
SIMPONI 100 mg SOLUTION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED PEN

How to use SIMPONI 100 mg SOLUTION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED PEN
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Simponi 100mg solution for injection in pre-filled pen
golimumab
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
In addition, your doctor will give you a Patient Alert Card, which contains important safety information that you need to know before and during treatment with Simponi.
Contents of the pack
- What Simponi is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use Simponi
- How to use Simponi
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Simponi
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Simponi is and what it is used for
Simponi contains the active substance golimumab.
Simponi belongs to a group of medicines called “TNF blockers”. It is used in adultsto treat the following inflammatory diseases:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Axial spondyloarthritis, which includes ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis
- Ulcerative colitis
Simponi works by blocking the action of a protein called “tumour necrosis factor alpha” (TNF‑α). This protein is involved in inflammatory processes in the body, and blocking it can reduce inflammation in your body.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joints. If you have active rheumatoid arthritis, you will first be given other medicines. If you do not respond well to those medicines, you may be given Simponi in combination with another medicine called methotrexate to:
- Reduce the signs and symptoms of your disease.
- Slow down the damage to your bones and joints.
- Improve your physical function.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joints, usually accompanied by psoriasis, an inflammatory disease of the skin. If you have active psoriatic arthritis, you will first be given other medicines. If you do not respond well to those medicines, you may be given Simponi to:
- Reduce the signs and symptoms of your disease.
- Slow down the damage to your bones and joints.
- Improve your physical function.
Ankylosing Spondylitis and Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis
Ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis are inflammatory diseases of the spine. If you have ankylosing spondylitis or non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis, you will first be given other medicines. If you do not respond well to those medicines, you may be given Simponi to:
- Reduce the signs and symptoms of your disease
- Improve your physical function.
Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory disease of the intestine. If you have ulcerative colitis, you will first be given other medicines. If you do not respond well to those medicines, you may be given Simponi to treat your disease.
2. What you need to know before you use Simponi
Do not use Simponi
- If you are allergic (hypersensitive) to golimumab or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- If you have tuberculosis (TB) or any other severe infection.
- If you have moderate or severe heart failure.
If you are not sure if any of the above applies to you, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before using Simponi.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before starting treatment with Simponi.
Infections
Tell your doctor immediately if you already have or develop any symptoms of infection during or after treatment with Simponi. Symptoms of infection include fever, cough, difficulty breathing, flu-like symptoms, diarrhea, wounds, dental problems, or a burning sensation when urinating.
- While using Simponi, you may be more likely to get infections.
- Infections can progress more quickly and can be more severe. Additionally, some previous infections may recur.
Tuberculosis (TB)
Tell your doctor immediately if you develop symptoms of TB during or after treatment. Symptoms of TB include persistent cough, weight loss, tiredness, fever, or night sweats.
- There have been reports of tuberculosis in patients treated with Simponi, and in rare cases even in patients who have been treated for TB. Your doctor will perform tests to see if you have TB. Your doctor will record these tests on your Patient Alert Card.
- It is very important that you inform your doctor if you have ever had TB or if you have had close contact with someone who has had or has TB.
- If your doctor believes you are at risk of getting TB, you may be treated with TB medicines before starting treatment with Simponi.
Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
- Tell your doctor if you are a carrier or if you have had hepatitis B before you are given Simponi
- Tell your doctor if you think you may be at risk of getting HBV
- Your doctor must perform HBV tests
- Treatment with TNF blockers like Simponi may cause reactivation of the hepatitis B virus in people who carry this virus, which in some cases can be potentially fatal.
Invasive fungal infections
Tell your doctor immediately if you have lived in or traveled to areas where certain types of fungal infections are common (such as histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, or blastomycosis) that can affect the lungs or other parts of your body. If you are not sure if these infections are common in the area where you have lived or traveled, consult your doctor.
Cancer and lymphoma
Tell your doctor if you have ever been diagnosed with lymphoma (a type of blood cancer) or any other cancer before using Simponi.
- If you use Simponi or another TNF blocker, the risk of developing lymphoma or another cancer may be increased.
- Patients with severe rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases who have had the disease for a long time may have a higher than average risk of developing lymphoma.
- In children and adolescents treated with TNF blockers, there have been cases of cancer, some of which were rare and sometimes fatal.
- In rare cases, a serious and specific type of lymphoma called hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma has been observed in patients taking other TNF blockers. Most of these patients were male adolescents or young adults. This type of cancer is usually fatal. Almost all of these patients had also received medicines such as azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine. Tell your doctor if you are taking azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine with Simponi.
- Patients with severe persistent asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or heavy smokers may have a higher risk of developing cancer when treated with Simponi. If you have severe persistent asthma, COPD, or are a heavy smoker, you should consult your doctor to see if treatment with a TNF blocker is suitable for you.
- Some patients treated with golimumab have developed certain types of skin cancer. Tell your doctor if you notice any changes in the appearance of your skin or abnormal skin growth during or after treatment.
Heart failure
Tell your doctor immediately if you develop new symptoms of heart failure or if your existing symptoms worsen. Symptoms of heart failure include difficulty breathing or swelling of your feet.
- During treatment with TNF blockers, including Simponi, there have been reports of the onset or worsening of congestive heart failure. Some of these patients died.
- If you have mild heart failure and are being treated with Simponi, your doctor will monitor you closely.
Nervous system disease
Tell your doctor immediately if you have ever been diagnosed with or have developed symptoms of a demyelinating disease such as multiple sclerosis. Symptoms may include changes in your vision, weakness in your arms or legs, or numbness or tingling in any part of your body. Your doctor will decide if you should receive Simponi.
Surgery or dental procedures
- Tell your doctor if you are going to have any surgery or dental procedure.
- Tell the surgeon or dentist who is going to perform the procedure that you are being treated with Simponi and show them your Patient Alert Card.
Autoimmune disease
Tell your doctor if you develop symptoms of a disease called lupus. Symptoms include persistent rash, fever, joint pain, and tiredness.
- In rare cases, people treated with TNF blockers have developed lupus.
Blood disorders
In some patients, the body may stop producing enough blood cells that help your body fight infections or stop bleeding. If you develop persistent fever, bruising, or bleeding easily, or become pale, tell your doctor immediately. Your doctor may decide to stop treatment.
If you are not sure if any of the above applies to you, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using Simponi.
Vaccines
Tell your doctor if you have been vaccinated or are going to be vaccinated.
- You should not be vaccinated with certain vaccines (live vaccines) while using Simponi.
- Some vaccines may cause infections. If you received treatment with Simponi during pregnancy, your baby may have a higher risk of getting these infections until about 6 months after your last dose of Simponi. It is important that you inform your baby's doctors and other healthcare professionals about your treatment with Simponi so they can decide when your baby should be vaccinated.
Therapeutic infectious agents
Tell your doctor if you have recently received or are going to receive treatment with therapeutic infectious agents (such as BCG instillation used for cancer treatment).
Allergic reactions
Tell your doctor immediately if you develop symptoms of an allergic reaction after treatment with Simponi. Symptoms of an allergic reaction can be swelling of the face, lips, mouth, or throat that can cause difficulty swallowing or breathing, skin rash, hives, swelling of the hands, feet, or ankles.
- Some of these reactions can be serious or, in rare cases, potentially fatal.
- Some of these reactions occurred after the first administration of Simponi.
Children and adolescents
Simponi 100 mg is not recommended for children and adolescents (under 18 years of age).
Other medicines and Simponi
- Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines, including other medicines to treat rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis, or ulcerative colitis.
- You must not use Simponi with medicines that contain the active substance anakinra or abatacept. These medicines are used to treat rheumatic diseases.
- Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using any other medicine that affects your immune system.
- You must not receive some vaccines (live vaccines) while being treated with Simponi.
If you are not sure if you are using any of the above medicines, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using Simponi.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Consult your doctor before using Simponi if:
- You are pregnant or plan to become pregnant while using Simponi. There is limited information on the effects of this medicine in pregnant women. If you are treated with Simponi, you should avoid becoming pregnant by using adequate contraceptive methods during treatment and for at least 6 months after the last injection of Simponi. You should only use Simponi during pregnancy if it is strictly necessary for you.
- Before starting breastfeeding, at least 6 months must have passed since your last treatment with Simponi. You must stop breastfeeding if you are given Simponi.
- If you received treatment with Simponi during pregnancy, your baby may have a higher risk of getting an infection. It is important that you inform your baby's doctors and other healthcare professionals about your treatment with Simponi before your baby is vaccinated (for more information, see the section on vaccines).
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Simponi has a minor influence on your ability to drive and use tools or machines. However, dizziness may occur after administration of Simponi. If this happens, do not drive or use any tools or machines.
Simponi contains latex and sorbitol
Latex sensitivity
A part of the pre-filled pen, the needle cap, contains latex. As latex can cause severe allergic reactions, consult your doctor before using Simponi if you or your caregiver are allergic to latex.
Sorbitol intolerance
This medicine contains 41 mg of sorbitol (E-420) in each pre-filled pen.
3. How to use Simponi
Follow the instructions for administration of this medicine exactly as told by your doctor or pharmacist. If you are not sure, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
How much Simponi is given
Rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and axial spondyloarthritis, which includes ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis:
- The recommended dose is 50 mg given once a month, on the same day each month.
- Consult your doctor before the fourth dose is given. Your doctor will decide if you should continue treatment with Simponi.
- If you weigh more than 100 kg, the dose may be increased to 100 mg (the content of 1 pre-filled pen) given once a month, on the same day each month.
Ulcerative colitis
- The following table shows how you will usually use this medicine.
Initial treatment | An initial dose of 200 mg (the content of 2 pre-filled pens) followed by 100 mg (the content of 1 pre-filled pen) 2 weeks later. |
Maintenance treatment |
|
How Simponi is given
- Simponi is given by injection under the skin (subcutaneously).
- At first, your doctor or nurse may give you Simponi. However, you and your doctor may decide that you can self-inject Simponi. In this case, you will be shown how to self-inject Simponi.
Consult your doctor if you have any questions about how to self-administer an injection. At the end of this leaflet, you will find detailed “Instructions for Use”.
If you use more Simponi than you should
If you have used or been given too much Simponi (by injecting too much at one time or using it too frequently), consult your doctor or pharmacist immediately. Always carry the outer packaging with you, even if it is empty, and this leaflet.
If you forget to use Simponi
If you miss a dose of Simponi on the scheduled date, inject the missed dose as soon as you remember.
Do not give yourself a double dose to make up for missed doses.
When to inject the next dose:
- If the dose is delayed by less than 2 weeks, inject the missed dose as soon as you remember and keep your original schedule.
- If the dose is delayed by more than 2 weeks, inject the missed dose as soon as you remember and consult your doctor or pharmacist when the next dose should be given.
If you are not sure what to do, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
If you stop treatment with Simponi
If you are thinking of stopping treatment with Simponi, consult your doctor or pharmacist first.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them. Some patients may experience serious adverse effects and may require treatment. The risk of certain adverse effects is higher with the 100 mg dose compared to the 50 mg dose. Adverse effects may appear up to several months after the last injection.
Inform your doctor immediately if you notice any of the serious adverse effects of Simponi, including:
- Allergic reactions that can be severe, or rarely, potentially life-threatening (rare).Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include swelling of the face, lips, mouth, or throat that can cause difficulty swallowing or breathing, skin rash, hives, swelling of the hands, feet, or ankles. Some of these reactions occurred after the first administration of Simponi.
- Severe infections (including tuberculosis, bacterial infections that include severe blood and pneumonia infections, severe fungal infections, and other opportunistic infections) (frequent).Symptoms of an infection may include fever, fatigue, cough (persistent), difficulty breathing, flu-like symptoms, weight loss, night sweats, diarrhea, wounds, dental problems, and a burning sensation when urinating.
- Reactivation of the hepatitis B virus if you are a carrier or have had hepatitis B previously (rare).Symptoms may include yellow eyes and skin, dark brown urine, abdominal pain on the right side, fever, dizziness, vomiting, and a feeling of extreme fatigue.
- Nervous system disease such as multiple sclerosis (rare).Symptoms of nervous system disease may include vision disturbances, weakness in arms or legs, numbness or tingling of any part of your body.
- Lymph node cancer (lymphoma) (rare).Symptoms of lymphoma may include swelling of the lymph nodes, weight loss, or fever.
- Heart failure (rare).Symptoms of heart failure may include difficulty breathing or swelling of your feet.
- Signs of immune system disorders called:
- Lupus (rare).Symptoms may include joint pain or a skin rash on the cheeks or arms that is sensitive to the sun.
- Sarcoidosis (rare).Symptoms may include persistent cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, fever, swelling of the lymph nodes, weight loss, skin rashes, and blurred vision.
- Swelling of small blood vessels (vasculitis) (rare).Symptoms may include fever, headache, weight loss, night sweats, skin rash, and nerve problems such as numbness and tingling.
- Skin cancer (uncommon).Symptoms of skin cancer may include changes in the appearance of the skin or abnormal skin growth.
- Blood disease (frequent).Symptoms of blood disease may include persistent fever, bruising, or easy bleeding or presence of paleness.
- Blood cancer (leukemia) (rare).Symptoms of leukemia may include fever, feeling of fatigue, frequent infections, easy bruising, and night sweats.
Inform your doctor immediately if you notice any of the above symptoms.
The following additional adverse effects have been observed with Simponi:
Very frequent adverse effects (may affect more than 1 in 10 patients):
- Upper respiratory tract infections, sore throat or hoarseness, runny nose
Frequent adverse effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 patients):
- Alteration of liver tests (increase in liver enzymes) detected during blood tests that your doctor requested
- Feeling of dizziness
- Headache
- Feeling of numbness or tingling
- Superficial fungal infections
- Abscess
- Bacterial infections (such as cellulitis)
- Low red blood cell count
- Low white blood cell count
- Positive blood test for lupus
- Allergic reactions
- Indigestion
- Stomach pain
- Feeling of dizziness (nausea)
- Flu
- Bronchitis
- Sinusitis
- Herpes
- High blood pressure
- Fever
- Asthma, feeling of shortness of breath, difficulty breathing
- Stomach and intestine disorders that include inflammation of the stomach and colon lining that can cause fever
- Pain and sores in the mouth
- Reactions at the injection site (including redness, hardness, pain, bruising, itching, tingling, and irritation)
- Hair loss
- Skin rash and itching
- Difficulty sleeping
- Depression
- Weakness
- Bone fractures
- Chest discomfort
Uncommon adverse effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 patients):
- Kidney infection
- Cancers, such as skin cancer and non-cancerous tumors or lumps, including moles
- Blisters on the skin
- Severe whole-body infection (sepsis), which sometimes includes low blood pressure (septic shock)
- Psoriasis (even on the palms of the hands and/or soles of the feet and/or of the type that presents with blisters on the skin)
- Low platelet count
- Low combined count of platelets, red and white blood cells
- Thyroid disorders
- Increased blood sugar levels
- Increased blood cholesterol levels
- Balance disorders
- Visual disturbances
- Eye inflammation (conjunctivitis)
- Eye allergy
- Feeling of irregular heartbeat
- Narrowing of the heart's blood vessels
- Blood clots
- Flushing
- Constipation
- Chronic inflammatory lung disease
- Reflux
- Gallstones
- Liver disorders
- Breast disorders
- Menstrual cycle disorders
Rare adverse effects (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 patients):
- Failure of the bone marrow to produce blood cells
- Severe decrease in the number of white blood cells in the blood
- Infection of the joints or the tissue surrounding them
- Healing problems
- Inflammation of blood vessels in internal organs
- Leukemia
- Melanoma (a type of skin cancer)
- Merkel cell carcinoma (a type of skin cancer)
- Lichenoid reactions (pruritic reddish-purple rash and/or thick white-gray lines on the mucous membranes)
- Scaly and flaky skin
- Immune system disorders that could affect the lungs, skin, and lymph nodes (usually presented as sarcoidosis).
- Pain and discoloration in the fingers or toes
- Taste disturbances
- Bladder disorders
- Kidney disorders
- Inflammation of blood vessels in the skin that produces a rash
Adverse effects with unknown frequency:
- A rare blood cancer that mainly affects young people (hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma)
- Kaposi's sarcoma, a rare cancer related to human herpesvirus 8 infection. Kaposi's sarcoma usually manifests more frequently as purple skin lesions
- Worsening of a disease called dermatomyositis (which manifests as a skin rash accompanied by muscle weakness)
Reporting of Adverse Effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is a possible adverse effect that is not listed in this prospectus. You can also report them directly through the national reporting system included in Appendix V. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Simponi
- Keep this medicine out of sight and reach of children.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiration date that appears on the label and on the packaging after "EXP". The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
- Store in a refrigerator (between 2°C and 8°C). Do not freeze.
- Keep the pre-loaded pen in the outer packaging to protect it from light.
- This medicine can also be stored outside the refrigerator at a temperature of up to a maximum of 25°C for a single period of up to 30 days, but not beyond the initial expiration date printed on the box. Write the new expiration date on the box, including day/month/year (not more than 30 days after the medicine is removed from the refrigerator). If it has reached room temperature, do not return this medicine to the refrigerator. Discard this medicine if it has not been used by the new expiration date or the expiration date printed on the box, whichever occurs first.
- Do not use this medicine if you observe that the liquid is not transparent or clear yellow, cloudy, or contains foreign particles.
- Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your doctor or pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Composition ofSimponi
The active substance is golimumab. A 1 ml pre-filled pen contains 100 mg of golimumab.
The other ingredients are sorbitol (E-420), histidine, histidine hydrochloride monohydrate, polysorbate 80, and water for injections. For more information on sorbitol (E-420), see section 2.
Appearance and Container Contents of the Product
Simponi is presented as a solution for injection in a single-use pre-filled pen. Simponi is available in packs containing 1 pre-filled pen and multiple packs containing 3 pre-filled pens (3 packs of 1). Only certain pack sizes may be marketed.
The solution is between transparent and slightly opalescent (with a pearlescent sheen), colorless to light yellow, and may contain a few small translucent or white protein particles. Do not use Simponi if the solution changes color, is cloudy, or if foreign particles are observed in it.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Janssen Biologics B.V.
Einsteinweg 101
2333 CB Leiden
Netherlands
You can request more information about this medicine by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorisation holder:
Belgium/Belgique/Belgien MSD Belgium Tel: +32(0)27766211 | Lithuania UAB Merck Sharp & Dohme Tel: + 370 5 278 02 47 |
Bulgaria Merck Sharp & Dohme Bulgaria EOOD Tel: +359 2 819 3737 | Luxembourg/Luxemburg MSD Belgium Tel: (+32(0)27766211) |
Czech Republic Merck Sharp & Dohme s.r.o. Tel: +420 233 010 111 | Hungary MSD Pharma Hungary Kft. Tel: +36 1 888 5300 |
Denmark MSD Danmark ApS Tel: + 45 4482 4000 | Malta Merck Sharp & Dohme Cyprus Limited Tel: 8007 4433 (+356 99917558) |
Germany MSD Sharp & Dohme GmbH Tel: 0800 673 673 673 (+49 (0) 89 4561 0) | Netherlands Merck Sharp & Dohme B.V. Tel: 0800 9999000 (+31 23 5153153) |
Estonia Merck Sharp & Dohme OÜ Tel: +372 6144 200 | Norway MSD (Norge) AS Tel: +47 32 20 73 00 |
Greece MSD Α.Φ.Β.Ε.Ε. Tel: +30 210 98 97 300 | Austria Merck Sharp & Dohme Ges.m.b.H. Tel: +43 (0) 1 26 044 |
Spain Merck Sharp & Dohme de España, S.A. Tel: +34 91 321 06 00 | Poland MSD Polska Sp. z o.o. Tel: +48 22 549 51 00 |
France MSD France Tel: + 33 (0) 1 80 46 40 40 | Portugal Merck Sharp & Dohme, Lda Tel: +351 21 4465700 |
Croatia Merck Sharp & Dohme d.o.o. Tel: + 385 1 6611 333 | Romania Merck Sharp & Dohme Romania S.R.L. Tel: +40 21 529 29 00 |
Ireland Merck Sharp & Dohme Ireland (Human Health) Limited Tel: +353 (0)1 2998700 | Slovenia Merck Sharp & Dohme, inovativna zdravila d.o.o. Tel: +386 1 5204 201 |
Iceland Vistor hf. Tel: + 354 535 7000 | Slovak Republic Merck Sharp & Dohme, s. r. o. Tel: +421 2 58282010 |
Italy MSD Italia S.r.l. Tel: 800 23 99 89 (+39 06 361911) | Finland MSD Finland Oy Tel: +358 (0)9 804 650 |
Cyprus Merck Sharp & Dohme Cyprus Limited Tel: 800 00 673 (+357 22866700) | Sweden Merck Sharp & Dohme (Sweden) AB Tel: +46 77 5700488 |
Latvia SIA Merck Sharp & Dohme Latvija Tel: + 371 67364224 | United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) Merck Sharp & Dohme Ireland (Human Health) Limited Tel: +35312998700 |
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet:
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency website: http://www.ema.europa.eu.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
If you want to inject Simponi yourself, you must be taught how to prepare the injection and inject yourself by a healthcare professional. If you have not been taught, contact your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist to schedule a training session.
In these instructions:
- Preparation for using the pre-filled pen
- Selection and preparation of the injection site
- Injection of the medicine
- After the injection
The following diagram (see Figure 1) shows what the "SmartJect" pre-filled pen looks like.
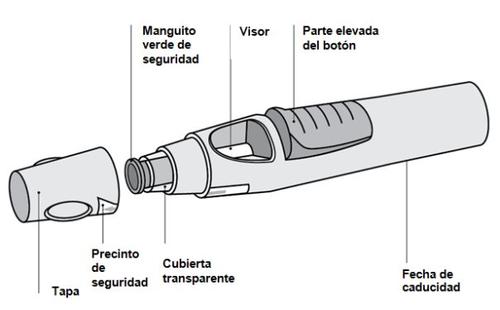
Figure 1
- Preparation for using the pre-filled pen
- Do not shake the pre-filled pen at any time.
- Do not remove the cap from the pre-filled pen until immediately before injection.
- Do not replace the cap on the pre-filled pen if you have removed it, to avoid bending the needle.
Check the number of pre-filled pens
Check the pre-filled pens to ensure that
- The number of pre-filled pens and the dose is correct
- If your dose is 100 mg, you will receive one 100 mg pre-filled pen
- If your dose is 200 mg, you will receive two 100 mg pre-filled pens and you will need to administer two injections yourself. Choose different injection sites for these injections and administer the injections one after the other.
Check the expiration date
- Check the expiration date printed or written on the carton.
- Check the expiration date (indicated by "EXP") on the pre-filled pen.
- Do not use the pre-filled pen if the expiration date has passed. The printed expiration date is the last day of the month indicated. Consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Check the safety seal
- Check the safety seal around the cap of the pre-filled pen.
- Do not use the pre-filled pen if the seal is broken. Consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Wait for 30 minutes to allow the pre-filled pen to reach room temperature
- To ensure proper injection, leave the pre-filled pen at room temperature outside the carton for 30 minutes, out of reach of children.
- Do not use any other method to heat the pre-filled pen (e.g., do not heat it in the microwave or in hot water).
- Do not remove the cap from the pre-filled pen while waiting for it to reach room temperature.
Prepare the rest of the materials
- While waiting, prepare the rest of the materials you need, such as an alcohol swab, a cotton ball, or gauze and a sharps container.
Check the liquid in the pre-filled pen
- Look through the viewer to check that the liquid in the pre-filled pen is between transparent and slightly opalescent (with a pearlescent sheen) and colorless to light yellow. The solution can be used if it contains a few small translucent or white protein particles.
- You will also see an air bubble, which is normal.
- Do not use the pre-filled pen if the liquid has an unusual color, is cloudy, or contains large particles. In such cases, inform your doctor or pharmacist.
- Selection and preparation of the injection site (see Figure 2)
- The medicine can be injected into the middle of the thigh.
- It can also be injected into the abdomen below the navel, except for the area of about 5 cm immediately below the navel.
- Do not inject into areas where the skin is sensitive, bruised, red, scaly, hard, or has scars or stretch marks.
- If multiple injections are needed for a single dose, the injections will be administered in different injection sites.
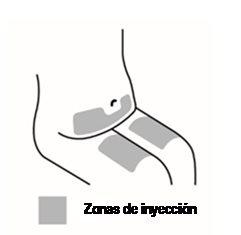
Figure 2
DO NOTinject into the arm to avoid failure of the pre-filled pen and/or accidental injuries.
Wash your hands and clean the injection site
- Wash your hands well with soap and warm water.
- Clean the injection site with an alcohol swab.
- Let the skin dry before injection. Do not fan or blow on the cleaned area.
- Do not touch that area again until you put the injection.
- Injection of the medicine
- Do not remove the cap until you are ready to inject the medicine.
- The medicine should be injected within 5 minutes of removing the cap.
Remove the cap (Figure 3)
- When you are ready, gently turn the cap to break the safety seal.
- Remove the cap and dispose of it after injection.
- Do not replace the cap because it may damage the needle inside the pre-filled pen.
- Do not use the pre-filled pen if it has fallen without the cap. If this happens, inform your doctor or pharmacist.
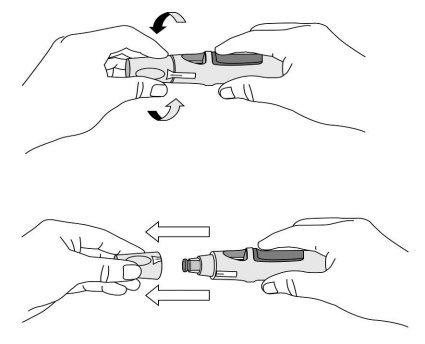
Figure 3
Push the pre-filled pen against the skin (see Figures 4 and 5) without pinching the skin.
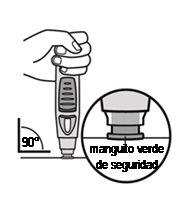
Figure 4
- Hold the pre-filled pen relaxedly with one hand above the blue button.
- Make sure the green safety sleeve is stable and as flat as possible against your skin. If the pre-filled pen is not stable during injection, you risk bending the needle.
- DO NOTpinch the skin to avoid accidental needlestick injuries.
- DO NOTtouch or press the blue button while placing the pre-filled pen on your skin.
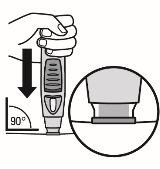
Figure 5
- Push the open end of the pre-filled pen against the skin at a 90-degree angle. Press until the green safety sleeve slides up and stays inside the transparent cover. Only the widest part of the green safety sleeve remains outside the transparent cover.
- DO NOTpress the blue button until the safety sleeve is slid inside the transparent cover. Pressing the blue button before the safety sleeve is retracted may cause the pen to fail.
- Perform the injection without pinching the skin.
Press the injection button (see Figures 6 and 7)
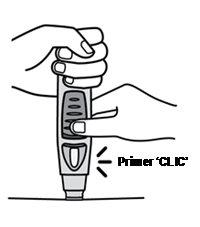
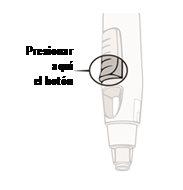
Figure 6 Figure 7
- Keep the pre-filled pen pressed against the skin.To start the injection, use your other handto press the raised part of the blue button. Do not press the button unless the pre-filled pen is pressed against the skinand the safety sleeve is slid inside the transparent cover.
- Once the button is pressed, it will remain pressed and does not need to be pressed further.
- If it seems difficult to press the button, do not press the button with more force. Release the button, lift the pre-filled pen, and start again. Make sure there is no pressure on the button until the green safety sleeve is fully retracted against the skin, then press the raised part of the blue button.
- You will hear a loud sound, a "click" - do not be alarmed.The first "click" indicates that the needle has been inserted and the injection has started. You may not feel the needle prick at this time.
Do not lift the pre-filled pen from the skin. If you remove the pre-filled pen from the skin, you may not receive the full dose.
Continue holding until the second "click" (see Figure 8), this usually takes between 3 and 6 seconds, but it may take up to 15 seconds until you hear the second "click".
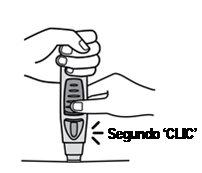
Figure 8
- Keep the pre-filled pen against the skin until you hear a second "click" (indicating that the injection is complete and the needle has retracted into the pre-filled pen).
- Lift the pre-filled pen from the injection site.
- Note: If you do not hear the second "click", wait 15 seconds from the moment you first pressed the button and then lift the auto-injector from the injection site.
- After the injection
Use a cotton ball or gauze
- You may see a little blood or liquid at the injection site. This is normal.
- With a cotton ball or gauze, press on the injection site for 10 seconds.
- If necessary, cover the injection site with a small adhesive bandage.
- Do not rub the skin.
Check the viewer - a yellow indicator confirms proper administration (see Figure 9)
- The yellow indicator is connected to the plunger of the pre-filled pen. If the yellow indicator does not appear in the viewer, the plunger has not moved properly, and the injection has not occurred.
- The yellow indicator will fill almost half of the viewer. This is normal.
- If the yellow indicator does not appear in the viewer, or if you suspect that you may not have received a full dose, inform your doctor or pharmacist. Do not administer a second dose without consulting your doctor.
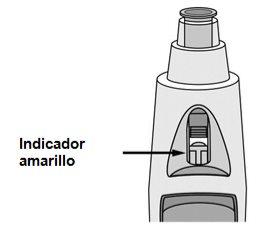
Figure 9
Dispose of the pre-filled pen (see Figure 10)
- Then, place the pre-filled pen in a sharps container. Follow the instructions of your doctor or nurse to dispose of the container when it is full.
If you think something has gone wrong during the injection or have any doubts, inform your doctor or pharmacist.
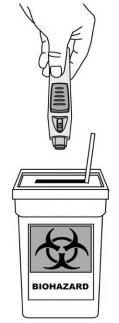
Figure 10
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to SIMPONI 100 mg SOLUTION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED PENDosage form: INJECTABLE, 50 mgActive substance: golimumabManufacturer: Janssen Biologics B.V.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 20 mgActive substance: adalimumabManufacturer: Amgen Europe B.V.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 20 mgActive substance: adalimumabManufacturer: Amgen Europe B.V.Prescription required
Online doctors for SIMPONI 100 mg SOLUTION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED PEN
Discuss questions about SIMPONI 100 mg SOLUTION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED PEN, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions






