ATROVENT MONODOSIS 500 mcg / 2ml SOLUTION FOR NEBULIZER INHALATION

How to use ATROVENT MONODOSIS 500 mcg / 2ml SOLUTION FOR NEBULIZER INHALATION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Atrovent Monodosis 500 micrograms/2 ml solution for inhalation by nebulizer
ipratropium bromide
Read this package leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine, because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this package leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this package leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the package leaflet
- What is Atrovent Monodosis and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you start using Atrovent Monodosis
- How to use Atrovent Monodosis
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Atrovent Monodosis
- Contents of the pack and further information
1. What is Atrovent Monodosis and what is it used for
Atrovent Monodosis belongs to a group of medicines called anticholinergic bronchodilators, which work by relaxing the muscle of the bronchi, making it easier to breathe.
Atrovent Monodosis 500 micrograms/2 ml solution for inhalation by nebulizer is a medicine used to treat bronchospasm associated with chronic obstructive diseases in adults and children over 12 years of age.
Atrovent Monodosis may be administered with beta-adrenergics (other bronchodilator medicines, such as salbutamol) in the treatment of acute bronchospasm that causes reversible airway obstruction, in cases where treatment with a beta-adrenergic medicine does not provide sufficient bronchodilation.
2. What you need to know before you start using Atrovent Monodosis
Do not use Atrovent Monodosis
- If you are allergic (hypersensitive) to ipratropium bromide, to substances similar to ipratropium such as atropine or its derivatives, or to any of the other ingredients of Atrovent Monodosis.
- In acute episodes of bronchospasm (breathing difficulties) where a rapid response is required.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before starting to use Atrovent Monodosis:
-If you have a predisposition to narrow-angle glaucoma (increased pressure inside the eye), prostatic hyperplasia (enlargement of the prostate) or urinary flow obstruction (difficulty urinating).
-There have been isolated cases of eye complications, such as mydriasis (pupil dilation), narrow-angle glaucoma (increased pressure inside the eye), and eye pain when ipratropium bromide, alone or in combination with a beta-2 adrenergic agonist (medicines that dilate bronchial muscles, such as salbutamol), has penetrated the eyes due to improper application.
-Eye pain or discomfort, blurred vision, halos (diffuse lights), or colored images associated with eye redness due to conjunctival congestion and corneal edema (swelling) may be signs of increased intraocular pressure (narrow-angle glaucoma). If any combination of these symptoms appears, you should consult your doctor immediately to initiate treatment with a miotic eye drop (which causes pupil contraction and decreases intraocular pressure).
-You should avoid the product coming into contact with the eyes during nebulization, especially in patients who have a predisposition to increased intraocular pressure, so it is recommended to use a mouthpiece or face mask.
-Patients with cystic fibrosis (a disease that alters the secretions of mucous and sweat glands, affecting several organs) may be more prone to gastrointestinal motility disorders.
-In exceptional cases, immediate hypersensitivity reactions (rapid allergic reactions) may occur after administration of Atrovent Monodosis, such as urticaria, angioedema (sudden swelling of the skin or mucous membranes), skin rash, bronchospasm (contraction of bronchial muscles that makes breathing difficult), and oropharyngeal edema (swelling of the mouth and pharynx).
-As with other drugs administered by inhalation, Atrovent Monodosis may cause paradoxical bronchospasm, which can be life-threatening. If this occurs, treatment should be discontinued immediately and the doctor informed to replace with an alternative treatment.
Other medicines and Atrovent Monodosis
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
It is not recommended to administer Atrovent Monodosis simultaneously for a long period with other anticholinergic drugs.
Beta-adrenergics (e.g., salbutamol) and xanthine derivatives (e.g., theophylline) are other bronchodilator medicines and may enhance the bronchodilator effect. Atrovent Monodosis may increase the anticholinergic effects of other medicines.
Atrovent Monodosis can be administered with other medicines commonly used in the treatment of reversible airway obstruction, including beta-adrenergic medicines (e.g., salbutamol), methylxanthines (e.g., theophylline), steroids, and sodium cromoglycate, without the appearance of interactions that require dose adjustment.
The simultaneous administration of nebulized ipratropium bromide and beta-mimetics may increase the risk of acute glaucoma in patients with a history of narrow-angle glaucoma (increased intraocular pressure).
The inhalation solutions of Atrovent Monodosis and sodium cromoglycate that contain benzalkonium chloride as a preservative should not be administered simultaneously in the same nebulizer, due to the risk of precipitation.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Although preclinical studies have not shown any risk, the safety of this medicine during pregnancy has not been established. Therefore, the usual precautions in the use of medicines during this period should be observed, especially during the first three months.
It is not known whether ipratropium bromide can pass into breast milk. However, it is unlikely to be ingested by the infant in significant amounts, especially since the preparation is administered by inhalation. Nevertheless, it should be administered with caution to breastfeeding women.
Driving and using machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been conducted. However, it is warned that side effects such as dizziness, eye difficulties in focusing, pupil dilation, and blurred vision may occur during treatment with Atrovent. Therefore, caution is recommended when driving and using machines.
3. How to use Atrovent Monodosis
Follow the instructions for administration of this medicine exactly as indicated by your doctor or pharmacist. If you are in doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
Remember to use your medicine.
Your doctor will determine the duration of treatment.
If you think the effect of Atrovent Monodosis is too strong or too weak, tell your doctor or pharmacist.
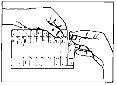
The solution of Atrovent Monodosis can be inhaled (inhaled) using devices called ultrasonic, electric, manual (e.g., Bird, De Vilbiss, Pari) nebulizers, or with assisted breathing at intermittent positive pressure. If there is a wall oxygen supply, the solution should be administered with a flow of 6-8 liters per minute.
It is recommended that the particle size of the nebulized solution be between 1 and 10 microns, although approximately 50% of the total aerosol mass should be contained in particles less than 5 microns.
If necessary, the solution can be diluted with physiological saline.
Guidelines for the use of monodose vials
Monodose vials should only be used for inhalation with suitable nebulizer devices and should not be administered orally.
|
Dilute with saline solution to a final volume of 2-4 ml.
|
Since the monodose vials do not contain preservatives, it is important that their contents be used immediately after opening the vial to avoid contamination. Partially used, opened, or damaged monodose vials should be discarded.
The administration of Atrovent Monodosis solution should be adapted to the individual needs of each patient; patients should be under medical supervision during treatment. It is recommended not to exceed the recommended daily dose for both acute and maintenance treatment. The recommended doses are:
Adults and children over 12 years of age
Maintenance treatment
1 monodose vial, 3-4 times a day.
Acute attacks
In cases where only a beta-adrenergic medicine is used, it may not provide sufficient bronchodilation. In these cases, Atrovent Monodosis can be administered in combination with an inhaled beta-adrenergic (e.g., salbutamol), whose dose will be established by the doctor.
The dose of Atrovent Monodosis, in this case, is one monodose vial; repeated doses can be administered until the patient stabilizes.
As a general rule, the recommended daily dose should not be exceeded during treatment. Daily doses of more than 2 mg (more than 4 monodose vials) should only be administered under medical supervision.
You should consult your doctor whenever you do not achieve significant improvement or your condition worsens, in order to determine a new treatment. In case of acute dyspnea or rapidly worsening dyspnea (breathing difficulties), you should consult your doctor immediately.
If you use more Atrovent Monodosis than you should
No specific manifestations of overdose have been described. Due to the wide therapeutic margin of Atrovent Monodosis and the inhalatory administration of the preparation, it is not expected to appear serious anticholinergic symptoms.
In case of minor anticholinergic symptoms such as dry mouth, visual accommodation disorders (eye problems focusing), and tachycardia (increased heart rate), the treatment to be followed should be to alleviate the symptoms.
If you have used more Atrovent Monodosis than you should, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or call the Toxicology Information Service, phone 91 562 04 20, indicating the medicine and the amount ingested.
If you forget to use Atrovent Monodosis
Do not use a double dose to make up for forgotten doses.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Frequent side effects (occurring in at least 1 in 100 patients) are headache (cephalalgia), dizziness, cough, throat irritation, nausea, dry mouth, gastrointestinal motility disorders (e.g., change in bowel habits, gastroesophageal reflux, dyspepsia (indigestion)).
Uncommon side effects (occurring in at least 1 in 1,000 patients) are
hypersensitivity, anaphylactic reaction (severe allergic reaction), blurred vision, mydriasis (pupil dilation), increased intraocular pressure, halos (diffuse lights), or colored images associated with eye redness (glaucoma), eye pain, halos (diffuse lights), eye redness, corneal edema (swelling of the cornea), palpitations, supraventricular tachycardia, constipation, diarrhea, vomiting, stomatitis (inflammation of the mouth), oral edema (swelling of the mouth), rash, pruritus (itching), angioedema (swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue, or throat that can cause difficulty swallowing or breathing), and urinary retention.
Rare side effects (occurring in at least 1 in 10,000 patients) are bronchospasm (chest tightness, wheezing, or shortness of breath), paradoxical bronchospasm (narrowing of the bronchial walls due to inhalation itself), laryngeal contraction, pharyngeal edema (swelling of the throat), throat dryness, visual accommodation disorder (difficulty focusing), urticaria, increased heart rate, and atrial fibrillation.
Very rare side effects (occurring in less than 1 in 10,000 patients) are tremors, metallic or unpleasant taste, nasal congestion, insomnia, unusual fatigue or weakness, and hypotension.
If you experience any side effect that is severe or if you notice any side effect not mentioned in this package leaflet, tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this package leaflet. You can also report side effects directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Atrovent Monodosis
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date is the last day of the month indicated.
Do not store above 30°C. Store in the original packaging.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Return the vials and medicines you no longer need to the pharmacy's SIGRE collection point. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the vials and medicines you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and further information
Composition of Atrovent Monodosis
- The active substance is ipratropium bromide. Each 2 ml monodose vial contains 522 micrograms of ipratropium bromide monohydrate (equivalent to 500 micrograms of anhydrous ipratropium bromide).
- The other ingredients are sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid, and purified water.
Appearance and packaging of the product
Atrovent Monodosis 500 micrograms/2 ml is a solution for inhalation by nebulizer presented in boxes of 20 monodose vials with 2 ml of solution for inhalation by nebulizer and in a clinical pack with 100 monodose vials of 2 ml of solution for inhalation by nebulizer.
Marketing authorization holder
Boehringer Ingelheim España, S.A.
Prat de la Riba, 50
08174 Sant Cugat del Vallès (Barcelona)
Spain
Manufacturer
Laboratoire Unither
Zone Industrialle de Longpré
10 rue Andre Durouchez
80084 AMIENS Cedex 2
France
This package leaflet was approved in April 2019
Detailed and updated information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to ATROVENT MONODOSIS 500 mcg / 2ml SOLUTION FOR NEBULIZER INHALATIONDosage form: PULMONARY INHALATION, 0.0040 g/aerosolActive substance: ipratropium bromideManufacturer: Laboratorio Aldo Union S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: PULMONARY INHALATION, 20 µgActive substance: ipratropium bromideManufacturer: Boehringer Ingelheim Espana S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: PULMONARY INHALATION, 250 µgActive substance: ipratropium bromideManufacturer: Boehringer Ingelheim Espana S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for ATROVENT MONODOSIS 500 mcg / 2ml SOLUTION FOR NEBULIZER INHALATION
Discuss questions about ATROVENT MONODOSIS 500 mcg / 2ml SOLUTION FOR NEBULIZER INHALATION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions