
PRIVENAX 110 MG CAPSULAS DURAS EFG

Cómo usar PRIVENAX 110 MG CAPSULAS DURAS EFG
Traducción generada por IA
Este contenido ha sido traducido automáticamente y se ofrece solo con fines informativos. No sustituye la consulta con un profesional sanitario.
Ver originalContenido del prospecto
Introducción
Prospecto: información para el paciente
Privenax 110 mg cápsulas duras EFG
dabigatrán etexilato
Lea todo el prospecto detenidamente antes de empezar a tomar este medicamento, porque contiene información importante para usted.
- Conserve este prospecto, ya que puede tener que volver a leerlo.
- Si tiene alguna duda, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico.
- Este medicamento se le ha recetado solamente a usted, y no debe dárselo a otras personas aunque tengan los mismos síntomas que usted, ya que puede perjudicarles.
- Si experimenta efectos adversos, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico, incluso si se trata de efectos adversos que no aparecen en este prospecto. Ver sección 4.
Contenido del prospecto
- Qué es Privenax y para qué se utiliza
- Qué necesita saber antes de empezar a tomar Privenax
- Cómo tomar Privenax
- Posibles efectos adversos
- Conservación de Privenax
- Contenido del envase e información adicional
1. Qué es Privenax y para qué se utiliza
Este medicamento contiene el principio activo dabigatrán etexilato y pertenece a un grupo de medicamentos denominados anticoagulantes. Funciona bloqueando una sustancia del cuerpo implicada en la formación de coágulos de sangre.
Dabigatrán se utiliza en adultos para:
- evitar la formación de coágulos de sangre en las venas tras una artroplastia de rodilla o cadera.
- evitar la formación de coágulos de sangre en el cerebro (ictus) y en otros vasos sanguíneos del cuerpo si usted padece una forma de ritmo cardíaco irregular denominado fibrilación auricular no valvular y presenta al menos un factor de riesgo adicional.
- tratar los coágulos de sangre en las venas de sus piernas y pulmones y para prevenir que vuelvan a aparecer coágulos de sangre en las venas de sus piernas y pulmones.
Dabigatrán se utiliza en niños para:
- tratar los coágulos de sangre y evitar que se vuelvan a formar coágulos de sangre.
2. Qué necesita saber antes de empezar a tomar Privenax
No tome Privenax
- si es alérgico a dabigatrán etexilato o a alguno de los demás componentes de este medicamento (incluidos en la sección 6).
- si su función renal está muy reducida.
- si actualmente padece hemorragias.
- si tiene alguna enfermedad en un órgano del cuerpo que aumente el riesgo de hemorragias graves (p. ej., úlcera de estómago, lesión o hemorragia cerebral, intervención quirúrgica reciente del cerebro o de los ojos).
- si es propenso a sangrar. Esta tendencia puede ser de nacimiento, de causa desconocida o provocada por otros medicamentos.
- si está tomando medicamentos para prevenir la formación de coágulos en la sangre (p. ej., warfarina, rivaroxabán, apixabán o heparina), excepto cuando esté cambiando de tratamiento anticoagulante, mientras tenga un catéter venoso o arterial y se le administre heparina a través de este catéter para mantenerlo abierto o mientras su latido cardíaco normal se esté restableciendo mediante un procedimiento denominado ablación con catéter para fibrilación auricular.
- si la función de su hígado está gravemente reducida o padece alguna enfermedad del hígado que pueda ser mortal.
- si está tomando ketoconazol oral o itraconazol, medicamentos utilizados en el tratamiento de las infecciones por hongos.
- si está tomando ciclosporina oral, un medicamento utilizado para la prevención del rechazo de órganos después de un trasplante.
- si está tomando dronedarona, un medicamento utilizado para tratar el latido cardíaco anormal.
- si está tomando un producto de asociación de glecaprevir y pibrentasvir, un medicamento antiviral que se usa para tratar la hepatitis C.
- si se le ha implantado una válvula cardíaca artificial que requiere tratamiento anticoagulante permanente.
Advertencias y precauciones
Consulte a su médico antes de empezar a tomar dabigatrán. Durante el tratamiento con este medicamento también puede necesitar consultar a su médico si experimenta algún síntoma o si se tiene que someter a cirugía.
Informe a su médicosi padece o ha padecido cualquier trastorno o enfermedad, especialmente cualquiera de los detallados a continuación:
- Si presenta un riesgo aumentado de hemorragia, por ejemplo:
- si recientemente ha padecido hemorragias.
- si se ha sometido a una extracción quirúrgica de tejido (biopsia) en el último mes.
- si ha sufrido una lesión grave (p. ej., una fractura ósea, una lesión en la cabeza o cualquier lesión que haya requerido tratamiento quirúrgico).
- si padece una inflamación del esófago o del estómago.
- si tiene problemas de reflujo del jugo gástrico en el esófago.
- si está recibiendo medicamentos que pueden aumentar el riesgo de hemorragia. Consulte “Otros medicamentos y dabigatrán” más adelante.
- si está utilizando medicamentos antiinflamatorios como por ejemplo diclofenaco, ibuprofeno o piroxicam.
- si padece una infección en el corazón (endocarditis bacteriana).
- si sabe que tiene el funcionamiento de los riñones disminuido o si sufre deshidratación (los síntomas incluyen sensación de sed y eliminación de pequeñas cantidades de orina de color oscuro [concentrada]/con espuma).
- si es mayor de 75 años.
- si es un paciente adulto y pesa 50 kg o menos.
- solo si se utiliza en niños: si el niño tiene una infección en el cerebro o alrededor de este.
- Si ha sufrido un ataque al corazón o si le han diagnosticado enfermedades que aumentan el riesgo de sufrir un ataque al corazón.
- Si padece una enfermedad del hígado asociada a cambios en los análisis de sangre. El uso de dabigatrán no se recomienda en este caso.
Tenga especial cuidado con dabigatrán
- Si tiene que someterse a una intervención quirúrgica:
En este caso, dabigatrán debe interrumpirse temporalmente debido a un mayor riesgo de hemorragia durante y poco después de una intervención quirúrgica. Es muy importante que tome este medicamento antes y después de la intervención quirúrgica exactamente en los momentos que le haya indicado su médico.
- Si una intervención quirúrgica requiere la colocación de un catéter o una inyección en la columna vertebral (por ejemplo, para anestesia epidural o espinal o para la reducción del dolor):
- Es muy importante que tome dabigatrán antes y después de la intervención quirúrgica exactamente en los momentos que le haya indicado su médico.
- Informe a su médico inmediatamente si presenta entumecimiento o debilidad en las piernas o problemas intestinales o en la vejiga después del final de la anestesia, ya que dicha situación requiere una atención urgente.
- Si se cae o lesiona durante el tratamiento, especialmente si se golpea la cabeza. Solicite asistencia médica urgente. Puede necesitar que un médico le examine, ya que puede tener un mayor riesgo de sangrado.
- Si sabe que padece una enfermedad denominada síndrome antifosfolipídico (un trastorno del sistema inmunitario que aumenta el riesgo de que se formen coágulos de sangre), informe a su médico para que decida si puede ser necesario modificar el tratamiento.
Otros medicamentos y dabigatrán
Informe a su médico o farmacéutico si está tomando, ha tomado recientemente o pudiera tener que tomar cualquier otro medicamento. En particular, debe informar a su médico antes de tomar dabigatrán si está tomando alguno de los medicamentos indicados a continuación:
- Medicamentos para reducir la coagulación de la sangre (p. ej., warfarina, fenprocumón, acenocumarol, heparina, clopidogrel, prasugrel, ticagrelor, rivaroxabán, ácido acetilsalicílico)
- Medicamentos para el tratamiento de infecciones por hongos (p. ej., ketoconazol, itraconazol), salvo si solo se aplican en la piel
- Medicamentos utilizados en el tratamiento del latido anormal del corazón (p. ej., amiodarona, dronedarona, quinidina, verapamilo)
Si está usando medicamentos que contienen amiodarona, quinidina o verapamilo, es posible que su médico le indique que utilice una dosis reducida de dabigatrán según la enfermedad para la que se le haya recetado. Ver sección 3.
- Medicamentos para la prevención del rechazo de órganos después de un trasplante (p. ej., tacrólimus, ciclosporina)
- Un producto de asociación de glecaprevir y pibrentasvir (un medicamento antiviral que se usa para tratar la hepatitis C)
- Medicamentos antiinflamatorios y calmantes del dolor (p. ej., ácido acetilsalicílico, ibuprofeno, diclofenaco)
- Hierba de San Juan, una planta medicinal para la depresión
- Medicamentos antidepresivos llamados inhibidores selectivos de la recaptación de serotonina o inhibidores selectivos de la recaptación de serotonina y norepinefrina
- Rifampicina o claritromicina (dos antibióticos)
- Medicamentos antivirales para el SIDA (p. ej., ritonavir)
- Ciertos medicamentos para el tratamiento de la epilepsia (p. ej., carbamazepina, fenitoína)
Embarazo y lactancia
Se desconocen los efectos de dabigatrán sobre el embarazo y el feto. No debe utilizar dabigatrán si está embarazada a menos que su médico le indique que es seguro hacerlo. Si está en edad fértil debe evitar quedarse embarazada durante el tratamiento con este medicamento.
No se recomienda la lactancia natural durante el tratamiento con dabigatrán.
Conducción y uso de máquinas
Dabigatrán no tiene efectos conocidos sobre la capacidad para conducir y utilizar máquinas.
3. Cómo tomar Privenax
Privenax cápsulas se puede usar en adultos y niños de 8 años de edad o mayores que sean capaces de tragar las cápsulas enteras.
Siga exactamente las instrucciones de administración de este medicamento indicadas por su médico. En caso de duda, consulte de nuevo a su médico.
Tome este medicamento según lo recomendado para las siguientes situaciones:
Prevención de la formación de coágulos de sangre tras una artroplastia de rodilla o cadera
La dosis recomendada es de 220 mg una vez al día(administrados en forma de 2 cápsulas de 110 mg).
Si su función renal está disminuidaen más de la mitad o si tiene 75 años de edad o más, la dosis recomendada es de 150 mg una vez al día(administrados en forma de 2 cápsulas de 75 mg).
Si está usando medicamentos que contienen amiodarona, quinidina o verapamilola dosis recomendada es de 150 mg una vez al día(administrados en forma de 2 cápsulas de 75 mg).
Si está usando medicamentos que contienen verapamilo y su función renal está disminuidaen más de la mitad, se le deberá indicar una dosis de dabigatrán reducida de 75 mgdebido a que su riesgo de sangrado puede aumentar.
En ambos tipos de cirugía, el tratamiento no debe iniciarse si hay sangrado en el lugar de la cirugía. Si el tratamiento no puede iniciarse hasta el día posterior a la operación, la dosificación debe iniciarse con 2 cápsulas una vez al día.
Después de una artroplastia de rodilla
Debe iniciar el tratamiento con dabigatrán de 1-4 horas después de la realización de la operación, tomando una única cápsula. Después deben tomarse 2 cápsulas una vez al día durante 10 días en total.
Después de una artroplastia de cadera
Debe iniciar el tratamiento con dabigatrán de 1-4 horas después de la realización de la operación, tomando una única cápsula. Después deben tomarse 2 cápsulas una vez al día durante 28-35 días en total.
Prevención de la obstrucción vascular cerebral o sistémica por formación de coágulos de sangre desarrollada tras latido anormal del corazón y tratamiento de los coágulos de sangre en las venas de sus piernas y pulmones, incluyendo la prevención para que no vuelvan a aparecer coágulos de sangre en las venas de sus piernas y pulmones
La dosis recomendada es de 300 mg administrados en forma de una cápsula de 150 mg dos veces al día.
Si tiene 80 años de edad o más, la dosis recomendada de dabigatrán es de 220 mg administrados en forma de una cápsula de 110 mg dos veces al día.
Si está usando medicamentos que contienen verapamilo, se le deberá indicar una dosis reducida de dabigatrán de 220 mg tomados en forma de una cápsula de 110 mg dos veces al día, ya que su riesgo de sangrado puede aumentar.
Si usted tiene un riesgo de sangrado potencialmente mayor, su médico puede decidir prescribirle una dosis de 220 mg administrados en forma de una cápsula de 110 mg dos veces al día.
Puede continuar tomando este medicamento si es necesario restablecer su latido cardíaco normal mediante un procedimiento denominado cardioversión. Tome dabigatrán tal como le haya indicado su médico.
Si se le ha colocado un dispositivo médico (endoprótesis vascular) en un vaso sanguíneo para mantenerlo abierto en un procedimiento denominado intervención coronaria percutánea con colocación de endoprótesis vascular, puede recibir tratamiento con dabigatrán una vez que su médico haya decidido que se ha alcanzado un control normal de la coagulación sanguínea. Tome este medicamento tal como le haya indicado su médico.
Tratamiento de los coágulos de sangre y prevención de que se vuelvan a formar coágulos de sangre en niños
Dabigatrán se debe tomar dos veces al día, una dosis por la mañana y una dosis por la noche, aproximadamente a la misma hora todos los días. El intervalo de administración debe ser lo más próximo posible a 12 horas.
La dosis recomendada depende de la edad y del peso. Su médico determinará la dosis correcta. Es posible que su médico le ajuste la dosis durante el tratamiento. Siga usando todos los demás medicamentos a menos que su médico le indique que deje de usar alguno.
La tabla 1 muestra las dosis únicas y las dosis totales diarias de Privenax en miligramos (mg). Las dosis dependen del peso en kilogramos (kg) y de la edad en años del paciente.
Tabla1: Tabla de posología para Privenax cápsulas:
Combinaciones de peso/edad | Dosis única en mg | Dosis total diaria en mg | |
Peso en kg | Edad en años | ||
11 a menos de 13 kg | 8 a menos de 9 años | 75 | 150 |
13 a menos de 16 kg | 8 a menos de 11 años | 110 | 220 |
16 a menos de 21 kg | 8 a menos de 14 años | 110 | 220 |
21 a menos de 26 kg | 8 a menos de 16 años | 150 | 300 |
26 a menos de 31 kg | 8 a menos de 18 años | 150 | 300 |
31 a menos de 41 kg | 8 a menos de 18 años | 185 | 370 |
41 a menos de 51 kg | 8 a menos de 18 años | 220 | 440 |
51 a menos de 61 kg | 8 a menos de 18 años | 260 | 520 |
61 a menos de 71 kg | 8 a menos de 18 años | 300 | 600 |
71 a menos de 81 kg | 8 a menos de 18 años | 300 | 600 |
81 kg o más | 10 a menos de 18 años | 300 | 600 |
Dosis únicas que requieren combinaciones de más de una cápsula:
300 mg: dos cápsulas de 150 mg o
cuatro cápsulas de 75 mg
260 mg: una cápsula de 110 mg más una cápsula de 150 mg o
una cápsula de 110 mg más dos cápsulas de 75 mg
220 mg: dos cápsulas de 110 mg
185 mg: una cápsula de 75 mg más cápsula una de 110 mg
150 mg: una cápsula de 150 mg o
dos cápsulas de 75 mg
Cómo tomar Privenax
Privenax se puede tomar con o sin alimentos. La cápsula debe tragarse entera con un vaso de agua, para asegurar la liberación en el estómago. No rompa, mastique, ni abra la cápsula para tomar solo su contenido ya que ello puede aumentar el riesgo de hemorragia.
Instrucciones para abrir los blísteres
Las siguientes imágenes ilustran cómo extraer las cápsulas de Privenax del blíster:
1
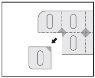 Separar un blíster individual de la tira de blíster a través de la línea perforada.
Separar un blíster individual de la tira de blíster a través de la línea perforada.
2
 Desprender la lámina posterior y extraer la cápsula.
Desprender la lámina posterior y extraer la cápsula.
- No presione las cápsulas a través de la lámina del blíster.
- No desprenda la lámina del blíster hasta que la cápsula sea necesaria.
Cambio del tratamiento anticoagulante
No cambie su tratamiento anticoagulante sin instrucciones específicas de su médico.
Si toma más Privenax del que debe
Tomar demasiada cantidad de Privenax aumenta el riesgo de hemorragia. Póngase en contacto con su médico inmediatamente si ha tomado demasiadas cápsulas de este medicamento. Hay disponibles opciones de tratamiento específicas.
En caso de sobredosis o ingestión accidental, consulte inmediatamente a su médico o farmacéutico o llame al Servicio de Información Toxicológica, teléfono: 91 562 04 20, indicando el medicamento y la cantidad ingerida.
Si olvidó tomar Privenax
Prevención de la formación de coágulos de sangre tras una artroplastia de rodilla o cadera
Tome las restantes dosis diarias de dabigatrán a la misma hora del siguiente día.
No tome una dosis doble para compensar las dosis olvidadas.
Uso en adultos: Prevención de la obstrucción vascular cerebral o sistémica por formación de coágulos de sangre desarrollada tras latido anormal del corazón y tratamiento de los coágulos de sangre en las venas de sus piernas y pulmones, incluyendo la prevención para que no vuelvan a aparecer coágulos de sangre en las venas de sus piernas y pulmones
Uso en niños: Tratamiento de los coágulos de sangre y prevención de que se vuelvan a formar coágulos de sangre
Una dosis olvidada se puede tomar hasta 6 horas antes de la próxima dosis.
Se debe omitir una dosis olvidada si el tiempo restante antes de la próxima dosis es inferior a 6 horas. No tome una dosis doble para compensar las dosis olvidadas.
Si interrumpe el tratamiento con Privenax
Tome Privenax exactamente como le ha sido prescrito. No interrumpa su tratamiento con Privenax sin consultar primero a su médico, ya que el riesgo de desarrollo de un coágulo de sangre podría ser mayor si interrumpiera el tratamiento demasiado pronto. Póngase en contacto con su médico si presenta indigestión después de tomar este medicamento.
Si tiene cualquier otra duda sobre el uso de este medicamento, pregunte a su médico o farmacéutico.
4. Posibles efectos adversos
Al igual que todos los medicamentos, este medicamento puede producir efectos adversos, aunque no todas las personas los sufran.
Dabigatrán actúa sobre la coagulación de la sangre; por lo tanto, la mayoría de los efectos adversos están relacionados con signos como cardenales o hemorragias. Pueden producirse episodios de sangrado mayor o grave, que constituyen los efectos adversos más graves y que, independientemente de su localización, pueden producir discapacidad, ser potencialmente mortales o incluso producir la muerte. En algunos casos estos sangrados pueden no ser evidentes.
Si experimenta cualquier episodio de sangrado que no para por sí solo o si experimenta signos de sangrado excesivo (debilidad excepcional, cansancio, palidez, mareo, dolor de cabeza o hinchazón inexplicable), consulte a su médico inmediatamente. Su médico puede decidir mantenerle en estrecha observación o cambiarle el medicamento.
Informe a su médico inmediatamente si experimenta una reacción alérgica grave que le provoca dificultad para respirar o mareo.
Los posibles efectos adversos se detallan a continuación, agrupados según la frecuencia en que se presentan.
Prevención de la formación de coágulos de sangre tras una artroplastia de rodilla o cadera
Frecuentes (pueden afectar a hasta 1 de cada 10 personas):
- Disminución de la cantidad de hemoglobina en la sangre (la sustancia presente en los glóbulos rojos de la sangre)
- Anomalías en las pruebas de función hepática
Poco frecuentes (pueden afectar a hasta 1 de cada 100 personas):
- El sangrado puede ser por la nariz, en el estómago o el intestino, del pene/vagina o del tracto urinario (incluyendo sangre en la orina que tiñe la orina de rosa o rojo), de hemorroides, del recto, bajo la piel, de una articulación, de o tras una lesión o después de una operación
- Formación de hematomas o de cardenales tras una operación
- Detección de sangre en heces en una prueba de laboratorio
- Disminución del número de glóbulos rojos en la sangre
- Disminución de la proporción de células sanguíneas
- Reacción alérgica
- Vómitos
- Deposiciones sueltas o líquidas frecuentes
- Sentir ganas de vomitar
- Supuración de heridas (secreción de líquido de una herida quirúrgica)
- Aumento de enzimas hepáticas
- Coloración amarillenta de la piel o del blanco de los ojos, causada por problemas hepáticos o sanguíneos
Raros (pueden afectar a hasta 1 de cada 1.000 personas):
- Sangrado
- El sangrado puede ser en el cerebro, en el lugar de una incisión quirúrgica, en el lugar de entrada de una inyección o en el lugar de entrada de un catéter en una vena
- Supuración sanguinolenta del lugar de entrada de un catéter en una vena
- Tos con sangre o esputo con manchas de sangre
- Disminución del número de plaquetas en sangre
- Disminución del número de glóbulos rojos en la sangre después de una operación
- Reacción alérgica grave que provoca dificultad para respirar o mareo
- Reacción alérgica grave que provoca hinchazón de la cara o la garganta
- Sarpullido de la piel con bultos rojos oscuros, prominentes y con picor, causados por una reacción alérgica
- Cambio repentino de la piel que afecta al color y al aspecto físico
- Picor
- Úlcera en el estómago o el intestino (incluyendo úlcera en el esófago)
- Inflamación del esófago y el estómago
- Reflujo del jugo gástrico al esófago
- Dolor en el abdomen o dolor de estómago
- Indigestión
- Dificultad para tragar
- Líquido saliendo de una herida
- Líquido saliendo de una herida tras una operación
Frecuencia no conocida (la frecuencia no puede estimarse a partir de los datos disponibles):
- Dificultad para respirar o respiración sibilante
- Disminución del número o incluso ausencia de leucocitos (los cuales ayudan a combatir las infecciones)
- Caída del cabello
Prevención de la obstrucción vascular cerebral o sistémica por formación de coágulos de sangre desarrollada tras latido anormal del corazón
Frecuentes (pueden afectar a hasta 1 de cada 10 personas):
- El sangrado puede ser por la nariz, en el estómago o el intestino, del pene/vagina o del tracto urinario (incluyendo sangre en la orina que tiñe la orina de rosa o rojo), o bajo la piel
- Disminución del número de glóbulos rojos en la sangre
- Dolor en el abdomen o dolor de estómago
- Indigestión
- Deposiciones sueltas o líquidas frecuentes
- Sentir ganas de vomitar
Poco frecuentes (pueden afectar a hasta 1 de cada 100 personas):
- Sangrado
- El sangrado puede ser de hemorroides, del recto o en el cerebro
- Formación de hematomas
- Tos con sangre o esputo con manchas de sangre
- Disminución del número de plaquetas en sangre
- Disminución de la cantidad de hemoglobina en la sangre (la sustancia presente en los glóbulos rojos de la sangre)
- Reacción alérgica
- Cambio repentino de la piel que afecta al color y al aspecto físico
- Picor
- Úlcera en el estómago o el intestino (incluyendo úlcera en el esófago)
- Inflamación del esófago y el estómago
- Reflujo del jugo gástrico al esófago
- Vómitos
- Dificultad para tragar
- Anomalías en las pruebas de función hepática
Raros (pueden afectar a hasta 1 de cada 1.000 personas):
- El sangrado puede ser en una articulación, en el lugar de una incisión quirúrgica, en una herida, en el lugar de entrada de una inyección o en el lugar de entrada de un catéter en una vena
- Reacción alérgica grave que provoca dificultad para respirar o mareo
- Reacción alérgica grave que provoca hinchazón de la cara o la garganta
- Sarpullido de la piel con bultos rojos oscuros, prominentes y con picor, causados por una reacción alérgica
- Disminución de la proporción de células sanguíneas
- Aumento de enzimas hepáticas
- Coloración amarillenta de la piel o del blanco de los ojos, causada por problemas hepáticos o sanguíneos
Frecuencia no conocida (la frecuencia no puede estimarse a partir de los datos disponibles):
- Dificultad para respirar o respiración sibilante
- Disminución del número o incluso ausencia de leucocitos (los cuales ayudan a combatir las infecciones)
- Caída del cabello
En un ensayo clínico, el índice de ataques al corazón con dabigatrán fue numéricamente superior que con warfarina. La incidencia global fue baja.
Tratamiento de los coágulos de sangre en las venas de sus piernas y pulmones, incluyendo la prevención para que no vuelvan a aparecer coágulos de sangre en las venas de sus piernas y/o pulmones
Frecuentes (pueden afectar a hasta 1 de cada 10 personas):
- El sangrado puede ser por la nariz, en el estómago o el intestino, del recto, del pene/vagina o del tracto urinario (incluyendo sangre en la orina que tiñe la orina de rosa o rojo), o bajo la piel
- Indigestión
Poco frecuentes (pueden afectar a hasta 1 de cada 100 personas):
- Sangrado
- El sangrado puede ser en una articulación o en una herida
- El sangrado puede ser de hemorroides
- Disminución del número de glóbulos rojos en la sangre
- Formación de hematomas
- Tos con sangre o esputo con manchas de sangre
- Reacción alérgica
- Cambio repentino de la piel que afecta al color y al aspecto físico
- Picor
- Úlcera en el estómago o el intestino (incluyendo úlcera en el esófago)
- Inflamación del esófago y el estómago
- Reflujo del jugo gástrico al esófago
- Sentir ganas de vomitar
- Vómitos
- Dolor en el abdomen o dolor de estómago
- Deposiciones sueltas o líquidas frecuentes
- Anomalías en las pruebas de función hepática
- Aumento de enzimas hepáticas
Raros (pueden afectar a hasta 1 de cada 1.000 personas):
- El sangrado puede ser en el lugar de una incisión quirúrgica, o en el lugar de entrada de una inyección, o en el lugar de entrada de un catéter en una vena o desde el cerebro
- Disminución del número de plaquetas en sangre
- Reacción alérgica grave que provoca dificultad para respirar o mareo
- Reacción alérgica grave que provoca hinchazón de la cara o la garganta
- Sarpullido de la piel con bultos rojos oscuros, prominentes y con picor, causados por una reacción alérgica
- Dificultad para tragar
Frecuencia no conocida (la frecuencia no puede estimarse a partir de los datos disponibles):
- Dificultad para respirar o respiración sibilante
- Disminución de la cantidad de hemoglobina en la sangre (la sustancia presente en los glóbulos rojos de la sangre)
- Disminución de la proporción de células sanguíneas
- Disminución del número o incluso ausencia de leucocitos (los cuales ayudan a combatir las infecciones)
- Coloración amarillenta de la piel o del blanco de los ojos, causada por problemas hepáticos o sanguíneos
- Caída del cabello
En el programa de ensayos clínicos, el índice de ataques al corazón con dabigatrán fue superior que con warfarina. La incidencia global fue baja. No se observó ningún desequilibrio en el índice de ataques al corazón en pacientes tratados con dabigatrán en comparación con pacientes tratados con placebo.
Tratamiento de los coágulos de sangre y prevención de que se vuelvan a formar coágulos de sangre en niños
Frecuentes (pueden afectar a hasta 1 de cada 10 personas):
- Disminución del número de glóbulos rojos en la sangre
- Disminución del número de plaquetas en sangre
- Sarpullido de la piel con bultos rojos oscuros, prominentes y con picor, causados por una reacción alérgica
- Cambio repentino de la piel que afecta al color y al aspecto físico
- Formación de hematomas
- Hemorragia nasal
- Reflujo del jugo gástrico al esófago
- Vómitos
- Sentir ganas de vomitar
- Deposiciones sueltas o líquidas frecuentes
- Indigestión
- Caída del cabello
- Aumento de enzimas hepáticas
Poco frecuentes (pueden afectar a hasta 1 de cada 100 personas):
- Disminución del número de leucocitos (los cuales ayudan a combatir las infecciones)
- El sangrado puede ser en el estómago o el intestino, del cerebro, del recto, del pene/vagina o del tracto urinario (incluyendo sangre en la orina que tiñe la orina de rosa o rojo), o bajo la piel
- Disminución de la cantidad de hemoglobina en la sangre (la sustancia presente en los glóbulos rojos de la sangre)
- Disminución de la proporción de células sanguíneas
- Picor
- Tos con sangre o esputo con manchas de sangre
- Dolor en el abdomen o dolor de estómago
- Inflamación del esófago y el estómago
- Reacción alérgica
- Dificultad para tragar
- Coloración amarillenta de la piel o del blanco de los ojos, causada por problemas hepáticos o sanguíneos
Frecuencia no conocida (la frecuencia no puede estimarse a partir de los datos disponibles):
- Falta de leucocitos (los cuales ayudan a combatir las infecciones)
- Reacción alérgica grave que provoca dificultad para respirar o mareo
- Reacción alérgica grave que provoca hinchazón de la cara o la garganta
- Dificultad para respirar o respiración sibilante
- Sangrado
- El sangrado puede ser en una articulación o en una herida, en una incisión quirúrgica, en el lugar de entrada de una inyección o en el lugar de entrada de un catéter en una vena
- El sangrado puede ser de hemorroides
- Úlcera en el estómago o el intestino (incluyendo úlcera en el esófago)
- Anomalías en las pruebas de función hepática
Comunicación de efectos adversos
Si experimenta cualquier tipo de efecto adverso, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico, incluso si se trata de posibles efectos adversos que no aparecen en este prospecto. También puede comunicarlos directamente a través del Sistema Español de Farmacovigilancia de Medicamentos de Uso Humano: www.notificaram.es. Mediante la comunicación de efectos adversos usted puede contribuir a proporcionar más información sobre la seguridad de este medicamento.
5. Conservación de Privenax
Mantener este medicamento fuera de la vista y del alcance de los niños.
No utilice este medicamento después de la fecha de caducidad que aparece en la caja o el blíster después de “CAD”. La fecha de caducidad es el último día del mes que se indica.
No conservar a temperatura superior a 30 ºC
Conservar en el embalaje original para protegerlo de la humedad.
Los medicamentos no se deben tirar por los desagües ni a la basura. Deposite los envases y los medicamentos que no necesite en el Punto SIGRE de la farmacia. En caso de duda pregunte a su farmacéutico como deshacerse de los envases y de los medicamentos que no necesita. De esta forma, ayudará a proteger el medio ambiente.
6. Contenido del envase e información adicional
Composición de Privenax
- El principio activo es dabigatrán. Cada cápsula dura contiene 110 mg de dabigatrán etexilato (en forma de mesilato).
- Los demás componentes son ácido tartárico, goma arábiga, hipromelosa 2910, dimeticona 350, talco e hidroxipropilcelulosa
- La cubierta de la cápsula contiene carragenona, cloruro potásico, dióxido de titanio (E-171), hipromelosa e azul FD&C 2/índigo carmín (E-132).
Aspecto del producto y contenido del envase
Privenax 110 mg son pellets de color blanquecino a amarillo pálido dentro de cápsulas duras azules de tamaño 1.
Privenax se presenta en envases que contienen 10 x 1, 30 x 1 o 60 x 1 cápsulas duras en blísteres unidosis perforados de aluminio/OPA-AL-PVC.
Puede que solamente estén comercializados algunos tamaños de envases.
Titular de la autorización de comercialización
Kern Pharma, S.L.
Venus, 72 – Pol. Ind. Colón II
08228 Terrassa - Barcelona
España
Responsable de la fabricación
Galenicum Health, S.L.U.
Sant Gabriel, 50,
08950 – Esplugues de Llobregat (Barcelona)
España
o
SAG Manufacturing S.L.U
Crta. N-I, Km 36
28750 San Agustin de Guadalix,
Madrid – España
Este medicamentoestá autorizado en los estados miembros del Espacio Económico Europeo con los siguientes nombres:
Malta – Privenax 110 mg hard capsules
Portugal – Dabigatrano etexilato Pharmakern 110 mg cápsulas
España – Privenax 110 mg cápsulas duras EFG
Fecha de la última revisión de este prospecto:junio 2024
La información actualizada y detallada de este medicamento está disponible en la página web de la Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios (AEMPS): http://www.aemps.gob.es/.
- País de registro
- Precio medio en farmacia16.53 EUR
- Disponibilidad en farmacias
Problema de suministro reportado
Los datos de la Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios (AEMPS) indican un problema de suministro que afecta a este medicamento.<br><br>La disponibilidad puede ser limitada en algunas farmacias.<br><br>Para actualizaciones o alternativas, consulte a su farmacéutico. - Principio activo
- Requiere recetaSí
- Fabricante
- Esta información es de carácter general y no sustituye la consulta con un profesional sanitario.
- Alternativas a PRIVENAX 110 MG CAPSULAS DURAS EFGForma farmacéutica: CAPSULA, 110 mgPrincipio activo: dabigatran etexilateFabricante: Adamed Laboratorios S.L.U.Requiere recetaForma farmacéutica: CAPSULA, 150 mgPrincipio activo: dabigatran etexilateFabricante: Adamed Laboratorios S.L.U.Requiere recetaForma farmacéutica: CAPSULA, 75 mgPrincipio activo: dabigatran etexilateFabricante: Adamed Laboratorios S.L.U.Requiere receta
Médicos online para PRIVENAX 110 MG CAPSULAS DURAS EFG
Comenta la dosis, los posibles efectos secundarios, interacciones, contraindicaciones o la revisión de receta de PRIVENAX 110 MG CAPSULAS DURAS EFG, sujeto a valoración médica y a la normativa local.
Preguntas frecuentes















