the direction of the arrow.
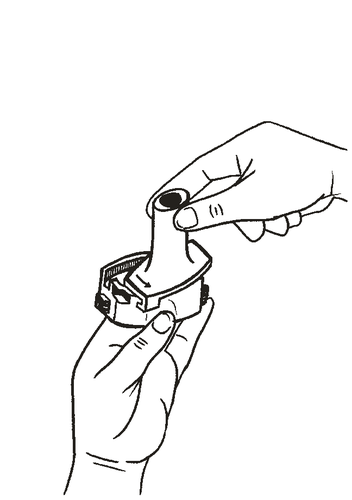
- 3. Place the capsule in the capsule-shaped compartment located in the inhaler base.
The capsule should be removed from the blister pack immediately before use.
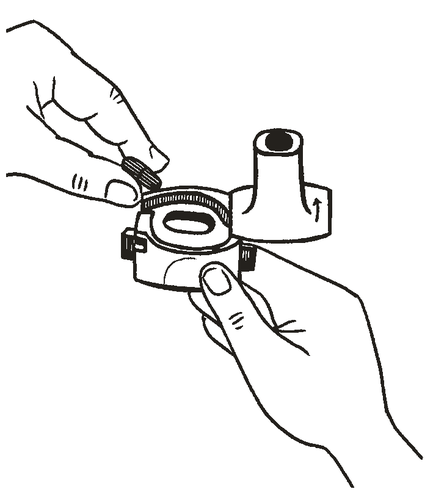
- 4. Turn the mouthpiece back to the closed position.
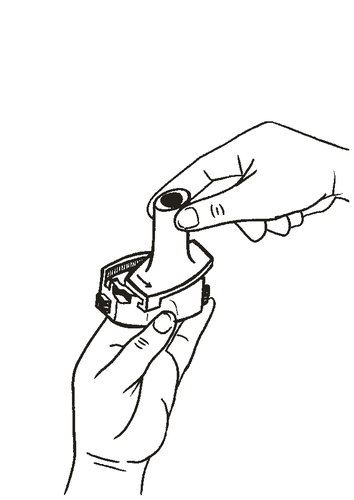
- 5. Press the buttons until they stop (only once), holding the inhaler in a vertical position, then release the buttons.
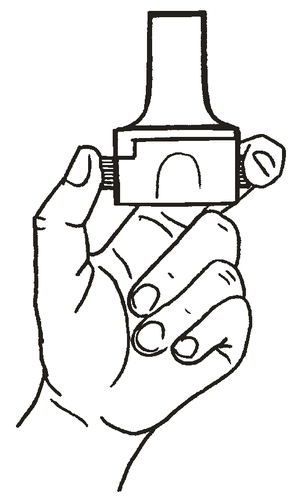
NOTE: at this point, the capsule may break and small pieces of gelatin may enter the mouth or throat after inhalation. Since gelatin is edible, its consumption is not harmful. The likelihood of such an event is minimal if the capsule is pierced in the inhaler only once, storage conditions are maintained, and the capsule is removed from the blister pack immediately before use.
- 6. Take a deep breath.
- 7. Place the mouthpiece in the mouth and tilt the head slightly backwards. Close the lips around the mouthpiece and take a smooth, deep breath. As the capsule rotates in the inhaler chamber and the powder is dispersed, a characteristic sound (rattle) should be heard. If this sound does not occur, it may indicate that the capsule is stuck in the compartment. In this case, the inhaler should be opened and the capsule removed from the compartment by lifting it. DO NOT lift the capsule by pressing the buttons multiple times.
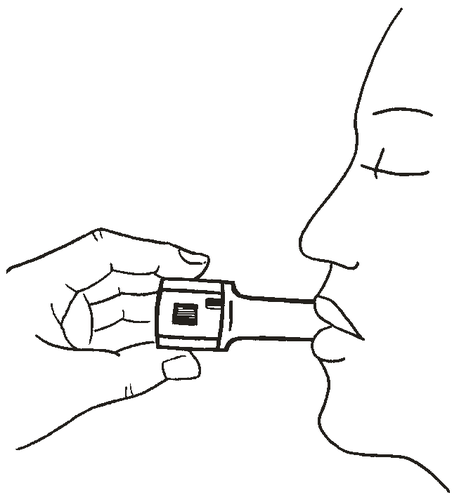
- 8. After hearing the characteristic sound, hold the breath for as long as possible without discomfort and remove the inhaler from the mouth. Exhale. Open the inhaler and check if there is still powder in the capsule. If powder remains in the capsule, repeat the steps described in points 6 to 8.
- 9. After use, open the inhaler, remove the empty capsule, close the mouthpiece, and put the cap back on.
Cleaning the inhaler
To remove powder residue, wipe the mouthpiece and capsule compartment with a dry cloth or a clean, soft brush.
Overdose of Zafiron
If a higher dose of Zafiron than recommended is taken accidentally, the patient should contact their doctor or pharmacist immediately. Nausea and/or vomiting, muscle tremors, headache, dizziness (possible symptoms of high blood pressure), rapid or irregular heartbeat, drowsiness, increased blood sugar levels, or decreased blood potassium levels may occur if the dose of Zafiron is too high. The patient should inform their doctor or go to the emergency room of the nearest hospital immediately. The patient may require appropriate treatment.
Missed dose of Zafiron
If a dose is missed, the medicine should be taken as soon as possible. If it is almost time for the next scheduled dose, do not take the missed dose, but return to the regular dosing schedule. Do not take a double dose to make up for the missed dose.
Stopping Zafiron treatment
If the patient has any further doubts about taking this medicine, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Zafiron can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. In clinical trials with Zafiron, severe asthma attacks (see section 4 "Possible side effects") have been observed. The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
The patient should inform their doctor immediately about any of the following serious side effects:
- bronchial constriction with coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. This effect occurs uncommonly (in 1 to 10 in 1000 people),
- allergic reactions, e.g., rash, urticaria, itching, swelling of the face, throat, and low blood pressure, and bronchial constriction. This effect occurs rarely (in 1 to 10 in 10,000 people),
- severe, described as tearing, chest pains (symptoms of angina pectoris), changes in the ECG. This effect occurs very rarely (less than 1 in 10,000 people),
- muscle symptoms, such as muscle weakness, muscle cramps, and heart rhythm disorders (these symptoms may be caused by low blood potassium levels). These symptoms occur uncommonly (in 1 to 10 in 1000 people),
- if the patient experiences an irregular heart rhythm (including faster heartbeat).
Common side effects(in 1 to 10 in 100 people):
headache, muscle tremors, palpitations.
Uncommon side effects(in 1 to 10 in 1000 people):
excitement, anxiety, nervousness, insomnia, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, irritation of the throat mucosa, muscle cramps, muscle pain.
Rare side effects(in 1 to 10 in 10,000 people):
low blood potassium levels, heart rhythm disorders, extra beats, nausea.
Very rare side effects(less than 1 in 10,000 people):
taste disorders, swelling of hands, ankles, and feet, excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue (these symptoms may indicate high blood sugar levels).
Side effects with unknown frequency(cannot be estimated from available data)
cough, rash, headache, and dizziness (possible symptoms of high blood pressure).
Zafiron may cause increased blood insulin, free fatty acids, glycerol, and ketone bodies. In some people, other side effects may occur during Zafiron treatment. If any side effect worsens or any side effect not mentioned in this leaflet occurs, the patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist.
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any not listed in this leaflet, the patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Post-Marketing Surveillance of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, 181C Jerozolimskie Avenue, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, Fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl. Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder or its representative. By reporting side effects, more information can be collected on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Zafiron
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Store in a temperature below 25°C. Store in the original package. Do not use Zafiron after the expiry date stated on the package after EXP. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Zafiron contains
- The active substance of Zafiron is formoterol fumarate. Each hard capsule contains 12 micrograms (μg) of formoterol fumarate (in the form of 12.5 μg formoterol fumarate dihydrate)
- Other ingredients are: micronized lactose monohydrate, lactose monohydrate; the capsule shell contains gelatin.
What Zafiron looks like and contents of the pack
Zafiron is a powder for inhalation in hard capsules. The powder in the capsule is intended for inhalation into the lungs using an inhaler. Zafiron is available in packs containing 60 capsules or 120 capsules with an inhaler in a cardboard box.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Adamed Pharma S.A., Pieńków, ul. M. Adamkiewicza 6A, 05-152 Czosnów
Date of last revision of the leaflet: 04.2023
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterAdamed Pharma S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to ZafironDosage form: Aerosol, 12 mcg/measured doseActive substance: formoterolManufacturer: Chiesi Farmaceutici S.p.A. Chiesi Pharmaceuticals GmbHPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 12 mcgActive substance: formoterolPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 12 mcg/inh. doseActive substance: formoterolPrescription required
Alternatives to Zafiron in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Zafiron in Ukraine
Alternative to Zafiron in Spain
Online doctors for Zafiron
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Zafiron – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














