
Beriate 1000

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Beriate 1000

How to use Beriate 1000
LEAFLET INCLUDED IN THE PACKAGING: INFORMATION FOR
THE USER
Beriate
Beriate 250, 250 IU Powder and solvent for solution for injection/infusion Beriate 500, 500 IU Powder and solvent for solution for injection/infusion Beriate 1000, 1000 IU Powder and solvent for solution for injection/infusion Beriate 2000, 2000 IU Powder and solvent for solution for injection/infusion Human coagulation factor VIII
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What is Beriate and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Beriate
- 3. How to use Beriate
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Beriate
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Beriate and what is it used for
What is Beriate?
Beriate consists of powder and solvent. The reconstituted solution is for intravenous injection or infusion. Beriate is produced from human plasma and contains human coagulation factor VIII. It is used for the prevention and treatment of bleeding caused by a lack of factor VIII (haemophilia type A) in the blood. It may also be used to treat acquired factor VIII deficiency.
2. Important information before using Beriate
The following sections contain information that should be considered before using Beriate.
When not to use Beriate
- If the patient is allergic (hypersensitive) to the active substance (human coagulation factor VIII) or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions
Identifiability It is strongly recommended that each administration of Beriate to the patient be recorded in the treatment diary, including the date of administration, batch number, and volume injected. Before starting treatment with Beriate, this should be discussed with a doctor or pharmacist.
- It is possible to experience allergic reactions. Patients should be informed by their doctor about early signs of allergic reactions, such as hives, generalised rash, chest tightness, wheezing, low blood pressure, and anaphylaxis (a severe allergic reaction causing serious breathing difficulties or dizziness). If such symptoms occur, patients should immediately discontinue the product and contact their treating doctor.
- The formation of inhibitors(antibodies) is a known complication that may occur during treatment with all factor VIII products. These inhibitors, especially at high levels, disrupt proper treatment, and the patient will be closely monitored for the production of these inhibitors. If bleeding in the patient is not properly controlled with Beriate, the doctor should be informed immediately.
- In case of existing heart disease or risk of its occurrence, the doctor or pharmacist should be informed.
- If the administration of Beriate requires a central venous access device (CVAD), the doctor should consider the risk of complications associated with CVAD, including local infections, the appearance of bacteria in the blood (bacteraemia), and the formation of blood clots in blood vessels (thrombosis) at the site of catheter insertion.
The doctor should carefully weigh the benefits of treatment with Beriate against the risk of these complications.
Safety of use in terms of the possibility of transmitting viruses
In the case of medicines produced from human blood or plasma, appropriate preventive measures are taken to prevent infection in patients. These measures include careful selection of blood and plasma donors to exclude carriers of infectious diseases and testing each donation and plasma pool for viruses/infections. Manufacturers of these products also include procedures in the production process that inactivate or remove viruses or other pathogens. Despite the use of these measures, when administering medicines derived from human blood or plasma, it is not possible to completely exclude the possibility of transmitting infectious agents. This applies to both known and newly discovered viruses and other types of infections. The safety measures used are considered effective against enveloped viruses, such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV, the virus that causes AIDS), hepatitis B and C viruses, as well as against non-enveloped viruses, such as hepatitis A virus and parvovirus B19. In the case of regular or repeated administration of products derived from human plasma (e.g. factor VIII), the doctor may recommend vaccination against hepatitis A and B.
Beriate and other medicines
- Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take.
- Beriate should not be mixed with other medicinal products, diluents, and solvents, except those recommended by the manufacturer (see section 6).
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
- If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
- Beriate should be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding only if clearly necessary.
- Data on fertility are not available.
Driving and using machines
Beriate does not affect the ability to drive and use machines.
Beriate contains sodium
Beriate 250 IU and 500 IU contain less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per vial, so it can be considered "essentially sodium-free". Beriate 1000 IU and 2000 IU contain 27.55 mg of sodium (the main component of common salt) per vial. This is equivalent to 1.4% of the recommended maximum daily intake of sodium for an adult.
3. How to use Beriate
This medicine should always be used exactly as prescribed by your doctor or pharmacist. In case of doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist. Treatment of haemophilia A should be started and controlled under the supervision of a doctor experienced in the treatment of this type of disease.
Recommended dose
The required amount of factor VIII and the duration of treatment depend on several factors, such as body weight, disease severity, location, and intensity of bleeding or the need to prevent bleeding during surgery or examination. If Beriate is prescribed for home use, the doctor should inform the patient about how to inject the medicine and what dose to use. Follow the instructions received from your doctor or haemophilia treatment centre.haemophilia.
Use in children and adolescents
The dose is determined based on body weight, using the same principle as for adults.
Overdose of Beriate
No symptoms of FVIII overdose have been reported.
Missed dose of Beriate
The next dose should be administered immediately and continued at regular intervals as prescribed by the doctor. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
Reconstitution and administration method General recommendations:
- 1. The powder should be reconstituted (mixed) with the solvent (liquid part) and drawn from the vial under aseptic conditions.
- 2. The reconstituted solution should be clear or slightly opalescent (may shine when observed in light). Sometimes, single strands or particles may appear in the vial. The filter, part of the Mix2Vial device, removes solid particles. Filtration does not affect dose calculation. Before administration, after filtration and drawing the product into a syringe (see below), the solution should be visually inspected for the presence of small particles and discoloration. Do not use the solution if it is cloudy or contains sediment or particles in the syringe.
- 3. After transferring to a syringe, the product should be used immediately. Do not store the product in a syringe.
- 4. Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations and the doctor's instructions.
Reconstitution:
Without opening the vials, warm the Beriate powder and solvent to room temperature or body temperature. This can be achieved by leaving the vials at room temperature for about an hour or holding them in your hands for a few minutes. DO NOTexpose the vials to direct heat sources. The vial should not be heated above body temperature (37°C). Carefully remove the protective caps from the vials of powder and solvent, wipe the rubber stoppers with an alcohol swab, and let them dry before opening the Mix2Vial package, then follow the instructions below.
- 1. Open the Mix2Vial package by removing the cap. DO NOTremove the Mix2Vial from the blister!
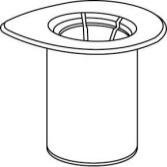
- 2. Place the vial of solventon a flat and clean surface and hold it firmly. Do not remove the Mix2Vial from the blister. Pressing the tip of the blue connector vertically downwardspierce the stopper of the solvent vial.
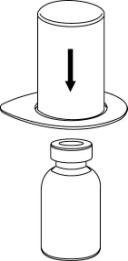
- 3. Carefully remove the blister from the Mix2Vial while holding the edge and pulling verticallyupwards. Make sure to remove only the blister, not the entire Mix2Vial.
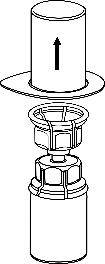
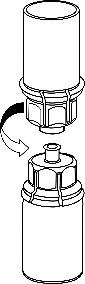
4. .Place the vial of product on a flat and hard surface. Invert the vial of solvent with the attached Mix2Vial and, pressing the tip of the transparent connector vertically downwards, pierce the stopper of the vial of product. The solvent will automatically flow into the vial of product.
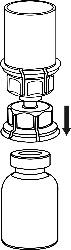
- 5. Hold the vial of medicinal product attached to the Mix2Vial with one hand and the vial of solvent also attached to the Mix2Vial with the other hand, and carefully unscrew the Mix2Vial into two parts by twisting in the opposite direction to the arrow. Remove the vial of solvent with the attached blue connector of the Mix2Vial.
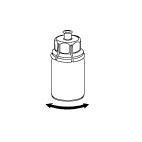
- 6. Bring the substance to complete dissolution by gently rotating the vial of product with the attached transparent connector. Do not shake.
7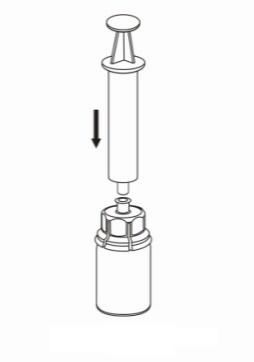 |
|
Withdrawal and administration:
- 8. Holding the plunger of the syringe in place, invert the entire set and fill the syringe with the solution by slowly pulling back the plunger of the syringe.
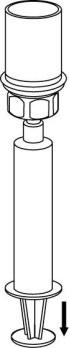
- 9. The solution is now in the syringe. Holding the syringe cylinder (with the plunger facing downwards) firmly, disconnect the transparent connector of the Mix2Vial from the syringe by twisting in the opposite direction to the arrow.
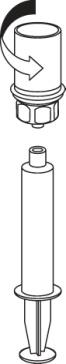
Insert the needle into a vein using the provided injection set. Allow blood to flow into the end of the tube. Connect the syringe to the threaded, locking end of the injection set. According to the doctor's instructions, slowly injectthe reconstituted solution intravenously. The injection or infusion rate should not exceed 2 ml per minute. Care should be taken to ensure that blood does not enter the syringe containing the product. If it is necessary to administer a larger volume, this can also be done by infusion. To do this, transfer the product after reconstitution to an approved infusion set. Perform the infusion according to the doctor's instructions. Pay attention to the occurrence of any side effects. If such an effect may be related to the administration of Beriate, the injection or infusion should be discontinued (see also section 2). In case of any further doubts about the use of this medicine, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If any of the following symptoms occur, tell your doctor or emergency services or the haemophilia treatment centre at the nearest hospital immediately:
- Symptoms of angioedema, such as
- swelling of the face, tongue, or throat
- difficulty swallowing
- hives and difficulty breathing The above side effects are very rare (may occur in less than 1 in 10,000 patients) and in some cases may lead to severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), including shock.
- Loss of efficacy of treatment (persistent bleeding). In the case of previously untreated children with factor VIII products, inhibitory antibodies (see section 2) may occur very frequently (in more than 1 in 10 patients). However, in patients who have previously been treated with factor VIII (more than 150 days of treatment), the risk is not very common (less than 1 in 100 patients). If this happens, the patient's medicines may stop working properly, and the patient may experience persistent bleeding. If this happens, the doctor should be informed immediately.
Other side effects:
- Allergic reactions (hypersensitivity), which may include:
- burning and stinging at the injection or infusion site
- chills, fever, generalised rash, blisters
- headache
- low blood pressure, anxiety, rapid heartbeat, chest tightness, wheezing
- feeling of fatigue (lethargy)
- nausea, vomiting
- tingling The above side effects are very rare and in some cases may lead to severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), including shock.
- Very rarely, elevated body temperature has been observed.
Side effects in children and adolescents
The frequency, type, and severity of adverse reactions in children are comparable to those in adults.
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or pharmacist or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, Fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl. Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorisation holder. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Beriate
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the label and carton after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
- Store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C).
- During the shelf life, Beriate may be stored at a temperature not above 25°C for a total period of 1 month. Individual periods of storage at room temperature should be recorded in the treatment documentation so that the total storage period at this temperature does not exceed one month.
- Beriate does not contain a preservative and should be administered immediately after reconstitution.
- If the reconstituted product is not administered immediately, its storage time in the vial should not exceed 8 hours at room temperature. After transfer to a syringe, the product should be used immediately.
- Do not freeze.
- Store the container in the outer packaging to protect from light.
- Medicines should be stored out of the sight and reach of children.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Beriate contains The active substance of Beriate is:
Beriate is available in powder form (containing nominally 250 IU, 500 IU, 1000 IU, or 2000 IU of human coagulation factor VIII per vial) and liquid part (solvent). The reconstituted solution is for injection or infusion. Beriate 250/500/1000 reconstituted with 2.5 ml, 5 ml, and 10 ml of water for injection, respectively, contains approximately 100 IU/ml of human coagulation factor VIII. Beriate 2000 should be reconstituted with 10 ml of water for injection, and the resulting solution contains approximately 200 IU/ml of human coagulation factor VIII. Other ingredients are:Glycine, calcium chloride, sodium hydroxide (in small amounts) to adjust pH, sucrose, sodium chloride. Solvent:water for injection 2.5 ml, 5 ml, and 10 ml, respectively.
What Beriate looks like and contents of the pack
Beriate is available as a white powder and is supplied with water for injection. The reconstituted solution should be clear to slightly opalescent (may shine when held in light), but it must not contain any visible particles. Available packsPack of 250 IU containing: 1 vial of powder 1 vial of water for injection 2.5 ml 1 Mix2Vial transfer system Administration set (inner packaging): 1 disposable syringe 5 ml 1 injection set 2 alcohol swabs 1 non-sterile plaster Pack of 500 IU containing: 1 vial of powder 1 vial of water for injection 5 ml 1 Mix2Vial transfer system Administration set (inner packaging): 1 disposable syringe 5 ml 1 injection set 2 alcohol swabs 1 non-sterile plaster Pack of 1000 IU containing: 1 vial of powder 1 vial of water for injection 10 ml 1 Mix2Vial transfer system Administration set (inner packaging): 1 disposable syringe 10 ml 1 injection set 2 alcohol swabs 1 non-sterile plaster Pack of 2000 IU containing: 1 vial of powder 1 vial of water for injection 10 ml 1 Mix2Vial transfer system Administration set (inner packaging): 1 disposable syringe 10 ml 1 injection set 2 alcohol swabs 1 non-sterile plaster Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorisation holder and manufacturer
CSL Behring GmbH Emil-von-Behring-Str. 76 35041 Marburg Germany
This medicinal product is authorised in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names
Austria: Beriate 100 I.E./ml Pulver und Lösungsmittel zur Herstellung einer Injektions- oder Infusionslösung (250 I.E., 500 I.E., 1000 I.E.) Beriate 200 I.E./ml Pulver und Lösungsmittel zur Herstellung einer Injektions- oder Infusionslösung (2000 I.E.) Bulgaria: Beriate 250 IU Powder and solvent for solution for injection or infusion Beriate 500 IU Powder and solvent for solution for injection or infusion Beriate 1000 IU Powder and solvent for solution for injection or infusion Beriate 2000 IU Powder and solvent for solution for injection or infusion Croatia: Beriate 250 IU prašak i otapalo za otopinu za injekciju ili infuziju Beriate 500 IU prašak i otapalo za otopinu za injekciju ili infuziju Beriate 1000 IU prašak i otapalo za otopinu za injekciju ili infuziju Beriate 2000 IU prašak i otapalo za otopinu za injekciju ili infuziju Czech Republic: Beriate 250 IU, Beriate 500 IU, Beriate 1000 IU, Beriate 2000 IU Estonia: Beriate Latvia: Beriate 250 SV pulveris un šķīdinātājs injekciju vai infūziju šķīduma pagatavošanai Beriate 500 SV pulveris un šķīdinātājs injekciju vai infūziju šķīduma pagatavošanai Beriate 1000 SV pulveris un šķīdinātājs injekciju vai infūziju šķīduma pagatavošanai Beriate 2000 SV pulveris un šķīdinātājs injekciju vai infūziju šķīduma pagatavošanai Lithuania: Beriate 250 IU milteliai ir tirpiklis injekciniam ar infuziniam tirpalui Beriate 500 IU milteliai ir tirpiklis injekciniam ar infuziniam tirpalui Beriate 1000 IU milteliai ir tirpiklis injekciniam ar infuziniam tirpalui Beriate 2000 IU milteliai ir tirpiklis injekciniam ar infuziniam tirpalui Germany: Beriate 250, Beriate 500, Beriate 1000, Beriate 2000 Hungary: Presentations of Beriate 250, 500 and 1000: BERIATE 100 NE/ml por és oldószer oldatos injekcióhoz vagy infúzióhoz Presentation 2000: BERIATE 200 NE/ml por és oldószer oldatos injekcióhoz vagy infúzióhoz Italy: Beriate Poland: Beriate 250 Beriate 500 Beriate 1000 Beriate 2000 Portugal: Beriate Romania: Beriate 250 pulbere și solvent pentru soluție injectabilă/perfuzabilă Beriate 500 pulbere și solvent pentru soluție injectabilă/perfuzabilă Beriate 1000 pulbere și solvent pentru soluție injectabilă/perfuzabilă Beriate 2000 pulbere și solvent pentru soluție injectabilă/perfuzabilă Spain: Beriate 250 UI polvo y disolvente para solución inyectable o perfusión Beriate 500 UI polvo y disolvente para solución inyectable o perfusión Beriate 1000 UI polvo y disolvente para solución inyectable o perfusión Beriate 2000 UI polvo y disolvente para solución inyectable o perfusión Slovakia: Beriate 250 IU Beriate 500 IU Beriate 1000 IU Beriate 2000 IU Slovenia: Beriate 250 i.e. prašek in vehikel za raztopino za injiciranje/infundiranje Beriate 500 i.e. prašek in vehikel za raztopino za injiciranje/infundiranje Beriate 1000 i.e. prašek in vehikel za raztopino za injiciranje/infundiranje Beriate 2000 i.e. prašek in vehikel za raztopino za injiciranje/infundiranje
Date of last revision of the leaflet: September 2021
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Dosing
Monitoring of treatment During treatment, factor VIII levels should be properly determined to measure the appropriate dose to be administered to the patient and the frequency of repeated infusions. The response of individual patients to factor VIII may vary, due to different recovery levels and half-lives. Dosing based on body weight may require adjustment in patients who are overweight or underweight. In particular, in the case of major surgical procedures, it is necessary to closely monitor substitution therapy through coagulation control (factor VIII activity level in plasma). Patients should be monitored for the development of factor VIII inhibitors. See also section 2. The number of factor VIII units administered to the patient is expressed in international units (IU), which refer to the current WHO standards for factor VIII concentrates. Factor VIII coagulation activity in plasma is expressed as a percentage (relative to normal human plasma) or preferably in IU (relative to international standards of factor VIII in plasma). One international unit of factor VIII activity is equal to the activity of factor VIII contained in 1 ml of normal human plasma. On-demand treatmentThe calculation of the required dose of factor VIII is based on the empirical finding that 1 IU of factor VIII per kilogram of body weight increases the activity of factor VIII in plasma by approximately 2% of normal activity (2 IU/dl). The required dose is calculated using the following formula: Required number of units = body weight [kg] x desired increase in factor VIII level [% or IU/dl] x 0.5. The dose of the product and the frequency of administration should always be individually tailored, depending on the clinical efficacy in individual patients. ProphylaxisIn long-term prophylactic treatment of bleeding in patients with severe haemophilia A, 20 to 40 IU of factor VIII per kilogram of body weight are usually administered at intervals of 2 to 3 days. In some cases, especially in young patients, more frequent administration of factor VIII or the use of higher doses may be necessary. Children and adolescentsDosing in children is based on body weight, using the same principle as for adults. The frequency of administration should always be individually tailored, depending on clinical efficacy.
Information on the pharmacological properties of VWF
In addition to its role as a protective protein for factor VIII, von Willebrand factor mediates platelet adhesion to the site of vascular injury and plays a role in platelet aggregation.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterCSL Behring GmbH
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Beriate 1000Dosage form: Powder, 2000 IUActive substance: coagulation factor VIIIManufacturer: CSL Behring GmbHPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 250 IUActive substance: coagulation factor VIIIManufacturer: CSL Behring GmbHPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 500 IUActive substance: coagulation factor VIIIManufacturer: CSL Behring GmbHPrescription required
Alternatives to Beriate 1000 in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Beriate 1000 in Spain
Alternative to Beriate 1000 in Ukraine
Online doctors for Beriate 1000
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Beriate 1000 – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














