
NITROPLAST 15 TRANSDERMAL PATCHES

How to use NITROPLAST 15 TRANSDERMAL PATCHES
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Nitroplast 15 mg Transdermal Patches
Nitroglycerin
Read the package leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this package leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the package leaflet
1. What is Nitroplast and what is it used for
2. What you need to know before you use Nitroplast
3. How to use Nitroplast
4. Possible side effects
5. Storage of Nitroplast
6. Contents of the pack and further information
1. What is Nitroplast and what is it used for
Nitroplast is a transdermal patch that contains nitroglycerin and is used to prevent angina pectoris, but not to treat acute attacks.
Nitroglycerin dilates blood vessels and improves heart performance.
Applied to the skin, Nitroplast releases nitroglycerin at a uniform rate throughout the recommended application period.
Nitroplast is indicated for the preventive treatment of angina pectoris, as a single treatment or in combination with other anti-anginal treatments.
2. What you need to know before you use Nitroplast
Do not use Nitroplast
? If you are allergic (hypersensitive) to nitroglycerin, organic nitrates in general, or any of the other components of Nitroplast (listed in section 6).
? If you have very low blood pressure (systolic blood pressure below 90 mmHg).
? In case of acute circulatory failure associated with marked hypotension (shock, collapse).
? If you have diseases associated with increased intracranial pressure.
? If you have heart failure due to valvular obstruction (narrowing of the heart valves) or pericardial inflammation that compresses the heart.
? In cases of severe hypovolemia (decrease in total blood volume).
? In cases of cardiogenic shock (circulatory collapse of cardiac origin), unless a diastolic blood pressure is maintained with adequate measures.
? In cases of cardiac tamponade (acute compression of the heart).
? If you have hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (thickening of the heart that makes circulation difficult).
? If you are taking medications that contain sildenafil, tadalafil, or vardenafil (medications used to treat impotence or pulmonary arterial hypertension).
? Do not use Nitroplast simultaneously with medications that contain riociguat (medication used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension).
Warnings and precautions
? If you have a decrease in cardiac filling pressure, for example, acute myocardial infarction, left ventricular failure. The reduction of systolic blood pressure below 90 mmHg should be avoided.
? If you have orthostatic hypotension (decrease in blood pressure when standing up).
? If you have anemia, consult your doctor, as Nitroplast may not be a suitable treatment for you.
? If you have or have had any lung or heart disease. Patients with angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, or cerebral ischemia may suffer from alterations in the small airways.
? In patients with angina pectoris produced by thickening of the heart (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy), treatment with Nitroplast may worsen it.
? There is a possibility of an increase in the frequency of angina pectoris during the patch-free interval. Your doctor may consider it necessary to use another anti-anginal treatment in addition to Nitroplast.
? There may be a loss of efficacy due to continued treatment with other medications that contain nitrates (tolerance).
? An increase in methemoglobin, an oxidized form of hemoglobin (blood pigment) that causes methemoglobinemia, may occur.
Nitroplast will only be used under strict clinical surveillance and/or hemodynamic monitoring in patients with acute myocardial infarction or congestive heart failure.
Treatment with Nitroplast should not be interrupted abruptly. Your doctor will gradually reduce the dose and increase the administration intervals. If you start another treatment for angina pectoris, during a period of time you may need to use both medications.
Nitroplast does not contain aluminum or other metals, and therefore it is not necessary to remove the patch before a magnetic resonance imaging or maneuvers to restore the normal heart rhythm (cardioversion), as there is no risk of skin burns from having the patch attached.
Children and adolescents
The safety and efficacy in children and adolescents (under 18 years) have not been established.
Using Nitroplast with other medications
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, or have recently used, any other medication, including those purchased without a prescription.
The use of nitrates at the same time as other vasodilating compounds, such as medications for treating hypertension, PDE5 inhibitors, calcium antagonists, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, diuretics, some antidepressants, and major tranquilizers, may excessively lower blood pressure.
Patients being treated with Nitroplast should never (even if the patch has been removed) take PDE5 inhibitors such as those containing sildenafil, tadalafil, or vardenafil (medications used to treat impotence and pulmonary arterial hypertension), as cardiovascular complications that may endanger the patient's life may occur. For more information, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs), except for acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), may reduce the action of Nitroplast.
Administration with acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) may potentiate the action of Nitroplast.
The use of Nitroplast at the same time as riociguat (medication used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension) may cause hypotension.
The use of Nitroplast at the same time as dihydroergotamine (medication used to treat migraine) may increase the amount of dihydroergotamine in the blood. This is important in patients with coronary artery disease, as dihydroergotamine counteracts the action of Nitroplast, causing coronary vasoconstriction.
The simultaneous administration of Nitroplast with amifostine (a medication used to reduce unwanted side effects of some chemotherapies and radiation therapies) and acetylsalicylic acid may lower blood pressure too much.
The simultaneous administration with sapropterin, a cofactor of an enzyme called nitric oxide synthase, may increase the hypotensive effect of Nitroplast.
Due to the development of tolerance to nitroglycerin, the effect of sublingual nitroglycerin may be partially reduced.
Using Nitroplast with food, drinks, and alcohol
The concomitant use of Nitroplast and alcohol may increase the hypotensive effect (decrease in blood pressure) of Nitroplast.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medication.
Pregnancy
In case of pregnancy or suspected pregnancy, the doctor should be informed. Nitroplast should be used with caution during pregnancy, especially in the first three months.
Breastfeeding
If you are breastfeeding, you should inform your doctor, as it will be necessary to decide whether to interrupt breastfeeding or treatment, considering the benefit of breastfeeding for the child and the benefit of treatment for the mother.
Fertility
There are no available data on the effect of nitroglycerin on fertility in humans.
Driving and using machines
Nitroplast may reduce reaction capacity or rarely cause orthostatic hypotension (decrease in blood pressure when standing up) and dizziness (as well as exceptionally syncope after an overdose). Patients who suffer from any of these effects should avoid driving vehicles or using machines.
3. How to use Nitroplast
Follow the administration instructions of Nitroplast indicated by your doctor. Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you have any doubts.
The doctor will establish the appropriate doses, both at the start of treatment and for maintenance, and determine the frequency and duration of treatment.
The patch will be applied daily to the skin for 12 to 16 hours, ensuring a nitrate-free period of 8 to 12 hours.
For the application of Nitroplast, any area of the skin that is not too thick and poorly irrigated can be suitable, as long as it is healthy, clean, relatively wrinkle-free, and hairless. The most recommended areas for application are the front and side of the chest. However, it can also be applied to the forearm, thigh, abdomen, and shoulder Figure 1
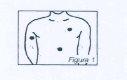
To avoid any skin irritation, Nitroplast should be applied to different areas each day, trying not to use the same area until at least 2-3 days have passed. Nitroplast should not be applied to the distal part of the limbs, skin folds, wide scars, or burned or irritated areas.
Nitroplast does not adhere well to wet or dirty skin, so it is essential to clean and dry the skin before application. Do not use skin care products before placing the patch. Nitroplast retains its function with bathing, showering, or physical exercise.
Each patch is packaged in an individual bag and should not be removed from it until it is ready to be used. The sealed bag can be easily broken through a notch on the edge. Figure 2

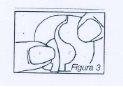
Remove the patch from the bag and hold it with both hands, with the protective film facing up. Then, lower one half of the patch, which opens the S-shaped cut. One half of this film can then be separated. The adhesive surface should not be touched. Figure 3
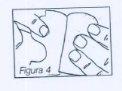
Next, apply the patch to the chosen area and remove the other half of the protective layer. Figure 4
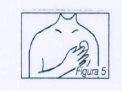
Press the patch with your hand to ensure that the entire adhesive surface adheres firmly to the skin. Figure 5After application, wash your hands thoroughly.
Nitroplast patches should not be cut.
Use in the elderly: No dose adjustment is required in elderly patients.
If you use more Nitroplast than you should
It is unlikely that symptoms of overdose will appear due to the type of formulation of the Nitroplast transdermal patch. If they do appear, the symptoms can be quickly eliminated by removing the patch.
The symptoms are decreased blood pressure (less than or equal to 90 mmHg), paleness, sweating, weak pulse, increased heart rate (tachycardia), postural dizziness, headache (cephalalgia), collapse, syncope with postural dizziness, feeling of weakness (asthenia), nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
In patients being treated with other organic nitrates, cases of methemoglobinemia have been described (since nitrite ions cause methemoglobinemia and cyanosis, with consequent tachypnea, anxiety, loss of consciousness, and heart attack). Although with the transdermal release method it is unlikely, at high doses, an increase in intracranial pressure may occur, leading to cerebral symptoms.
- General procedure:
Interrupt the administration of the medication by removing the patch.
- General procedure in nitrate-related hypotension events:
Place the patient in a horizontal position with the legs elevated, or if necessary, apply a compression bandage to the patient's legs.
Provide oxygen.
Plasma volume expanders (intravenous fluids).
Specific treatment for shock (admit the patient to an intensive care unit).
- Special procedures:
Increase blood pressure if it is too low.
Administration of a vasoconstrictor, e.g., norepinephrine hydrochloride.
Treatment of methemoglobinemia:
Reduction of the treatment of choice with vitamin C, methyl blue, or toluidine blue.
Administration of oxygen (if necessary).
Initiate artificial respiration.
Hemodialysis (if necessary).
Treatment of methemoglobinemia with methyl blue is contraindicated in patients with glucose-6-phosphate or methemoglobin reductase deficiency. For cases where treatment is contraindicated or not effective, a blood transfusion or transfusion of a red blood cell concentrate is recommended.
Resuscitation measures:
In case of respiratory and circulatory arrest, initiate resuscitation measures immediately.
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult the Toxicology Information Service, phone 91 562 04 20.
If you forget to use Nitroplast
Do not use a double dose to make up for forgotten doses. Contact your doctor.
If you interrupt treatment with Nitroplast
If you have any further questions about the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medications, Nitroplast can cause side effects, although not everyone will experience them.
The following side effects have been reported during treatment with Nitroplast:
? Very common: may affectmore than1 in 10 patients: headache.
? Common: may affect up to1 in 10 patients: dizziness (including postural dizziness), somnolence, tachycardia, postural hypotension, feeling of weakness (asthenia).
? Uncommon: may affect up to1 in 100 patients: increase in angina pectoris symptoms, circulatory collapse (sometimes accompanied by bradycardia and syncope), nausea, vomiting, pruritus, skin irritation (itching or burning at the application site, redness, irritation), contact dermatitis (which disappears spontaneously a few hours after removing the patch or with the use of topical corticosteroids), allergic skin reactions (e.g., rash).
? Rare: may affect up to 1 in 10,000 patients: heartburn.
? Frequency not known: cannot be estimated from the available data: palpitations, flushing, hypotension, exfoliative dermatitis, generalized skin rash, increased heart rate.
As with some medications used to treat heart diseases, Nitroplast frequently causes dose-dependent headaches due to the dilation of blood vessels in the brain. These headaches disappear after a few days, even if treatment with Nitroplast continues. If the headache persists during intermittent treatment, it should be treated with mild analgesics. If the headaches persist despite this, your doctor may need to reduce the dose or discontinue treatment with Nitroplast.
Any redness that appears on the skin will normally disappear within a few hours after removing the patch.
You should regularly change the application site to prevent local irritation.
Your doctor may prescribe another treatment simultaneously to prevent a small increase in your heart rate.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medications: https://www.notificaram.es
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Storage of Nitroplast
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not store above 25°C.
Do not use Nitroplast 15 mg after the expiration date stated on the packaging and carton after "EXP". The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Medications should not be disposed of through wastewater or household waste. Deposit the packaging and medications you no longer need at the Sigre Collection Point in your pharmacy. If in doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medications you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Content and Additional Information
Composition of Nitroplast 15 mg Transdermal Patches
The active ingredient is nitroglycerin. One patch contains 56.2 mg of nitroglycerin in a 27 cm2 patch, which releases 15 mg every 24 hours.
The other components are acrylate/vinyl acetate copolymer, polypropylene backing layer, siliconized polyethylene terephthalate film, and ink.
Product Appearance and Container Content
Nitroplast are white translucent, square transdermal patches with rounded edges. Containers with 7 and 30 transdermal patches are available.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder
LACER, S.A. - Boters, 5
08290 Cerdanyola del Vallès
Barcelona – Spain
Manufacturer
Aesica Pharmaceuticals GmbH
Alfred-Nobel Strasse 10
40789 Monheim - Germany
or
LACER, S.A. - Boters, 5
08290 Cerdanyola del Vallès
Barcelona – Spain
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet: June 2017
Detailed and updated information on this medication is available on the website of
the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
- Country of registration
- Average pharmacy price23.14 EUR
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to NITROPLAST 15 TRANSDERMAL PATCHESDosage form: TRANSDERMAL PATCH, 37.4 mg nitroglycerinActive substance: glyceryl trinitrateManufacturer: Merus Labs Luxco Ii S.À.R.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: TRANSDERMAL PATCH, 18.7 mg nitroglycerinActive substance: glyceryl trinitrateManufacturer: Merus Labs Luxco Ii S.À.R.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: TRANSDERMAL PATCH, 31.37 mgActive substance: glyceryl trinitrateManufacturer: Casen Recordati S.L.Prescription required
Online doctors for NITROPLAST 15 TRANSDERMAL PATCHES
Discuss questions about NITROPLAST 15 TRANSDERMAL PATCHES, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions











