FOSTIPUR 75 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVEL


Como usar FOSTIPUR 75 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVEL
Introdução
Prospecto: Informação para o utilizador
Fostipur 75 ui pó e dissolvente para solução injetável
Urofolitropina
Leia todo o prospecto atentamente antes de começar a usar este medicamento, porque contém informações importantes para si.
- Conserva este prospecto, porque pode ter que voltar a lê-lo.
- Se tiver alguma dúvida, consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico.
- Este medicamento foi prescrito apenas para si, e não deve dá-lo a outras pessoas, embora tenham os mesmos sintomas que si, porque pode prejudicá-las.
- Se experimentar efeitos adversos, consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico, mesmo que se trate de efeitos adversos que não aparecem neste prospecto. Ver secção 4.
Conteúdo do prospecto
- O que é Fostipur e para que é utilizado
- O que precisa saber antes de começar a usar Fostipur
- Como usar Fostipur
- Posíveis efeitos adversos
- Conservação de Fostipur
- Conteúdo do envase e informação adicional
1. O que é Fostipur e para que é utilizado
- Fostipur é utilizado para estimular a ovulação em mulheres que não ovulam e que não respondem a outros tratamentos (citrato de clomifeno).
- Na indução do desenvolvimento multifolicular (e, por conseguinte, de vários óvulos) em mulheres submetidas a tratamentos de fertilidade.
A urofolitropina é uma hormona foliculostimulante humana altamente purificada, que pertence a um grupo de medicamentos chamados gonadotropinas.
Este medicamento deve ser utilizado sob controlo do seu médico.
2. O que precisa saber antes de começar a usar Fostipur
Antes de iniciar o tratamento, deve avaliar-se a fertilidade do casal.
Não use Fostipur
- Se é alérgica à urofolitropina ou a qualquer um dos outros componentes deste medicamento (incluídos na secção 6).
- Aumento do tamanho dos ovários ou quistes no ovário sem ser consequência de um
distúrbio hormonal (síndrome do ovário poliquístico).
- Hemorragia de origem desconhecida.
- Câncer de ovários, útero ou de mama.
- Inchação anormal (tumor) da glândula hipofisária ou hipotálamo (no cérebro).
Não deve utilizar este medicamento em caso de que tenha distúrbios como menopausa prematura, malformação dos órgãos sexuais ou tumores próprios da matriz que lhe impeçam ter um embarazo normal.
Advertências e precauções
Embora não se disponha de informação sobre reações alérgicas com Fostipur, deve comunicar ao seu médico se tem alguma reação alérgica a medicamentos semelhantes.
Este tratamento aumenta o risco de desenvolver uma doença conhecida como síndrome de hiperestimulação ovárica (SHO) (ver Posíveis efeitos adversos). Se se produzir hiperestimulação ovárica, deve interromper o tratamento e evitará ficar grávida. Os primeiros sinais de hiperestimulação ovárica são dor na região baixa do abdómen, bem como náuseas (malestar), vómitos e aumento de peso. Se aparecerem estes sintomas, deve ser examinada pelo seu médico o mais breve possível. Nos casos graves, mas raros, os ovários podem aumentar de tamanho e pode acumular-se líquido no abdómen ou no peito.
O medicamento utilizado para lograr a libertação final dos óvulos maduros (que contém a gonadotrofina coriónica humana, hCG) pode aumentar a probabilidade de padecer SHO. Por conseguinte, não é aconselhável utilizar hCG nos casos em que se está a desenvolver uma hiperestimulação ovárica e também não deve manter relações sexuais, mesmo utilizando métodos anticonceptivos de barreira, durante um mínimo de 4 dias.
Deve ter-se em conta que as mulheres com problemas de fertilidade têm um índice de abortos espontâneos superior ao da população normal.
A ocorrência de embarazos múltiplos e nascimentos em pacientes que recebem tratamento de indução à ovulação aumenta se comparada com a concepção natural. No entanto, este risco pode ser reduzido se for utilizada a dose recomendada.
Existe um ligeiro aumento do risco de embarazo ectópico (embarazo fora do útero) em mulheres com as trompas de Falópio danificadas.
Os embarazos múltiplos e as características dos pais submetidos a tratamentos de fertilidade (por exemplo, idade da mãe, características do esperma) podem estar associados a um maior risco de anomalias no nascimento.
O tratamento com Fostipur, assim como o embarazo em si, pode aumentar o risco de padecer trombose. A trombose é a formação de um coágulo de sangue num vaso sanguíneo, a maior parte das vezes nas veias das pernas ou nos pulmões.
Consulte o seu médico antes de começar o tratamento, especialmente:
- se já sabe que tem um maior risco de padecer trombose.
- se si ou um familiar próximo sofreu em alguma ocasião trombose,
- se tem um sobrepeso excessivo.
Este medicamento é preparado a partir de urina de origem humana. O risco de transmissão de infecção ou doença ao organismo não pode ser eliminado por completo. No entanto, este risco fica limitado pelas fases de eliminação de vírus no processo de fabricação, particularmente SIDA, Herpes víruse Papillomavírus.
Não se publicaram casos de contaminação viral.
Uso de Fostipur com outros medicamentos
Informe o seu médico ou farmacêutico se está a utilizar, utilizou recentemente ou poderia ter que utilizar qualquer outro medicamento.
Embarazo e lactação
Fostipur não deve ser utilizado se está grávida ou em período de amamentação.
Fostipur contém sódio
Este medicamento contém menos de 1mmol de sódio (23 mg) por dose, isto é, essencialmente “isento de sódio”.
3. Como usar Fostipur
Dose e duração do tratamento:
Siga exatamente as instruções de administração deste medicamento indicadas pelo seu médico. Em caso de dúvida, consulte novamente o seu médico ou farmacêutico.
Mulheres que não ovulam e têm menstruações irregulares ou incompletas:
Se você tem menstruação, o tratamento deve ser iniciado dentro dos 7 dias que seguem o início da menstruação (os primeiros 7 dias do ciclo menstrual).
A dosagem consiste em 1 injeção por dia, sob a pele (por via subcutânea) ou no músculo (por via intramuscular).
A dose inicial comum é de 75 UI até 150 UI de FSH (Fostipur) por dia. Esta dose pode ser aumentada, se necessário, de 37,5 até 75 UI em intervalos de 7 dias ou, preferencialmente, 14 dias, para obter uma resposta adequada.
A dose máxima diária de FSH não deve exceder, em geral, 225 UI.
Se o seu médico não encontrar uma resposta adequada após 4 semanas de tratamento, este ciclo de tratamento deve ser interrompido. Para o próximo ciclo, o seu médico indicará um tratamento com uma dose inicial mais alta.
Quando se obtém uma boa resposta (crescimento folicular satisfatório), será administrada apenas uma injeção de outro medicamento (hCG), utilizado para induzir a maturação folicular e a liberação dos óvulos. Isso ocorrerá 24 a 48 horas após a última injeção de Fostipur. Recomenda-se ter relações sexuais no mesmo dia da administração de hCG e no dia seguinte.
Se se obtém uma resposta ovárica excessiva, o tratamento deve ser interrompido e não se administrará hCG (ver Efeitos adversos possíveis). Para o próximo ciclo, o seu médico indicará uma dose inicial mais baixa.
Mulheres submetidas a estimulação ovárica por desenvolvimento folicular múltiplo prévio à fertilizaçãoin vitroou outras técnicas de reprodução assistida:
Situação 1 – Se você tem menstruação.
O tratamento deve ser iniciado nos 2 ou 3 dias do início da sua menstruação (os primeiros 2 ou 3 dias do ciclo menstrual).
A dosagem consiste em 1 injeção por dia por via subcutânea ou intramuscular.
Uma dose habitualmente utilizada de superovulação consiste na administração de 150 a 225 UI de Fostipur por dia. O tratamento prossegue, com o ajuste da dose de acordo com a sua resposta, até alcançar um desenvolvimento folicular adequado. Isso é geralmente alcançado no 10º dia de tratamento (média de 5 a 20 dias) e é avaliado mediante a coleta de amostras de sangue e/ou exames ecográficos.
A dose máxima é, em geral, de 450 UI/dia.
Uma vez alcançado o desenvolvimento folicular, será administrada uma única injeção de um medicamento utilizado para induzir a maturação folicular final; este medicamento contém até 10.000 UI de gonadotropina coriônica humana (hCG). Será administrado entre 24-48 horas após a última injeção de Fostipur.
A punção dos oócitos será realizada aproximadamente 35 horas mais tarde.
Situação 2 - Quando se utiliza um agonista da hormona liberadora de gonadotropina (GnRH)
Fostipur deve ser administrado aproximadamente 2 semanas após o início deste tratamento. Ambos os tratamentos são mantidos até alcançar o desenvolvimento folicular adequado. Será administrada uma injeção de Fostipur por dia, por via intramuscular ou subcutânea. Por exemplo, após 2 semanas de tratamento com um agonista de GnRH, serão administrados 150 a 225 UI de Fostipur durante os primeiros 7 dias. A dose será ajustada, então, de acordo com a resposta ovárica.
Instruções de administração:
Fostipur é administrado por injeção tanto sob a pele (por via subcutânea) quanto no músculo (por via intramuscular).
Cada frasco é de uso único e a injeção deve ser administrada imediatamente após a sua preparação.
Após aconselhamento e prática convenientes, o seu médico pode pedir que você mesma se administre a injeção de Fostipur.
Em primeiro lugar, o seu médico deve:
- Deixá-lo praticar administrando-se a injeção subcutânea.
- Indicar quais são as zonas possíveis para que você se administre a injeção.
- Indicar como preparar minuciosamente a solução para a injeção.
- Explicar como preparar a dose correta que deve ser administrada.
Outros tipos de apresentações, distintos das ampolas, são projetados para a autoadministração pelas pacientes.
Antes de você se administrar a injeção de Fostipur, leia cuidadosamente as seguintes instruções:
Como preparar e injetar Fostipur, utilizando 1 frasco de pó
A solução deve ser preparada justo antes de se colocar a injeção. Cada frasco é utilizado para um único uso. O medicamento deve ser reconstituído sob condições assépticas.
Fostipur deve ser reconstituído apenas com o diluente fornecido no estojo.
Prepare uma superfície limpa e lave as suas mãos antes de reconstituir a solução. É importante que tanto as suas mãos quanto os utensílios que você vai usar estejam o mais limpos possível.
Estenda os seguintes materiais sobre uma superfície limpa:
- 2 pedaços de algodão com álcool (não vêm na caixa)
- 1 frasco que contém o pó de Fostipur
- 1 ampola de diluente
- 1 seringa (não vem na caixa)
- 1 agulha para preparar a injeção (não vem na caixa)
- 1 agulha fina para a injeção subcutânea (não vem na caixa)
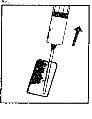
Reconstituição da solução para a injeção, utilizando 1 frasco de pó
Preparar a solução para a injeção:
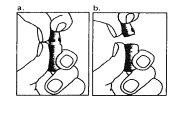
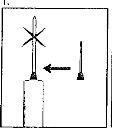
| 1. O pescoço da ampola está projetado para quebrar mais facilmente abaixo do ponto colorido. Agite suavemente a parte superior da ampola para remover qualquer líquido residual na ponta. Mantenha a ampola com o ponto colorido voltado para fora e retire a parte superior da ampola como mostrado na imagem. O uso de um pano ou um quebrador de ampolas para segurar a ampola ajudará a proteger os seus dedos. Coloque cuidadosamente a ampola aberta em posição vertical sobre a superfície limpa. |
| 2. Retire o capuchão protetor da agulha. Adicione a agulha para a reconstituição (agulha grande) à seringa. Com a seringa em uma mão, pegue a ampola aberta do diluente, insira a agulha e retire todo o diluente para a seringa. Adicione o capuchão protetor da agulha. Coloque cuidadosamente a seringa na superfície. |
| 3. Retire o tampão de plástico colorido do frasco de pó empurrando suavemente para cima. Desinfete a parte superior do tampão de borracha esfregando com um algodão com álcool e deixe secar. |
| 4. Pegue a seringa, retire o capuchão protetor da agulha e injete lentamente o diluente pela parte central superior do tampão de borracha do frasco de pó. Pressione o êmbolo firmemente para baixo para arremessar toda a solução sobre o pó. NÃO AGITE, mas mova suavemente o frasco entre as suas mãos até que o pó esteja completamente dissolvido, tentando evitar a criação de espuma. |
| 5. Uma vez que o pó já se dissolveu (o que, em geral, ocorre imediatamente), retire lentamente a solução para a seringa.
|
Preparação de doses mais altas, utilizando mais de 1 frasco de pó.
Se o seu médico recomendou doses mais altas, você pode consegui-las utilizando mais de 1 frasco de pó com uma ampola de diluente.
Quando se reconstitui mais de 1 frasco de Fostipur, no final da fase 4 descrita anteriormente, introduza o conteúdo reconstituído do primeiro frasco novamente na seringa e injete lentamente em um segundo frasco. Repita as fases 2 a 4 para o segundo frasco e subsequentes, até que se dissolva o conteúdo do número de frascos necessário equivalente à dose prescrita (dentro do limite da dose máxima total de 450 UI, correspondente a um máximo de 6 frascos de Fostipur 75 UI ou 3 frascos de Fostipur 150 UI).
O seu médico pode aumentar a dose em 37,5 UI, que representa a metade de um frasco de Fostipur 75 UI.
Para isso, você deve reconstituir o conteúdo do frasco de 75 UI de acordo com as fases 2 a 3 descritas anteriormente e introduzir a metade dessa solução reconstituída (0,5 ml) na seringa de acordo com a fase 4.
Nessa situação, você terá duas preparações para injetar: a primeira preparação reconstituída em 1 ml e a segunda contendo 37,5 UI em 0,5 ml.
Ambas as preparações devem ser injetadas com as suas próprias seringas de acordo com as seguintes fases.
A solução deve ser transparente e incolor.
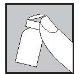
Injete o medicamento por via subcutânea:
|
|
|
|
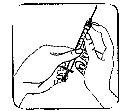
O local da injeção:
- O seu médico ou enfermeira terão indicado em que parte do seu corpo o medicamento pode ser injetado. Os locais mais comuns são a coxa ou a parede abdominal inferior abaixo do umbigo.
- Limpe o local da injeção com um algodão com álcool.
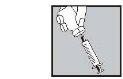
Colocação da agulha:
|
|
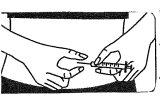
Injeção da solução:
- Injete abaixo da pele como lhe ensinaram. Não a injete diretamente em uma veia. Empurre o êmbolo lentamente e de forma constante, de modo que a solução seja injetada corretamente e a pele não seja danificada.
Leve todo o tempoque precisarpara se injetar o volume da soluçãoprescrito.Como descrito na preparação da solução, dependendo da dose prescrita pelo seu médico, pode ser que você não precise usar o volume total da solução.
Retirada da agulha:
- Retire a seringa rapidamente e pressione no local da injeção com um algodão com desinfetante. Um suave massagem no local, enquanto ainda mantém a pressão, ajuda a dispersar a solução de Fostipur e alivia as dores.
Eliminação de todos os utensílios utilizados:
Qualquer produto não utilizado ou material de descarte deve ser eliminado de acordo com os requisitos locais (uma vez finalizada a injeção, todas as agulhas e seringas vazias devem ser descartadas em um contenedor apropriado).
Se usar mais Fostipur do que deve
Os efeitos de uma sobredose de Fostipur são desconhecidos, embora se possa supor que poderia ocorrer um síndrome de hiperestimulação ovárica (ver Efeitos adversos possíveis). Se for administrado mais Fostipur do que o necessário, entre em contato com o seu médico ou farmacêutico.
Em caso de sobredose ou ingestão acidental, consulte imediatamente o seu médico ou farmacêutico ou o Serviço de Informação Toxicológica, telefone: 915 620 420, indicando o medicamento e a quantidade ingerida.
Se esquecer de usar Fostipur
Coloque a próxima injeção no momento que estava previsto. Não use uma dose dupla para compensar as doses esquecidas.
Se interromper o tratamento com Fostipur
Não interrompa o tratamento por sua própria iniciativa. Consulte sempre o seu médico se está considerando deixar de usar este medicamento. Se tiver alguma outra dúvida sobre o uso deste medicamento, consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico.
4. Efeitos adversos possíveis
Como todos os medicamentos, Fostipur pode produzir efeitos adversos, embora nem todas as pessoas os sofram.
Os efeitos adversos seguintes são importantes e requererão ação imediata se os experimentar. Deve interromper a administração de Fostipur e procurar imediatamente o seu médico se lhe ocorrer o seguinte:
Frequentes, podem afetar até 1 de cada 10 pessoas:
- Síndrome de hiperestimulação ovárica (ver seção 2 para informações adicionais).
Os seguintes efeitos adversos também foram notificados:
Frequentes, podem afetar até 1 de cada 10 pessoas:
- dor de cabeça,
- sensação de inchaço no abdômen,
- constipação,
- dor na zona da injeção.
Pouco frequentes, podem afetar até 1 de cada 100 pessoas:
- aumento da atividade da glândula tireoide,
- mudanças de humor,
- fadiga,
- tontura,
- dificuldade para respirar (dispneia),
- sangramento pelo nariz,
- náuseas, indigestão, dor abdominal,
- erupção cutânea, coceira,
- sofocos,
- cistite,
- aumento de mamas, dor de mamas,
- dificuldade para parar as hemorragias.
Pode ocorrer vermelhidão, dor e hematomas no local da injeção (frequência não estabelecida).
Ver seção 2 da informação adicional sobre o risco de coágulos sanguíneos, gravidez ectópica, gravidezes múltiplas e abortos.
Se considerar que algum dos efeitos adversos que sofre é grave ou se notar qualquer efeito adverso não mencionado neste prospecto, informe o seu médico ou farmacêutico.
Comunicação de efeitos adversos:
Se experimentar qualquer tipo de efeito adverso, consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico, mesmo que se trate de possíveis efeitos adversos que não aparecem neste prospecto. Também pode comunicá-los diretamente através do Sistema Espanhol de Farmacovigilância de Medicamentos de Uso Humano: https://www.notificaram.es.
Ao comunicar efeitos adversos, você pode contribuir para fornecer mais informações sobre a segurança deste medicamento.
5. Conservação de Fostipur
Mantenha este medicamento fora da vista e do alcance das crianças.
Não conserve a uma temperatura superior a 25ºC. Conserve o frasco e a ampola de diluente no embalagem exterior, para protegê-lo da luz.
Não use Fostipur após a data de validade que aparece no estojo e no frasco.
Use imediatamente após a sua reconstituição.
Não use Fostipur se notar que a solução não é transparente. Após a reconstituição, a solução deve ser transparente e incolor.
Os medicamentos não devem ser jogados nos esgotos nem na lixeira. Deposite os recipientes e os medicamentos que não precisa no Ponto SIGRE da farmácia. Em caso de dúvida, pergunte ao seu farmacêutico como se livrar dos recipientes e dos medicamentos que não precisa. Dessa forma, você ajudará a proteger o meio ambiente.
6. Conteúdo do envase e informação adicional
Composição de Fostipur
O princípio ativo é urofolitropina. Cada frasco contém 75 UI de urofolitropina (hormona foliculostimulante: FSH): 1 ml de solução reconstituída pode conter 75 UI, 150 UI, 225 UI, 300 UI, 375 UI ou 450 UI de urofolitropina, quando se reconstitui 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ou 6 frascos, respetivamente, em 1 ml de dissolvente.
A atividade específica in vivoé igual ou superior a 5.000 UI de FSH por mg de proteína.
Os outros componentes são:
Pó: lactosa monohidrato.
Dissolvente: cloreto de sódio e água para preparações injetáveis.
Aspecto do produto e conteúdo do envase
Fostipur apresenta-se em pó e dissolvente para solução injetável.
Caixa com 1, 5 ou 10 estuches. Cada estuche contém: 1 frasco com pó que contém 75 UI de urofolitropina e 1 ampola de dissolvente (1 ml).
O aspecto do pó é de uma massa endurecida branca a esbranquiçada e o dissolvente é transparente e incolor.
Titular da autorização de comercialização e responsável pela fabricação
Titular da autorização de comercialização
IBSA Farmaceutici Italia srl
Via Martiri di Cefalonia 2
26900 Lodi (Itália)
Responsável pela fabricação
IBSA Farmaceutici Italia S.r.L, Via Martiri di Cefalonia - 26900 Lodi (Itália)
Pode solicitar mais informações respeito a este medicamento dirigindo-se ao representante local do titular da autorização de comercialização:
Instituto Bioquímico Ibérico IBSA S.L.
Avenida Diagonal 605,
Piso 8, Local 1,
08028 Barcelona (Espanha)
Este medicamento está autorizado nos estados membros do Espaço Económico Europeu com os seguintes nomes (as concentrações e formas farmacêuticas são idênticas em todos os países, só mudam os nomes comerciais)
Áustria: Fostimon
Bélgica: Fostimon
Chipre: Fostimon
Dinamarca: Fostimon
Finlândia: Fostimon
França: Fostimon
Luxemburgo: Fostimon
Irlanda: Fostimon
Holanda: Fostimon
Noruega: Fostimon
Espanha: Fostipur
Suécia: Fostimon
Grã-Bretanha: Fostimon
Data da última revisão deste prospecto:fevereiro 2024
A informação detalhada e actualizada deste medicamento está disponível na página web da Agência Espanhola de Medicamentos e Produtos Sanitários (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
- País de registo
- Substância ativa
- Requer receita médicaSim
- Fabricante
- Esta informação é apenas para referência e não constitui aconselhamento médico. Consulte sempre um médico antes de tomar qualquer medicamento. A Oladoctor não se responsabiliza por decisões médicas baseadas neste conteúdo.
- Alternativas a FOSTIPUR 75 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVELForma farmacêutica: INJETÁVEL, 150 UI urofolitropina/ mlSubstância ativa: urofollitropinFabricante: Ibsa Farmaceutici Italia S.R.L.Requer receita médicaForma farmacêutica: INJETÁVEL, 150 UI por 1 mL de solução reconstituídaSubstância ativa: urofollitropinFabricante: Ibsa Farmaceutici Italia S.R.L.Requer receita médicaForma farmacêutica: INJETÁVEL, 225 UISubstância ativa: urofollitropinFabricante: Ibsa Farmaceutici Italia S.R.L.Requer receita médica
Alternativas a FOSTIPUR 75 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVEL noutros países
As melhores alternativas com o mesmo princípio ativo e efeito terapêutico.
Alternativa a FOSTIPUR 75 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVEL em Polónia
Alternativa a FOSTIPUR 75 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVEL em Ukraine
Médicos online para FOSTIPUR 75 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVEL
Avaliação de posologia, efeitos secundários, interações, contraindicações e renovação da receita de FOSTIPUR 75 UI PÓ E SOLVENTE PARA SOLUÇÃO INJETÁVEL – sujeita a avaliação médica e regras locais.