
RISPERIDONA STADA 1 mg/ml SOLUCION ORAL EFG

Cómo usar RISPERIDONA STADA 1 mg/ml SOLUCION ORAL EFG
Traducción generada por IA
Este contenido ha sido traducido automáticamente y se ofrece solo con fines informativos. No sustituye la consulta con un profesional sanitario.
Ver originalContenido del prospecto
Introducción
Prospecto: información para el usuario
Risperidona Stada 1 mg/ml solución oral EFG
Lea todo el prospecto detenidamente antes de empezar a tomar este medicamento, porque contiene información importante para usted.
- Conserve este prospecto, ya que puede tener que volver a leerlo.
- Si tiene alguna duda, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico.
- Este medicamento se le ha recetado solamente a usted, y no debe dárselo a otras personas aunque tengan los mismos síntomas que usted, ya que puede perjudicarles.
- Si experimenta efectos adversos, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico, incluso si se trata de efectos adversos que no aparecen en este prospecto. Ver sección 4.
Contenido del prospecto:
- Qué es Risperidona Stada y para qué se utiliza
- Qué necesita saber antes de empezar a tomar Risperidona Stada
- Cómo tomar Risperidona Stada
- Posibles efectos adversos
- Conservación de Risperidona Stada
- Contenido del envase e información adicional
1. Qué es Risperidona Stada y para qué se utiliza
Risperidona pertenece a un grupo de medicamentos denominados “antipsicóticos”.
Risperidona se utiliza para tratar lo siguiente:
- Esquizofrenia, con la que puede ver, oír, o sentir cosas que no están ahí, creer en algo que no es cierto, o sentirse particularmente suspicaz o confuso.
- Manía, con la que puede sentirse muy excitado, exaltado, agitado, entusiasmado o hiperactivo. La manía aparece en una enfermedad llamada “trastorno bipolar”.
- Tratamiento a corto plazo (hasta 6 semanas) de la agresión persistente en personas con demencia de tipo Alzheimer, que se hacen daño a sí mismos o a otros. Deben haber intentado otros tratamientos alternativos (no farmacológicos) previamente.
- Tratamiento a corto plazo (hasta 6 semanas) de la agresión persistente en niños intelectualmente disminuidos (al menos de 5 años de edad) y adolescentes con trastornos de conducta.
Risperidona puede ayudar a disminuir los síntomas de su enfermedad y a evitar que vuelvan a aparecer.
2. Qué necesita saber antes de empezar a tomar Risperidona Stada
No tome Risperidona Stada:
- Si es alérgico a risperidona o a cualquiera de los componentes de este medicamento (incluidos en la sección 6).
Si no está seguro de serlo, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico antes de empezar a tomar risperidona.
Advertencias y precauciones
Consulte a su médico o farmacéutico antes de tomar risperidona si:
- Tiene algún problema de corazón. Los ejemplos incluyen las alteraciones del ritmo cardíaco, o si es propenso a tener la tensión arterial baja o si utiliza medicamentos para la presión arterial. Risperidona puede reducir la presión arterial. Puede que necesite que le ajusten la dosis.
- Sabe de algún factor que le pueda hacer propenso a tener un infarto cerebral, tales como la tensión alta, enfermedades cardiovasculares o problemas en los vasos sanguíneos del cerebro.
- Ha presentado alguna vez movimientos involuntarios de la lengua, boca y cara.
- Ha presentado alguna vez síntomas que incluyen fiebre, rigidez muscular, sudoración o una disminución del nivel de consciencia (también conocido como Síndrome Neuroléptico Maligno).
- Tiene enfermedad de Parkinson o demencia.
- Si ha tenido en el pasado niveles bajos de células blancas de la sangre (que puede o no haber sido causado por otros medicamentos).
- Es diabético.
- Tiene epilepsia.
- Es varón y en alguna ocasión ha tenido una erección prolongada o dolorosa.
- Tiene problemas para controlar su temperatura corporal o siente un calor excesivo.
- Tiene problemas de riñón.
- Tiene problemas de hígado.
- Tiene un nivel anormalmente alto en su sangre de la hormona prolactina o si tiene un tumor, que posiblemente sea dependiente de la prolactina.
- Usted o alguien de su familia tiene antecedentes de problemas de coágulos en la sangre dado que los antipsicóticos se han asociado con la formación de coágulos en la sangre.
Si tiene dudas sobre si lo leído anteriormente le afecta, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico antes de tomar risperidona.
Debido a que en muy raras ocasiones se ha observado en pacientes tratados con risperidona un número peligrosamente bajo de un tipo de células blancas necesarias para combatir las infecciones en la sangre, su médico puede comprobar el número de células blancas.
Risperidona puede hacerle aumentar de peso. Un aumento significativo de peso puede afectar desfavorablemente su salud. Su médico realizará regularmente un seguimiento de su peso.
Debido a que se ha visto diabetes mellitus o un empeoramiento de diabetes mellitus preexistente en pacientes que toman risperidona, su médico debe comprobar los signos de una elevación de azúcar en sangre. En pacientes con diabetes mellitus preexistente, se debe monitorizar regularmente el azúcar en sangre.
Risperidona aumenta frecuentemente los niveles de una hormona llamada prolactina. Esto puede causar efectos adversos como trastornos del periodo menstrual o problemas de fertilidad en mujeres o hinchazón de las mamas en hombres (ver Posibles efectos adversos). Si aparecen estos efectos adversos, se recomienda la evaluación de los niveles de prolactina en sangre.
Durante la intervención en el ojo por turbidez de las lentes (cataratas), la pupila (el círculo negro situado en medio del ojo), puede no aumentar de tamaño como se necesita. Además, el iris (la parte coloreada del ojo) se puede poner flácido durante la cirugía y esto puede causar daño en el ojo. Si usted está pensando en operarse de los ojos, asegúrese de informar a su oftalmólogo que está usando este medicamento.
Pacientes de edad avanzada con demencia
En pacientes de edad avanzada con demencia, hay un aumento en el riesgo de tener un infarto cerebral. No debe tomar risperidona si tiene demencia provocada por un infarto cerebral.
Durante el tratamiento con risperidona debe ver a su médico con frecuencia.
Si usted o su cuidador observan un cambio súbito de su estado mental o la aparición repentina de debilidad o entumecimiento de la cara, los brazos o las piernas, sobre todo si es un lado, o habla confusa, aunque sea por poco tiempo, busque tratamiento médico inmediatamente. Puede ser signo de un infarto cerebral.
Niños y adolescentes
Se deben haber descartado otras causas del comportamiento agresivo antes de empezar el tratamiento para desórdenes de conducta.
Si durante el tratamiento con risperidona sufre fatiga, cambiando las horas de administración, pueden mejorar sus dificultades para prestar atención.
Antes de iniciar el tratamiento, se puede medir su peso o el de su hijo y se puede seguir midiendo de forma regular durante el tratamiento.
Un estudio pequeño e inconcluso ha notificado un aumento en la altura de niños que tomaron risperidona, pero se desconoce si esto es un efecto del fármaco o es debido a otra razón.
Otros medicamentos y Risperidona Stada
Comunique a su médico o farmacéutico si está tomando, ha tomado recientemente o podría tener que tomar cualquier otro medicamento.
Es especialmente importante que hable con su médico o farmacéutico si toma cualquiera de los siguientes:
- Medicamentos que actúan sobre su cerebro, como los utilizados para calmarse (benzodiazepinas), o algunos medicamentos para el dolor (opiáceos), medicamentos para la alergia (algunos antihistamínicos), ya que risperidona puede aumentar su acción sedante.
- Medicamentos capaces de modificar la actividad eléctrica de su corazón, como los utilizados para el paludismo, los problemas del ritmo del corazón, alergias (antihistamínicos), algunos antidepresivos u otros medicamentos para problemas mentales.
- Medicamentos que provocan un latido lento del corazón.
- Medicamentos que provocan un nivel bajo de potasio en sangre (como algunos diuréticos).
- Medicamentos para tratar la tensión arterial alta. Risperidona puede disminuir la tensión arterial.
- Medicamentos para la enfermedad de Parkinson (como la levodopa).
- Medicamentos que aumentan la actividad del sistema nervioso central (psicoestimulantes, como el metilfenidato).
- Diuréticos, que se utilizan para los problemas cardiacos o para tratar la hinchazón de algunas partes del cuerpo debido a una retención de líquidos (como furosemida o clorotiazida). Risperidona, tomado solo o con furosemida, puede aumentar el riesgo de infarto cerebral o de muerte en personas de edad avanzada con demencia.
Los siguientes medicamentos pueden disminuir el efecto de risperidona
- Rifampicina (un medicamento para tratar algunas infecciones).
- Carbamazepina, fenitoína (medicamentos para la epilepsia).
- Fenobarbital.
Si empieza o deja de tomar estos medicamentos puede necesitar una dosis distinta de risperidona.
Los siguientes medicamentos pueden aumentar el efecto de risperidona
- Quinidina (utilizada para ciertos tipos de enfermedades del corazón).
- Antidepresivos como paroxetina, fluoxetina y antidepresivos tricíclicos.
- Medicamentos conocidos como betabloqueantes (utilizados para tratar la tensión sanguínea alta).
- Fenotiazinas (como los medicamentos utilizados para tratar la psicosis o como calmantes).
- Cimetidina, ranitidina (bloqueantes de los ácidos del estómago).
- Itraconazol y ketoconazol (medicamentos que se utilizan para el tratamiento de las infecciones fúngicas).
- Algunos medicamentos que se utilizan para el tratamiento del VIH/SIDA, como ritonavir.
- Verapamilo, medicamento que se utiliza para el tratamiento de la presión sanguínea elevada y/o para el ritmo cardiaco anormal.
- Sertralina y fluvoxamina, medicamentos que se utilizan para el tratamiento de la depresión y otros trastornos psiquiátricos.
Si empieza o deja de tomar estos medicamentos puede necesitar una dosis distinta de risperidona.
Si tiene dudas sobre si lo leído anteriormente le afecta, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico antes de tomar risperidona.
Toma de Risperidona Stada con alimentos, bebidas y alcohol
Puede tomar este medicamento con o sin alimentos. Debe evitar consumir alcohol mientras toma risperidona.
Embarazo, lactancia y fertilidad
- Si está embarazada o en periodo de lactancia, cree que podría estar embarazada o tiene intención de quedarse embarazada, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico antes de tomar este medicamento. Su médico decidirá si puede tomarlo.
- Se pueden producir los siguientes síntomas en bebés recién nacidos, de madres que han sido tratadas con risperidona en el último trimestre de embarazo (últimos tres meses de su embarazo): temblor, rigidez y/o debilidad muscular, somnolencia, agitación, problemas al respirar y dificultad en la alimentación. Si su bebé desarrolla cualquiera de estos síntomas se debe poner en contacto con su médico.
- Risperidona puede aumentar los niveles de una hormona llamada “prolactina” que puede afectar a la fertilidad (ver Posibles efectos adversos).
Conducción y uso de máquinas
Risperidona puede producir síntomas tales como somnolencia, mareo o alteraciones en la vista, y disminuir la capacidad de reacción. Estos efectos así como la propia enfermedad pueden dificultar su capacidad para conducir vehículos o manejar máquinas. Por lo tanto no conduzca, ni maneje máquinas, ni practique otras actividades que requieran especial atención, hasta que su médico valore su respuesta a este medicamento.
Risperidona Stada solución oral contiene sodio
Este medicamento contiene 11,10 mg de sodio (componente principal de la sal de mesa/para cocinar) en cada ml de solución oral. Esto equivale al 0,55% de la ingesta diaria máxima de sodio recomendada para un adulto.
3. Cómo tomar Risperidona Stada
Siga exactamente las instrucciones de administración de este medicamento indicadas por su médico o farmacéutico. En caso de duda, consulte de nuevo a su médico o farmacéutico.
La dosis recomendada es la siguiente:
Para el tratamiento de la esquizofrenia
Adultos
- La dosis inicial habitual es de 2 miligramos al día, puede aumentarse a 4 miligramos al día el segundo día.
- Su médico puede ajustarle la dosis dependiendo de cómo responda al tratamiento.
- La mayoría de la gente se encuentra mejor con dosis diarias de 4 a 6 miligramos.
- Esta dosis diaria total se puede dividir en una o dos tomas al día. Su médico le indicará qué es lo mejor para usted.
Pacientes de edad avanzada
- La dosis inicial será de 0,5 miligramos dos veces al día, normalmente.
- Puede que más adelante su médico le aumente la dosis gradualmente de 1 a 2 miligramos dos veces al día.
- Su médico le indicará qué es lo mejor para usted.
Para el tratamiento de la manía
Adultos
- La dosis inicial será de 2 miligramos una vez al día, normalmente.
- Puede que más adelante su médico le ajuste la dosis gradualmente dependiendo de su respuesta al tratamiento.
- La mayoría de la gente se encuentra mejor con dosis de 1 a 6 miligramos una vez al día.
Pacientes de edad avanzada
- La dosis inicial será de 0,5 miligramos dos veces al día, normalmente.
- Puede que más adelante su médico le ajuste la dosis gradualmente de 1 miligramo a 2 miligramos dos veces al día dependiendo de su respuesta al tratamiento.
Para el tratamiento de la agresión a largo plazo en personas con demencia tipo Alzheimer
Adultos (pacientes de edad avanzada incluidos)
- La dosis inicial será de 0,25 miligramos dos veces al día, normalmente.
- Puede que más adelante su médico le ajuste la dosis gradualmente dependiendo de su respuesta al tratamiento.
- La mayoría de la gente se encuentra mejor con dosis de 0,5 miligramos dos veces al día. Algunos pacientes pueden necesitar 1 miligramo dos veces al día.
- La duración del tratamiento en pacientes con demencia tipo Alzheimer no debe ser superior a 6 semanas.
Uso en niños y adolescentes
- Los niños y adolescentes menores de 18 años no deben recibir tratamiento con risperidona para la esquizofrenia o la manía.
Para el tratamiento de los desórdenes de conducta
La dosis dependerá del peso de su hijo:
Si pesa menos de 50 kilogramos
- La dosis inicial será de 0,25 miligramos una vez al día, normalmente.
- La dosis puede aumentarse un día sí y otro no en aumentos de 0,25 miligramos por día.
- La dosis normal de mantenimiento es de 0,25 miligramos a 0,75 miligramos una vez al día.
Si pesa 50 kilogramos o más
- La dosis inicial será de 0,5 miligramos una vez al día, normalmente.
- La dosis puede aumentarse un día sí y otro no en aumentos de 0,5 miligramos por día.
- La dosis normal de mantenimiento es de 0,5 miligramos a 1,5 miligramos una vez al día.
La duración del tratamiento en pacientes con desórdenes de conducta no debe ser superior a 6 semanas.
Los niños menores de 5 años no deben recibir tratamiento con risperidona para desórdenes de conducta.
Pacientes con problemas de riñón o de hígado
Sin tener en cuenta la enfermedad a tratar, todas las dosis de inicio y dosis consecutivas de risperidona se deben reducir a la mitad. Los aumentos de dosis se deben realizar de forma más lenta en estos pacientes.
Risperidona se debe utilizar con precaución en este grupo de pacientes.
Forma de administración
Vía oral
Risperidona Stada solución oral
La solución viene con una jeringuilla (pipeta). Utilice solo la pipeta suministrada con este medicamento para medir la dosis prescrita por el médico. Mida la dosis exacta de medicación que necesita. Preste atención al medir una dosis pequeña, por ejemplo, para 0,25 mg es preciso medir 0,25 ml (un cuarto de mililitro); para 0,5 mg es preciso medir 0,5 ml (medio mililitro).
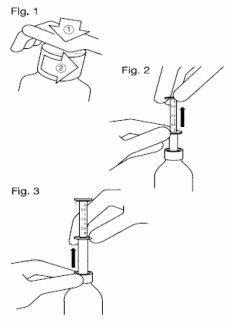
Siga estos pasos:
- Quite el tapón a prueba de niños. Empuje el tapón de plástico hacia abajo, girándolo al mismo tiempo contra el sentido de las agujas del reloj (Figura 1).
- Inserte la pipeta en el frasco.
- Sujetando el anillo inferior, tire del superior hasta la marca que corresponde al número de mililitros o miligramos que deba administrar (Figura 2).
- Sujetando el anillo inferior, saque toda la pipeta del frasco (Figura 3).
- Vacíe la pipeta en una bebida no alcohólica que no sea té. Deslice el anillo superior hacia abajo.
- Cierre el frasco.
- Lave la pipeta con agua y deje secar al aire.
Si toma más Risperidona Stada del quedebe
En caso de sobredosis se puede sentir somnoliento o cansado, presentar movimientos corporales anómalos, problemas para mantenerse de pie y caminar, sensación de mareo por la disminución de la tensión arterial o tener latidos anómalos o convulsiones.
Consulte inmediatamente a su médico, farmacéutico o llame al Servicio de Información Toxicológica, teléfono 91.562.04.20, indicando el medicamento y la cantidad tomada. Se recomienda llevar el envase y el prospecto del medicamento al profesional sanitario.
Si olvidó tomar Risperidona Stada
- Si olvida tomar una dosis, tómela en cuanto se acuerde. Pero si se acerca la hora de la siguiente dosis, prescinda de la olvidada y siga con normalidad. Si se olvida de dos dosis o más, póngase en contacto con su médico.
- No tome una dosis doble (dos dosis a la vez) para compensar la dosis olvidada.
Si interrumpe el tratamiento con Risperidona Stada
No se debe dejar de tomar este medicamento a menos que se lo indique su médico. Los síntomas pueden reaparecer. Si su médico decide interrumpir este tratamiento, se puede disminuir su dosis gradualmente durante unos días.
Si tiene cualquier otra duda sobre el uso de este medicamento, pregunte a su médico o farmacéutico.
4. Posibles efectos adversos
Al igual que todos los medicamentos, este medicamento puede producir efectos adversos, aunque no todas las personas los sufran.
Informe inmediatamente a su médico si presenta algunos de los siguientes efectos adversos poco frecuentes (pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 100 pacientes):
- Tiene demencia y presenta un cambio repentino de su estado mental o debilidad repentina o entumecimiento de la cara, brazos o piernas especialmente en uno de los lados, o le cuesta hablar incluso durante un periodo corto de tiempo. Pueden ser signos de un infarto cerebral.
- Presenta discinesia tardía (espasmos o movimientos espasmódicos que no se pueden controlar en la cara, lengua u otras partes del cuerpo). Informe a su médico inmediatamente si experimenta movimientos rítmicos involuntarios de la lengua, boca y cara. Puede ser necesaria la retirada de risperidona.
Informe inmediatamente a su médico si presenta algunos de los siguientes efectos adversos raros (pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 1.000 pacientes):
- Presenta coágulos sanguíneos en las venas, especialmente en las piernas (los síntomas incluyen hinchazón, dolor y enrojecimiento de la pierna), que pueden circular a través de los vasos sanguíneos a los pulmones causando dolor en el pecho y dificultad al respirar. Si usted nota alguno de estos síntomas pida consejo médico inmediatamente.
- Presenta fiebre, rigidez muscular, sudoración o una disminución del nivel de consciencia (trastorno conocido como “Síndrome Neuroléptico Maligno”). Puede necesitar tratamiento médico inmediato.
- Es hombre y presenta una erección prolongada o dolorosa. Se conoce como priapismo. Puede necesitar tratamiento médico inmediato.
- Presenta una reacción alérgica grave caracterizada por fiebre, hinchazón de la boca, cara, labios o lengua, dificultad para respirar, picor, erupción de la piel o bajada de la tensión arterial.
También pueden aparecer los siguientes efectos secundarios:
Muy frecuentes (pueden afectar a más de 1 de cada 10 personas):
- Dificultad para quedarse o permanecer dormido.
- Parkinsonismo: Esta enfermedad puede incluir movimiento lento o alterado, sensación de rigidez o tirantez de los músculos (haciendo movimientos bruscos) y algunas veces una sensación de “congelación” del movimiento que después se reinicia. Otros signos del parkinsonismo incluyen caminar despacio arrastrando los pies, temblor en reposo, aumento de la saliva y/o babear y pérdida de expresividad de la cara.
- Sentirse somnoliento o menos atento.
- Dolor de cabeza.
Frecuentes (pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 10 personas):
- Neumonía, infección de pecho (bronquitis), síntomas de un resfriado común, sinusitis, infección del tracto urinario, infección del oído, sentir como si tuviese gripe.
- Aumento de los niveles de una hormona llamada “prolactina” que se detecta en los análisis de sangre (lo cual puede o no causar síntomas). Los síntomas del aumento de la prolactina ocurren raramente y pueden incluir en hombres, hinchazón de los pechos, dificultad en tener o mantener erecciones, disminución del deseo sexual u otras disfunciones sexuales. En mujeres pueden incluir malestar de las mamas, secreción de leche por las mamas, pérdida de períodos menstruales u otros problemas con el ciclo o problemas de fertilidad.
- Aumento de peso, aumento del apetito, disminución del apetito.
- Trastornos del sueño, irritabilidad, depresión, ansiedad, inquietud.
- Distonía: Es una enfermedad que implica contracción involuntaria lenta o continua de los músculos. Aunque puede estar afectada cualquier parte del cuerpo (y puede originar posturas anormales), la distonía afecta con frecuencia a los músculos de la cara, incluyendo movimientos anormales de los ojos, boca, lengua o mandíbula.
- Mareos.
- Discinesia: Esta enfermedad implica movimientos musculares involuntarios y puede incluir movimientos repetitivos, espasmódicos o de retorcimiento, o espasmos.
- Temblor (agitación).
- Visión borrosa, infección de ojos u “ojo rojo”.
- Latido rápido del corazón, aumento de la presión arterial, respiración entrecortada.
- Dolor de garganta, tos, sangrados nasales, congestión nasal.
- Dolor abdominal, malestar abdominal, vómitos, náuseas, estreñimiento, diarrea, indigestión, sequedad de boca, dolor de muelas.
- Erupción, enrojecimiento de la piel.
- Espasmos musculares, dolor de huesos o músculos, dolor de espalda, dolor de las articulaciones.
- Incontinencia (pérdida de control) urinaria.
- Hinchazón del cuerpo, brazos o piernas, fiebre, dolor de pecho, debilidad, fatiga (cansancio), dolor.
- Caídas.
Poco frecuentes (pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 100 personas):
- Infección de las vías respiratorias, infección de la vejiga, infección de ojos, amigdalitis, infección de las uñas por hongos, infección de la piel, infección localizada en una única zona de la piel o parte del cuerpo, infección vírica, inflamación cutánea causada por ácaros.
- Disminución de un tipo de células blancas de la sangre que ayudan a combatir las infecciones, disminución del número de células blancas de la sangre, disminución de las plaquetas (células de la sangre que ayudan a detener las hemorragias), anemia, disminución de las células rojas de la sangre, aumento del número de eosinófilos (un tipo de célula blanca de la sangre) en la sangre.
- Reacción alérgica.
- Diabetes o empeoramiento de la diabetes, nivel alto de azúcar en sangre, ingesta excesiva de agua.
- Pérdida de peso, pérdida de apetito que causa malnutrición y disminución del peso corporal.
- Aumento del colesterol en sangre.
- Euforia (manía), confusión, disminución del deseo sexual, nerviosismo, pesadillas.
- Ausencia de respuesta a los estímulos, pérdida de consciencia, disminución del nivel de consciencia.
- Convulsiones (crisis epilépticas), desmayo.
- Una inquietud que provoca el movimiento de partes del cuerpo, trastorno del equilibrio, coordinación anormal, mareos al ponerse de pie, alteración de la atención, problemas con el habla, pérdida o alteraciones del gusto, disminución de la sensibilidad de la piel al dolor o al tacto, sensación de hormigueo, pinchazos o entumecimiento de la piel.
- Hipersensibilidad de los ojos a la luz, sequedad de ojos, aumento del lagrimeo, enrojecimiento de los ojos.
- Sensación de que todo gira (vértigo), zumbido en los oídos, dolor de oído.
- Fibrilación auricular (ritmo cardiaco anormal), interrupción de la conducción entre las partes superiores e inferiores del corazón, anomalía en la actividad eléctrica del corazón, prolongación del intervalo QT en el corazón, latido lento del corazón, anomalía en la conducción eléctrica del corazón (electrocardiograma o ECG), sensación de aleteo o de golpeteo en el pecho (palpitaciones).
- Disminución de la presión arterial, disminución de la presión arterial al ponerse de pie (como consecuencia, algunas personas que toman risperidona pueden sentir debilidad, mareo o pérdida del conocimiento al levantarse o sentarse de repente), rubor.
- Neumonía causada por aspiración de alimentos, congestión pulmonar, congestión de las vías respiratorias, ruidos crepitantes de los pulmones, jadeo, trastorno de la voz, dificultad respiratoria.
- Infección de estómago o de intestino, incontinencia fecal, heces muy duras, dificultad para tragar, exceso de gas o flatulencia.
- Ronchas (o “urticaria”), picor, pérdida de pelo, engrosamiento de la piel, eccema, sequedad de la piel, decoloración de la piel, acné, piel o cuero cabelludo escamoso y con picor, trastorno de la piel, lesión de la piel.
- Aumento de la CPK (creatina fosfoquinasa) en sangre, una enzima que algunas veces se libera con la degradación muscular.
- Postura anormal, rigidez de las articulaciones, hinchazón de las articulaciones, debilidad muscular, dolor de cuello.
- Orinar con frecuencia, incapacidad para orinar, dolor al orinar.
- Disfunción eréctil, trastorno de la eyaculación.
- Pérdida de la menstruación, pérdida de períodos menstruales u otros problemas con el ciclo (mujeres).
- Desarrollo de las mamas en los hombres, secreción de leche por las mamas, disfunción sexual, dolor de las mamas, malestar de las mamas, secreción vaginal.
- Hinchazón de la cara, boca, ojos o labios.
- Escalofríos, un aumento de la temperatura corporal.
- Cambio en la forma de andar.
- Sensación de sed, sensación de malestar, malestar de pecho, sentirse “indispuesto”, malestar.
- Aumento de las transaminasas del hígado en la sangre, aumento de la GGT (una enzima del hígado llamada gamma-glutamiltransferasa) en sangre, aumento de las enzimas del hígado en sangre.
- Dolor debido al procedimiento.
Raros (pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 1.000 personas):
- Infección.
- Secreción inapropiada de una hormona que controla el volumen de orina.
- Sonambulismo.
- Trastorno alimentario relacionado con el sueño.
- Azúcar en la orina, disminución del azúcar en la sangre, aumento de triglicéridos en sangre (un tipo de grasa).
- Ausencia de emociones, incapacidad para alcanzar el orgasmo.
- Falta de movimiento o de respuesta estando despierto (catatonía).
- Problemas en los vasos sanguíneos del cerebro.
- Coma debido a diabetes incontrolada.
- Agitación de la cabeza.
- Glaucoma (aumento de la presión del globo ocular), problemas con el movimiento de los ojos, giro de los ojos, costras en el borde del párpado.
- Problemas oculares durante la cirugía de cataratas. Durante la cirugía de cataratas puede darse una alteración llamada síndrome del iris flácido intraoperatorio (IFIS) si está tomando o ha tomado risperidona. Si necesita someterse a cirugía de cataratas asegúrese de informar a su oftalmólogo si está tomando o ha tomado este medicamento.
- Número peligrosamente bajo de un tipo de células blancas necesarias para combatir las infecciones en la sangre.
- Ingesta de agua peligrosamente excesiva.
- Latido irregular del corazón.
- Problemas en la respiración durante el sueño (apnea del sueño), respiración rápida, superficial.
- Inflamación del páncreas, obstrucción intestinal.
- Hinchazón de la lengua, labios agrietados, erupción en la piel relacionada con el medicamento.
- Caspa.
- Rotura de las fibras musculares y dolor muscular (rabdomiólisis).
- Retraso de los períodos menstruales, aumento de las glándulas mamarias, aumento de las mamas, secreción por las mamas.
- Aumento de la insulina (una hormona que controla los niveles de azúcar en sangre) en sangre.
- Endurecimiento de la piel.
- Disminución de la temperatura corporal, frialdad en brazos y piernas.
- Síndrome de abstinencia a medicamentos.
- Color amarillo de la piel y los ojos (ictericia).
Muy raros (pueden afectar hasta a 1 de cada 10.000 personas):
- Complicaciones de la diabetes no controlada, con peligro para la vida
- Reacción alérgica grave con hinchazón, que puede afectar a la garganta causando dificultad respiratoria
- Falta de movimiento de los músculos del intestino que causa obstrucción.
Frecuencia no conocida: no puede estimarse a partir de los datos disponibles
- Erupción grave o mortal con ampollas y descamación de la piel que puede comenzar alrededor de la boca, nariz, ojos, genitales y extenderse a otras zonas del cuerpo (Síndrome de Stevens Johnson o necrólisis epidérmica tóxica).
El siguiente efecto adverso ha aparecido con el uso de otro medicamento llamado paliperidona que es muy similar a risperidona, por tanto, también se espera que aparezca con risperidona: latido rápido del corazón al ponerse de pie.
Otros efectos adversos en niños y adolescentes
En general, se espera que los efectos adversos en niños sean similares a los que aparecieron en adultos.
Los siguientes efectos adversos se notificaron con mayor frecuencia en niños y adolescentes (5 a 17 años) que en adultos: sentirse adormecido o menos atento, fatiga (cansancio), dolor de cabeza, aumento del apetito, vómitos, síntomas de resfriado común, congestión nasal, dolor abdominal, mareo, tos, fiebre, temblor (sacudidas), diarrea e incontinencia (falta de control) urinaria.
Comunicación de efectos adversos:
Si experimenta cualquier tipo de efecto adverso, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico, incluso si se trata de posibles efectos adversos que no aparecen en este prospecto. También puede comunicarlos directamente a través del Sistema Español de Farmacovigilancia de medicamentos de Uso Humano: https://www.notificaram.es. Mediante la comunicación de efectos adversos usted puede contribuir a proporcionar más información sobre la seguridad de este medicamento.
5. Conservación de Risperidona Stada
Mantener este medicamento fuera de la vista y del alcance de los niños.
No utilizar este medicamento después de la fecha de caducidad que aparece en el envase después de CAD. La fecha de caducidad es el último día del mes que se indica.
No conservar a temperatura superior a 30°C.
No congelar.
Conservar en el embalaje original para protegerlo de la luz.
Una vez que el frasco esté abierto, lo que no se haya utilizado de Risperidona Stada solución oral debe desecharse después de 3 meses.
Los medicamentos no se deben tirar por los desagües ni a la basura. Deposite los envases y los medicamentos que no necesita en el Punto SIGRE de la farmacia. En caso de duda pregunte a su farmacéutico cómo deshacerse de los envases y de los medicamentos que no necesita. De esta forma ayudará a proteger el medio ambiente.
6. Contenido del envase e información adicional
Composición de Risperidona Stada
El principio activo es risperidona.
Cada ml de solución oral de Risperidona Stada contiene 1 mg de risperidona.
Los demás componentes (excipientes) son: cloruro de sodio, bromuro de domifén , ácido cítrico, hidrogenofosfato de sodio dodecahidrato, aroma de limón y agua purificada.
Aspecto de Risperidona Stada y contenido del envase
Risperidona Stada solución oral se presenta en forma de solución transparente e incolora a ligeramente amarillenta.
Cada envase contiene 30 ml o 100 ml de solución oral y una jeringuilla dosificadora. La cantidad más pequeña que esta jeringa puede dosificar es de 0,25 ml y la máxima de 3 ml.
Titular de la autorización de comercialización y responsable de la fabricación
Titular de la autorización de comercialización:
Laboratorio STADA, S.L.
Frederic Mompou, 5
08960 Sant Just Desvern (Barcelona)
España
Responsable de la fabricación:
Meiji Pharma Spain, S.A.
Avda. de Madrid, 94
28802 Alcalá de Henares (Madrid)
España
o
Medinfar Manufacturing, S.A.
Parque Industrial Armando Martins Tavares,
Rua Oteiro de Armada, 5,
Condeixa-a-Nova, 3150-194, Sebal
Portugal
Fecha de la última revisión de este prospecto:marzo 2025
La información detallada de este medicamento está disponible en la página web de la Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios (AEMPS) www.aemps.gob.es.
- País de registro
- Precio medio en farmacia13.66 EUR
- Principio activo
- Requiere recetaSí
- Fabricante
- Esta información es de carácter general y no sustituye la consulta con un profesional sanitario.
- Alternativas a RISPERIDONA STADA 1 mg/ml SOLUCION ORAL EFGForma farmacéutica: COMPRIMIDO, 1 mgPrincipio activo: RisperidonaFabricante: Neuraxpharm Spain S.L.Requiere recetaForma farmacéutica: COMPRIMIDO, 3 mgPrincipio activo: RisperidonaFabricante: Neuraxpharm Spain S.L.Requiere recetaForma farmacéutica: COMPRIMIDO, 6 mgPrincipio activo: RisperidonaFabricante: Neuraxpharm Spain S.L.Requiere receta
Médicos online para RISPERIDONA STADA 1 mg/ml SOLUCION ORAL EFG
Comenta la dosis, los posibles efectos secundarios, interacciones, contraindicaciones o la revisión de receta de RISPERIDONA STADA 1 mg/ml SOLUCION ORAL EFG, sujeto a valoración médica y a la normativa local.
Preguntas frecuentes











