SYNTOCINON 10 IU/mL Injectable Solution and Perfusion Solution


How to use SYNTOCINON 10 IU/mL Injectable Solution and Perfusion Solution
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Syntocinon 10 UI/ml Solution for Injection and Infusion
oxytocin
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or nurse.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack:
- What Syntocinon is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use Syntocinon
- How to use Syntocinon
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Syntocinon
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Syntocinon is and what it is used for
Syntocinon is presented as a solution for injection and infusion.
Syntocinon belongs to a group of medicines called oxytocics (medicines that promote labor by stimulating uterine contractions). The action produced is identical to that produced by oxytocin, a natural hormone released by the pituitary glands.
Syntocinon is indicated in the following cases:
- Induction of labor at term.
- Stimulation of contractility in cases of uterine inertia.
- Prevention and treatment of postpartum hemorrhage.
2. What you need to know before you use Syntocinon
Do not use Syntocinon:
- if you are allergic to oxytocin or any of the other components of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- if the fetus has cephalopelvic disproportion, abnormal presentation.
- if there is a predisposition to amniotic fluid embolism (dead fetus in utero, premature placental abruption).
- if you have a history of cesarean section or any surgical act affecting the uterus, placenta previa, vasa previa, hypertonic contractions.
- if there is fetal distress and if delivery is not imminent.
- if you are being administered prostaglandins or other uterine contraction stimulants in combination, and in any case, at least six hours must have passed since the administration of those.
- In the case of multiple births.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor or nurse before starting to use Syntocinon.
The use of oxytocin for labor induction should be done strictly for medical reasons, not for convenience.
Syntocinon should not be used for prolonged periods in patients with resistant uterine inertia, severe pre-eclampsia, or severe cardiovascular disorders.
Special caution should be exercised in the presence of borderline cephalopelvic disproportion, secondary uterine inertia, mild or moderate pregnancy-induced hypertension or heart disease, and in patients over 35 years of age or with a history of lower uterine segment cesarean section.
Cardiovascular disorders
To avoid significant changes in blood pressure and heart rate, Syntocinon should be used with caution in patients with pre-existing cardiovascular diseases (such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, valvular heart disease, and/or ischemic heart disease, including coronary artery vasospasm). Inform your doctor if you have any of these diseases.
QT syndrome
Syntocinon should be administered with caution to patients with long QT syndrome or related symptoms and to patients being treated with medications known to prolong the QT interval (see "Use of Syntocinon with other medications").
Fetal distress and death
The administration of oxytocin in excess doses produces uterine overstimulation that can cause fetal distress, asphyxia, and death, or may lead to hypertonicity, tetanic contractions, or uterine rupture. Your doctor will monitor you for fetal heart rate and uterine motility.
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC):
Rarely, pharmacological induction of labor using uterotonic agents, including oxytocin, increases the risk of postpartum DIC. This risk is particularly increased in women who have additional risk factors for DIC, such as being 35 years or older, complications during pregnancy, and gestational age of more than 40 weeks.
Water intoxication
Due to the fact that oxytocin has a slight antidiuretic activity, its prolonged intravenous administration at high doses along with large volumes of fluid, such as may be the treatment of inevitable or deferred abortion, or in the treatment of postpartum hemorrhage, may therefore cause water intoxication associated with hyponatremia. Special caution should be exercised in patients with severe renal failure, due to possible water retention and accumulation of oxytocin.
Renal failure
Special caution should be exercised in patients with severe renal failure, due to possible water retention and accumulation of oxytocin.
Latex allergy
The active ingredient of Syntocinon may cause a severe allergic reaction (anaphylactic reaction) in patients allergic to latex. Inform your doctor if you are allergic to latex.
Children and adolescents
The safety and efficacy of Syntocinon in children and adolescents (under 18 years of age) have not been established. No data are available.
Use of Syntocinon with other medications:
Inform your doctor if you are using, have recently used, or may need to use any other medication. Certain medications may interact with Syntocinon, in these cases, your doctor may change the dose or interrupt treatment with one of them. In particular:
- Inhaled anesthetics with great uterine relaxant power (such as halothane, chloroform, etc.), as they may decrease the effect of Syntocinon.
- Vasopressor agents (medications that produce vasoconstriction), as Syntocinon may potentiate their effect and produce severe arterial hypertension during the postpartum period.
- Prostaglandins or other uterine contraction stimulants, as Syntocinon may potentiate their effect (see section 2).
- Medications that produce prolongation of the QT interval (which cause irregular heartbeats), as Syntocinon may potentiate this effect.
- Caudal anesthesia, when administered during or after caudal block, Syntocinon may potentiate the pressor effect of sympathomimetic vasoconstrictor agents.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Data on a limited number of pregnancies indicate that oxytocin during pregnancy does not show adverse reactions when administered according to therapeutic indications.
Oxytocin may be excreted in small amounts in breast milk. However, it is unlikely to cause harmful effects in the newborn, as oxytocin is rapidly inactivated in the baby's digestive tract.
Driving and using machines
No data are available on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines.
Syntocinon contains ethanol (alcohol) and sodium
This medicine contains 0.6% ethanol (alcohol), which corresponds to an amount of 4.8 mg per ml, equivalent to less than 1 ml of beer or wine. The small amount of alcohol in this medicine has no noticeable effect.
This medicine contains less than 23 mg of sodium (1 mmol) per ml; this is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to use Syntocinon
Oxytocin will always be administered in a hospital setting and under medical control.
Induction of labor or stimulation of uterine contractility
For labor induction, it will always be administered intravenously.
The healthcare professional will control the infusion rate and use an infusion pump or similar equipment (see section "Instructions for correct use of Syntocinon", at the end of this leaflet).
The initial infusion rate is usually set between 1-4 mIU/minute (2-8 drops/minute). It can be gradually increased, at intervals of no less than 20 minutes, until a pattern of contractions similar to those of a normal labor is established, with a maximum recommended rate of 20 mIU/minute (40 drops/minute).
In women at term who have not initiated regular contractions after administering an amount of oxytocin of 5 IU (equivalent to 500 ml of the prepared solution according to the section "Instructions for correct use of Syntocinon"), it is recommended to interrupt labor induction and repeat the next day, starting again from a dose of 1-4 mIU/minute.
The dose must be adjusted at all times to the individual response. To do this, you will be carefully monitored (fetal heart rate, blood pressure, etc.). In case of uterine hyperactivity or fetal distress, the infusion will be suspended immediately.
Prevention of postpartum hemorrhage
The usual dose is 5 IU by intravenous infusion (5 IU diluted in a physiological saline solution) or 5 to 10 IU by intramuscular route after placental expulsion.
Treatment of postpartum hemorrhage
The usual dose is 5 IU by intravenous infusion (5 IU diluted in a physiological saline solution) or 5 to 10 IU by intramuscular route, in severe cases, followed by another intravenous infusion of a solution containing 5-20 IU of oxytocin.
If you use more Syntocinon than you should
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult your doctor or pharmacist or call the Toxicology Information Service. Telephone 915 620 420, indicating the medicine and the amount used.
When signs or symptoms of overdose occur during continuous intravenous administration of Syntocinon, your doctor should immediately interrupt the infusion and administer oxygen to the mother.
In case of water intoxication, it is essential to restrict fluid intake, promote diuresis, correct electrolyte imbalance, and control any convulsions that may occur.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following side effects have been reported. Side effects are classified under frequency headings, the most frequent first, using the following convention: Very common (≥ 1/10); common (≥ 1/100, <1>
Side effects derived from post-marketing experience with Syntocinon have been obtained through spontaneous reports and cases described in the literature. As these side effects are reported voluntarily from an unknown population size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency, therefore, they are classified as unknown.
Table 1: Side effects in the mother
Classification of organs and systems | Side effect |
Blood and lymphatic system disorders Frequency not known: | Disseminated intravascular coagulation |
Immune system disorders Rare: | Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions associated with dyspnea and hypotension; Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid shock |
Metabolism and nutrition disorders Frequency not known: | Water intoxication, hyponatremia |
Nervous system disorders Common: | Headache |
Cardiac disorders Common: Uncommon: Frequency not known: | Tachycardia, bradycardia Arrhythmia Myocardial ischemia, prolongation of the QT interval on the electrocardiogram |
Vascular disorders Frequency not known: | Hypotension |
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders Frequency not known: | Acute pulmonary edema |
Gastrointestinal disorders Common: | Nausea, vomiting |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders Rare: Frequency not known: | Rash Angioedema |
Pregnancy, puerperium, and perinatal disorders Frequency not known: | Uterine hypertonia, tetanic contractions of the uterus, uterine rupture |
General disorders and administration site conditions Frequency not known: | Flushing |
Table 2: Side effects in the fetus/newborn
Classification of organs and systems | Side effect |
Metabolism and nutrition disorders Frequency not known: | Neonatal hyponatremia |
Pregnancy, puerperium, and perinatal disorders Frequency not known: | Fetal distress syndrome, asphyxia, and death |
Reporting of side effects
If you notice any side effects, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Syntocinon
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
- Store in the original package in the refrigerator (between 2 and 8 °C). Do not freeze.
- Store in the original package to protect it from light.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiration date that appears on the package. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Deposit the packages and medicines you no longer need at the SIGRE point in the pharmacy. In case of doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of packages and medicines you no longer need. This way, you will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
Composition of Syntocinon
- The active ingredient is oxytocin. Each ml of solution contains 10 IU of oxytocin.
- The other components (excipients) are ethanol, sodium acetate trihydrate, chlorobutanol, sodium chloride, glacial acetic acid, water for injections.
Appearance of the product and contents of the pack
Transparent glass ampoules containing 1 ml of a clear, sterile, and colorless solution.
Package containing 10 ampoules.
Marketing authorization holder
Alfasigma S.p.A.
Via Ragazzi del ’99, n.5
40133 Bologna. ITALY
Manufacturer:
Alfasigma, S.p.A.
Via Pontina Km 30.400
00071 Pomezia (Rome). ITALY
Local representative:
Alfasigma España, S.L
C/ Aribau 195, 4º
08021 Barcelona. Spain
Date of the last revision of this leaflet:February 2021
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals.
Instructions for correct use of Syntocinon
Prepare the oxytocin solution by aseptically dissolving one 10 IU ampoule in 1,000 ml of physiological saline or 5% glucose. Ensure, by gentle agitation or rotation of the bottle, that the mixture is homogeneous (the solution contains 10 mIU/ml of oxytocin).
Instructions for the correct opening of the ampoule
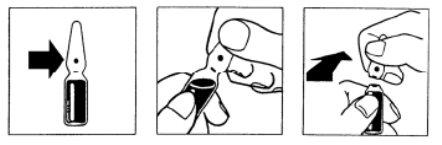
Breakable ampoule. The break line is located below the colored point. Place your thumb above the colored point and break the ampoule by pressing backwards.
“Detailed and updated information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.es/”
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to SYNTOCINON 10 IU/mL Injectable Solution and Perfusion SolutionDosage form: INJECTABLE, 16.7 µg/mlActive substance: oxytocinManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi España, S.A.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 100 microgramsActive substance: carbetocinManufacturer: Gp Pharm S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 100 micrograms/milliliterActive substance: carbetocinManufacturer: Ferring S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for SYNTOCINON 10 IU/mL Injectable Solution and Perfusion Solution
Discuss questions about SYNTOCINON 10 IU/mL Injectable Solution and Perfusion Solution, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions