OCTANINE 100 IU/ml POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION

How to use OCTANINE 100 IU/ml POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Octanine 100 UI/ml, powder and solvent for solution for injection
Human coagulation factor IX
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack:
- What is Octanine and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Octanine
- How to use Octanine
- Possible side effects
- Storing Octanine
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Octanine and what is it used for
Octanine belongs to a group of medicines called coagulation factors and contains human coagulation factor IX. It is a special protein that increases the blood's ability to clot.
Octanine is used to treat and prevent bleeding in patients with bleeding disorders (haemophilia B). This is a condition where bleeding can last longer than expected. It is due to a birth deficiency in the amount of factor IX coagulant in the blood.
Octanine is supplied as a powder and solvent to prepare an injectable solution. After reconstitution, it is administered intravenously (injected into a vein).
2. What you need to know before you use Octanine
Do not use Octanine:
- if you are allergic to human coagulation factor IX or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- if you have type II heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, which is a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood after heparin administration. Platelets are blood cells that help stop bleeding. Heparin is a medicine used to prevent blood clots.
Warnings and precautions
- Consult your doctor, pharmacist or nurse before starting treatment with Octanine.
- As with all medicines that contain proteins and are administered intravenously, allergic hypersensitivity reactions can occur. Octanine contains very small amounts of human proteins other than factor IX and heparin. The first signs of hypersensitivity reactions include:
- rash
- skin rash (hives)
- chest tightness
- difficulty breathing
- decrease in blood pressure
- acute and severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis when any or all of the above symptoms develop rapidly and are intense)
If you experience these symptoms, stop the injection immediately and consult your doctor. In case of anaphylactic shock, treatment should be initiated as soon as possible.
- Your doctor may recommend that you consider vaccination against hepatitis A and B if you regularly or repeatedly receive human plasma-derived products containing factor IX.
- It is known that individuals with haemophilia B can develop inhibitors (neutralizing antibodies) of factor IX, produced by immune cells. Inhibitors can increase the risk of anaphylactic shock (severe allergic reactions). Therefore, if you experience an allergic reaction, you should be tested for the presence of an inhibitor. Patients with factor IX inhibitors may have a higher risk of anaphylaxis if they are treated with factor IX. Therefore, your doctor may decide to administer the first injection of factor IX under medical supervision, in order to provide adequate care in case of allergic reactions.
- Factor IX protein concentrates can cause a blockage in your blood vessels due to a blood clot. Due to this risk, which is higher in low-purity products, you should be monitored for symptoms of blood clot formation after administration of factor IX products if you:
- have signs of fibrinolysis (blood clots that have broken down)
- have disseminated intravascular coagulation (widespread blood clotting in the blood vessels)
- have been diagnosed with liver disease
- have documented cardiovascular risk factors
- have recently undergone surgery
- are at high risk of blood clot formation or disseminated intravascular coagulation.
If any of the above symptoms occur in you, your doctor will only administer Octanine if the benefit outweighs the risks.
- After repeated treatment with human coagulation factor IX products, patients should be monitored for the possible development of neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) that should be quantified in Bethesda Units (BU) using appropriate biological tests.
Viral safety of blood products
- When administering medicines derived from human plasma or blood, certain measures must be taken to prevent infections from being transmitted to patients. These measures include careful selection of donors to exclude those at risk of being carriers of infectious diseases, analysis of specific infection markers in individual donations and plasma pools, as well as the inclusion of stages in the manufacturing process to eliminate/inactivate viruses. Despite this, when administering medicines derived from human blood or plasma, the possibility of transmitting infectious agents cannot be entirely excluded. This also applies to emerging or unknown viruses or other types of infections.
- These measures are considered effective against enveloped viruses such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus, and against the non-enveloped hepatitis A virus. The measures taken may have limited value against other non-enveloped viruses such as parvovirus B19. Parvovirus B19 infection can be severe for a pregnant woman (fetal infection) and for individuals with impaired immune systems or patients with certain types of anaemia (e.g. sickle cell anaemia or haemolytic anaemia).
- Your doctor may recommend that you be vaccinated against hepatitis A and B if you are regularly or repeatedly administered human plasma-derived products.
- It is strongly recommended that every time you receive a dose of Octanine, a record be kept of the name of the medicine and batch number administered in order to maintain a record of the batches used.
Children
If Octanine is administered to a newborn, you should be closely monitored for signs of disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Other medicines and Octanine
- As far as we know, human coagulation factor IX products do not interact with any other medicines.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using or have recently used or might use other medicines, including those obtained without a prescription.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
No data are available on the use of factor IX during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Therefore, factor IX should only be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding if clearly indicated.
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
No effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been observed.
Octanine contains sodium
This medicine contains up to 69 mg of sodium (main component of cooking/table salt) in 1 vial of Octanine 500 UI, equivalent to 3.45% of the maximum daily recommended sodium intake for an adult, and up to 138 mg of sodium in 1 vial of Octanine 1000 UI, equivalent to 6.9% of the maximum daily recommended sodium intake for an adult.
This should be taken into account in the treatment of patients on low-sodium diets.
3. How to use Octanine
Follow exactly the administration instructions of this medicine given by your doctor. If you are unsure, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
Octanine should be administered intravenously (injected into a vein) after reconstitution with the supplied solvent.
Only use the infusion equipment provided. The use of other injection/infusion equipment may cause additional risks and treatment failure.
Treatment should be initiated under the supervision of a doctor experienced in the treatment of haemophilia. The amount of Octanine you should use and the duration of replacement therapy depend on the severity of your factor IX deficiency. It also depends on the location and severity of the bleeding, as well as your clinical condition.
Dose calculation:
Your doctor will tell you how often and how much Octanine you need to be injected.
The dose of factor IX is expressed in International Units (IU). Factor IX activity in plasma refers to the amount of factor IX present in plasma. It is expressed either as a percentage (relative to normal human plasma) or in International Units (relative to an international standard for factor IX in plasma).
One International Unit (IU) of factor IX activity is equivalent to the amount of factor IX in one millilitre of normal human plasma. The calculation of the required dose of factor IX is based on the observation that 1 IU of factor IX per kilogram of body weight increases the factor IX activity in plasma by 1% of normal activity. To calculate the dose you need, the level of factor IX activity in your blood plasma is measured. This will indicate how much activity needs to be increased.
The required dose is calculated using the following formula:
Units required = body weight (kg) x desired increase in factor IX (%) (IU/dl) x 0.8
The amount of your dose and how often it should be administered will depend on how you respond to the medicine and will be decided by your doctor. Factor IX products are rarely required to be administered more than once a day.
Your response to factor IX products may be variable. Therefore, your factor IX levels should be measured during treatment to calculate the correct dose and infusion frequency. In particular, during surgical operations, your doctor will use blood tests (plasma factor IX activity) to closely monitor replacement therapy.
Bleeding prevention:
If you have severe haemophilia B, you should be injected with 20 to 40 IU of factor IX per kilogram of body weight (BW). This dose should be administered twice a week for long-term prevention. Your dose should be adjusted according to your response. In some cases, especially in young patients, shorter administration intervals or higher doses may be necessary.
Use in children:
In a study conducted in children under 6 years of age, the average dose administered per day of exposure was 40 IU/kg BW.
If bleeding cannot be stopped due to inhibitors:
If the expected factor IX activity is not achieved after an injection or bleeding is not stopped after administration of the correct dose, you should inform your doctor. They will examine your blood plasma to see if you have developed inhibitors (antibodies) against the factor IX protein. These inhibitors can reduce the activity of factor IX. In this case, a different treatment may be necessary. Your doctor will discuss this with you and recommend another treatment if necessary.
If you use more Octanine than you should
No symptoms of overdose have been observed with human coagulation factor IX. However, you should not exceed the recommended dose.
For "Instructions for home treatment", see the package insert of the equipment.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Octanine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
- Rarely, allergic or hypersensitivity reactions have been observed in patients treated with products containing factor IX. These reactions can include:
- involuntary contraction of blood vessels (spasms) with swelling in the face, mouth and throat
- burning and stinging at the infusion site
- chills
- flushing
- skin rash
- headache
- hives
- decrease in blood pressure
- fatigue
- malaise
- restlessness
- rapid heartbeat
- chest tightness
- tingling
- vomiting
- difficulty breathing
In some cases, these allergic reactions can lead to a severe reaction called anaphylaxis, which can include shock. These reactions are usually associated with the development of factor IX inhibitors. If you experience any of the above symptoms, inform your doctor.
- If you have haemophilia B, you may develop neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) of factor IX. These antibodies can disrupt the functioning of your medicine. Your doctor will discuss this with you and recommend another treatment if necessary.
A study was conducted in 25 children with haemophilia B, of whom 6 patients had not been previously treated. No inhibitors were observed during the study. The tolerability of all injections was estimated as "very good" or "good".
- Some patients with haemophilia B and factor IX inhibitors with immunotolerance therapy and a history of allergic reactions developed nephrotic syndrome (a severe kidney disease).
- Rarely, fever may occur.
- Low-purity factor IX products can rarely cause a blood clot to form in the blood vessels. This can lead to complications such as:
- heart attack
- widespread blood clotting in the blood vessels (disseminated intravascular coagulation)
- blood clots in the veins (venous thrombosis)
- blood clots in the lungs (pulmonary embolism).
These side effects are more common if you use low-purity factor IX products and are rare if you use high-purity products like Octanine.
- The heparin in the preparation can cause a sudden drop in the number of platelets in the blood to below 100,000 per microlitre or less than 50% of the initial count. This is an allergic reaction called "heparin-induced thrombocytopenia type II". In rare cases, in patients who are not previously hypersensitive to heparin, this drop in platelet count can occur 6-14 days after the start of treatment. In patients with pre-existing hypersensitivity to heparin, this alteration can develop within hours of starting treatment. This severe form of platelet reduction can be accompanied by, or result in:
- blood clots in the arteries and veins
- obstruction of a blood vessel by a clot from another area
- a severe coagulation disorder called consumption coagulopathy
- skin gangrene at the injection site
- bleeding with a mosquito bite-like appearance
- bruises
- black stools.
If you experience these allergic reactions, stop the Octanine injections immediately and do not use heparin-containing medicines in the future.Due to this rare effect on blood platelets, your doctor will closely monitor your blood platelet count, especially when starting treatment.
For safety with respect to transmissible agents, see section 2.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly through the Spanish Medicines Monitoring System for Human Use: www.notificaRAM.es.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storing Octanine
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Store the vial in the outer packaging to protect it from light and below 25°C. Do not freeze.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the label and carton. The expiry date is the last day of the month stated.
The reconstituted product should be used immediately, and if not, at least within 8 hours when stored at room temperature (25°C). Use Octanine for single use only.
Do not use this medicine if you notice cloudy or not completely dissolved solutions. Dispose of unused contents. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medicines you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Octanine
The active ingredientis human coagulation factor IX.
The other componentsare heparin, sodium chloride, sodium citrate, arginine hydrochloride, and lysine hydrochloride.
Appearance of Octanine and Package Contents
Octanine is available in 2 package sizes with the following doses:
- Octanine 100 UI/ml presentation for reconstitution with 5 ml of water for injectables, presented as powder and solvent for injection with a nominal content of 500 UI of human coagulation factor IX per vial.
- Octanine 100 UI/ml presentation for reconstitution with 10 ml of water for injectables, presented as powder and solvent for injection with a nominal content of 1000 UI of human coagulation factor IX per vial.
Octanine is produced from human donor plasma.
The potency (UI) is determined using the one-stage coagulation test of the European Pharmacopoeia, compared to the international standard of the World Health Organization (WHO). The specific activity of Octanine is approximately 100 UI/mg protein.
Package Description:
Octanine is supplied as a combined package containing two attached cases with a plastic seal:
One case contains 1 vial with powder for injectable solution and the package insert.
The other case contains the vial with the solvent (water for injectables, 5 ml for the 500 UI presentation and 10 ml for the 1000 UI presentation).
This package also contains the following medical devices:
- 1 set of equipment for intravenous injection (1 transfer set, 1 infusion set, 1 disposable syringe)
- 2 alcohol swabs
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
For any information about this medicinal product, please contact the marketing authorization holder.
Octapharma S.A.
Parq. Em. S. Fernando,
Avda. Castilla 2 - Edif. Dublin - 2ª Planta,
San Fernando de Henares (Madrid) 28830
Manufacturer:
Octapharma Pharmazeutika Produktionsges.m.b.H.
Oberlaaer Strasse 235
A-1100 Vienna
Austria
or
Octapharma S.A.S.
70-72 Rue du Maréchal Foch
67380 Lingolsheim
France
Date of the Last Revision of this Package InsertNovember 2020.
Detailed and updated information about this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS)
http://www.aemps.gob.es/
Instructions for Ambulatory Treatment
- Please read all instructions and follow them carefully.
- Do not useOctanine after the expiration date shown on the label and carton.
- During the procedure described below, sterility must be maintained.
- Visually inspect the reconstituted medicinal product for particles or color change before administration.
- The solution should be clear or slightly opalescent. Do not use cloudy solutions or those containing sediment.
- Use the prepared solution immediately to avoid microbial contamination.
- Use only the infusion set provided. Using other injection/infusion equipment may cause additional risk and treatment failure.
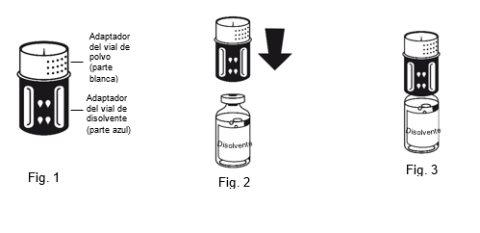
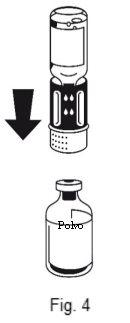
Instructions for Preparing the Solution:
|
|
|
|
|
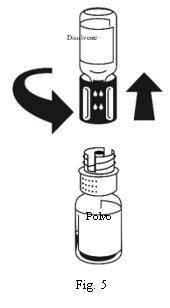
The dissolution is complete in less than 10 minutes at room temperature. A slight foam may appear during preparation. Unscrew the two parts of the transfer equipment (Fig. 5). The foam will disappear. Discard the empty solvent vial along with the blue part of the transfer equipment. |
|
Instructions for Injection:
As a precaution, measure your pulse rate before and during the injection. If your pulse rate increases significantly, reduce the injection rate or interrupt the administration for a short period.
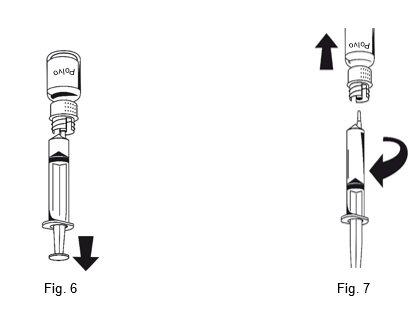
- Attach the syringe to the white part of the transfer equipment. Turn the vial over and withdraw the solution into the syringe (Fig.6). The solution should be clear or slightly opalescent.
Once the solution has been transferred, firmly hold the syringe plunger (keeping it downwards) and withdraw the syringe from the transfer equipment (Fig. 7). Discard the empty vial along with the white part of the transfer equipment.
- Clean the injection site with one of the included alcohol swabs.
- Attach the provided infusion set to the syringe.
- Insert the injection needle into the chosen vein. If you have used a tourniquet to make the vein more visible, release the tourniquet before starting the injection.
There should be no blood flow into the syringe due to the risk of fibrin clot formation.
- Inject the solution into the vein at a slow rate, not exceeding 2-3 ml per minute.
If you use more than one vial of Octanine powder for a treatment, you can use the same injection needle and syringe.
The transfer equipment is for single use.
Disposal of unused medicinal products and all materials that have come into contact with them will be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to OCTANINE 100 IU/ml POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 1,000 IUActive substance: coagulation factor IXManufacturer: Swedish Orphan Biovitrum Ab (Publ)Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 2,000 IUActive substance: coagulation factor IXManufacturer: Swedish Orphan Biovitrum Ab (Publ)Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 250 IUActive substance: coagulation factor IXManufacturer: Swedish Orphan Biovitrum Ab (Publ)Prescription required
Online doctors for OCTANINE 100 IU/ml POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Discuss questions about OCTANINE 100 IU/ml POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions