
NABILA 10 mg/ml ORAL SOLUTION


How to use NABILA 10 mg/ml ORAL SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
NABILA 10 mg/ml Oral Solution EFG
Memantine Hydrochloride
Read the entire package leaflet carefully before starting to take this medication, as it contains important information for you.
- Keep this package leaflet, as you may need to read it again. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medication has been prescribed to you only, and you should not give it to others, even if they have the same symptoms as you, as it may harm them.
- If you experience side effects, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are not listed in this package leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the Package Leaflet
- What is Nabila and what is it used for
- What you need to know before taking Nabila
- How to take Nabila
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Nabila
- Package Contents and Additional Information
1. What is Nabila and what is it used for
How Nabila Works
Nabila contains memantine hydrochloride as the active ingredient, which belongs to a group of medications known as anti-dementia medications.
Memory loss in Alzheimer's disease is due to an alteration in brain signals. The brain contains so-called N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors that participate in the transmission of important nerve signals in learning and memory.
Nabila belongs to the group of medications called NMDA receptor antagonists.
This medication acts on these receptors, improving the transmission of nerve signals and memory.
What Nabila is Used For
Nabila is used for the treatment of patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease.
2. What you need to know before taking Nabila
Do Not Take Nabila:
- if you are allergic to memantine hydrochloride or any of the other components of this medication (listed in section 6).
Warnings and Precautions
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting to take Nabila:
- if you have a history of epileptic seizures.
- if you have recently had a myocardial infarction (heart attack), if you suffer from congestive heart failure, or if you have uncontrolled hypertension (high blood pressure).
In these situations, treatment should be carefully monitored, and your doctor should regularly reassess the clinical benefit of Nabila.
You should inform your doctor if you have recently changed or plan to change your diet substantially (e.g., from a normal diet to a strict vegetarian diet) or if you have renal tubular acidosis (RTA, excess of acid-producing substances in the blood due to kidney dysfunction) or severe urinary tract infections (structure that carries urine), as your doctor may need to adjust the dose of the medication.
If you have renal impairment (kidney problems), your doctor should closely monitor your renal function and, if necessary, adapt the memantine doses.
The use of memantine with other medications such as amantadine (for Parkinson's disease treatment), ketamine (a medication generally used to induce anesthesia), dextromethorphan (a medication to treat cough), and other NMDA antagonists should be avoided.
Children and Adolescents
The use of Nabila is not recommended in children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
Taking Nabila with Other Medications
Inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or may need to use another medication.
In particular, the administration of Nabila may produce changes in the effects of the following medications, so your doctor may need to adjust the dose:
- amantadine, ketamine, dextromethorphan
- dantrolene, baclofen
- cimetidine, ranitidine, procainamide, quinidine, quinine, nicotine
- hydrochlorothiazide (or any combination with hydrochlorothiazide)
-anticholinergics (substances generally used to treat movement disorders or intestinal spasms)
- anticonvulsants (substances used to prevent and eliminate convulsions),
- barbiturates (substances generally used to induce sleep),
- dopaminergic agonists (substances such as L-dopa, bromocriptine),
- neuroleptics (substances used in the treatment of mental illnesses),
- oral anticoagulants.
If you are hospitalized, inform your doctor that you are taking Nabila.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medication.
Pregnancy: The use of memantine is not recommended in pregnant women.
Breastfeeding: Women taking memantine should not breastfeed.
Driving and Using Machines
Your doctor will inform you if your condition allows you to drive and use machines safely. Additionally, Nabila may alter your reaction ability, so driving or operating machines may be inappropriate.
Nabila Contains Sorbitol
This medication contains 100 mg of sorbitol per ml of solution.
3. How to Take Nabila
Follow the administration instructions of this medication exactly as indicated by your doctor or pharmacist. If in doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
Dose
Each milliliter (ml) of Nabila oral solution contains 10 milligrams (mg) of memantine hydrochloride.
The recommended dose of Nabila in adult and elderly patients is 2 ml, equivalent to 20 mg, administered once a day. To reduce the risk of side effects, this dose is gradually achieved by following the daily scheme:
Week 1 | 0.5 ml |
Week 2 | 1 ml |
Week 3 | 1.5 ml |
Week 4 and onwards | 2 ml |
? The usual starting dose is 0.5 ml once a day (5 mg) during the first week.
? This dose is increased in the second week to 1 ml once a day (10 mg).
? In the third week, it is increased to 1.5 ml once a day (15 mg).
? From the fourth week onwards, the recommended dose is 2 ml once a day (20 mg).
Dose for Patients with Reduced Renal Function
If you have reduced renal function, your doctor will decide on the appropriate dose for your condition. In this case, your doctor should periodically monitor your renal function.
Administration
? Nabila should be administered orally once a day.
? To get the most out of your medication, you should take it every day and at the same time.
? The solution can be taken directly or with a little water.
? The solution can be taken with or without food.
Instructions for Correct Use
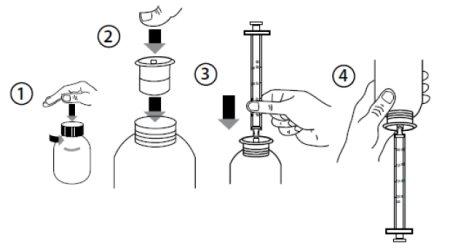
? Open the bottle: press and turn the cap counterclockwise (Figure 1).
? Insert the adapter for the syringe into the neck of the bottle (Figure 2).
? Take the syringe and insert it into the adapter opening (Figure 3).
? Place the bottle upside down (Figure 4).
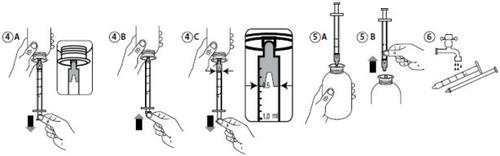
? Fill the syringe with a small amount of solution by pulling the plunger down (Figure 4A). Then, press the plunger in to eliminate any air bubbles (Figure 4B). Finally, fill the syringe by pulling the plunger up to the corresponding milliliter (ml) mark prescribed by your doctor. The flat part of the plunger should coincide with the graduation mark being measured (Figure 4C).
? Place the bottle in a vertical position (Figure 5A).
? Remove the syringe from the adapter (Figure 5B).
? Insert the syringe into your mouth and press the plunger gradually to take the medication. Alternatively, transfer the medication to a spoon or a glass with a small amount of water and take it directly.
? Wash the syringe with water and let it dry for the next use (Figure 6).
? Close the bottle with the cap – leave the adapter in place on the bottle.
Duration of Treatment
Continue taking Nabila while it benefits you. Your doctor should evaluate your treatment periodically.
If You Take More Nabila Than You Should
Generally, taking an excessive amount of Nabila should not cause you any harm. You may experience an increase in the symptoms described in section 4 "Possible Side Effects". In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult your doctor or pharmacist immediately or call the Toxicology Information Service, phone: 91 562 04 20, indicating the medication and the amount ingested.
If You Forget to Take NABILA
If you realize you have forgotten to take your dose of Nabila, wait and take the next dose at the usual time.
Do not take a double dose to make up for the forgotten doses.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Side Effects
Like all medications, this medication can cause side effects, although not everyone will experience them.
Generally, side effects are classified as mild to moderate.
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 patients):
? Headache
? Drowsiness
? Constipation
? Elevated liver function tests (according to blood analysis)
? Dizziness
? Balance disorder
? Difficulty breathing
? High blood pressure
? Hypersensitivity to the medication
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 patients):
? Fatigue
? Fungal infections
? Confusion
? Hallucinations
? Vomiting
? Gait disturbance
? Heart failure
? Formation of blood clots in the venous system (thrombosis/venous thromboembolism)
Very Rare(may affect up to 1 in 10,000 patients):
? Seizures
Frequency Not Known(cannot be estimated from available data):
- Pancreatitis
- Hepatitis (liver inflammation)
- Psychotic reactions.
Alzheimer's disease has been associated with depression, suicidal ideation, and suicide. These events have been reported in patients treated with memantine.
Reporting Side Effects
If you experience any side effects, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are not listed in this package leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Medication Surveillance System for Human Use: www.notificaram.es
By reporting side effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Storage of Nabila
Keep out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medication after the expiration date stated on the carton and on the label of the vial after EXP. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
No special storage conditions are required.
Once opened, the contents of the vial should be used within 3 months.
Medications should not be disposed of through wastewater or household waste. Deposit the packaging and any unused medication in the pharmacy's SIGRE collection point. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and any unused medication. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
NABILA Composition
- The active ingredient is memantine hydrochloride. Each ml of solution contains 10 mg of memantine hydrochloride, equivalent to 8.32 mg of memantine.
- The other components (excipients) are: potassium sorbate (E202), non-crystallizable sorbitol liquid (E-420), and purified water.
Appearance of the Product and Package Contents
Nabila oral solution is a clear and colorless solution.
Nabila oral solution is presented in a 100 ml bottle with a dosing syringe and an adapter for the syringe.
Marketing Authorization Holder
Exeltis Healthcare, S.L.
Avda. de Miralcampo, 7.
Polígono Industrial Miralcampo.
19200 Azuqueca de Henares (Guadalajara).
Spain
Manufacturer
Jenson R+ (Ireland) Ltd.
Unit 15, Daingean Hall,
N4 Axis Centre,
Longford,
N39 W6K0, Ireland
Date of Last Revision of this Package Leaflet: April 2018
Detailed and updated information on this medication is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS)
http://www.aemps.gob.es/
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to NABILA 10 mg/ml ORAL SOLUTIONDosage form: TABLET, 10 mgActive substance: memantineManufacturer: Merz Pharmaceuticals GmbhPrescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 10 mgActive substance: memantineManufacturer: Merz Pharmaceuticals GmbhPrescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 20 mgActive substance: memantineManufacturer: Merz Pharmaceuticals GmbhPrescription required
Online doctors for NABILA 10 mg/ml ORAL SOLUTION
Discuss questions about NABILA 10 mg/ml ORAL SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions














