
Sabumalin

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Sabumalin

How to use Sabumalin
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
Sabumalin, 100 micrograms/dose, inhalation aerosol, suspension
Salbutamol
Please read the contents of the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Please keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if necessary.
- In case of any doubts, please consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Sabumalin and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Sabumalin
- 3. How to use Sabumalin
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Sabumalin
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Sabumalin and what is it used for
Sabumalin is used to treat breathing difficulties caused by the following diseases:
asthma
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including:
- chronic bronchitis
- emphysema.
Additionally, Sabumalin is used to prevent the onset of symptoms of asthmacaused by:
physical exertion or
allergens, such as house dust, pollen, cat hair, dog hair, and cigarette smoke.
Sabumalin expands the airways, making it easier to breathe. Sabumalin should be used to relieve symptoms rather than for systematic treatment.
Sabumalin is indicated for adults, adolescents, and children aged 4 to 11 years.
2. Important information before using Sabumalin
When not to use Sabumalin:
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to use Sabumalin, the patient should discuss with their doctor if they have any of the following conditions:
heart disease, such as irregular or rapid heartbeat or angina pectoris in their medical history
severe and untreated high blood pressure
hyperthyroidism
low potassium levels in the blood
aneurysm (aortic aneurysm)
diabetes (at the beginning of treatment with Sabumalin, it is recommended to additionally monitor blood glucose levels)
adrenal gland tumor (the adrenal glands are two glands located above the kidneys).
Sabumalin and other medicines
The patient should inform their doctor or pharmacist about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take.
The following medicines and Sabumalin may interact with each other:
medicines that affect the heart and blood vessels, which can narrow the airways and contain active substances with names ending in "-ol", such as propranolol (beta-adrenergic blockers).
They can cause bronchospasm.
some medicines used to treat depression:
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors (e.g., moclobemide)
- tricyclic antidepressants, such as amitriptyline anesthetics(medicines that cause partial or complete loss of sensation), such as halothane medicines used to treat heart rhythm disorders, such as digoxin xanthine derivatives(used to facilitate breathing), such as theophylline corticosteroids(a group of hormones), such as cortisone diuretics, such as furosemide
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Experience with the use of the medicine during pregnancy is limited, but if asthma is not treated during pregnancy, it poses a risk to the unborn child. Therefore, Sabumalin can be used during pregnancy only if the doctor considers it absolutely necessary.
The patient should not change the dose on their own, but always use the medicine as recommended by the doctor.
It is not known whether salbutamol passes into breast milk. Therefore, Sabumalin can be used during breastfeeding only if the doctor considers it absolutely necessary.
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
No studies have been conducted on the effect of the medicine on the ability to drive and use machines. Therefore, the patient should not engage in these activities before ensuring how the medicine affects their body.
Sabumalin contains ethanol
This medicine contains 0.72 mg of alcohol (ethanol) per dose, which is equivalent to 2.1% w/w. The amount of alcohol in the dose of this medicine is equivalent to less than 1 ml of beer or 1 ml of wine.
The small amount of alcohol in this medicine will not cause noticeable effects.
3. How to use Sabumalin
This medicine should always be used as recommended by the doctor. In case of doubts, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
Sabumalin should be used as needed, and not regularly.
If the patient's asthma is active (e.g., frequent symptoms or exacerbations, such as shortness of breath that interferes with speaking, eating, or sleeping, coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, or limited physical activity), they should immediately inform their doctor, who may start treatment or increase the dose of a medicine that helps control asthma symptoms, such as an inhaled corticosteroid.
If the patient thinks the medicine is not working as well as usual, they should inform their doctor as soon as possible (e.g., the patient needs larger doses to relieve breathing problems or asthma symptoms do not improve for at least 3 hours after using the inhaler), because asthma may worsen and another medicine may be needed.
If the patient uses Sabumalin more than twice a week to relieve asthma symptoms, excluding preventive use before physical exertion, it means that asthma is poorly controlled and the risk of severe asthma attacks (exacerbations) may increase, which can cause serious complications and be life-threatening.
The patient should contact their doctor as soon as possible to verify their asthma treatment.
Adults and adolescents aged 12 years and older
Relieving attacks:
1-2 inhalations, as needed.
Preventing asthma symptoms caused by exercise or allergens:
2 inhalations 10-15 minutes before exposure to the triggering factor.
Maximum dose: 8 inhalations per day.
Children aged 4 to 11 years
Relieving attacks:
1 inhalation, as needed. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 2 inhalations.
Preventing asthma symptoms caused by exercise or allergens:
1 inhalation or, if necessary, 2 inhalations 10-15 minutes before exposure to the triggering factor.
Maximum dose: 8 inhalations per day.
Children under 4 years of age
The effect of the medicine has not been studied in children of this age group, so a dose cannot be determined for them.
The patient should contact their doctor if the treatment is not effective enough or if they need more doses per day than usual. The patient should never increase the dose of the medicine or change the time of its use without the doctor's consent.
Checking the inhaler before use
If a new inhaler is being used or the previous inhaler has not been used for at least 7 days, the patient should check its operation. To do this, they should remove the protective cap, shake the inhaler, and spray the medicine twice into the air.
Method of use
Inhalations should be performed while sitting or standing, if possible.
- 1. Remove the protective cap. Check if the outer and inner parts of the mouthpiece are clean.
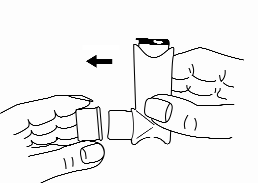
- 2. Shake the inhaler for a few seconds before use.
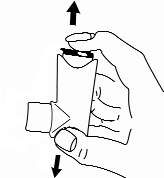
- 3. Holding the inhaler upright with the canister facing upwards, place the thumb on the body of the container below the mouthpiece. Perform a slow and complete exhalation, but do not exhale into the mouthpiece.
- 4. Place the mouthpiece in the mouth between the teeth and seal it with the lips (do not bite).
- 5. Immediately after starting to inhale through the mouth, press the inhaler canister to release the dose. Continue with a slow and complete inhalation.
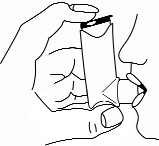
- 6. Hold the breath for 5-10 seconds. Remove the inhaler from the mouth and release the finger from the canister.
- 7. If another inhalation of the medicine is necessary, hold the inhaler in an upright position and wait for about half a minute, then repeat the steps described in points 2 to 6.
- 8. After use, always replace the protective cap on the mouthpiece to protect it from dust and contamination. The cap should be pressed firmly to ensure a tight seal.
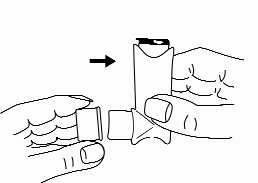
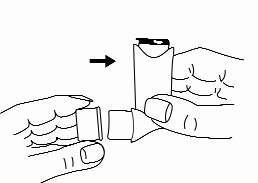
Some people have difficulty releasing the dose of the medicine immediately after starting to inhale. In such cases, as well as for children, a spacer (e.g., Vortex or AeroChamber) can be used. To learn how to use the spacer, the patient should read the leaflet provided with it.
Cleaning
To prevent the inhaler from becoming blocked or if it becomes blocked, it should be cleaned according to the following instructions. This should be done at least once a week.
It is best to clean the inhaler just before going to bed.
- 1. Remove the metal container from the plastic casing and remove the mouthpiece cap.
- 2. Rinse the plastic casing and mouthpiece cap in warm water. If there is a buildup of medicine around the mouthpiece, do not try to clear it with a sharp object, such as a pin. A mild detergent can be used. Before drying, rinse thoroughly with clean water. Do not put the metal container in water.
- 3. Leave the plastic casing and mouthpiece cap to dry in a warm place. Avoid excessive heat.
- 4. Replace the casing and mouthpiece cap.
If the inhaler is blocked and needs to be used immediately, the following steps can be taken:
- 1. Hold the inhaler upright with the canister facing upwards. Turn the metal container clockwise inside the plastic casing for one full turn.
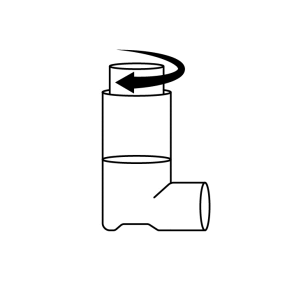
- 2. Remove the metal container from the plastic casing of the inhaler.
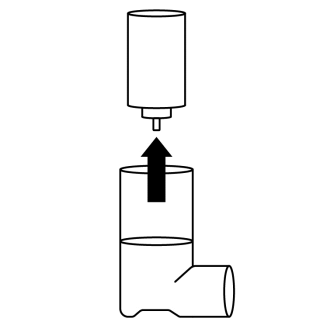
- 3. Hold the bottom of the container facing upwards. With two fingers of the other hand, gently pull the small white plastic stem downwards carefully. Do not use any tools, such as tweezers.
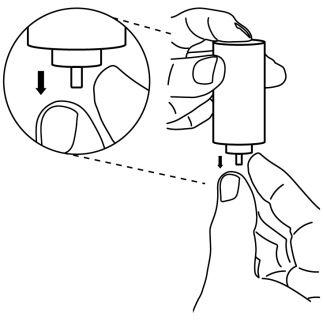
- 4. Replace the container in the plastic casing.
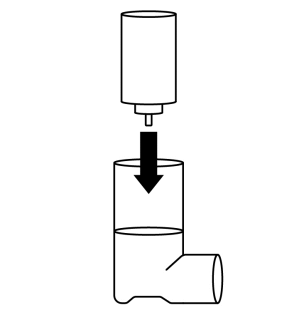
Contents of the inhaler
The patient should shake the inhaler to check the amount of medicine left. The patient should not use Sabumalin if they do not see the liquid in the inhaler when shaking it.
Use in low temperatures
If the inhaler has been stored at a temperature below 0°C, the patient should warm it in their hands for 2 minutes, shake it, and spray the medicine twice into the air before use.
Using a higher dose of Sabumalin than recommended
In such cases, the patient should always contact their doctor or hospital.
Typical symptoms of overdose are:
tremors
headache
rapid heartbeat
nausea or vomiting
inability to sit still
irritability, restlessness
seizures
drowsiness
In case of any further doubts about the use of this medicine, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Sabumalin can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If any of the following very rare symptoms occur, the patient should stop using Sabumalin and contact their doctor immediately:
symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as:
- swelling of the face, tongue, or throat
- difficulty swallowing
- symptoms similar to hives
- difficulty breathing, worsening of breathing difficulties immediately after taking Sabumalin, although it relieves symptoms. This may indicate that the disease has worsened and another treatment should be used quickly.
The patient should contact their doctor as soon as possibleif:
they experience chest pain (a symptom of angina pectoris) while using Sabumalin. The patient should not stop using the medicine without the doctor's advice. The frequency of this side effect is not known.
Side effects may occur with the following frequency:
Common (may occur in less than 1 in 10 people):
tremors
rapid heartbeat
headache
muscle cramps
Uncommon (may occur in less than 1 in 100 people):
rapid heartbeat
irritation of the mouth and throat
Rare (may occur in less than 1 in 1,000 people):
low potassium levels in the blood
sudden flushing of the skin (especially the face)
Very rare (may occur in less than 1 in 10,000 people):
low blood pressure
collapse
increased activity
sleep disturbances
irregular heartbeat
itching rash
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data):
lactic acidosis (a condition in which the body produces too much lactic acid)
Reporting side effects
If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety, Ministry of Health: Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw,
phone: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309, e-mail: [email protected]
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Sabumalin
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not store above 30°C.
Store the inhaler in a lying or inverted position, with the mouthpiece facing downwards.
The container contains a pressurized liquid. Do not expose to temperatures above 50°C, even for a short time. Protect from high temperatures, direct sunlight, and frost! Do not puncture or burn the container, even if it is empty.
Do not use Sabumalin after the expiry date stated on the label and carton after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Sabumalin contains
The active substance of the medicine is salbutamol.
Each dose contains 100 micrograms of salbutamol (as sulfate).
Each delivered dose through the mouthpiece contains 90 micrograms of salbutamol (as sulfate).
The other ingredients are: norflurane (HFA 134a), anhydrous ethanol, and oleic acid.
What Sabumalin looks like and what the pack contains
The medicine is a white suspension in an aluminum container with a metering valve and a polypropylene mouthpiece.
Pack sizes:
200 doses (equivalent to 8.5 g of inhalation aerosol, suspension).
2 x 200 doses (equivalent to 2 x 8.5 g of inhalation aerosol, suspension).
3 x 200 doses (equivalent to 3 x 8.5 g of inhalation aerosol, suspension).
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder:
Sandoz GmbH
Biochemiestrasse 10
6250 Kundl, Austria
Manufacturer:
AEROPHARM GmbH
Francois-Mitterrand-Allee 1
07407 Rudolstadt, Germany
To obtain more detailed information about the medicine and its names in other European Economic Area countries, please contact:
Sandoz Polska Sp. z o.o.
ul. Domaniewska 50 C
02-672 Warsaw
phone: +48 22 209 7000
Date of last revision of the leaflet:05/2024
{Logo of the marketing authorization holder}
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterAeropharm GmbH
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to SabumalinDosage form: Aerosol, 100 mcg/dose inh.Active substance: salbutamolManufacturer: Laboratorio Aldo-Union S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 100 mcg/doseActive substance: salbutamolManufacturer: Orion CorporationPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 200 mcg/doseActive substance: salbutamolManufacturer: Orion CorporationPrescription required
Alternatives to Sabumalin in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Sabumalin in Spain
Alternative to Sabumalin in Ukraine
Online doctors for Sabumalin
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Sabumalin – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














