
PACLITAXEL KABI 6 mg/ml CONCENTRATE FOR INFUSION SOLUTION

How to use PACLITAXEL KABI 6 mg/ml CONCENTRATE FOR INFUSION SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Paclitaxel Kabi 6mg/ml concentrate for solution for infusion EFG
The name of your medicine is 'Paclitaxel Kabi 6 mg/ml concentrate for solution for infusion EFG' but in the rest of the package leaflet it will be called 'Paclitaxel Kabi'.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or nurse.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack:
- What is Paclitaxel Kabi and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Paclitaxel Kabi
- How to use Paclitaxel Kabi
- Possible side effects
5 Conservation of Paclitaxel Kabi
- Pack contents and additional information
1. What is Paclitaxel Kabi and what is it used for
Paclitaxel Kabi belongs to a group of anti-cancer medicines called taxanes. These agents inhibit the growth of cancer cells.
Paclitaxel Kabi is used to treat:
Ovarian cancer
- as first-line treatment (after initial surgery in combination with the platinum-based drug cisplatin)
- after the reference treatment with platinum-based drugs has not worked.
Breast cancer
- as first-line treatment for advanced or metastatic cancer. Paclitaxel Kabi is combined with an anthracycline(e.g. doxorubicin) or with a drug called trastuzumab(for patients who are not indicated for anthracyclines or who have cancer cells with a protein on their surface called HER2; see the trastuzumab package leaflet).
- as additional treatment with anthracycline and cyclophosphamide (AC).
- as second-line treatment for patients who have not responded to anthracycline-based treatments or who cannot use these treatments.
Advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- in combination with cisplatin, when surgery, radiotherapy, or both are not indicated.
AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma
- after another treatment (e.g. liposomal anthracyclines) has not worked.
2. What you need to know before you use Paclitaxel Kabi
You should not be given Paclitaxel Kabi
- if you are allergicto paclitaxel or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6), especially to castor oil (macrogolglycerol ricinoleate).
- if you are breast-feeding
- if you have very low white blood cell counts(basal neutrophil count <1.5 x 10^9/l or <1.0 x 10^9/l for patients with Kaposi's sarcoma; your doctor will inform you about this). Your doctor will take a blood sample to check this.
- if you have a severe and uncontrolled infection(except in the case of Kaposi's sarcoma).
If you are in any of the above situations, talk to your doctor before starting treatment with Paclitaxel Kabi.
Paclitaxel Kabi is not recommendedfor use in children and adolescents(under 18 years).
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor before starting treatment with Paclitaxel Kabi.
Before starting treatment with Paclitaxel Kabi, you will be given other medicines to minimize the risk of allergic reactions.
- if you experience allergic reactions (e.g. difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, low blood pressure, dizziness, feeling of dizziness, skin reactions such as rash or inflammation).
- if you have a fever, severe chills, sore throat, or mouth ulcers (signs of bone marrow suppression),
- if you experience numbness, tingling, prickling sensationsin the skin, sensitivity to touch or weaknessin arms and legs(signs of peripheral neuropathy); a dose reduction of Paclitaxel Kabi may be necessary
- if you have severe liver problems; in this case, the use of Paclitaxel Kabi is not recommended
- if you have conduction disorders.
- if you develop severe or persistent diarrheawith fever and stomach pain, during treatment with Paclitaxel Kabi or immediately after its administration. You may have inflammation of the colon (pseudomembranous colitis).,
- if you have previously received radiotherapy to the chest(since it may increase the risk of pulmonary inflammation)
- if you have mouth sores or redness(signs of mucositis) and are being treated for Kaposi's sarcoma.You may need a lower dose.
Due to the possibility of extravasation, it is recommended to strictly monitor the infusion site for possible infiltration during the administration of the medicine.
Tell your doctor immediately if any of these cases apply to you.
Paclitaxel Kabi should always be administered into a vein. Administration of Paclitaxel Kabi into an artery can cause inflammation of the artery and you may experience pain, inflammation, redness, and heat.
Using Paclitaxel Kabi with other medicines
Talk to your doctor when taking paclitaxel at the same time as:
- medicines to treat infections (i.e. antibiotics such as erythromycin, rifampicin, etc.; ask your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist if you are not sure if the medicine you are taking is an antibiotic), including medicines to treat fungal infections (e.g. ketoconazole)
- medicines used to help stabilize your mood, sometimes called antidepressants (e.g. fluoxetine)
- medicines used to treat seizures (epilepsy) (e.g. carbamazepine, phenytoin)
- medicines used to help lower lipid levels in the blood (e.g. gemfibrozil)
- medicines used to treat stomach ulcers or heartburn (e.g. cimetidine)
- medicines used to treat HIV or AIDS (e.g. ritonavir, saquinavir, indinavir, nelfinavir, efavirenz, nevirapine)
- a medicine called clopidogrel used to prevent blood clots.
The amount of alcohol in this medicine may alter the effects of other medicines. Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking other medicines.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding, and fertility
Pregnancy
Before receiving treatment with Paclitaxel, tell your doctor if you are pregnantor think you may be. If you may become pregnant, use a safe and effective contraceptive method during treatment. Paclitaxel should not be used during pregnancy, unless clearly necessary. Men and women of childbearing age, and/or their partners,
should use contraceptive methods during at least the 6 months following the end of treatment with paclitaxel. Male patients should ask about sperm freezing before treatment with paclitaxel, due to the possibility of irreversible infertility.
Breast-feeding
If you are breast-feeding, tell your doctor.It is not known if paclitaxel is excreted in breast milk. Given the possibility of harming the baby, stop breast-feeding if you are receiving Paclitaxel Kabi. Do not restart breast-feeding until your doctor tells you to.
Driving and using machines
There is no reason why you cannot drive between Paclitaxel Kabi cycles, but you should remember that this medicine contains alcohol and it may be inadvisable to drive immediately after a treatment cycle due to the possible effects on the central nervous system. As with all cases, you should not drive or use machines if you feel dizzy or drowsy. Paclitaxel Kabi contains castor oil which may cause allergic reactions. If you are allergic to castor oil, talk to your doctor before receiving Paclitaxel Kabi.
The amount of alcohol in this medicine may affect your ability to drive or use machines. This is because it may affect your judgment and reaction speed.
Paclitaxel Kabi contains castor oil (macrogolglycerol ricinoleate) and alcohol.
Paclitaxel Kabi contains castor oil and may cause severe allergic reactions. If you are allergic to castor oil, talk to your doctor before receiving Paclitaxel Kabi.
This medicine contains 393 mg of alcohol (ethanol) per 1 ml, which is equivalent to 39.3% p/v. The amount in 52.5 ml of this medicine is equivalent to 515.8 ml of beer or 206.3 ml of wine.
If you have epilepsy or liver problems, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine.
If you are addicted to alcohol, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine.
3. How to use Paclitaxel Kabi
- To minimize the risk of allergic reactions,before starting treatment with Paclitaxel Kabi, you will be given other medicines. These medicines may be administered in the form of tablets or intravenous infusion, or both.
- Paclitaxel Kabi will be administered to you by dripinto one of your veins (intravenous infusion), through an in-line filter. It will be administered by a healthcare professional who will prepare the infusion solution before administering it to you. The dose you receive will also depend on the results of your blood tests. Depending on the type and severity of the cancer, you will receive Paclitaxel Kabi alone or in combination with another anti-cancer agent.
- Paclitaxel Kabi should always be administered into a vein over a period of 3 to 24 hours. It is usually administered every 2 or 3 weeks, unless your doctor indicates a different dosing schedule. Your doctor will inform you of the number of treatment cycles with Paclitaxel Kabi that you need to receive.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
If you consider that you are suffering from any sign of an allergic reaction, inform your doctor immediately.You may experience one or more of the following signs:
- redness (rubefaction)
- skin reactions
- itching (pruritus)
- chest tightness
- shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- inflammation
All of these can be signs of serious adverse effects.
Inform your doctor immediately if you experience:
- fever, severe chills, sore throat, or mouth ulcers(signs of bone marrow suppression).
- numbness or weakness in arms and legs(symptoms of peripheral neuropathy).
- severe or persistent diarrhea, with fever and stomach pain.
Very Common Adverse Effects: may affect more than 1 in 10 people
- Mild allergic reactions, such as redness (rubefaction), rash (exanthema), itching (pruritus)
- Infections: mainly upper respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections
- Sore throat or mouth ulcers, mouth sores and redness, diarrhea, discomfort (nausea, vomiting).
- Hair loss (most cases of hair loss occurred less than a month after starting paclitaxel. When it occurs, it is a pronounced hair loss (over 50%) in most patients).
- Muscle pain, cramps, joint pain
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in arms and legs (all symptoms of peripheral neuropathy) *
- *May persist for more than 6 months after discontinuation of paclitaxel treatment
- Analytical tests may show: decreased platelets that can cause bleeding or bruising more easily than normal, decreased white blood cells or red blood cells, low blood pressure
Common Adverse Effects: may affect up to 1 in 10 people
- Mild and transient changes in nails and skin, reactions at the injection site (localized inflammation, pain, and redness of the skin)
- Analytical tests may show: slowing of heart rate, severe elevation of liver enzymes (alkaline phosphatase and AST-SGOT)
Uncommon Adverse Effects: may affect up to 1 in 100 people
- Shockdue to infections (known as "septic shock")
- Palpitations, heart dysfunction (AV block, cardiomyopathy), rapid heartbeat, infarction, respiratory distress
- Fatigue, sweating, syncope, significant allergic reactions, phlebitis (inflammation of a vein), swelling of the face, lips, mouth, or throat
- Back pain, chest pain, pain in hands and feet, chills, abdominal pain (stomach)
- Analytical tests may show: significant elevation of bilirubin (jaundice), high blood pressure, and blood clots
Rare Adverse Effects: may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people.
- Decrease in white blood cells, with fever and increased risk of infection (febrile neutropenia)
- Affecting the nerves, with a feeling of weakness in the muscles of the arms and legs (motor neuropathy)
- Heart failure (heart failure)
- Shortness of breath, narrowing, and blockage of blood vessels in the lungs that can cause shortness of breath (pulmonary embolism), inflammatory reaction of lung tissue with changes and hardening of tissue (pulmonary fibrosis), inflammation of the lungs (interstitial pneumonia), difficulty breathing, lung damage, and fluid around the lungs (pleural effusion)
- Intestinal obstruction, intestinal perforation, inflammation of the colon (ischemic colitis), inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis)
- Itching (pruritus), rashes (exanthema), redness of the skin (erythema)
- Blood infection (septicemia), inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis), pneumonia
- Fever (pyrexia), dehydration, weakness (asthenia), accumulation of fluid in body tissues (edema), discomfort
- Severe and potentially life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions (anaphylactic reactions)
- Analytical tests may show: increased creatinine in blood, indicating kidney dysfunction
Very Rare Adverse Effects: may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people.
- Rapid and irregular heart rhythm (atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia)
- Sudden disorder in hematopoietic cells (acute myeloid leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome)
- Visual disturbances and/or optic nerve (scintillating scotoma)
- Hearing loss (ototoxicity), ringing in the ears (tinnitus), vertigo
- Cough
- Blood clot in a blood vessel in the abdomen and intestine (mesenteric thrombosis), colon inflammation, sometimes with severe persistent diarrhea (pseudomembranous colitis, neutropenic colitis), fluid retention in the abdomen (ascites), esophagus inflammation (esophagitis), constipation
- Severe hypersensitivity reactions, such as fever, skin redness, joint pain, and/or eye inflammation (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), local skin exfoliation (necrotizing epidermolysis), redness with irregular red spots (erythema multiforme), skin inflammation with blisters and peeling (exfoliative dermatitis), hives, onycholysis (patients under treatment should wear sun protection on hands and feet)
- Lack of appetite (anorexia)
- Severe and potentially life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions with shock(anaphylactic reactions)
- Liver function changes (liver necrosis, hepatic encephalopathy [both with reported fatal outcomes])
- State of confusion.
- Grand mal seizures, disorder of the brain nerves (autonomic neuropathy, alteration of involuntary body functions, which can produce ileus and low blood pressure), seizures, brain disease (encephalopathy), dizziness, headache, coordination problems (ataxia)
Adverse Effects of Unknown Frequency: the frequency cannot be estimated from the available data
- Rapid destruction of tumor cells (tumor lysis syndrome)
- Fluid accumulation in the eyes (macular edema), flashes in the eyes (photopsia), small spots or particles floating in the visual field (vitreous floaters)
- Inflammation of the veins (phlebitis)
- Narrowing and hardening of the skin as well as blood vessels and internal organs (scleroderma)
- "Butterfly-shaped rash" (systemic lupus erythematosus)
- Blood clotting disorders. Disseminated intravascular coagulation or "DIC" has been reported. This is a serious condition that causes bleeding or blood clots, or both.
- Redness and swelling of the palms of the hands and soles of the feet that can cause skin peeling
Reporting of Adverse Effects:
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor, even if it is a possible adverse effect that is not listed in this prospectus. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Conservation of Paclitaxel Kabi
Keep this medicine out of sight and reach of children.
Do not store at a temperature above 25°C.
Keep the vial in the outer packaging to protect it from light.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date that appears on the packaging after CAD. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Do not use this medicine if a turbid solution or an insoluble precipitate is observed.
Medicines should not be thrown away through drains or waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of packaging and medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Composition ofPaclitaxel Kabi
- The active ingredient is paclitaxel
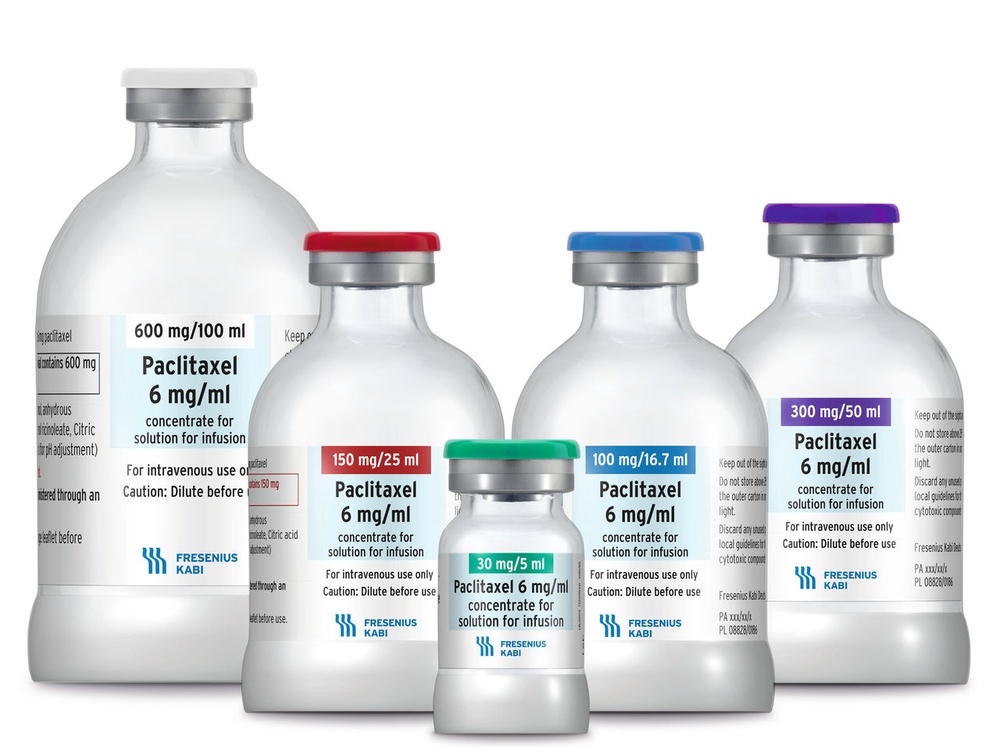
Each ml of concentrate for solution for infusion contains 6 mg of paclitaxel.
A 5 ml vial contains 30 mg of paclitaxel
A 16.7 ml vial contains 100 mg of paclitaxel
A 25 ml vial contains 150 mg of paclitaxel
A 50 ml vial contains 300 mg of paclitaxel
A 100 ml vial contains 600 mg of paclitaxel.
- The other components are anhydrous ethanol, macrogolglycerol ricinoleate, and anhydrous citric acid (to adjust the pH).
Appearance of the Product and Package Contents
Concentrate for solution for infusion
Paclitaxel is a clear, slightly yellowish solution.
Paclitaxel is available in glass vials. The glass vials are closed with chlorobutyl or bromobutyl rubber stoppers with an aluminum seal and a removable plastic cap.
Package sizes: packages containing 1 or 5 glass vials.
Not all package sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder
Fresenius Kabi España S.A.U.
C/ Marina 16-18
08005 Barcelona (Spain)
Manufacturer
Fresenius Kabi Deutschland GmbH
Pfingstweide 53
61169 Friedberg
Germany
Or
Corden Pharma Latina S.P.A.
Via del Murillo, KM 2,800
04013 – Sermoneta (LT) - Italy
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Germany | Paclitaxel Kabi 6 mg/ml Konzentrat zur Herstellung einer Infusionslösung |
Austria | Paclitaxel Kabi 6 mg/ml Konzentrat zur Herstellung einer Infusionslösung |
Belgium | Paclitaxel Fresenius Kabi |
Bulgaria | Paclitaxel Kabi 6 mg/ml ?????????? ?? ?????????? ??????? |
Denmark | Paclitaxel Fresenius Kabi 6 mg/ koncentrat til infusionsvaeske, opløsning |
Slovakia | Paclitaxel Kabi 6 mg/ml |
Slovenia | Paklitaksel Kabi 6 mg/ml koncentrat za raztopino za infundiranje |
Estonia | Paclitaxel Kabi 6 mg/ml infusioonilahuse kontsentraat |
Finland | Paclitaxel Fresenius Kabi 6 mg/ml infuusiokonsentraatti, liuosta varten |
France | Paclitaxel Kabi 6 mg/ml solution à diluer pour perfusion |
Hungary | Paclitaxel Kabi 6 mg/ml koncentrátum oldatos infúzióhoz |
Ireland | Paclitaxel 6 mg/ml concentrate for solution for infusion |
Italy | Paclitaxel Kabi 6 mg/ml concentrato per soluzione per infusione |
Latvia | Paclitaxel Kabi 6 mg/ml koncentrats infuziju škiduma pagatavošanai |
Lithuania | Paclitaxel Kabi 6 mg/ml koncentratas infuziniam tirpalui |
Luxembourg | Paclitaxel Kabi 6 mg/ml Konzentrat zur Herstellung einer Infusionslösung |
Norway | Paclitaxel Fresenius Kabi 6 mg/ml konsentrat til infusjonsvæske |
Netherlands | Paclitaxel Fresenius Kabi |
Poland | Paclitaxel Kabi |
Portugal | Paclitaxel Kabi 6 mg/ml concentrado para solução para perfusão |
United Kingdom | Paclitaxel 6 mg/ml concentrate for solution for infusion |
Czech Republic | Paclitaxel Kabi 6 mg/ml koncentrát pro prípravuinfuzního roztoku |
Romania | Paclitaxel Kabi 6 mg/ml concentrat pentru solutie perfuza |
Sweden | Paclitaxel Fresenius Kabi 6 mg/ml koncentrat till infusionsvätska, lösning |
Date of the Last Revision of this Prospectus March 2021
Detailed and updated information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
Handling
As with all antineoplastics, paclitaxel should be handled with caution. Dilutions should be carried out under aseptic conditions by experienced personnel and in a specific area. Appropriate protective gloves should be used. Precautions should be taken to avoid any contact with the skin and mucous membranes. In case of skin contact, the affected area should be washed with water and soap. After topical exposure, tingling, burning sensation, and redness have been described. In case of contact with mucous membranes, they should be thoroughly washed with plenty of water. After inhalation, shortness of breath, chest pain, throat burning, and nausea have been described.
If the vials are refrigerated without opening, a precipitate may form that redissolves with little or no agitation when it reaches room temperature. This does not affect the quality of the product. If the solution remains turbid or an insoluble precipitate is observed, the vial should be discarded.
After several punctures with a needle and extractions of the product, the vials maintain their microbial, chemical, and physical stability for a maximum of 28 days at 25°C. Other times and storage conditions are the responsibility of the user.
The "Chemo-Dispensing Pin" devices or similar ones with spikes should not be used, as they can cause the vial stopper to collapse, resulting in loss of sterility integrity.
Preparation for Intravenous Administration
Before infusion, Paclitaxel Kabi should be diluted using aseptic techniques in 5% glucose solution or 0.9% sodium chloride solution, 5% glucose solution in Ringer's solution, and 5% glucose/0.9% sodium chloride solution to a final concentration of 0.3 to 1.2 mg/ml.
The chemical and physical stability during the use of the prepared infusion solution has been demonstrated at 25°C for 24 hours when diluted in a 5% glucose solution, 0.9% sodium chloride solution, 5% glucose solution in Ringer's solution, and 5% glucose/0.9% sodium chloride solution.
From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, the storage times and conditions before use are the responsibility of the user and, in general, should not exceed 24 hours at 2-8°C, unless the dilution has been carried out under controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
After dilution, the solution is for single use only.
After preparation, these solutions may present a slightly turbid appearance that is attributed to the formulation vehicle, and that is not eliminated by filtration. Paclitaxel Kabi should be administered with an in-line filter with a microporous membrane ≤ 0.22 μm. No significant losses in potency have been observed after simulated administration of the solution through IV equipment with an in-line filter.
Isolated cases of precipitation have been reported during paclitaxel infusions, usually towards the end of the 24-hour infusion period. Although the cause of this precipitation has not been established, it is likely related to the supersaturation of the diluted solution. To reduce the risk of precipitation, Paclitaxel Kabi should be administered as soon as possible after dilution, and excessive agitation, vibration, or shaking should be avoided. Infusion equipment should be thoroughly washed before use. During infusion, the appearance of the solution should be regularly examined, and if precipitation is observed, the infusion should be interrupted.
To minimize patient exposure to DEHP that may leach from PVC plastic bags, infusion equipment, or other medical instruments, the diluted Paclitaxel Kabi solutions should be stored in non-PVC containers (glass, polypropylene) or plastic bags (polypropylene, polyolefin) and administered with a polyethylene-coated administration set. The use of filter devices (e.g., IVEX-2) that have a short PVC plasticized tube has not produced significant DEHP leaching.
Instructions for Protection during Preparation of Paclitaxel Solution for Infusion
- A protective chamber and protective gloves, as well as a laboratory coat, should be used. If a protective chamber is not available, a suitable mask and safety glasses should be used.
- The product should not be handled by pregnant women or women who may become pregnant.
- Open containers, as well as injection vials and infusion bottles, cannulas, syringes, catheters, and tubes used, and remnants of cytostatic substances should be considered hazardous waste and disposed of according to local regulations for the handling of HAZARDOUS WASTE.
- In case of spillage, follow the instructions below: - Use protective clothing. Broken glass should be collected and placed in a HAZARDOUS WASTE container. Contaminated surfaces should be thoroughly washed with plenty of cold water; then, the washed surfaces should be thoroughly cleaned, and the material used for cleaning should be disposed of as HAZARDOUS WASTE.
- In case of contact of the concentrate for solution for infusion of paclitaxel with the skin, the area should be rinsed with plenty of running water and then washed with water and soap. In case of contact with mucous membranes, the area should be thoroughly washed with water. If there is any discomfort, consult a doctor.
- In case of contact of the concentrate for solution for infusion of paclitaxel with the eyes, they should be thoroughly washed with plenty of cold water. Consult an ophthalmologist immediately.
Elimination
The elimination of unused medicine and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out according to local regulations.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to PACLITAXEL KABI 6 mg/ml CONCENTRATE FOR INFUSION SOLUTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 100 mgActive substance: paclitaxelManufacturer: Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharma EeigPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 5 mg/mlActive substance: paclitaxelManufacturer: Whiteoak Pharmaceutical B.V.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 5 mg/mlActive substance: paclitaxelManufacturer: Laboratorio Stada S.L.Prescription required
Online doctors for PACLITAXEL KABI 6 mg/ml CONCENTRATE FOR INFUSION SOLUTION
Discuss questions about PACLITAXEL KABI 6 mg/ml CONCENTRATE FOR INFUSION SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions






