
VENTODUO 100 micrograms/50 micrograms/puff pressurized inhalation suspension

How to use VENTODUO 100 micrograms/50 micrograms/puff pressurized inhalation suspension
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Ventoduo 100 micrograms/50 micrograms per actuation inhalation powder, pre-filled inhaler
Salbutamol / Beclometasone dipropionate
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again. If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What Ventoduo is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use Ventoduo
- How to use Ventoduo
- Possible side effects
- Storing Ventoduo
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Ventoduo is and what it is used for
Ventoduo contains two active substances, salbutamol and beclometasone dipropionate.
Salbutamol is a short-acting bronchodilator. Bronchodilators relax the muscles in the walls of the airways in the lungs, making it easier to breathe.
Beclometasone dipropionate is a corticosteroid that acts by reducing inflammation and irritation in the lungs.
Ventoduo is indicated for the treatment of asthma in patients who require a corticosteroid and a short-acting bronchodilator.
2. What you need to know before you use Ventoduo
Do not use Ventoduo:
- if you are allergic to salbutamol, beclometasone dipropionate or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions:
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting to use Ventoduo:
- If you have had thrush in your mouth
- If your asthma gets worse or you have more difficulty breathing. You may notice more "wheezing" or shortness of breath or have to use your medication more often than usual. If any of these things happen, you should see your doctor as soon as possible.
- If you have active or latent tuberculosis.
- If you have severe heart and blood vessel problems (severe cardiomyopathy, history of heart disease, irregular heartbeat, angina or uncontrolled high blood pressure). If you experience chest pain or your heart disease symptoms worsen, consult your doctor immediately.
- If you have thyrotoxicosis (overactive thyroid gland), hypokalemia (low potassium levels in the blood), known aneurysm (arterial dilation) or diabetes mellitus (your doctor may perform additional glucose tests before starting treatment).
- If you have pheochromocytoma (a tumor of the adrenal gland).
- If you have acute asthma. This medicine may cause a drop in potassium levels, which could be increased by hypoxia (low oxygen levels).
The drop in potassium levels that this medicine can cause may also be increased by medications used to treat asthma.
- If you have previously been treated with oral corticosteroids. Your doctor may recommend regular checks on your adrenal gland function and will indicate how to gradually reduce the dose of your previous treatment. You may need additional symptomatic treatment.
- Your doctor will indicate how to use the inhaler. You should use this medicine even if you do not have symptoms.
- Always use the dose indicated by your doctor. Do not increase it, as it may cause side effects.
- Treatment with Ventoduo should not be stopped abruptly, but gradually. Your doctor will indicate how to do it.
Contact your doctor if you experience blurred vision or other visual disturbances.
Children
It is recommended to regularly monitor the height of children who receive prolonged treatment with inhaled corticosteroids.
Use in athletes
This medicine contains salbutamol, which may produce a positive result in doping tests.
Use of Ventoduo with other medicines
Tell your doctor if you are taking or have recently taken other medicines, including those obtained without a prescription.
Some medicines may increase the effects of Ventoduo, so your doctor will monitor you closely if you are taking these medicines (including some for HIV: ritonavir, cobicistat).
Tell your doctor if you are taking the following medicines:
- Cardiac and vascular medications that can narrow the airways (non-selective β-blockers such as atenolol, propranolol).
- Other bronchodilator medications.
- Certain medications for treating depression, known as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (e.g., moclobemide) and tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline).
- Anesthetics (inducers of partial or total loss of sensitivity) such as halothane.
- Medications for irregular heartbeat, such as digoxin.
- Xanthine derivatives (used to help with breathing), such as theophylline.
- Diuretics (medications to urinate), such as furosemide.
- Disulfiram or metronidazole.
- Other corticosteroids.
- Medications for HIV (e.g., ritonavir, cobicistat).
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
Ventoduo will only be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding if, in the doctor's opinion, the expected benefits to the mother outweigh any possible risks to the fetus.
Driving and using machines
Although no effects on the ability to drive or use machines are expected, you should take into account the possibility of dizziness and tremors.
3. How to use Ventoduo
Follow your doctor's instructions for using this medicine exactly. If you are unsure, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
Ventoduo is administered by inhalation and should be used as needed and not regularly.
If your asthma is active (e.g., you have symptoms or frequent crises, such as difficulty breathing that makes it hard to speak, eat, or sleep, coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, or limited physical ability), you should inform your doctor immediately, who may start administering a medication or increase the dose of treatment, such as an inhaled corticosteroid, to control your asthma.
Tell your doctor as soon as possible if your medication seems to be not working as well as usual (e.g., if you need higher doses to relieve your respiratory problems or if your inhaler does not provide relief for at least 3 hours), as your asthma may be worsening and you may need a different medication.
If you use Ventoduo more than twice a week to treat your asthma symptoms, without including preventive use before exercise, this indicates poorly controlled asthma and may increase the risk of severe asthma attacks (asthma worsening) that can have serious complications and can be life-threatening. You should contact your doctor as soon as possible to review your asthma treatment.
If you use a daily medication to reduce inflammation in your lungs, e.g., an "inhaled corticosteroid," it is essential that you continue to use it regularly, even if you feel better.
The recommended and maximum doses are:
Use in adults and adolescents (from 12 years):
Recommended dose: 2 inhalations (200 micrograms of salbutamol and 100 micrograms of beclometasone dipropionate), 1 or 2 times a day.
Maximum dose: 2 inhalations (200 micrograms of salbutamol and 100 micrograms of beclometasone dipropionate), 3 or 4 times a day.
Use in children from 5 to 11 years:
Recommended dose: 1 inhalation (100 micrograms of salbutamol and 50 micrograms of beclometasone dipropionate), 1 or 2 times a day.
Maximum dose: 2 inhalations (200 micrograms of salbutamol and 100 micrograms of beclometasone dipropionate), 2 times a day.
Do not increase the dose or frequency of administration on your own, as side effects may occur when excessively high doses are administered.
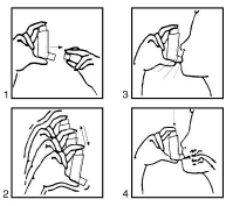
Instructions for use:
- Remove the cap (fig. 1). If it is a new inhaler or has not been used for several days, shake the aerosol (fig. 2) and perform a puff to ensure the proper functioning of the inhaler. If the inhaler is used regularly, proceed to the following instructions:
- Shake the inhaler (fig. 2).
- Remove as much air as possible from your lungs.
- Place the aerosol in your mouth according to the position indicated in the drawing (fig. 3).
- Make a deep inhalation.
You should press, according to the arrows in the drawing (fig. 4), the device while making this inhalation.
- Remove the aerosol from your mouth and try to hold your breath for a few seconds.
- You should periodically wash the actuator mouthpiece of the aerosol. To do this, remove the actuator from the aerosol and clean it with a cloth or paper towel.
- Store it with the cap on and protect it from dust and dirt.
- It is recommended to rinse your mouth with water after each application.
The inhaler has a dose indicator that can be seen through a small hole or window on the actuator and indicates how many applications are left. In a new inhaler, you can read "200" through the window on the actuator. This number corresponds to the dose left in the inhaler. As the inhaler is used, the dose indicator rotates downward every 5-7 puffs until it reaches 0.
When there are approximately 40 doses left, the indicator changes from green to red (see figure 5) to remind the patient to consult their doctor if they need to continue treatment or need a new prescription. Discard the inhaler once the indicator reaches "0".

(figure 5)
If you use more Ventoduo than you should
It is essential that you take your dose as indicated by your doctor. Do not increase or decrease your dose without medical supervision.
If you use more Ventoduo than recommended, neuromuscular disorders may occur, ranging from muscle weakness to paralysis and respiratory failure. Changes in your electrocardiogram (ECG) and an increased risk of toxicity from other medications you may be using (digoxin) may also occur.
In case of overdose, consult your doctor or pharmacist immediately or call the Toxicology Information Service, phone 91 562 04 20, indicating the medication and the amount used.
If you forget to take Ventoduo
Do not take a double dose to make up for forgotten doses. Inhale the next dose when it is due.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Ventoduo can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. The following side effects are associated with Ventoduo, classified by frequency.
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- Oral candidiasis (thrush)
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Tremor, usually in the hands, which is related to the dose
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Hoarseness and/or throat irritation
- Tachycardia (rapid heart rate)
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Palpitations (rapid or irregular heart rate)
- Transient muscle cramps
- Skin rashes, urticaria, pruritus, and/or erythema, hypotension
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- Hypokalemia (low potassium levels in the blood)
The therapy with β2 agonists may lead to potentially severe hypokalemia, and this effect may be increased by the concomitant administration of salbutamol and a corticosteroid.
- Eosinophilic pneumonia (lung disorder)
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- Allergic reactions, which manifest with swelling of the eyelids, face, lips, and/or throat (angioedema)
- Respiratory disorders such as dyspnea (feeling of shortness of breath or difficulty breathing) and/or bronchospasm (narrowing of the bronchial walls with decreased air intake)
- Anaphylactic or anaphylactoid reactions (severe allergic reactions that can make breathing difficult or alter your level of consciousness)
- Ventoduo may increase the normal production of steroid hormones, particularly if you have been taking high doses for long periods. The effects include:
- Delayed growth in children and adolescents
- Decreased bone mineral density (weakening of bones)
- Cataracts and glaucoma (increased eye pressure)
- Cushing's syndrome (round face)
- Anxiety, sleep disorders, and mood changes, including hyperactivity and irritability (mainly in children)
- Cardiac arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, and extrasystoles (heart rhythm disorders)
Frequency not known
- Depression or aggression. These effects are more likely to occur in children.
- Myocardial ischemia (lack of blood flow to the heart)
- Blurred vision
In patients who experience hoarseness or throat irritation, it may be helpful to rinse their mouth with water immediately after inhalation.
As with other inhalation therapies, the possibility of paradoxical bronchospasm should be considered. Treatment with Ventoduo should be stopped immediately, the patient should be evaluated, and if necessary, alternative therapy should be initiated. This should be treated immediately with a rapid-acting bronchodilator administered by inhalation.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines. Website: www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storing Ventoduo
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not store above 30°C. Store in the original packaging to protect from light. Do not freeze.
The container is under pressure. It should not be pierced, broken, or burned, even if it appears to be empty.
If the inhaler is cold, remove the cartridge and warm it with your hand for a few minutes before use. Do not use any other method to heat it.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging after EXP. The expiry date is the last day of the month indicated.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Place the packaging and any unused medication in the pharmacy's SIGRE collection point. If in doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and any unused medication. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
Composition of Ventoduo
The active substances are: salbutamol (as sulfate) and beclometasone dipropionate.
The other ingredients are: oleic acid, ethanol, and 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane (HFA-134a).
Each puff contains 100 micrograms of salbutamol (as sulfate) and 50 micrograms of beclometasone dipropionate.
Appearance of the product and packaging contents
Ventoduo is presented in a 10 ml pressurized container (200 puffs) that releases the medication in the form of a suspension for inhalation.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Laboratorio ALDO-UNIÓN, S.L.
Baronesa de Maldá, 73
08950 Esplugues de Llobregat (Barcelona)
SPAIN
Date of last revision of this leaflet:August/2019
Other sources of information
Detailed and updated information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS)
http://www.aemps.gob.es/
- Country of registration
- Average pharmacy price8.85 EUR
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to VENTODUO 100 micrograms/50 micrograms/puff pressurized inhalation suspensionDosage form: PULMONARY INHALATION, 50 micrograms/250 microgramsActive substance: salmeterol and fluticasoneManufacturer: Sandoz Farmaceutica S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: PULMONARY INHALATION, 50 micrograms/500 microgramsActive substance: salmeterol and fluticasoneManufacturer: Sandoz Farmaceutica S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: PULMONARY INHALATION, 50 micrograms / 100 microgramsActive substance: salmeterol and fluticasoneManufacturer: Zentiva K.S.Prescription required
Online doctors for VENTODUO 100 micrograms/50 micrograms/puff pressurized inhalation suspension
Discuss questions about VENTODUO 100 micrograms/50 micrograms/puff pressurized inhalation suspension, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















