
NEVIRAPINE TEVA 400 mg PROLONGED-RELEASE TABLETS

How to use NEVIRAPINE TEVA 400 mg PROLONGED-RELEASE TABLETS
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Leaflet:information for the user
Nevirapine Teva 400 mg prolonged-release tablets EFG
Read the entire leaflet carefully before starting to take this medication,as it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, as you may need to read it again.
- If you have any doubts, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medication has been prescribed to you only, and you should not give it to others, even if they have the same symptoms as you, as it may harm them.
- If you experience side effects, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the leaflet
- What is Nevirapine Teva 400 mg prolonged-release tablets EFG and what is it used for
- What you need to know before taking Nevirapine Teva 400 mg
- How to take Nevirapine Teva 400 mg
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Nevirapine Teva 400 mg
- Package contents and additional information
1. What is Nevirapine Teva 400mg prolonged-release tablets EFG and what is it used for
Nevirapine belongs to a group of medications called antiretrovirals, which are used to treat Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infection.
The active ingredient of this medication is called nevirapine. Nevirapine belongs to a class of anti-HIV medications called non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs). Reverse transcriptase is an enzyme that HIV needs to multiply. Nevirapine prevents the action of reverse transcriptase. By blocking the action of reverse transcriptase, Nevirapine helps control HIV-1 infection.
Nevirapine is indicated for the treatment of adults, adolescents, and children aged three years or older who can swallow tablets, infected with HIV-1. You should take Nevirapine with other antiretroviral medications. Your doctor will indicate the appropriate medications for you.
Nevirapine prolonged-release tablets should only be used after a two-week treatment with another type of medication containing nevirapine (suspension or immediate-release tablets), unless you are currently being treated with Nevirapine and are switching to the prolonged-release form.
2. What you need to know before taking Nevirapine Teva 400 mg
DO NOT takeNevirapine Teva 400 mg
- if you are allergic to nevirapine or any of the other components of this medication (listed in section 6 "Composition of Nevirapine Teva").
- if you have previously taken nevirapine and had to discontinue treatment because you experienced:
- severe skin rash
- skin rash with other symptoms such as:
- fever
- blistering
- mouth sores
- eye inflammation
- facial swelling
- general swelling
- difficulty breathing
- muscle or joint pain
- general malaise
- abdominal pain
- hypersensitivity reactions (allergy)
- liver inflammation (hepatitis)
- if you have severe liver disease
- if you had to discontinue nevirapine treatment in the past due to changes in liver function
- if you are using any medication containing St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum). This product may cause nevirapine to stop working properly.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting to take Nevirapine Teva 400 mg.
During the first 18 weeks of treatment with nevirapine, it is very important that you and your doctor monitor the appearance of liver or skin reactions. These reactions can be severe and even life-threatening. The risk of experiencing these reactions is higher during the first 6 weeks of treatment.
If you experience a severe rash or hypersensitivity (allergic reactions that can appear as a rash) along with other side effects such as:
YOU MUST STOP TAKING NEVIRAPINE AND CONTACT your doctor IMMEDIATELY, as these reactions can be life-threatening or cause death. If you experience only mild rash symptoms without any other reaction, inform your doctor immediately, who will indicate whether you should stop taking nevirapine. If you experience symptoms suggesting liver damage, such as:
you must stop taking nevirapine and contact your doctor immediately. If you experience severe liver, skin, or hypersensitivity reactions while taking nevirapine, DO NOT TAKE NEVIRAPINE AGAIN without first consulting your doctor. You must take your nevirapine dose as indicated by your doctor. This is especially important during the first 14 days of treatment (see more information in "How to take Nevirapine Teva 400 mg"). |
The following patients are at higher risk of developing liver problems:
- women
- patients infected with hepatitis B or C
- abnormal liver function tests
- patients naive to nevirapine with higher CD4 cell counts at the start of treatment
(women with more than 250 cells/mm³, men with more than 400 cells/mm³)
- pre-treated patients with detectable HIV-1 viral load in plasma and CD4 cell counts
higher at the start of treatment with nevirapine (women with more than 250 cells/mm³, men with more than 400 cells/mm³)
In some patients with advanced HIV infection (AIDS) and a history of opportunistic infections (AIDS-defining illnesses), signs and symptoms of inflammation of previous infectionsmay appearshortly after starting anti-HIV treatment. These symptoms are believed to be due to an improvement in the body's immune response, allowing it to fight off infections that were present without apparent symptoms. If you notice any symptoms of infection, please inform your doctor immediately.
In addition to opportunistic infections, autoimmune disorders(a condition that occurs when the immune system attacks healthy body tissue) may also appear after you start taking medications for the treatment of your HIV infection. Autoimmune disorders can appear many months after starting treatment. If you notice any symptoms of infection or other symptoms such as muscle weakness, weakness starting in the hands and feet and moving up towards the trunk of the body, palpitations, tremors, or hyperactivity, inform your doctor immediatelyto receive the necessary treatment.
Changes in body fat may occur in patients receiving combined antiretroviral therapy. Consult your doctor if you notice changes in body fat (see section 4. "Possible side effects").
In some patients receiving combined antiretroviral therapy, a bone disease called osteonecrosis(death of bone tissue caused by loss of blood supply to the bone) may develop. The duration of combined antiretroviral therapy, the use of corticosteroids, alcohol consumption, severe immune system weakness, and high body mass index may be some of the many risk factors for developing this disease. The symptoms of osteonecrosis are: joint stiffness, pain, and discomfort, especially in the hip, knee, and shoulder, and difficulty moving. If you notice any of these symptoms, inform your doctor.
If you are taking nevirapine and zidovudine together, inform your doctor because you may need to have your white blood cell count checked.
Do nottake Nevirapine after exposure to HIV unless you have been diagnosed with HIV and your doctor has indicated that you should.
Prednisone should not be used to treat rashes associated with Nevirapine.
If you are taking oral contraceptives(e.g., "the pill") or other hormonal methods of birth control while being treated with Nevirapine, you should also use a barrier contraceptive method (e.g., condoms) to prevent pregnancy and HIV transmission.
If you are receiving post-menopausal hormone therapy, consult your doctor before taking this medication.
If you are taking or are prescribed rifampicin to treat tuberculosis, inform your doctor before taking this medication with nevirapine.
The prolonged-release tablets of nevirapine or parts of the tablets may be eliminated and seen occasionally in the feces. These may appear to be whole tablets, but they have not been shown to affect the efficacy of nevirapine.
Children and adolescents
Nevirapine Teva 400 mg prolonged-release tablets may be used in children if:
- they are ≥ 8 years old and weigh 43.8 kg or more
- they are over 3 years old and under 8 years old and weigh 25 kg or more
- they have a body surface area of 1.17 square meters or greater
For younger children, a liquid suspension is available.
Use ofNevirapine Teva 400 mgprolonged-release tablets EFGwith other medications
Inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or may need to use any other medication. Before starting treatment with nevirapine, inform your doctor of all other medications you are taking. Your doctor may need to check if your other medications are still working and adjust the doses. Read carefully the leaflet of all other anti-HIV medications you are taking in combination with nevirapine.
It is especially important that you inform your doctor if you are using or have recently used:
- St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum, a herbal remedy for the treatment of depression)
- rifampicin (a medication for the treatment of tuberculosis)
- rifabutin (a medication for the treatment of tuberculosis)
- macrolides, e.g., clarithromycin (a medication for the treatment of bacterial infections)
- fluconazole (a medication for the treatment of fungal infections)
- ketoconazole (a medication for the treatment of fungal infections)
- itraconazole (a medication for the treatment of fungal infections)
- methadone (a medication used for the treatment of opioid addiction)
- warfarin (a medication for reducing blood clot formation)
- hormonal contraceptives (e.g., "the pill")
- atazanavir (another medication for the treatment of HIV infection)
- lopinavir/ritonavir (another medication for the treatment of HIV infection)
- fosamprenavir (another medication for the treatment of HIV infection)
- efavirenz (another medication for the treatment of HIV infection)
- etravirine (another medication for the treatment of HIV infection)
- rilpivirine (another medication for the treatment of HIV infection)
- zidovudine (another medication for the treatment of HIV infection)
- elvitegravir/cobicistat (another medication for the treatment of HIV infection)
Your doctor will carefully monitor the effect of nevirapine and any of these medications if you are using them at the same time.
TakingNevirapine Teva 400 mgwith food and drinks
There are no restrictions on taking nevirapine with food and drinks.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medication.
It is not recommendedthat HIV-positive women breastfeed because HIV infection can be transmitted to the baby through breast milk.
If you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed, you must consultyour doctor as soon as possible.
Driving and using machines
When taking nevirapine, you may experience fatigue. Be cautious when participating in activities such as driving or using tools or machines. If you experience fatigue, you should avoid potentially hazardous tasks such as driving and using tools or machines.
3. How to take Nevirapine Teva 400 mg
Do not use nevirapine on your own. You must use it with at least two otherantiretroviral medications. Your doctor will recommend the appropriate medications for you.
Follow exactly the administration instructions of this medication as indicated by your doctor. In case of doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
Dose:
Adults:
The dose is one 200 mg nevirapine tablet per day for the first 14 days of treatment (initial period). There are other formulations available for this initial period. After 14 days, the usual dose is one 400 mg prolonged-release tablet once a day.
It is very important that you take only one 200 mg nevirapine tablet per day during the first 14 days (initial period). If you experience a rash during this period, do not start taking Nevirapine Teva 400 mg prolonged-release tablets and consult your doctor. |
It has been shown that the 14-day initial period reduces the risk of experiencing a skin rash.
Patients who are already being treated with immediate-release tablets or oral suspension may be switched to prolonged-release tablets without an initial period.
Since Nevirapine must always be taken in combination with other antiretroviral medications, you must follow the instructions of your other medications carefully. These are provided in the leaflets of these medications.
Your doctor will check, if necessary, the availability of other nevirapine formulations, such as an oral suspension (for all age groups, weights, and body surface areas).
You must continue taking nevirapine as long as your doctor indicates.
As explained earlier in the 'Warnings and precautions' section, your doctor will monitor you with liver tests and watch for the appearance of side effects such as rash. Depending on the results, your doctor may decide to discontinue or suspend nevirapine treatment. Similarly, your doctor may decide to restart treatment at a lower dose.
If you have kidneyor liverfailure of any degree, you should only take nevirapine 200 mg tablets or nevirapine 50 mg/5 ml oral suspension. If necessary, your doctor will assess these additional formulations.
Take nevirapine prolonged-release tablets only by mouth. Do not chew the prolonged-release tablets. You can take nevirapine with or without food.
If you take moreNevirapine Teva 400 mgthan you should
Do not take more nevirapine than your doctor has prescribed and as described in this leaflet. There is currently little information on the effects of a nevirapine overdose. Consult your doctor if you have taken more nevirapine than you should. In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, contact the Toxicology Information Service, phone: 91 562 04 20, and indicate the amount ingested.
If you forget to takeNevirapine Teva 400 mg
Try not to miss any dose. If you realize you have missed a dose within 12 hours of the scheduled time, take the missed dose as soon as possible. If more than 12 hours have passed since the scheduled time, only take the next dose at your usual time.
If you interrupt treatment withNevirapine Teva 400 mg
Taking the doses at the indicated times:
- greatly increases the effectiveness of your combination of antiretroviral medications
- reduces the likelihood that the HIV infection will become resistant to the antiretroviral medications
It is essential that you continue taking nevirapine correctly, as described above, unless your doctor indicates that you should stop treatment.
If you interrupt nevirapine administration for more than 7 days, your doctor will indicate that you should start again with the 14-day initial period with nevirapine tablets (as described above) before returning to the daily dose with nevirapine prolonged-release tablets.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
During HIV treatment, there may be an increase in body weight and glucose and lipid levels in the blood. This may be partly related to the recovery of health and lifestyle, and in the case of increased blood lipids, it may sometimes be due to HIV medications themselves. Your doctor will monitor these changes.
Like all medications, this medication can produce adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
As already mentioned in 'Warnings and Precautions', the most important adverse effects of nevirapine are severe skin reactions and life-threatening liver damage. These reactions occur mainly during the first 18 weeks of nevirapine treatment. This is, therefore, an important period that requires close monitoring by your doctor.
If you notice any symptoms of a rash, inform your doctor immediately.
When a rash occurs, it is usually mild to moderate. However, in some patients, a rash appears in the form of a blistering skin reaction that can be severe or life-threatening (Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis), and there have been reported fatalities. Most cases of rash, both severe and mild/moderate, occur during the first six weeks of treatment.
If a rash appears and you also feel unwell, you must stop treatment and see your doctor immediately.
Hypersensitivity reactions (allergies) can occur. Such reactions can appear as anaphylaxis (a severe allergic reaction) with symptoms such as:
- rash
- facial swelling
- difficulty breathing (bronchospasm)
- anaphylactic shock
Hypersensitivity reactions can also present as a rash with other adverse effects such as:
- fever
- blistering of the skin
- mouth ulcers
- eye inflammation
- facial swelling
- generalized swelling
- difficulty breathing
- muscle or joint pain
- decrease in white blood cell count (granulocytopenia)
- general malaise
- severe liver or kidney problems (liver or kidney failure)
If you experience a rash and any of the other adverse effects of a hypersensitivity reaction (allergy), inform your doctor immediately. These reactions can be fatal.
Abnormalities in liver function have been described with the use of Nevirapine. This includes some cases of liver inflammation (hepatitis), which can be sudden and severe (fulminant hepatitis) and liver failure, both of which can be fatal.
Inform your doctor if you experience any of the following clinical symptoms of liver damage:
- loss of appetite
- general malaise (nausea)
- vomiting
- yellowing of the skin (jaundice)
- abdominal pain
The following adverse effects have been reported in patients who received nevirapine 200 mg tablets during the initial 14-day phase:
Frequent (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- rash
- fever
- headache
- abdominal pain
- general malaise (nausea)
- diarrhea
- fatigue
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- allergic reactions (hypersensitivity)
- allergic reactions characterized by rash, facial swelling, difficulty breathing (bronchospasm) or anaphylactic shock
drug reaction with systemic symptoms (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms)
- sudden and severe liver inflammation (fulminant hepatitis)
- severe and potentially fatal skin reactions (Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis)
yellowing of the skin (jaundice)
- urticaria
- fluid under the skin (angioedema)
- vomiting
- muscle pain (myalgia)
- joint pain (arthralgia)
- decrease in white blood cell count (granulocytopenia)
- abnormalities in liver function tests
- decrease in blood phosphorus
- increase in blood pressure
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- liver inflammation (hepatitis)
- decrease in red blood cell count (anemia)
The following adverse effects have been reported in patients who received nevirapine prolonged-release tablets once daily in the maintenance phase:
Frequent (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- rash
- headache
- abdominal pain
- general malaise (nausea)
- liver inflammation (hepatitis)
- fatigue
- abnormalities in liver function tests
- decrease in blood phosphorus
- increase in blood pressure
- vomiting
- diarrhea
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- allergic reactions (hypersensitivity)
- allergic reactions characterized by rash, facial swelling, difficulty breathing (bronchospasm) or anaphylactic shock
drug reaction with systemic symptoms (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms)
- sudden and severe liver inflammation (fulminant hepatitis)
- severe and potentially fatal skin reactions (Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis)
decrease in red blood cell count (anemia)
- decrease in white blood cell count (granulocytopenia)
- yellowing of the skin (jaundice)
- urticaria
- fluid under the skin (angioedema)
- muscle pain (myalgia)
- joint pain (arthralgia)
- fever
When nevirapine has been used in combination with other antiretroviral medications, the following events have also been reported:
- decrease in red blood cell or platelet count
- pancreatitis
- decrease or abnormalities in skin sensations
These effects are generally associated with other antiretroviral agents and may occur when nevirapine is used in combination with other agents; however, it is unlikely that these effects are due to treatment with nevirapine.
Other Adverse Effects in Children and Adolescents
A decrease in white blood cell count (granulocytopenia) may occur, more frequently in children. A decrease in red blood cell count (anemia), which may be related to treatment with nevirapine, is also more frequent in children. As with symptoms of rash, inform your doctor of any adverse effect.
Reporting of Adverse Effects
If you experience any adverse effect, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if it is a possible adverse effect not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the national pharmacovigilance system for human use www.notificaRAM.es By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Storage of Nevirapina Teva 400 mg
Keepthis medicationout of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medication after the expiration date shown on the carton and blister or label on the bottle after "EXP". The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
This medication does not require special storage conditions.
Medications should not be disposed of through wastewater or household waste. Deposit the packaging and medications you no longer need at the SIGRE point in the pharmacy. In case of doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medications you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Composition ofNevirapina Teva 400 mg
- The active ingredient is nevirapine.
Each prolonged-release tablet contains 400 mg of nevirapine.
- The other ingredients are microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, polyethylene oxide, anhydrous colloidal silica, and magnesium stearate.
Appearance of the Product and Package Contents
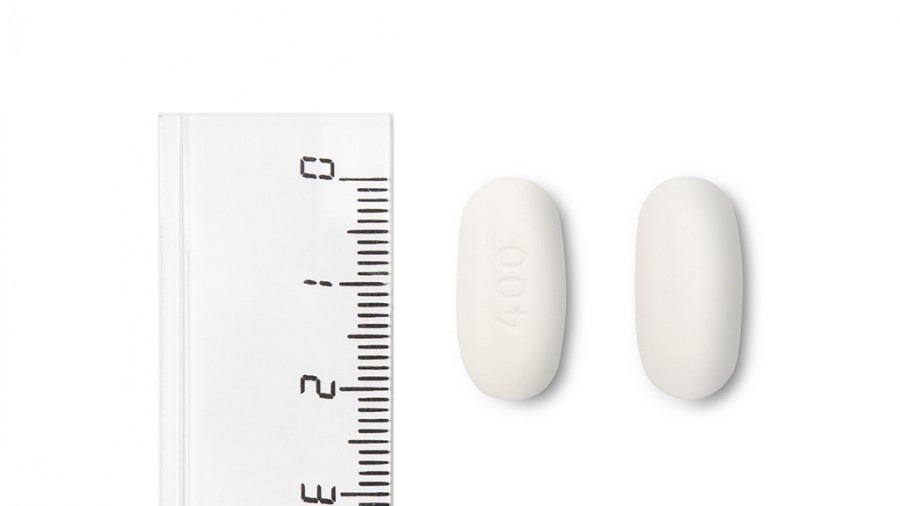
Nevirapina Teva 400 mg prolonged-release tablets EFG are white to off-white, oval, and biconvex tablets, approximately 20.5 mm long and 10 mm wide, engraved with "400" on one side and flat on the other.
Aluminum blisters containing 10, 10x1, 30, 30x1, 60, 60x1, 90, 90x1, 100, and 100x1 prolonged-release tablets, and a high-density polyethylene (HDPE) bottle containing 30 prolonged-release tablets.
Only some pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder
TEVA PHARMA, S.L.U.
C/ Anabel Segura, 11, Edificio Albatros B, 1ª planta,
Alcobendas, Madrid
28108 Spain
Manufacturers
TEVA Gyógyszergyár Zrt.
Pallagi út 13, Debrecen,
4042 Hungary
or
Teva Operations Poland Sp. z.o.o.
ul. Mogilska 80., Kraków
31-546 Poland
This medication is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
DENevirapin-ratiopharm 400 mg Retardtabletten
DKNevirapine Teva B.V.
ESNevirapina Teva 400mg prolonged-release tablets EFG
FRNevirapine Teva LP 400mg, prolonged-release tablet
ITNevirapina Teva Italia
NLNevirapine retard Teva 400 mg, prolonged-release tablets
PTNevirapina Teva
Date of the Last Revision of thisLeaflet:April 2023
Other Sources of Information
Detailed information on this medication is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to NEVIRAPINE TEVA 400 mg PROLONGED-RELEASE TABLETSDosage form: MODIFIED-RELEASE TABLET, 400 mgActive substance: nevirapineManufacturer: Aurovitas Spain, S.A.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 200 mgActive substance: nevirapineManufacturer: Kern Pharma S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 200 mgActive substance: nevirapineManufacturer: Laboratorios Normon S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for NEVIRAPINE TEVA 400 mg PROLONGED-RELEASE TABLETS
Discuss questions about NEVIRAPINE TEVA 400 mg PROLONGED-RELEASE TABLETS, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















