
Emla

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Emla

How to use Emla
Leaflet attached to the packaging: information for the user
Warning! Keep the leaflet! Information on the immediate packaging in a foreign language.
EMLA, 25 mg/g + 25 mg/g, cream
Lidocaine + Prilocaine
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is EMLA and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using EMLA
- 3. How to use EMLA
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store EMLA
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is EMLA and what is it used for
EMLA contains two active substances - lidocaine and prilocaine. They belong to a group of medicines called local anesthetics.
The action of EMLA is to temporarily remove the sensation from the surface layers of the skin. The cream is applied to the skin before performing certain procedures and medical procedures.
This helps to remove pain from the skin; however, the patient may still feel pressure and touch.
Adults, adolescents, and children
EMLA can be used to anesthetize the skin before:
- injecting a needle into the skin (e.g., when giving an injection or taking blood for tests),
- minor surgical procedures on the skin.
Adults and adolescents
EMLA can also be used:
- to anesthetize the genital area before: performing an injection, performing medical procedures such as removing warts. The application of EMLA cream to the genital area should be performed under the supervision of a doctor or nurse.
Adults
EMLA can also be used to anesthetize the skin before:
- debridement or removal of damaged skin on lower limbs with ulcers.
2. Important information before using EMLA
When not to use EMLA:
- 6).
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to use EMLA, you should discuss it with your doctor or pharmacist:
- EMLA should not be used on areas of skin with a rash, cuts, scratches, or other open wounds, except for ulcers on the lower limbs. If the patient has any of these changes, before using the cream, they should contact their doctor or pharmacist,
Due to the possibility of increased absorption from freshly shaved skin, it is essential to follow the recommended dosage, area of application, and time of application on the skin.
One should avoid contact between EMLA and the eyes, as it may cause irritation and chemical burns to the eyes. If the EMLA cream accidentally gets into the eye, it should be rinsed immediately with lukewarm water or a physiological saline solution (0.9% NaCl solution).
One should be careful not to get anything into the eye until the sensation returns.
Children should be closely monitored when using EMLA on any part of the body to prevent them from transferring EMLA to the eye (eyes).
EMLA should not be used on a diseased eardrum.
When EMLA is used in a patient before administering a live vaccine (e.g., a vaccine against tuberculosis), one should remember to report to the doctor at the appointed time for a follow-up visit to assess the effectiveness of the vaccination.
Children and adolescents
In infants and newborns under 3 months of age, a transient, clinically insignificant increase in methemoglobin concentration in the blood (a form of hemoglobin, i.e., a blood pigment) is commonly observed within 12 hours of using EMLA.
The efficacy of EMLA during blood sampling from the heel in newborns or to ensure adequate pain relief during circumcision has not been confirmed in clinical trials.
EMLA should not be used on the mucous membrane of the genital organs (e.g., vagina) in children (under 12 years of age) due to insufficient data on the absorption of active substances.
EMLA should not be used in children under 12 months of age who are being treated with other medications that affect the blood pigment and may cause methemoglobinemia (e.g., sulfonamides; see also section 2 "EMLA and other medications").
EMLA should not be used in premature newborns.
EMLA and other medications
You should inform your doctor or pharmacist about any other medications you are currently taking or have recently taken or may take. This includes medications that can be purchased without a prescription and herbal remedies. This is important because the ingredients of EMLA may affect the action of some other medications, and some other medications may affect the action of EMLA.
In particular, the patient should inform their doctor or pharmacist if they have used or taken any of the following medications recently:
- Medications used to treat infections called sulfonamides and nitrofurantoin.
- Medications used to treat epilepsy: phenytoin and phenobarbital.
- Other local anesthetics.
- Medications used to treat irregular heart rhythm, such as amiodarone.
- Cimetidine or beta-adrenergic blockers, which may increase the concentration of lidocaine in the blood. This interaction is not clinically significant in short-term use of EMLA in recommended doses.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Occasional use of EMLA during pregnancy is not associated with any risk of side effects in the fetus.
The active substances of EMLA (lidocaine and prilocaine) are excreted into breast milk. However, the amount that passes into the milk is so small that there is essentially no risk to the breastfed child.
In animal studies, no fertility disorders were found in males or females treated with the active ingredients of EMLA.
Driving and using machines
EMLA has no effect or insignificant effect on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machines when used in recommended doses.
EMLA contains macrogolglycerol hydroxystearate
Macrogolglycerol hydroxystearate may cause skin reactions.
3. How to use EMLA
EMLA should always be used as directed by a doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
Using EMLA
- The site of application, amount of cream, and time of application depend on the purpose for which it is used.
- The doctor, pharmacist, or nurse will apply the cream to the appropriate area or show the patient how to do it themselves.
- When EMLA is used on the genital area, the doctor or nurse should supervise its use.
EMLA should not be used in the following areas:
- Areas of cuts, scratches, or open wounds, except for ulcers on the lower limbs.
- Areas with skin rash or eczema.
- Eyes or near the eyes.
- Inside the nose, ears, or mouth.
- Rectum.
- Genital area in children.
People who frequently apply or remove the cream from the patient's body should ensure that they effectively avoid contact with the cream to prevent the development of hypersensitivity.
The protective membrane of the tube is pierced with the tube cap.
Application to the skin before minor procedures (such as needle insertion or minor surgical procedures on the skin):
- The cream is applied to the skin in a thick layer. The doctor, pharmacist, or nurse will tell the patient where to apply the cream.
- Then, the layer of cream is covered with a dressing (plastic foil). The dressing is removed immediately before the procedure starts. If the patient applies the cream themselves, they should ensure that they have received dressings from their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- Usually, the dose used in adults and adolescents over 12 years old is 2 g (grams).
- In adults and adolescents over 12 years old, the cream should be applied at least 60 minutes before the planned procedure time (except when the cream is to be applied to the genital area). However, the cream should not be applied more than 5 hours before the procedure or earlier.
- In children, the amount of EMLA cream used and the time of application depend on the child's age. The doctor, nurse, or pharmacist will inform the patient about the amount of cream to be used and when to apply it.
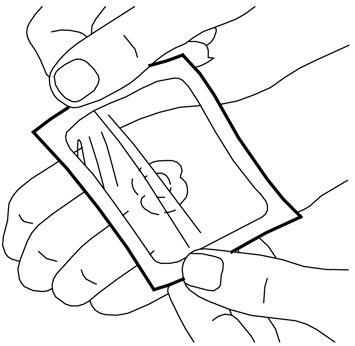
When applying the EMLA cream, it is very important to follow the following instructions carefully:
- 1. Squeeze out a portion of the cream from the tube to form a mound at the site where it is needed on the skin (e.g., where the needle is to be inserted). Half of the contents of the 5 g tube corresponds to about 2 g of EMLA cream. Do not rub the cream into the skin.
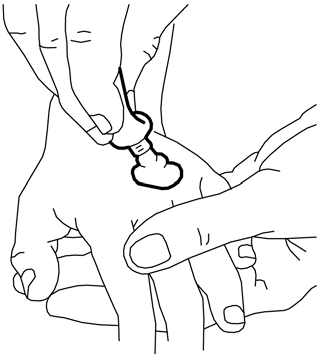
- 2. Peel off the paper layer from the middle window of the non-adhesive side of the dressing (leaving the paper frame).
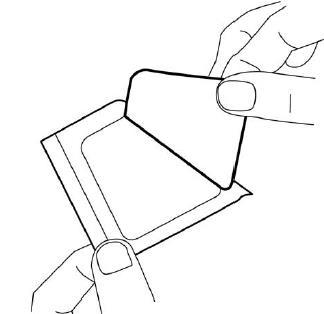
- 3. Remove the top layer of the adhesive dressing.
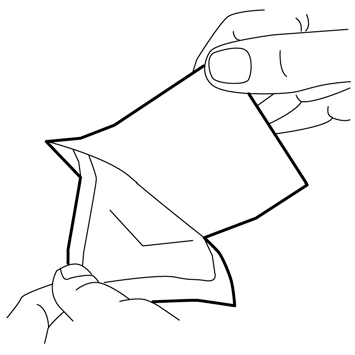
- 4. Carefully place the dressing over the mound of cream. Do not spread the cream under the dressing.
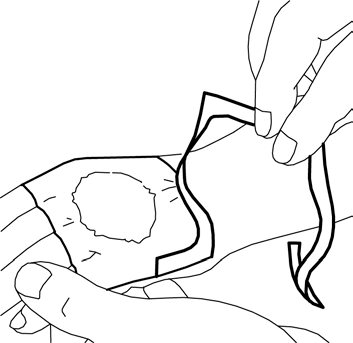
- 5. Remove the paper stiffener. Carefully smooth the edges of the dressing. Then, leave the dressing on for at least 60 minutes if the skin is not damaged. The cream should not be left on for more than 60 minutes in children under 3 months of age or more than 30 minutes in children with atopic dermatitis. When applying the cream to the genital area or ulcers, shorter application times can be used as described below.
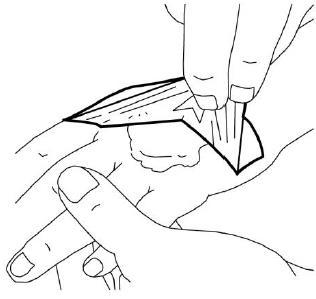
- 6. The doctor or nurse will remove the dressing and remove the cream immediately before the medical procedure (e.g., before inserting the needle).
Using EMLA on larger areas of freshly shaved skin before procedures in outpatient settings (such as hair removal):
Usually, the dose of EMLA used is 1 g of cream per 10 cm² (10 square centimeters) of skin surface, applied for 1 to 5 hours under a dressing. EMLA should not be used on an area of freshly shaved skin larger than 600 cm² (600 square centimeters, e.g., 30 cm x 20 cm). The maximum dose is 60 g.
Using EMLA on the skin before procedures in a hospital setting (e.g., before a skin transplant of intermediate thickness), which require deeper skin anesthesia:
- EMLA can be used in this way in adults and adolescents over 12 years old.
- Usually, the dose used is 1.5 g to 2 g of cream per 10 cm² (10 square centimeters) of skin surface.
- The cream is applied and covered with a dressing for 2 to 5 hours.
Using EMLA on the skin before removing wart-like lesions
- EMLA can be used in children and adolescents with atopic dermatitis.
- Usually, the dose used depends on the child's age and is applied for 30 to 60 minutes (30 minutes in patients with atopic dermatitis). The doctor, nurse, or pharmacist will inform the patient about the amount of cream to be used.
Using EMLA on the genital skin before injecting local anesthetics
- EMLA can be used in this way only in adults and adolescents over 12 years old.
- Usually, the dose used is 1 g of cream (1 g to 2 g in the case of genital skin in women) per 10 cm² (10 square centimeters) of skin surface.
- The cream is applied and covered with a dressing. The dressing is left on for 15 minutes in men and 60 minutes in women.
on the genital skin.
Using EMLA on the genital skin before minor surgical procedures on the skin (such as removing warts)
- EMLA can be used in this way only in adults and adolescents over 12 years old.
- Usually, the dose used is 5 g to 10 g of cream for 10 minutes. No dressing is used. The procedure should be started immediately after.
Using EMLA on ulcers on the lower limbs before debridement or removal of damaged skin
- Usually, the dose used is 1 g to 2 g of cream per 10 cm² (10 square centimeters) of skin surface and no more than 10 g.
- The cream is applied and covered with a tight dressing, e.g., plastic foil. The cream and dressing are applied 30 to 60 minutes before the debridement procedure. The cream should be removed with a cotton swab and the debridement started immediately.
- EMLA can be used before debridement of ulcers on the lower limbs up to 15 times over a period of 1-2 months.
- When using the cream on ulcers on the lower limbs, the EMLA tube should be used as a single-use product: after each use of the cream in the patient, the tube with the remaining amount of cream should be discarded.
Using a larger dose of EMLA than recommended
If a larger amount of EMLA than recommended by the doctor, pharmacist, or nurse is used, they should be contacted immediately, even if the patient does not feel any discomfort.
Problems and discomfort that may occur after using too much EMLA are listed below. These discomforts should not occur when using EMLA as directed.
- Feeling of "emptiness" in the head or dizziness.
- Numbness or tingling of the skin around the mouth and tongue.
- Disturbed sense of taste.
- Blurred vision.
- Ringing in the ears.
- There is also a risk of methemoglobinemia (a problem with the concentration of a blood pigment). This is more likely if the patient is taking certain other medications. In this case, the skin becomes blue-gray due to insufficient oxygen in the blood.
In severe cases of overdose, symptoms such as seizures, decreased blood pressure, decreased breathing rate, respiratory arrest, and abnormal heart rhythm may occur. These problems can be life-threatening.
If you have any further doubts about using this medicine, you should consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, EMLA can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
- Local reactions (pallor or redness of the skin, slight swelling, initial burning or itching sensation) are common reactions to the cream and anesthetics, which disappear after a short time without the need for any medical intervention.
If the patient experiences any worrying or unusual reactions or effects while using EMLA, they should stop using it and contact their doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible.
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Transient local skin reactions (pallor, redness, swelling) at the site of application during use on the skin, mucous membrane of the genital organs, or ulcers on the lower limbs.
- Initial mild burning sensation, itching, or warmth at the site of application during use on the mucous membrane of the genital organs or ulcers on the lower limbs.
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Initial mild burning sensation, itching, or warmth at the site of application during use on the skin.
- Numbness (tingling) at the site of application during use on the mucous membrane of the genital organs.
- Irritation of the skin at the site of application during use on ulcers on the lower limbs.
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- Allergic reactions, which in rare cases can lead to anaphylactic shock (skin rash, swelling, fever, difficulty breathing, and fainting) during use on the skin, mucous membrane of the genital organs, or ulcers on the lower limbs.
- Methemoglobinemia (a blood disorder) during use on the skin.
- Minor pinpoint bleeding (petechiae) at the site of application (especially in children with eczema after longer application time) during use on the skin.
- Irritation of the eyes if the cream accidentally comes into contact with the eyes during use on the skin.
Frequency not known(cannot be estimated from the available data):
- Chemical burns to the eyes if the cream accidentally comes into contact with the eyes during treatment.
Additional side effects in children
Methemoglobinemia, a blood disorder, which is more often observed in children, often in connection with overdose in newborns and infants from 0 to 12 months of age.
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any not listed in this leaflet, the patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products, Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl.
By reporting side effects, more information can be collected on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store EMLA
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not freeze. Store the tube tightly closed.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What EMLA contains
- The active substances of EMLA are lidocaine and prilocaine. 1 g of cream contains 25 mg of lidocaine and 25 mg of prilocaine.
- EMLA also contains macrogolglycerol hydroxystearate, carbomers, sodium hydroxide (to adjust pH), and purified water.
What EMLA looks like and what the pack contains
White, homogeneous cream.
EMLA is packaged in an aluminum tube with a membrane coated with a protective epoxy lacquer and a polypropylene cap with a piercer, in a cardboard box.
EMLA is available in packaging:
1 tube containing 5 g of cream and 2 dressings in a cardboard box.
For more detailed information, you should contact the marketing authorization holder or parallel importer.
Marketing authorization holder in Belgium, the country of export:
Aspen Pharma Trading Limited
3016 Lake Drive
Citywest Business Campus
Dublin 24, Ireland
Manufacturer:
Aspen Bad Oldesloe GmbH
32-36 Industriestrasse, 23843 Bad Oldesloe, Germany
AstraZeneca AB
Astraallén, Gärtunaporten (B 674:5), SE-151 85 Södertälje, Sweden
Recipharm Karlskoga AB
Bjorkbornsvagen 5, SE-691 33 Karlskoga, Sweden
AstraZeneca UK Limited
Silk Road Business Park, Macclesfield, Cheshire, SK10 2NA, United Kingdom
AstraZeneca GmbH
Tinsdaler Weg 183, DE-22880, Germany
Parallel importer:
InPharm Sp. z o.o.
ul. Strumykowa 28/11
03-138 Warsaw
Repackaged by:
InPharm Sp. z o.o. Services sp. k.
ul. Chełmżyńska 249
04-458 Warsaw
Marketing authorization number in Belgium, the country of export:BE177055
Parallel import authorization number: 125/24
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Austria
Emla 5% - Creme
Belgium
Emla 25mg/25mg crème
Cyprus
Emla Cream 5%
Finland
EMLA
France
EMLA 5 POUR CENT, crème
Greece
EMLA
Iceland
Emla
Ireland
EMLA 5% w/w Cream
Italy
EMLA
Luxembourg
Emla 25mg/25mg crème
Malta
EMLA 5% w/w Cream
Norway
Emla
Poland
EMLA
Spain
EMLA 25 mg/g + 25 mg/g crema
Sweden
EMLA
Netherlands
Emla
Date of approval of the leaflet: 20.03.2024
[Information about the trademark]
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Marketing authorisation holder (MAH)Aspen Pharma Trading Limited
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to EmlaDosage form: Plaster, 25 mg + 25 mgActive substance: combinationsPrescription not requiredDosage form: Plaster, 25 mg + 25 mgActive substance: combinationsPrescription not requiredDosage form: Plaster, 25 mg + 25 mgActive substance: combinationsPrescription not required
Alternatives to Emla in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Emla in Spain
Alternative to Emla in Ukraine
Online doctors for Emla
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Emla – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














