
LAURAK 100 MG/ML SOLUCION ORAL EFG

Cómo usar LAURAK 100 MG/ML SOLUCION ORAL EFG
Traducción generada por IA
Este contenido ha sido traducido automáticamente y se ofrece solo con fines informativos. No sustituye la consulta con un profesional sanitario.
Ver originalContenido del prospecto
Introducción
Prospecto: información para el paciente
Laurak 100 mg/ml solución oral EFG
Levetiracetam
Lea todo el prospecto detenidamente antes de que usted o su hijo empiece a tomar este medicamento, porque contiene información importante para usted.
- Conserve este prospecto ya que puede tener que volver a leerlo.
- Si tiene alguna duda, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico.
- Este medicamento se le ha recetado solamente a usted y no debe dárselo a otras personas aunque tengan los mismos síntomas que usted, ya que puede perjudicarles.
- Si experimenta efectos adversos, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico, incluso si se trata de efectos adversos que no aparecen en este prospecto. Ver sección 4.
Contenido del prospecto
- Qué es Laurak solución y para qué se utiliza
- Qué necesita saber antes de empezar a tomar Laurak solución
- Cómo tomar Laurak solución
- Posibles efectos adversos
- Conservación de Laurak solución
- Contenido del envase e información adicional
1. Qué es Laurak solución y para qué se utiliza
Levetiracetam es un medicamento antiepiléptico (un medicamento para el tratamiento de crisis en epilepsia).
Laurak solución se utiliza:
- en solitario en adultos y adolescentes de 16 años de edad o mayores con epilepsia diagnosticada recientemente para tratar una forma de epilepsia. La epilepsia es una enfermedad donde los pacientes tienen ataques (crisis). Levetiracetam se utiliza para la forma de epilepsia en la cual las crisis inicialmente afectan sólo a un lado del cerebro, pero pueden después extenderse a zonas más amplias en los dos lados del cerebro (crisis de inicio parcial con o sin generalización secundaria). Su médico le ha recetado levetiracetam para reducir el número de crisis.
- conjuntamente con otros medicamentos antiepilépticos para tratar:
- las crisis de inicio parcial con o sin generalización en adultos, adolescentes, niños y lactantes a partir de 1 mes de edad.
- las crisis mioclónicas (sacudidas tipo shock, cortas, de un músculo o grupo de músculos) en adultos y adolescentes a partir de 12 años con epilepsia mioclónica juvenil.
- las crisis tónico-clónicas generalizadas primarias (crisis mayores, incluyendo pérdida de consciencia) en adultos y adolescentes a partir de 12 años de edad con epilepsia idiopática generalizada (tipo de epilepsia que se piensa que tiene una causa genética).
2. Qué necesita saber antes de empezar a tomar Laurak solución
No tome Laurak solución
- Si es alérgico a levetiracetam, a los derivados de pirrolidona o a cualquiera de los demás componentes de este medicamento (incluidos en la sección 6).
Advertencias y precauciones
Consulte a su médico antes de empezar a tomar este medicamento
- Si usted padece problemas de riñón, siga las instrucciones de su médico quien decidirá si debe ajustarle la dosis a tomar.
- Si observa cualquier disminución en el crecimiento de su hijo o un desarrollo de la pubertad inesperado, contacte con su médico.
- Un pequeño número de personas en tratamiento con antiepilépticos tales como levetiracetam han tenido pensamientos de hacerse daño o suicidarse. Si tiene cualquier síntoma de depresión y/o pensamientos suicidas, contacte con su médico.
Informe a su médico o farmacéutico si alguno de los siguientes efectos adversos se agrava o dura más de unos pocos días:
Pensamientos anormales, sensación de irritabilidad o reacciona de forma más agresiva de lo
normal o si usted o su familia y amigos notan cambios importantes en el estado de ánimo o
comportamiento.
Niños y adolescentes
- El tratamiento exclusivo con levetiracetam (monoterapia) no está indicado en niños y adolescentes menores de 16 años.
Uso de Laurak solución con otros medicamentos
Informe a su médico o farmacéutico si está utilizando, ha utilizado recientemente o pudiera tener que utilizar cualquier otro medicamento.
No tome macrogol (medicamento utilizado como laxante) durante una hora antes y una hora después de tomar levetiracetam ya que podría reducir su efecto.
Embarazo y lactancia
Si está embarazada o en periodo de lactancia, cree que podría estar embarazada o tiene intención de quedarse embarazada, consulte a su médico antes de utilizar este medicamento. Levetiracetam sólo se puede utilizar durante el embarazo si, después de una cuidadosa evaluación, su médico lo considera necesario.
No debe abandonar su tratamiento sin comentarlo antes con su médico.
No se puede excluir completamente el riesgo de defectos de nacimiento para el bebé.
No se recomienda la lactancia natural durante el tratamiento.
Conducción y uso de máquinas
Levetiracetam puede alterar su capacidad para conducir o manejar herramientas o maquinaria, puesto que puede producirle sensación de sueño. Esto es más probable al inicio del tratamiento o cuando se aumenta la dosis. No debería conducir o utilizar maquinaria hasta que se compruebe que su capacidad para realizar estas actividades no está afectada.
Laurak solución contiene parahidroxibenzoato de metilo, parahidroxibenzoato de propilo y maltitol
Laurak solución puede producir reacciones alérgicas (posiblemente retardadas) porque contiene parahidroxibenzoato de metilo (E218) y para hidroxibenzoato de propilo (E216).
Este medicamento contiene maltitol. Si su médico le ha indicado que padece una intolerancia a ciertos azúcares, consulte con él antes de tomar este medicamento.
Este medicamento contiene 3,4 mg de propilenglicol en cada ml.
Si el bebé tiene menos de 4 semanas de edad, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico, en particular si al bebé se le han administrado otros medicamentos que contengan propilenglicol o alcohol.
3. Cómo tomar Laurak solución
Siga exactamente las instrucciones de administración de este medicamento indicadas por su médico o farmacéutico. En caso de duda, consulte de nuevo a su médico o farmacéutico.
Levetiracetam se debe tomar dos veces al día, una vez por la mañana y otra por la noche, aproximadamente a la misma hora cada día.
Tome la solución oral según las instrucciones de su médico.
Monoterapia
Dosis en adultos y adolescentes (desde 16 años de edad):
Para pacientes a partir de 4 años de edad, medir la dosis adecuada utilizando la jeringa de 10 ml incluida en la caja.
Dosis general: levetiracetam se toma dos veces al día, en dos dosis iguales, cada dosis individual entre 5 ml (500 mg) y 15 ml (1500 mg).
Cuando empiece a tomar este medicamento, su médico le prescribirá una dosis inferiordurante dos semanas antes de administrarle la dosis general más baja.
Terapia concomitante
Dosis en adultos y adolescentes (de 12 a 17 años):
Para pacientes a partir de 4 años de edad, medir la dosis adecuada utilizando la jeringa de 10 ml incluida en la caja.
Dosis general: levetiracetam se toma dos veces al día, en dos dosis iguales, cada dosis individual entre 5 ml (500 mg) y 15 ml (1500 mg).
Dosis en niños a partir de 6 meses de edad:
Su médico le prescribirá la forma farmacéutica de levetiracetam más apropiada según la edad, el peso y la dosis.
Para niños de 6 meses a 4 años de edad, medir la dosis adecuada utilizando la jeringa de 3 mlincluida en la caja.
Para niños mayores de 4 años de edad, medir la dosis adecuada utilizando la jeringa de 10 mlincluida en la caja.
Dosis general: levetiracetam se toma dos veces al día, en dos dosis iguales, cada dosis individual entre 0,1 ml (10 mg) y 0,3 ml (30 mg) por kg de peso corporal del niño (ver en la siguiente tabla los ejemplos de dosis).
Dosis en niños a partir de 6 meses de edad :
Peso | Dosis inicial: 0,1 ml/kg dos veces al día | Dosis máxima: 0,3 ml/kg dos veces al día |
6 kg | 0,6 ml dos veces al día | 1,8 ml dos veces al día |
8 kg | 0,8 ml dos veces al día | 2,4 ml dos veces al día |
10 kg | 1 ml dos veces al día | 3 ml dos veces al día |
15 kg | 1,5 ml dos veces al día | 4,5 ml dos veces al día |
20 kg | 2 ml dos veces al día | 6 ml dos veces al día |
25 kg | 2,5 ml dos veces al día | 7,5 ml dos veces al día |
A partir de 50 kg | 5 ml dos veces al día | 15 ml dos veces al día |
Dosificación en lactantes (de 1 mes a menos de 6 meses):
Para lactantes de 1 mes a menos de 6 meses de edad, medir la dosis adecuada utilizando la jeringa de 1 mlincluida en la caja.
Dosis general: levetiracetam se toma dos veces al día, en dos dosis iguales, cada dosis individual entre 0,07 ml (7 mg) y 0,21 ml (21 mg) por kg de peso corporal del lactante (ver en la siguiente tabla los ejemplos de dosis).
Dosis en lactantes (de 1 mes a menos de 6 meses de edad):
Peso | Dosis inicial: 0,07 ml/kg dos veces al día | Dosis máxima: 0,21 ml/kg dos veces al día |
4 kg | 0,3 ml dos veces al día | 0,85 ml dos veces al día |
5 kg | 0,35 ml dos veces al día | 1,05 ml dos veces al día |
6 kg | 0,45 ml dos veces al día | 1,25 ml dos veces al día |
7 kg | 0,5 ml dos veces al día | 1,5 ml dos veces al día |
Forma de administración:
Después de medir la dosis correcta con la jeringa adecuada, Laurak solución oral se puede diluir en un vaso de agua o en un biberón. Puede tomar Laurak solución con o sin alimentos. Tras la administración oral de levetiracetam se puede apreciar su sabor amargo.
Instrucciones para la correcta administración:
- Abrir el frasco: apretar el tapón y desenroscar en sentido contrario a las agujas del reloj (figura 1)
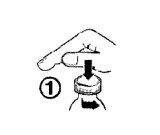
- Insertar el adaptador de la jeringa en el cuello del frasco (figura 2). Asegurarse de que está bien fijada.
- Coger la jeringa e introducirla en la abertura del adaptador (figura 2).
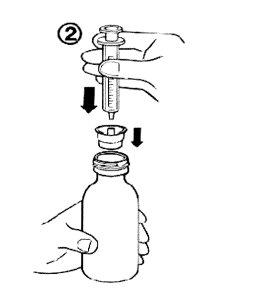
Poner el frasco boca abajo (figura 3).
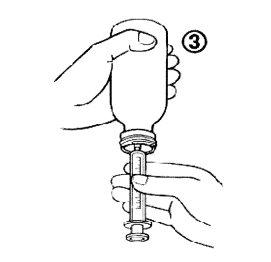
- Llenar la jeringa con una pequeña cantidad de solución bajando el émbolo (figura 4A) y después subiéndolo para eliminar cualquier posible burbuja (figura 4B). Baje el émbolo hasta la marca de graduación que corresponda con la dosis en mililitros (ml) prescrita por su médico (figura 4C).
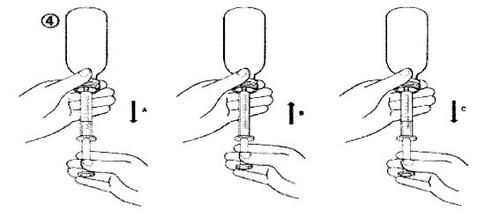
- Poner el frasco boca arriba. Retirar la jeringa del adaptador.
- Vaciar el contenido de la jeringa en un vaso de agua o en un biberón, bajando el émbolo hasta el final de la jeringa (figura 5).
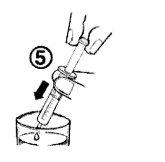
- Beber el contenido del vaso o del biberón entero.
- Lavar la jeringa sólo con agua (figura 6).
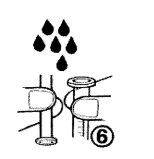
- Cerrar el frasco con el tapón de rosca de plástico.
Duración del tratamiento:
- Levetiracetam se utiliza como un tratamiento crónico. Debe continuar con el tratamiento con levetiracetam durante el tiempo indicado por su médico.
- No deje su tratamiento sin la recomendación de su médico ya que pueden aumentar sus crisis.
Si toma más Laurak solución del que debe
En caso de sobredosis o ingestión accidental, consulte inmediatamente con su médico, farmaceútico o llame al Servicio de Informacion Toxicológica 91 562 04 20 indicando el medicamento y la cantidad ingerida. Los posibles efectos adversos de una sobredosis de Laurak solución son somnolencia, agitación, agresividad, disminución de la alerta, inhibición de la respiración y coma.
Si olvidó tomar Laurak solución:
Contacte con su médico si ha dejado de tomar una o más dosis.
No tome una dosis doble para compensar las dosis olvidadas.
Si interrumpe el tratamiento con Laurak solución:
La finalización del tratamiento con este medicamento debe efectuarse de forma gradual para evitar un incremento de las crisis. Si su médico decide parar su tratamiento con levetiracetam, él/ella le dará las instrucciones para la retirada gradual del mismo.
Si tiene cualquier otra duda sobre el uso de este medicamento, pregunte a su médico o farmacéutico.
4. Posibles efectos adversos
Al igual que todos los medicamentos, este medicamento puede producir efectos adversos, aunque no todas las personas los sufran.
Informe a su médico inmediatamente, o vaya al servicio de urgencias de su hospital más cercano si experimenta:
- debilidad, mareo o dificultad para respirar, ya que éstos pueden ser signos de una reacción alérgica (anafiláctica) grave
- hinchazón de la cara, labios, lengua o garganta (edema de Quincke)
- síntomas de gripe y erupción en la cara seguido de una erupción prolongada con temperatura elevada, niveles de enzimas hepáticos elevados en tests sanguíneos y un aumento en un tipo de células blancas sanguíneas (eosinofilia) y nódulos linfáticos agrandados (Reacción de hipersensibilidad al medicamento con eosinofilia y síntomas sistémicos (DRESS))
- síntomas como bajo volumen de orina, cansancio, nauseas, vómitos, confusión e hinchazón de piernas, brazos o pies, ya que puede ser un signo de disminución súbita de la función renal
- una erupción cutánea que puede formar ampollas y puede aparecer como pequeñas dianas (puntos centrales oscuros rodeados por un área más pálida, con un anillo oscuro alrededor del borde) (eritema multiforme)
- una erupción generalizada con ampollas y descamación de la piel, especialmente alrededor de la boca, nariz, ojos y genitales (síndrome de Stevens-Johnson)
- una forma más grave que causa descamación de la piel en más del 30% de la superficie corporal (necrólisis epidérmica tóxica)
- signos de cambios mentales graves o si alguien a su alrededor nota signos de confusión, somnolencia (adormecimiento), amnesia (pérdida de memoria), deterioro de la memoria (olvidos), comportamiento anormal u otros signos neurológicos incluyendo movimientos involuntarios o incontrolados. Éstos pueden ser síntomas de encefalopatía.
Los efectos adversos notificados más frecuentemente son nasofaringitis, somnolencia (sensación de sueño), dolor de cabeza, fatiga y mareo. Los efectos adversos como sensación de sueño, sensación de debilidad y mareos pueden ser más frecuentes cuando se inicia el tratamiento o se aumenta la dosis. Sin embargo, estos efectos adversos deben disminuir con el tiempo.
Muy frecuentes: pueden afectar a más de 1 de cada 10 personas
- nasofaringitis;
- somnolencia (sensación de sueño), dolor de cabeza.
Frecuentes: pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 10 personas
- anorexia (pérdida de apetito);
- depresión, hostilidad o agresividad, ansiedad, insomnio, nerviosismo o irritabilidad;
- convulsiones, trastorno del equilibrio, mareos (sensación de inestabilidad), letargo (falta de energía y entusiasmo), temblor (temblor involuntario);
- vértigo (sensación de rotación);
- tos;
- dolor abdominal, diarrea, dispepsia (digestión pesada, ardor y acidez),vómitos, náuseas;
- erupción en la piel;
- astenia/fatiga (sensación de debilidad).
Poco frecuentes: pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 100 personas
- disminución del número de plaquetas, disminución de los glóbulos blancos;
- pérdida de peso, aumento de peso;
- intento de suicidio y pensamientos suicidas, alteraciones mentales, comportamiento anormal, alucinaciones, cólera, confusión, ataque de pánico, inestabilidad emocional/cambios de humor, agitación;
- amnesia (pérdida de memoria), deterioro de la memoria (falta de memoria), coordinación anormal/ataxia (coordinación de los movimientos alterada), parestesia (hormigueo), alteraciones de la atención (pérdida de concentración);
- diplopía (visión doble), visión borrosa;
- valores elevados/anormales en las pruebas sobre la funcionalidad del hígado;
- pérdida de cabello, eczema, picor;
- debilidad muscular, mialgia (dolor muscular);
- lesión.
Raros: pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 1.000 personas
- infección;
- disminución de todos los tipos de células sanguíneas;
- reacciones alérgicas graves (DRESS, reacción anafiláctica (reacción alérgica importante y grave), edema de Quincke (hinchazón de cara, labios, lengua y garganta));
- disminución de la concentración de sodio en sangre;
- suicidio, trastornos de la personalidad (problemas de comportamiento), pensamiento anormal (pensamiento lento, dificultad para concentrarse);
- delirio
- encefalopatía (ver subsección “Informe a su médico inmediatamente” para ver una descripción detallada de los síntomas);
- espasmos musculares incontrolables que afectan a la cabeza, al torso y a las extremidades, dificultad para controlar los movimientos, hipercinesia (hiperactividad);
- pancreatitis (inflamación del páncreas);
- insuficiencia hepática, hepatitis (inflamación del hígado);
- disminución súbita de la función renal;
- erupción cutánea, que puede dar lugar a ampollas que pueden aparecer como pequeñas dianas (puntos centrales oscuros rodeados por un área más pálida, con un anillo oscuro alrededor del borde) (eritema multiforme), una erupción generalizada con ampollas y descamación de la piel, especialmente alrededor de la boca, nariz, ojos y genitales (síndrome de Stevens-Johnson) y una forma más grave que causa descamación de la piel en más del 30% de la superficie corporal (necrólisis epidérmica tóxica);
- rabdomiólisis (rotura del tejido muscular) y aumento de creatinfosfoquinasa sanguínea asociado. La prevalencia es significativamente mayor en pacientes japoneses en comparación con pacientes no japoneses;
- cojera o dificultad para caminar.
Comunicación de efectos adversos
Si experimenta cualquier tipo de efecto adverso, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico, incluso si se trata de posibles efectos adversos que no aparecen en este prospecto. También puede comunicarlos directamente a través del Sistema Español de Farmacovigilancia de Medicamentos de Uso Humano https://www.notificaram.es. Mediante la comunicación de efectos adversos usted puede contribuir a proporcionar más información sobre la seguridad de este medicamento.
5. Conservación de Laurak solución
Mantener este medicamento fuera de la vista y del alcance de los niños.
No utilice este medicamento después de la fecha de caducidad que aparece en la caja y en el frasco después de CAD.
La fecha de caducidad es el último día del mes que se indica.
No usar después de 6 meses de la primera apertura del envase.
Este medicamento no requiere condiciones especiales de conservación.
Los medicamentos no se deben tirar por los desagües ni a la basura. Deposite los envases y los medicamentos que no necesita en el Punto SIGRE de la farmacia. En caso de duda pregunte a su farmacéutico cómo deshacerse de los envases y de los medicamentos que no necesita. De esta forma ayudará a proteger el medio ambiente.
6. Contenido del envase e información adicional
Composición de Laurak solución
La sustancia activa es levetiracetam.
Cada ml contiene 100 mg de levetiracetam.
Jeringa oral de 1 ml (graduada cada 0,05 ml):
Cada 0,05 ml contiene 5 mg de levetiracetam
Jeringa oral de 3 ml (graduada cada 0,1 ml):
Cada 0,1 ml contiene 10 mg de levetiracetam
Jeringa oral de 10 ml (graduada cada 0,25 ml):
Cada 0,25 ml contiene 25 mg de levetiracetam
Los demás componentes son: citrato de sodio, ácido cítrico anhidro, agua purificada, parahidroxibenzoato de metilo (E218), parahidroxibenzoato de propilo (E216), glicirrizato de amonio, glicerol (E422), maltitol (E965), acesulfamo potásico (E950), aroma fantasie (incluye propilenglicol y mentol), aroma contramarum (incluye propilenglicol, triacetina).
Aspecto del producto y contenido del envase
Laurak solución 100 mg/ml solución oral es un líquido transparente, de incoloro a ligeramente pardusco.
El frasco de vidrio de 300 ml de Laurak solución (para niños a partir de 4 años de edad, adolescentes y adultos) se acondiciona en una caja de cartón acompañado de una jeringa oral de 10 ml (graduada cada 0,25 ml) y de un adaptador para la jeringa.
El frasco de vidrio de 150 ml de Laurak solución (para lactantes y niños pequeños desde 6 meses a menos de 4 años de edad) se acondiciona en una caja de cartón acompañado de una jeringa oral de 3 ml (graduada cada 0,1 ml) y de un adaptador para la jeringa.
El frasco de vidrio de 150 ml de Laurak solución (para lactantes de 1 mes a menos de 6 meses de edad) se acondiciona en una caja de cartón acompañado de una jeringa oral de 1 ml (graduada cada 0,05 ml) y de un adaptador para la jeringa.
Envases de 150 ml y 300 ml de solución oral.
Puede que solamente estén comercializados algunos tamaños de envases.
Titular de la autorización de comercialización y Responsable de la fabricación
Titular de la autorización de comercialización
Neuraxpharm Spain, S.L.U.
Avda. Barcelona, 69
08970 Sant Joan Despí
Barcelona
España
Responsable de la fabricación
Neuraxpharm Arzneimittel GmbH
Elisabeth-Selbert-Strasse 23
Langenfeld – 40764
Alemania
Este medicamento está autorizado en los Estados Miembros del Espacio Económico Europeo con los siguientes nombres:
Portugal: Laurak
España: Laurak 100 mg/ml solución oral EFG
Fecha de la última revisión de este prospecto:Febrero 2021
La información detallada y actualizada de este medicamento está disponible en la página Web de la Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
- País de registro
- Precio medio en farmacia56.64 EUR
- Principio activo
- Requiere recetaSí
- Fabricante
- Esta información es de carácter general y no sustituye la consulta con un profesional sanitario.
- Alternativas a LAURAK 100 MG/ML SOLUCION ORAL EFGForma farmacéutica: INYECTABLE PERFUSION, 100 mgPrincipio activo: LevetiracetamFabricante: Ucb PharmaRequiere recetaForma farmacéutica: INYECTABLE PERFUSION, 100 mg/mlPrincipio activo: LevetiracetamFabricante: Ucb PharmaRequiere recetaForma farmacéutica: SOLUCIÓN/SUSPENSIÓN ORAL, 100 mgPrincipio activo: LevetiracetamFabricante: Ucb PharmaRequiere receta
Médicos online para LAURAK 100 MG/ML SOLUCION ORAL EFG
Comenta la dosis, los posibles efectos secundarios, interacciones, contraindicaciones o la revisión de receta de LAURAK 100 MG/ML SOLUCION ORAL EFG, sujeto a valoración médica y a la normativa local.
Preguntas frecuentes








