
Immunate 500 Iu Fviii/375 Iu Vvf

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Immunate 500 Iu Fviii/375 Iu Vvf

How to use Immunate 500 Iu Fviii/375 Iu Vvf
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF Powder and Solvent for Solution for Injection
for injection
human coagulation factor VIII / human von Willebrand factor
Read the package leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this package leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Package Leaflet
- 1. What is Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF
- 3. How to use Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF and what is it used for
What is Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF
Immunate is a complex of coagulation factor VIII / von Willebrand factor, produced from human plasma. The coagulation factor VIII contained in Immunate replaces the missing or malfunctioning factor VIII in hemophilia A. Hemophilia A is a sex-linked, inherited bleeding disorder caused by a decrease in factor VIII levels. This leads to severe bleeding into joints, muscles, and internal organs, occurring spontaneously or as a result of accidental injuries or surgical procedures. Administration of Immunate temporarily supplements the deficiency of factor VIII and reduces the tendency to bleed. In addition to its action as a protective protein for factor VIII, von Willebrand factor (VWF) mediates the process of platelet adhesion at the site of vascular injury and plays a role in platelet aggregation.
What is Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF used for
Immunate is used for the treatment and prevention of bleeding in congenital (hemophilia A) or acquired factor VIII deficiency. Immunate is also used in the treatment of bleeding in patients with von Willebrand disease with factor VIII deficiency, if no specific effective product for von Willebrand disease is available and when treatment with desmopressin (DDAVP) is ineffective or contraindicated.
2. Important information before using Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF
When not to use Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF
Warnings and precautions
In case of allergic reactions:
- There is a small probability of an anaphylactic reaction (severe allergic reaction) to Immunate. The patient should be familiar with the early symptoms of allergic reactions, such as sudden facial flushing, rash, hives, itching, swelling of the lips, eyelids, and tongue, difficulty breathing, wheezing, chest pain, feeling of compression in the chest, general malaise, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, and low blood pressure. These symptoms may be early signs of anaphylactic shock, which can also include severe dizziness, loss of consciousness, and severe breathing difficulties.
- In case of any of these symptoms, the injection/infusion should be stopped immediately and a doctor should be consulted. Severe symptoms require immediate treatment as in emergency cases.
When monitoring is required:
- The doctor may request tests to ensure that the currently used dose is sufficient to achieve and maintain adequate levels of factor VIII and von Willebrand factor.
If bleeding persists:
- The formation of inhibitors (antibodies) is a known complication that can occur during treatment with all factor VIII products. These inhibitors, especially at high levels, disrupt proper treatment, and the patient will be closely monitored for the production of these inhibitors. If the patient's bleeding is not properly controlled with Immunate, the doctor should be informed immediately. Patients with von Willebrand disease, especially type 3, may produce neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) against von Willebrand factor. The doctor may order tests to confirm their presence. Inhibitors against von Willebrand factor are antibodies in the blood that block the administered von Willebrand factor. As a result, von Willebrand factor is less effective in controlling bleeding. For products manufactured from human blood or plasma, appropriate preventive measures are taken to prevent infection transmission to patients. These include careful selection of blood and plasma donors to ensure that individuals at risk of infection transmission are excluded, testing of each donated blood unit and plasma pool for viruses/infection, and inclusion of procedures in the blood or plasma processing that inactivate or remove viruses. Despite these measures, when administering products derived from human blood or plasma, it is not possible to completely exclude the possibility of infection transmission. This also applies to unknown or newly discovered viruses and other types of infections.
Measures used are considered effective against enveloped viruses, such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B and C, and non-enveloped hepatitis A virus. The measures used may have limited effectiveness against non-enveloped viruses, such as parvovirus B19. Parvovirus B19 infection can have serious consequences for pregnant women (fetal infection) and patients with immune deficiencies or certain types of anemia (e.g., congenital spherocytosis or hemolytic anemia). In the case of regular or repeated administration of factor VIII products derived from human plasma, the doctor may recommend vaccinations against hepatitis A and B. It is particularly recommended that when administering Immunate to a patient, the product name and batch number should be recorded to maintain a record of the batch used. Immunate contains blood group isoagglutinins (anti-A and anti-B). In patients with blood group A, B, or AB, hemolysis may occur due to repeated administration in a short period or administration of very large doses.
Children
The product should be used with caution in children under 6 years of age who have been limitedly exposed to factor VIII products, as clinical data on this patient group are limited.
Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are taking, have recently taken, or might take. No interactions with other medicines have been reported for Immunate. Immunate should not be mixed with other medicines or solvents before administration, except for the supplied water for injection, as they may negatively affect the product's efficacy and safety. It is recommended to flush the established venous access with an appropriate solution, e.g., saline solution, before and after administering Immunate.
Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF with food and drink
There are no special recommendations regarding the administration of Immunate with respect to meals.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Since hemophilia A is rare in women, there is limited experience with the use of Immunate during pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility. Immunate should be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding only if justified. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
There is no information on the effect of Immunate on the ability to drive and use machines.
Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF contains sodium
The medicine contains 9.8 mg of sodium (the main component of common salt) per vial. This corresponds to 0.5% of the maximum recommended sodium intake in the diet for adults.
3. How to use Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF
Treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor experienced in the treatment of hemostasis disorders.
This medicine should always be used as directed by your doctor. If you are unsure, consult your doctor.
Dosing for prophylaxis of bleeding
If Immunate is used for prophylaxis of bleeding, the dose will be calculated by the doctor, taking into account the individual needs of the patient. The usual dose is between 20 and 40 IU of factor VIII per kilogram of body weight, administered at intervals of 2-3 days. However, in some cases, especially in younger patients, shorter intervals between doses or higher doses may be necessary. If you feel that the effect of Immunate is too weak, consult your doctor.
Dosing for treatment of bleeding
If Immunate is used for the treatment of bleeding, the dose will be calculated by the doctor, taking into account the individual needs of the patient. If you feel that the effect of Immunate is too weak, consult your doctor.
Monitoring of treatment by the doctor
To ensure that factor VIII levels are adequate, the doctor will perform appropriate laboratory tests. This is especially important for major surgical procedures.
Dosing in von Willebrand disease
The doctor will control bleeding according to the guidelines for hemophilia A.
Route and/or method of administration
Immunate is administered intravenously after preparation of the solution using the supplied solvent. Follow the doctor's instructions. Only use the infusion set provided in the package, as adsorption of human coagulation factor VIII to the inner surfaces of some infusion sets may lead to treatment failure. Immunate should be dissolved immediately before administration. The solution should be used immediately, as it does not contain preservatives.
Dissolving the powder to prepare the solution for injection Use aseptic technique!
- 1. Warm the unopened vial containing the solvent (water for injection) to room temperature (up to 37°C).
- 2. Remove the protective caps from the vials of powder and solvent (Fig. A) and clean the rubber stoppers of both vials.
- 3. Place the tapered end of the transfer device on the solvent vial and press (Fig. B).
- 4. Remove the protective cover from the other end of the transfer device, taking care not to touch the exposed end.
- 5. Invert the transfer device with the attached solvent vial over the powder vial and insert the free needle through the rubber stopper of the powder vial (Fig. C). The solvent will be drawn into the powder vial by vacuum.
- 6. After about one minute, separate the vials by removing the transfer device with the attached solvent vial from the powder vial (Fig. D). As dissolution is easy, the vial with the concentrate should be handled very gently or not at all. DO NOT SHAKE THE CONTENTS OF THE VIAL. DO NOT INVERT THE POWDER VIAL UNTIL IT IS READY FOR TRANSFER.
- 7. After dissolution, before administration, inspect the prepared solution for the presence of insoluble particles and color change. The solution should be clear or slightly opalescent. However, even if the dissolution procedure is followed carefully, a small amount of fine particles may sometimes be observed. The provided filter set will remove particles, and the labeled potency of the product will not be reduced. A solution that is cloudy or contains sediment should be discarded. Do not refrigerate the prepared solution.
Administration Use aseptic technique!
Use the provided filter set to prevent the administration of rubber particles from the stopper with the product (risk of microembolism). To draw up the dissolved product, attach the filter set to the supplied syringe and insert it through the rubber stopper (Fig. E). For a moment, detach the syringe from the filter set. Air will enter the powder vial, and any foam inside will settle. Through the filter set (Fig. F), draw the solution into the syringe. Detach the syringe from the filter set and slowly inject the solution intravenously (maximum injection rate: 2 ml per minute) using the supplied infusion set - butterfly needle (or the supplied single-use needle).
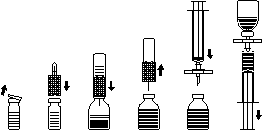
Fig. A
Fig. B
Fig. C
Fig. D
Fig. E
Fig. F
Any unused medicinal product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements. Administration of Immunate should be documented, and the batch number recorded. A detachable label is provided with each vial, which should be attached to the patient's documentation.
Frequency of administration
The doctor will inform you how often and at what intervals you should take Immunate. This will be determined based on the effectiveness of the treatment for each individual patient.
Duration of treatment
Replacement therapy with Immunate is usually used for life.
Overdose of Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF
- No symptoms of overdose of factor VIII have been reported. In case of doubt, consult a doctor.
- Thromboembolic events may occur.
- Hemolysis may occur in patients with blood group A, B, or AB.
Missed dose of Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF
- Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
- Take the next regular dose and continue treatment at the intervals recommended by your doctor.
Stopping Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF
Do not stop using Immunate without consulting your doctor. If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Immunate can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Serious side effects that may occur after using factor VIII products derived from human plasma
factor VIII products
Rarely, allergic reactions have been observed, which in some cases have led to severe and life-threatening reactions (anaphylaxis). Therefore, you should be familiar with the early symptoms of allergic reactions, such as sudden facial flushing, rash, hives, itching, swelling of the lips and tongue, difficulty breathing, wheezing, chest pain, feeling of compression in the chest, general malaise, dizziness, rapid heartbeat, and low blood pressure. These symptoms may be early signs of anaphylactic shock, which can also include severe dizziness, loss of consciousness, and severe breathing difficulties. In case of any allergic reaction or anaphylaxis, the injection/infusion should be stopped immediately, and a doctor should be consulted. Severe symptoms require immediate treatment as in emergency cases. In children not previously treated with factor VIII products, inhibitory antibodies (see section 2) may develop very frequently (more than 1 in 10 patients). However, in patients who have been previously treated with factor VIII (treatment for more than 150 days), the risk is not very common (less than 1 in 100 patients). If this happens, the patient's medicines may stop working properly, and the patient may experience persistent bleeding. If this happens, you should contact your doctor immediately. The formation of neutralizing antibodies against von Willebrand factor is a known complication of treatment in patients with von Willebrand disease. If neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) develop, this may result in an insufficient clinical response to treatment (bleeding is not controlled with the proper dose) or as an allergic reaction. In such cases, it is recommended to contact a specialized hemophilia treatment center. After administration of large doses, hemolysis may occur in patients with blood group A, B, or AB.
Side effects reported after using Immunate Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- inhibitor of factor VIII (in children who have not been previously treated with factor VIII products). Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- hypersensitivity;
- inhibitor of factor VIII [in patients who have been previously treated with factor VIII (treatment for more than 150 days)]. Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data)
- coagulation disorders (inability to form clots);
- anxiety;
- paresthesia (tingling or prickling sensation);
- dizziness;
- headache;
- conjunctivitis;
- tachycardia (rapid heartbeat);
- palpitations;
- hypotension (low blood pressure);
- flushing;
- pallor (pale appearance);
- dyspnea (breathing difficulties);
- cough;
- vomiting;
- nausea;
- urticaria (hives);
- rash;
- pruritus (itching);
- erythema (redness of the skin);
- hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating);
- neurodermatitis (itchy or rough skin);
- myalgia (muscle pain);
- chest pain;
- discomfort in the chest;
- edema (fluid retention);
- fever;
- chills;
- burning and stinging at the injection site (injection site reactions);
- pain.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products Al. Jerozolimskie 181 C 02-222 Warsaw Tel.: + 48 22 49 21 301 Fax: + 48 22 49 21 309 Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF
Keep out of the sight and reach of children. Store and transport in a cool place (2°C – 8°C). Do not freeze. Store in the original package to protect from light. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the label and carton after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated. Within the shelf-life, the product can be stored at room temperature (up to 25°C) for a single period not exceeding 6 months. Note the start date of storage at room temperature on the package. After storage at room temperature, Immunate should not be refrigerated again but used immediately or discarded. Do not use this medicine if the prepared solution is cloudy or contains sediment. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF contains
Powder:
- The active substances are human coagulation factor VIII and human von Willebrand factor. Each vial contains nominally 500 IU of factor VIII and 375 IU of von Willebrand factor derived from human plasma. After dissolution in the supplied solvent, the product contains approximately 100 IU/ml of factor VIII from human plasma and 75 IU/ml of von Willebrand factor from human plasma.
- The other ingredients are human albumin, glycine, sodium chloride, sodium citrate, lysine hydrochloride, and calcium chloride.
Solvent:
- Water for injection
What Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF looks like and contents of the pack
Powder and solvent for solution for injection. White or pale yellow powder or brittle, crystalline mass. The powder and solvent are available in single-dose glass vials, Ph. Eur. (powder: type II glass; solvent: type I glass), closed with butyl rubber stoppers, Ph. Eur. Each pack contains: 1 vial of Immunate 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF 1 vial of water for injection (5 ml) 1 transfer device or filter set 1 single-use syringe (5 ml) 1 single-use needle 1 infusion set (butterfly needle). Pack size: 1 x 500 IU FVIII/ 375 IU VWF
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Takeda Pharma Sp. z o.o. ul. Prosta 68 00-838 Warsaw
Manufacturer
Takeda Manufacturing Austria AG Industriestrasse 67 1221 Vienna Austria
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Immunate: Austria, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Sweden Immunate Stim Plus: Czech Republic Immunate S/D: Hungary Talate: Italy Date of last revision of the leaflet:12/2021 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Other sources of information
Information intended for healthcare professionals only: Dosing in hemophilia AThe dose and duration of substitution therapy depend on the severity of the factor VIII deficiency, the location and extent of the bleeding, and the patient's clinical condition. The administered dose of factor VIII is expressed in international units (IU), referring to the current WHO standard for factor VIII products. Factor VIII activity in plasma is expressed as a percentage (relative to normal human plasma) or in IU (relative to the International Standard for plasma factor VIII). One international unit (IU) of factor VIII activity corresponds to the amount of factor VIII in one milliliter of normal human plasma. The required dose of factor VIII is calculated based on empirical observations that 1 IU of factor VIII per kg of body weight increases the factor VIII activity in plasma by approximately 2% of normal activity. The required dose is calculated using the following formula:
Required dose (in IU) = body weight (in kg) x desired increase in factor VIII activity (%) x 0.5
Administration and frequency should always be based on the clinical response in each individual case (see section 4.4). In some cases, especially in younger patients, shorter intervals between doses or higher doses may be necessary. Bleeding and surgical proceduresIn the following types of bleeding, factor VIII activity at the appropriate time should not fall below the specified level of activity in plasma (% of normal or IU/dl). When determining the dose based on the type of bleeding and surgical procedure, the following table can be used:
| Bleeding severity / type of surgical procedure | Required factor VIII level (% of normal) (IU/dl) | Dosing frequency (hours) / treatment duration (days) |
| Bleeding Early bleeding into joints, muscles, or oral bleeding More severe bleeding into joints, muscles, or hematoma Life-threatening bleeding | 20–40 30–60 60–100 | Repeat every 12–24 hours. At least 1 day, until bleeding stops, as assessed by pain relief or wound healing. Repeat infusions every 12–24 hours for 3–4 days or more, until pain and acute disability subside. Repeat infusions every 8–24 hours, until the risk subsides. |
| Surgical procedures Minor, including tooth extraction Major | 30–60 80–100 (pre- and post-operative) | Every 24 hours, for at least 1 day, until wound healing. Repeat infusions every 8–24 hours, to achieve adequate wound healing, then continue treatment for at least 7 consecutive days, to maintain factor VIII activity at 30–60% (IU/dl). |
In certain circumstances (e.g., in the presence of low-titer inhibitors), higher doses than calculated may be required. Long-term prophylaxisIn long-term prophylaxis of bleeding in patients with severe hemophilia A, the usual doses of factor VIII are 20–40 IU per kilogram of body weight, administered at intervals of 2–3 days. In some cases, especially in younger patients, shorter intervals between doses or higher doses may be necessary. Dosing in von Willebrand diseaseSubstitution therapy with Immunate to control bleeding is based on the guidelines for hemophilia A. Immunate contains a relatively high amount of factor VIII compared to von Willebrand factor, so the treating physician should be aware that continued treatment may lead to excessive increase in FVIII:C, which may increase the risk of thromboembolic events. Children and adolescentsThe product should be used with caution in children under 6 years of age who have been limitedly exposed to factor VIII products, as clinical data on this patient group are limited. Dosing in hemophilia A in children and adolescents under 18 years of age is based on body weight, and therefore usually follows the same guidelines as for adult patients. The dose and frequency of administration should always be based on the clinical response in each individual case (see section 4.4). In some cases, especially in younger patients, shorter intervals between doses or higher doses may be necessary.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterTakeda Manufacturing Austria AG
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Immunate 500 Iu Fviii/375 Iu VvfDosage form: Powder, 1000 IUActive substance: coagulation factor VIIIManufacturer: CSL Behring GmbHPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 2000 IUActive substance: coagulation factor VIIIManufacturer: CSL Behring GmbHPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 250 IUActive substance: coagulation factor VIIIManufacturer: CSL Behring GmbHPrescription required
Alternatives to Immunate 500 Iu Fviii/375 Iu Vvf in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Immunate 500 Iu Fviii/375 Iu Vvf in Spain
Alternative to Immunate 500 Iu Fviii/375 Iu Vvf in Ukraine
Online doctors for Immunate 500 Iu Fviii/375 Iu Vvf
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Immunate 500 Iu Fviii/375 Iu Vvf – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














