OROXELAM 2.5 mg ORAL SOLUTION
Ask a doctor about a prescription for OROXELAM 2.5 mg ORAL SOLUTION

How to use OROXELAM 2.5 mg ORAL SOLUTION
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Oroxelam 2.5 mg Buccal Solution
Oroxelam 5 mg Buccal Solution
Oroxelam 7.5 mg Buccal Solution
Oroxelam 10 mg Buccal Solution
midazolam
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What Oroxelam is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use Oroxelam
- How to use Oroxelam
- Possible side effects
- Storing Oroxelam
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Oroxelam is and what it is used for
Oroxelam buccal solution contains a medicine called midazolam. Midazolam belongs to a group of medicines known as benzodiazepines.
Oroxelam is used to stop a sudden and prolonged seizure in infants from 3 months to adults.
In infants from 3 months to less than 6 months, treatment should only be given in a hospital where the patient can be monitored and has access to resuscitation equipment.
This medicine should only be used by parents/caregivers when the patient has been diagnosed with epilepsy.
2. What you need to know before you use Oroxelam
- Do not use Oroxelam if the patient has:
- allergy to midazolam, to benzodiazepines (such as diazepam) or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- a disease of the nerves and muscles that causes muscle weakness (myasthenia gravis);
- severe breathing difficulties at rest (Oroxelam may make breathing difficulties worse);
- a disease that causes frequent interruptions of breathing while sleeping (sleep apnea syndrome);
- severe liver problems.
Warnings and precautions:
Children:
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting to use Oroxelam if the patient:
- Has a kidney, liver or heart condition;
- Has a lung condition that causes periodic breathing difficulties.
Adults:
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting to use Oroxelam if:
- You are over 60 years old.
- You have a chronic disease (such as respiratory, renal, hepatic or cardiac insufficiency).
- You are debilitated (you have a disease that makes you feel very weak, exhausted and without energy).
This medicine may cause people to forget what happened after they were given it. Patients should be closely observed after being given this medicine.
This medicine should be avoided in patients with a history of alcoholism or drug abuse.
It is more likely that potentially fatal incidents will occur in patients with breathing difficulties or heart problems, especially when higher doses of Oroxelam are given.
Children under 3 months: Oroxelam should not be given to children under 3 months due to lack of information in this age group.
Elderly patients:
Elderly patients are more sensitive to the effects of benzodiazepines.
If you are unsure if any of the above applies to the patient, consult your doctor or pharmacist before giving this medicine.
Other medicines and Oroxelam
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if the patient is using, has recently used or might use any other medicines. If you are unsure about any medicine the patient is taking that may affect the use of Oroxelam, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
This is especially important because using more than one medicine at the same time can increase or decrease the effect of the medicines taken.
The effects of Oroxelam may be increased by the following medicines:
- antiepileptics (for treating epilepsy), e.g. phenytoin
- antibiotics, e.g. erythromycin, clarithromycin
- antifungals, e.g. ketoconazole, voriconazole, fluconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole
- medicines for ulcers, e.g. cimetidine, ranitidine and omeprazole
- medicines used to treat blood pressure, e.g. diltiazem, verapamil
- some medicines used to treat HIV and AIDS, e.g. saquinavir, lopinavir/ritonavir combination
- narcotic analgesics (very strong painkillers), e.g. fentanyl
- medicines used to reduce blood fat, e.g. atorvastatin
- medicines used to treat nausea, e.g. nabilone
- hypnotics (sleep-inducing medicines)
- sedative antidepressants (medicines for treating depression that cause sleepiness)
- sedatives (medicines to help relax)
- anesthetics (medicines to relieve pain)
- antihistamines (medicines for treating allergies)
The effects of Oroxelam may be reduced by the following medicines:
- rifampicin (used to treat tuberculosis)
- xanthines (used to treat asthma)
- St. John's Wort (a herbal medicine). This should be avoided in patients taking Oroxelam.
Oroxelam may increase the effect of some muscle relaxants, e.g. baclofen (causing increased sleepiness). This medicine may also cause some medicines to stop working as well, e.g. levodopa (a medicine used to treat Parkinson's disease).
Consult your doctor or pharmacist for more information about the medicines the patient should avoid while taking Oroxelam.
Using Oroxelam with food and drink
The patient should not drink alcohol while taking Oroxelam. Alcohol may increase the sedative effects of this medicine and cause excessive sleepiness.
The patient should not drink grapefruit juice while taking Oroxelam. Grapefruit juice may increase the sedative effects of this medicine and cause excessive sleepiness.
Pregnancy
If the patient who is to receive this medicine is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks she may be pregnant or is planning to have a baby, consult your doctor before using this medicine.
Administration of high doses of Oroxelam during the last 3 months of pregnancy may cause abnormal heart rhythm in the fetus. Children born after administration of this medicine during delivery may also experience difficulty feeding, breathing difficulties and poor muscle tone at birth.
Breastfeeding
Tell your doctor if the patient is breastfeeding. Although small amounts of Oroxelam may pass into breast milk, it may not be necessary to stop breastfeeding. Your doctor will advise whether the patient should breastfeed the baby after receiving a single dose of this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Oroxelam may cause the patient to feel sleepy, forgetful or affect their concentration and coordination. This may interfere with the performance of tasks that require skill such as driving, cycling or using machines.
After receiving this medicine, the patient should not drive, cycle or use machines until they have fully recovered. Ask your doctor if you need more information.
Oroxelam contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per oral syringe, i.e. it is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to administer Oroxelam
Follow the instructions for administering this medicine exactly as told by your doctor. If you are unsure, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
Dose
Your doctor will prescribe the correct dose of Oroxelam, which will normally depend on the patient's age. Each dose has a different color, which is shown on the box, the tube and the syringe that contains the medicine.
Depending on the age, the patient will receive one of the following doses, in a color-coded container:
Age range | Dose | Label color |
3 months to less than 1 year | 2.5 mg | Yellow |
1 year to less than 5 years | 5 mg | Blue |
5 years to less than 10 years | 7.5 mg | Purple |
10 years to adults | 10 mg | Orange |
An oral syringe contains a complete dose. Do not administer more than one dose.
Infants from 3 months to less than 6 months should only receive treatment in a hospital where the patient can be monitored and has access to resuscitation equipment.
Preparation for administration of this medicine
If the patient has a seizure, let their body move freely, do not try to hold them. Only move them if they are in danger, for example, near deep water, fire or sharp objects.
Support the patient's head on a cushion or your lap. Check that the medicine contains the correct dose for the patient, according to their age.
How to administer this medicine
Ask a doctor, pharmacist or nurse to show you how to take or administer this medicine. If you are unsure, always ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
Information on how to administer this medicine is also shown on the label of the tube.
Oroxelam should not be injected. Do not put a needle in the syringe.
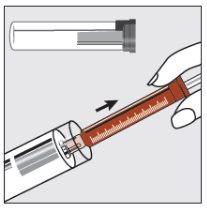
Step 1 | |
| Hold the plastic tube, break the seal at one end and remove the cap. Take the syringe out of the tube. |
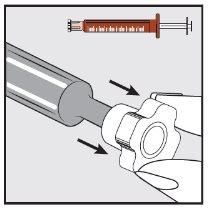
Step 2 | |
| Remove the clear cap from the tip of the syringe and dispose of it safely. |
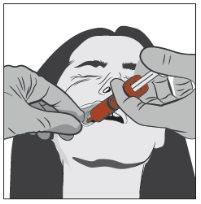
Step 3 | |
| With the help of your index finger and thumb, gently pinch and pull back the patient's cheek. Place the tip of the syringe in the back of the space between the inside of the cheek and the lower gum. |
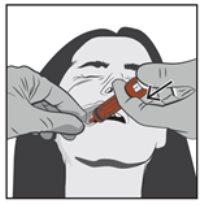
Step 4 | |
| Slowly press the plunger of the syringe until it stops. Slowly insert the entire solution into the space between the gum and the cheek (buccal cavity). If prescribed by your doctor (for large volumes and/or smaller patients), you can administer approximately half of the dose on one side of the mouth and then the other half on the other side of the patient's mouth. |
When to call an ambulance
Always follow the treatment recommendations provided by the patient's doctor or as indicated by the healthcare professional. If you are unsure, seek urgent medical help if:
- The seizure does not stop within 10 minutes.
- You are unable to empty the contents of the syringe or spill some of it.
- The patient's breathing slows down or stops (e.g. slow or shallow breathing or blue lips).
- You observe signs of a heart attack that may include chest pain or pain that radiates to the neck and shoulders and extends to the left arm.
- The patient vomits and the seizure does not stop within 10 minutes.
- You give too much Oroxelam and observe signs of overdose that include:
- Sleepiness, tiredness, fatigue
- Confusion or disorientation
- Absence of knee reflex or response to a pinch
- Breathing difficulties (slow or shallow breathing)
- Low blood pressure (dizziness and feeling of fainting)
- Coma
Keep the syringe to show to the ambulance staff or doctor.
Do not administer more medicine than prescribed by the doctor for the patient.
If the patient vomits
- Do not administer another dose of Oroxelam to the patient.
- If the seizure does not stop within 10 minutes, call an ambulance.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Serious side effects
Seek immediate medical attention or call for an ambulance if the patient experiences the following side effects:
- Severe breathing difficulties, e.g. slow or shallow breathing or blue lips. In very rare cases, breathing may stop.
- Heart attack. Signs may include chest pain that may radiate to the neck and shoulders and extend to the left arm.
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue or throat that makes swallowing or breathing difficult, or pale skin, weak and rapid pulse, or feeling of loss of consciousness. You may be having a severe allergic reaction.
Other side effects
If the patient experiences any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse, even if it is possible side effects not listed in this leaflet.
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Feeling and being sick (nausea and vomiting).
- Sleepiness or being less conscious
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Skin rash, hives (itchy rash)
Rare side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
- Agitation, restlessness, hostility, anger or aggression, excitement, confusion, euphoria (excessive feeling of happiness or excitement) or hallucinations (seeing and possibly hearing things that are not really there)
- Muscle spasms and muscle tremors (trembling of the muscles that cannot be controlled)
- Reduced level of alertness
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Difficulty coordinating muscles
- Seizures (convulsions)
- Temporary loss of memory. The duration depends on the amount of Oroxelam administered.
- Low blood pressure, slow heart rate or reddening of the face and neck (flushing)
- Laryngeal spasm (contraction of the vocal cords that causes breathing difficulties and noise when breathing)
- Constipation
- Dry mouth
- Fatigue
- Hiccups
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse, even if it is possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storing Oroxelam
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the packaging and on the labels of the tube and oral syringe, after EXP. The expiry date is the last day of the month shown.
Store below 30°C
Keep the oral syringe in the protective plastic tube. Do not use this medicine if the packaging is open or damaged.
The medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Dispose of the packaging and any unused medicine in the SIGRE collection point at the pharmacy. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and any unused medicine. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
Composition of Oroxelam
The active ingredient is midazolam
- Oroxelam 2.5 mg - Each pre-filled oral syringe contains midazolam hydrochloride equivalent to 2.5 mg of midazolam in 0.5 ml of solution.
- Oroxelam 5 mg - Each pre-filled oral syringe contains midazolam hydrochloride equivalent to 5 mg of midazolam in 1 ml of solution.
- Oroxelam 7.5 mg - Each pre-filled oral syringe contains midazolam hydrochloride equivalent to 7.5 mg of midazolam in 1.5 ml of solution.
- Oroxelam 10 mg - Each pre-filled oral syringe contains midazolam hydrochloride equivalent to 10 mg of midazolam in 2 ml of solution.
The other components are sodium chloride, purified water, hydrochloric acid, and sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment).
Appearance and Packaging of the Product
Oroxelam 2.5 mg – packaging with yellow label
Oroxelam 5 mg – packaging with blue label
Oroxelam 7.5 mg – packaging with purple label
Oroxelam 10 mg – packaging with orange label
Oroxelam oral solution is a clear and colorless liquid.
It is presented in a pre-filled oral syringe of amber color, without a needle, with a plunger and cap. Each oral syringe is individually packaged in a protective plastic tube.
Oroxelam is presented in boxes containing 2 or 4 pre-filled oral syringes (of the same dose).
Only some package sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder
Exeltis Healthcare, S.L.
Avenida de Miralcampo, 7.
Polígono Industrial Miralcampo.
19200 Azuqueca de Henares.
Guadalajara.
Spain
Manufacturer
Laboratorios Liconsa S.A.
Av. de Miralcampo, 7
19200 Azuqueca de Henares
Guadalajara.
Spain
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
SE: Midazolam medical valley 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg munhålelösning.
FI: Midazolam medical valley 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg liuos suuonteloon.
DE: Midazaxiro 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg lösung zur anwendung in der mundhöhle.
NO: Midazolam medical valley 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg munnvann, oppløsning.
NL: Midazolam xiromed 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg oplossing voor oromucosaal gebruik.
DK: Midazolam medical valley 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg mundhulevæske, opløsning.
IS: Midazolam medical valley 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg munnholslausn.
FR: Midazolam liconsa 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg solution buccale.
IE: Midazolam liconsa 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg oromucosal solution.
RO: Midazolam desitin 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg solu?ie bucofaringiana.
ES: Oroxelam 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10 mg oral solution
PL: Soloxelam.
IT: Oroxelam.
Date of the last revision of this prospectus:March 2025
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to OROXELAM 2.5 mg ORAL SOLUTIONDosage form: GEL/PASTE/ORAL LIQUID, 10 mg midazolam hydrochlorideActive substance: midazolamManufacturer: Neuraxpharm Pharmaceuticals S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: GEL/PASTE/ORAL LIQUID, 2.5 mg midazolam hydrochlorideActive substance: midazolamManufacturer: Neuraxpharm Pharmaceuticals S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: GEL/PASTE/ORAL LIQUID, 5 mg midazolam hydrochlorideActive substance: midazolamManufacturer: Neuraxpharm Pharmaceuticals S.L.Prescription required
Alternatives to OROXELAM 2.5 mg ORAL SOLUTION in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to OROXELAM 2.5 mg ORAL SOLUTION in Poland
Alternative to OROXELAM 2.5 mg ORAL SOLUTION in Ukraine
Online doctors for OROXELAM 2.5 mg ORAL SOLUTION
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for OROXELAM 2.5 mg ORAL SOLUTION – subject to medical assessment and local rules.