
Fibriga

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Fibriga

How to use Fibriga
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Fibryga, 1 g
Powder and Solvent for Solution for Injection/Infusion
Human Fibrinogen
Read the package leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this package leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this package leaflet, please inform your doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Contents of the Package Leaflet
- 1. What Fibryga is and what it is used for
- 2. Important information before using Fibryga
- 3. How to use Fibryga
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Fibryga
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Fibryga is and what it is used for
What Fibryga is
Fibryga contains human fibrinogen, which is an important protein in the blood clotting process. A lack of fibrinogen means that the blood does not clot as well as it should, leading to an increased tendency to bleed. Replacing the missing fibrinogen with Fibryga corrects this clotting defect.
What Fibryga is used for
Fibryga is used for:
- treatment of bleeding episodes and prevention during surgical procedures in patients with congenital fibrinogen deficiency (hypofibrinogenemia or afibrinogenemia) with a tendency to bleed.
- fibrinogen supplementation in patients with uncontrolled severe bleeding accompanied by acquired fibrinogen deficiency during surgical procedures.
2. Important information before using Fibryga
When not to use Fibryga:
- if you are allergic to human fibrinogen or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- if you have had an allergic reaction to Fibryga in the past.
Tell your doctor if you are allergic to any medicine.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Fibryga, discuss it with your doctor or pharmacist.
Blood clot risk
Your doctor will assess the benefits of using this medicine against the risk of blood clots, especially if:
- you have received a large dose or multiple doses of this medicine,
- you have had a heart attack (coronary artery disease or myocardial infarction) in the past,
- you have liver disease,
- you are a post-surgical patient,
- you are undergoing surgery (perioperative patient),
- you are a newborn,
- you have a high risk of blood clots or clotting disorders (patients at risk of thromboembolic events or disseminated intravascular coagulation). Your doctor may order additional coagulation tests to monitor the risk.
Allergic reactions and anaphylaxis
Any medicine, such as Fibryga, that is produced from human blood (containing proteins) and is administered intravenously may cause allergic reactions. If you have had allergic reactions to Fibryga in the past, your doctor will decide whether it is necessary to use an anti-allergic medicine.
Your doctor will explain to you what the warning signs of an allergic reaction or anaphylaxis are.
Pay attention to early signs of an allergic reaction (hypersensitivity), such as:
- hives,
- rash,
- chest tightness,
- wheezing,
- low blood pressure,
- or anaphylactic reaction (if any of the above symptoms occur suddenly and severely). If such symptoms occur, the administration of Fibryga should be stopped immediately.
Viral safety
When medicines are produced from human blood or plasma, certain precautions are taken to prevent the transmission of infections to patients. These include:
- careful selection of blood and plasma donors to ensure the exclusion of donors who may be carriers of infections,
- testing of each donation and pool of collected plasma for the presence of viruses/infections,
- inclusion in the processing of blood or plasma of steps aimed at inactivating or removing viruses. Despite these precautions, when administering medicines prepared from human blood or plasma, it is not possible to completely exclude the possibility of transmitting an infection. This also applies to unknown or newly emerging viruses or other types of infections. The measures taken are considered effective against enveloped viruses, such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), and hepatitis C virus (HCV), as well as non-enveloped hepatitis A virus (HAV). The measures taken may have limited effectiveness against non-enveloped viruses, such as parvovirus B19. Parvovirus B19 infection can be serious in pregnant women (infection of the unborn child) and in individuals with impaired immunity or with certain types of anemia (e.g., sickle cell anemia or hemolytic anemia). It is strongly recommended that when administering Fibryga to a patient, the name and batch number of the product be recorded in order to be able to associate the patient with the batch of the administered medicinal product. If a patient is regularly/repeatedly administered products containing fibrinogen of human plasma origin, the doctor may recommend that the patient consider vaccination against viral hepatitis A and B.
Older children and adolescents
There are no specific or additional warnings or precautions for children and adolescents.
Fibryga and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are taking, have recently taken, or might take.
Fibryga must not be mixed with other medicines except for those mentioned in the section "Information intended for healthcare professionals only / Reconstitution".
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine. This medicine should be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding only after consulting a doctor or pharmacist.
Driving and using machines
Fibryga has no influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
Fibryga contains sodium
This medicine contains sodium (a major component of common salt) in an amount of up to 132 mg per vial. This corresponds to 6.6% of the recommended maximum daily intake of sodium for adults. This should be taken into consideration if you are on a low-sodium diet.
3. How to use Fibryga
This medicine should always be used exactly as your doctor has told you. If you are not sure, ask your doctor.
Fibryga is administered as an intravenous infusion by medical personnel.
The dose and dosing regimen depend on:
- your body weight,
- the severity of the disease,
- the location of the bleeding,
- the nature of the surgical procedure,
- your overall health.
Use in children and adolescents
The way Fibryga is administered to children and adolescents (intravenously) does not differ from that in adults.
Overdose of Fibryga
Your doctor will regularly perform blood tests to determine the fibrinogen concentration in order to reduce the risk of overdose.
In case of overdose, the risk of pathological blood clots in blood vessels increases.
If you have any further questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Method of administration
This medicine should be administered by injection or infusion (drip) into a vein after reconstitution using the supplied solvent. If you have any further questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Immediately contact your doctor:
- if you experience any side effects,
- if you experience any side effects not listed in this package leaflet.The following side effects have been reported with Fibryga and other products containing fibrinogen (the frequency of the following side effects is unknown):
- allergic reactions or anaphylaxis: skin reactions, such as rash or redness of the skin (see section 2 "Warnings and precautions").
- related to the cardiovascular system: vein inflammation and blood clot formation (see section 2 "Warnings and precautions").
- increase in body temperature (fever).
If you experience any of the above symptoms, contact your doctor.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this package leaflet, please inform your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products:
Jerozolimskie Avenue 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Fibryga
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the label and carton. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Do not store above 25°C. Do not freeze. Store the vial in the outer carton to protect from light.
The powder should only be reconstituted immediately before injection/infusion. The reconstituted solution has been shown to be stable for 24 hours at room temperature (up to 25°C). However, the solution should be used immediately and only once to prevent contamination. The prepared solution should not be stored in the refrigerator or freezer.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Fibryga contains
- The active substance is human fibrinogen.
Fibryga contains 1 g of human fibrinogen per vial or 20 mg of human fibrinogen per ml after reconstitution in the supplied solvent (50 ml of water for injection).
- The other ingredients are L-arginine hydrochloride, glycine, sodium chloride, and disodium citrate dihydrate. Solvent: water for injection
What Fibryga looks like and contents of the pack
Fibryga is a powder and solvent for solution for injection/infusion and is available in glass vials.
A white or pale yellow hygroscopic powder or a brittle, solid mass.
The solvent is a colorless and clear liquid.
The reconstituted solution should be almost colorless and slightly opalescent.
Fibryga is marketed in a cardboard box containing:
- 1 vial of powder for solution for injection/infusion,
- 1 vial of 50 ml solvent (water for injection),
- 1 reconstitution device (nextaro).
Marketing authorization holder
Octapharma (IP) SPRL
Allee de la Recherche 65
1070 Anderlecht
Belgium
Manufacturer
Octapharma Pharmazeutika Produktionsges.m.b.H.
Oberlaaer Strasse 235, 1100 Vienna, Austria
Octapharma AB
Lars Forssells gata 23, 112 75 Stockholm, Sweden
Octapharma GmbH
Elisabeth-Selbert-Strasse 11
40764 Langenfeld, Germany
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Fibryga: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Spain, Netherlands, Ireland, Iceland, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Latvia, Malta, Germany, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Sweden, Hungary, Italy, United Kingdom (Northern Ireland)
Fibrema: Slovenia
Date of last revision of the package leaflet: 2023-12-22
Information intended for healthcare professionals only: Dosing
Dosing and duration of replacement therapy depend on the severity of the disorder, location, and intensity of bleeding, as well as the patient's clinical condition.
Fibrinogen concentration (functional) should be determined to calculate individual dosing and the amount and frequency of doses for each patient through regular measurements of fibrinogen concentration in plasma and continuous monitoring of the patient's clinical condition and other replacement therapies.
In the case of major surgical procedures, it is necessary to closely monitor replacement therapy by determining coagulation parameters.
- 1. Prophylaxis in patients with congenital fibrinogen deficiency or afibrinogenemia and known bleeding tendency To prevent excessive bleeding during surgical procedures, prophylactic administration is recommended to increase the fibrinogen concentration to 1 g/l and maintain it at this level until hemostasis is achieved and above 0.5 g/l until wound healing is complete. For surgical procedures or treatment of bleeding episodes, the dose should be calculated as follows:
Dose (mg/kg body weight) = [Target concentration (g/l) - measured concentration (g/l)]
0.018 (g/l per mg/kg body weight)
Further dosing (doses and frequency of injections) should be adjusted according to the patient's clinical condition and laboratory test results.
The biological half-life of fibrinogen is 3-4 days. In the absence of consumption, re-treatment with human fibrinogen is usually not required. Taking into account accumulation, which occurs with repeated administration for prophylactic purposes, the dose and frequency should be determined based on the therapeutic goals set by the doctor for the individual patient.
Children and adolescents
For surgical procedures or treatment of bleeding episodes, the dose for adolescents should be calculated using the formula for adults, while the dose for children under 12 years of age should be calculated as follows:
Dose (mg/kg body weight) = [Target concentration (g/l) - measured concentration (g/l)]
0.014 (g/l per mg/kg body weight)
Further dosing should be adjusted according to the patient's clinical condition and laboratory test results.
Elderly
Clinical studies of Fibryga did not include patients aged 65 and over to provide conclusive evidence of whether there were differences in response to treatment compared to younger patients.
- 2. Treatment of bleeding
Bleeding in patients with congenital fibrinogen deficiency or afibrinogenemia
Treatment of bleeding episodes should be performed according to the formulas above for adults/adolescents and children to achieve the recommended target fibrinogen concentration in plasma of 1 g/l. This concentration should be maintained until hemostasis is achieved.
Bleeding in patients with acquired fibrinogen deficiency Adults
Usually, an initial dose of 1-2 g is administered, and subsequent infusions are given as needed. In the case of severe bleeding, e.g., during major surgery, a larger amount of fibrinogen (4-8 g) may be required.
Children and adolescents
Dosing should be determined based on body weight and clinical indications, but usually ranges from 20-30 mg/kg.
Instructions for preparation and administration General instructions
- The reconstituted solution should be almost colorless and slightly opalescent. Do not use solutions that are cloudy or contain sediment.
- The medicinal product Fibryga is intended for single use only. Do not reuse any of the components.
- To ensure microbiological safety, the solution should be administered immediately after reconstitution. The chemical and physical stability of the reconstituted solution has been demonstrated for 24 hours at room temperature (up to 25°C). Do not store in the refrigerator or freeze the reconstituted Fibryga.
Reconstitution
- 1. Make sure the vial of powder (Fibryga) and the vial of solvent have reached room temperature. Maintain this temperature throughout the reconstitution process. If a water bath is used for warming, be careful not to let the water come into contact with the rubber stoppers or removed caps of the containers. The temperature of the water bath should not exceed +37°C.
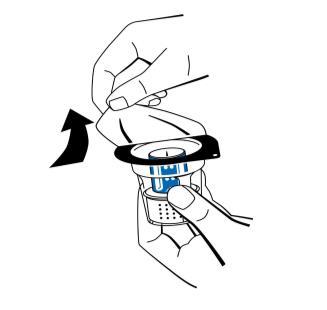
- 2. Remove the tear-off caps from the vial of powder (Fibryga) and the vial of solvent to expose the central part of the infusion stopper. Wipe the rubber stoppers with an alcohol swab and let them dry.
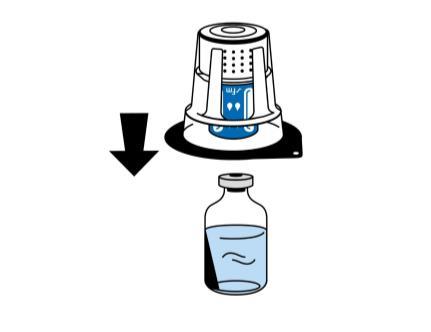
- 3. Open the packaging of the reconstitution device (nextaro) by pulling off the cover (Fig. 1). To maintain sterility, leave the reconstitution device in its transparent blister packaging. Do not touch the spike.
- 4. Place the vial of solvent on a flat, clean surface and hold it firmly. With the reconstitution device still in its blister packaging, place the blue part of the reconstitution device on top of the vial of solvent. Press down firmly until it clicks (Fig. 2). Do not twist while connecting.
Warning:
The reconstitution device should be attached to the vial of solvent first, and then to the vial of lyophilized powder. Otherwise, the vacuum will be lost, and the transfer of solvent will not occur.
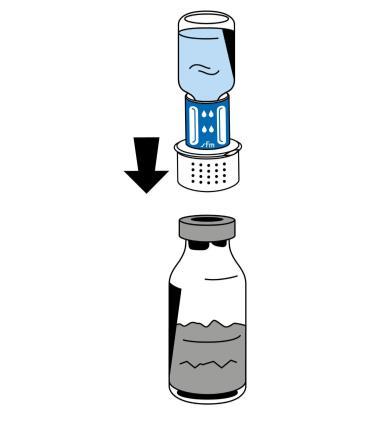
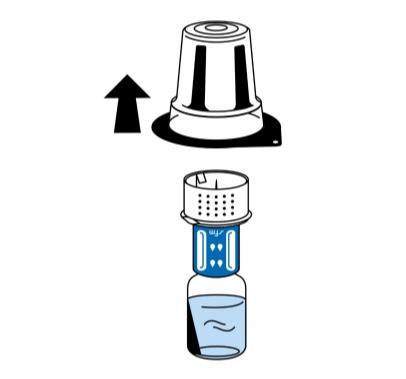
- 5. Holding the vial of solvent, carefully remove the blister packaging from the reconstitution device (nextaro) by pulling it vertically upwards. Make sure the reconstitution device is firmly attached to the vial of solvent (Fig. 3).
- 6. Place the vial of powder (Fibryga) on a flat, clean surface and hold it firmly. Take the vial of solvent with the attached reconstitution device and turn it upside down. Place the white part of the reconstitution device connector on top of the vial of powder (Fibryga) and press down firmly until it clicks (Fig. 4). Do not twist while connecting. The solvent will automatically flow into the vial of powder (Fibryga).
- 7. With the vial of solvent still attached, gently rotate the vial of Fibryga until the powder is completely dissolved. To avoid foaming, do not shake the vial. The powder should dissolve completely within about 5 minutes.
Dissolution of the powder should not take longer than 20 minutes. If the powder does not dissolve within 20 minutes, the product should be discarded.
- 8. In the rare case where, during the transfer of water for injection, undissolved product is observed on the surface or the reconstitution time is unexpectedly prolonged, the dissolution process can be accelerated by more vigorous mixing of the vial in a horizontal direction.
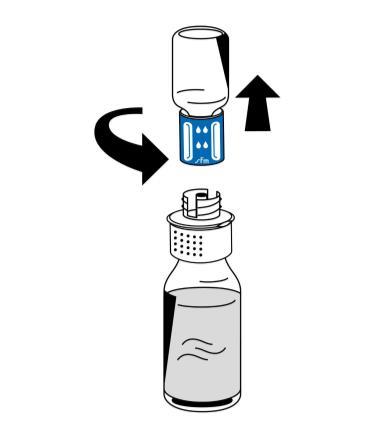
- 9. After reconstitution is complete, unscrew the reconstitution device (blue part) in a counter-clockwise direction into two parts (Fig. 5). Do not touch the luer lock connector on the white part of the reconstitution device.
- 10. Discard the empty vial of solvent along with the attached blue part of the reconstitution device.
Administration
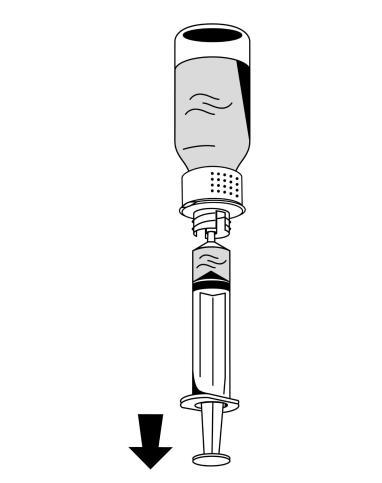
- 1. Carefully attach a syringe to the luer lock connector on the white part of the reconstitution device (Fig. 6).
- 2. Turn the Fibryga vial upside down and draw the solution into the syringe (Fig. 7).

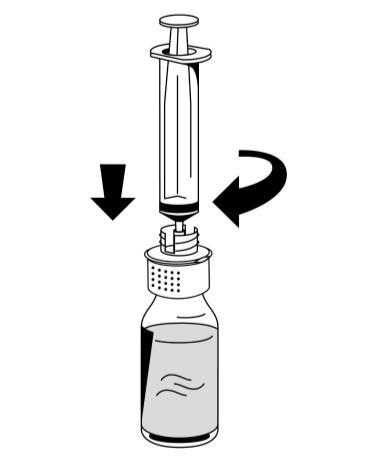
- 3. With the plunger of the syringe held firmly (plunger facing downwards), remove the syringe from the reconstitution device (Fig. 8).
It is recommended to administer the reconstituted solution intravenously at room temperature using a standard infusion set.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
Method of administration
Intravenous infusion or injection.
Fibryga should be administered slowly intravenously at a maximum recommended rate of 5 ml per minute in patients with congenital hypofibrinogenemia or afibrinogenemia and at a maximum recommended rate of 10 ml per minute in patients with acquired fibrinogen deficiency.
Incompatibilities
Do not mix the medicinal product with other medicinal products.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterOctapharma AB Octapharma GmbH Octapharma Pharmazeutika Produktionsges.m.g.H.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to FibrigaDosage form: Powder, 1 gActive substance: fibrinogen, humanManufacturer: CSL Behring GmbHPrescription not requiredDosage form: Powder, 1000 IUActive substance: coagulation factor VIIIManufacturer: CSL Behring GmbHPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 2000 IUActive substance: coagulation factor VIIIManufacturer: CSL Behring GmbHPrescription required
Alternatives to Fibriga in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Fibriga in Ukraine
Alternative to Fibriga in Spain
Online doctors for Fibriga
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Fibriga – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














