
ISOFUNDIN SOLUTION FOR INFUSION

How to use ISOFUNDIN SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Isofundin Solution for Infusion
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the Package Leaflet
- What is Isofundin and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Isofundin
- How to use Isofundin
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Isofundin
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Isofundin and what is it used for
Isofundin is a solution for intravenous infusion.
This solution is used for the replacement of fluid losses from the circulation. It can be used in conditions where your blood may become or has become slightly acidic.
2. What you need to know before you use Isofundin
Do not use Isofundin
If you have:
? too much fluid in the circulation,
? severe heart disease with breathing difficulties and swelling in the feet and legs,
? severe kidney disease with inability or difficulty to urinate,
? swelling of body tissues due to fluid accumulation,
? high levels of potassium or calcium in the blood,
? or if your blood is too alkaline.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting to use Isofundin.
Be particularly careful with Isofundin if you have:
? any disease that requires reduced salt intake, such as mild or moderate heart failure, tissue swelling, or fluid accumulation in the lungs,
? sarcoidosis (a chronic disorder of the immune system that affects lymph nodes and connective tissue),
? mild or moderate increase in blood pressure,
? acute dehydration, for example, after severe burns or due to adrenal gland dysfunction,
? high levels of sodium and chloride in the blood,
? eclampsia (a complication that occurs during pregnancy),
? mild or moderate kidney function impairment,
? respiratory problems,
? any disease or medication that you are taking that may reduce sodium excretion,
If any of the above warnings apply to you, your doctor will carefully decide whether the solution is suitable for you.
Your doctor will monitor your fluid and electrolyte levels while you are receiving Isofundin to ensure they are normal.
Using Isofundin with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using or have recently used or might use any other medicines.
It is particularly important that your doctor knows if you are taking, using, or receiving:
? Medicines associated with sodium and water retention, such as:
- corticosteroids, or
- carbenoxolone.
If these medicines are used with Isofundin, your body water and blood sodium levels may increase, causing edema and increased blood pressure.
? Medicines associated with potassium levels in the blood, such as
- suxamethonium
- some diuretics (pills that help eliminate water) that decrease potassium excretion, for example, amiloride, spironolactone, triamterene
- tacrolimus, cyclosporin (medicines used, for example, to prevent organ transplant rejection).
If these medicines are used with Isofundin, your potassium level in the blood may increase, which can cause adverse effects on your heart function. This is more likely to happen if you have kidney failure.
? Digitalis glycoside preparations (e.g., digoxin), which are used to treat heart weakness.
Their effects are enhanced by an increase in calcium levels in the blood, and adverse effects such as irregular heartbeat may appear. Therefore, your doctor will need to adjust your digoxin dose.
? Vitamin D, which can cause an increase in calcium levels in the blood.
Your doctor will be aware of the adverse effects that may appear after combining Isofundin with the aforementioned medicines. In turn, they will ensure that the infusion you receive is properly dosed.
Some medicines do not mix with Isofundin. Doctors will only administer medicines with Isofundin if they are sure the mixture is safe.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Your doctor will decide if this solution is suitable for you when you are pregnant.
This medicine will be used with caution in pregnancy toxemia, a special complication that can occur during pregnancy.
Driving and using machines
Isofundin has no influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
Isofundin contains sodium
If you are on a low-sodium diet, note that this medicine contains 145 mmol of sodium per 1000 ml.
3. How to use Isofundin
Method of administration
This medicine will be administered into a vein by drip.
Dose
Your doctor will determine the amount of solution you need.
In adults, elderly patients, and adolescents, this can be 500 milliliters to 3 liters per day. The daily dose in infants and children may range from 20 to 100 milliliters per kilogram of body weight per day.
Rate of administration
Your doctor will determine the infusion rate of the solution, depending on your body weight and condition.
Duration of treatment
Your doctor will determine how long you should receive this solution.
While you are receiving the infusion, your fluid and electrolyte levels and acid-base balance should be monitored.
If you receive more Isofundin than you should
Since the dose administered to you will be controlled by your doctor or nurse, it is unlikely that you will receive an excess of this solution.
However, if you accidentally receive more solution than you should or the solution flows too quickly, you may experience symptoms such as:
- increased skin tension,
- congestion in the veins or swelling,
- fluid accumulation in the lungs,
- shortness of breath,
- abnormalities in the composition of body fluids
Excessively high levels of any of the individual components of Isofundin may be associated with specific symptoms that your doctor should be aware of.
In case of overdose, the infusion should be stopped immediately and corrective treatment initiated.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Some side effects can be due to the administration technique. These can include feverish states, infections at the injection site, local reaction or pain, venous irritation, blood clots in veins, or inflammation of the veins extending from the injection site.
Allergic reactions characterized by hives have been occasionally reported after magnesium salt infusion.
The frequency of these reactions cannot be estimated from the available data.
In rare cases, intestinal paralysis has been reported after magnesium sulfate infusion. This can affect up to 1 in 1000 people.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Medicines and Healthcare Products Agency (AEMPS) website: www.notificaRAM.es
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Isofundin
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Glass bottles and polyethylene plastic bottles: Do not refrigerate or freeze. Plastic bags: Do not store above 25°C. Do not refrigerate or freeze.
Do not use this medicine if the solution contains particles, is cloudy, or discolored. Do not use this product if the packaging is damaged or shows signs of deterioration. This product is for single use; partially used containers must not be reconnected.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the label or carton after EXP.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
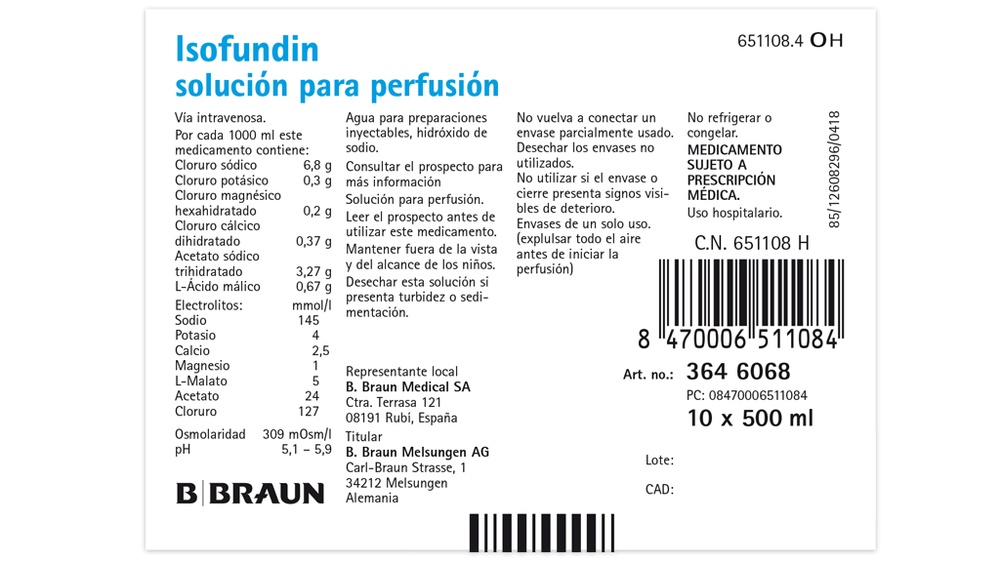
Composition of Isofundin
The active ingredients of Isofundin solution for infusion are:
Per 1000 ml, this medicine contains:
Sodium chloride 6.8 g
Potassium chloride 0.3 g
Magnesium chloride hexahydrate 0.2 g
Calcium chloride dihydrate 0.37 g
Sodium acetate trihydrate 3.27 g
Malic acid 0.67 g
The other ingredients are: Water for injections, sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment).
Appearance and packaging of the product
Isofundin is a solution for infusion (for intravenous administration with a drip). It is a clear and colorless solution.
It is available in:
- Polyethylene plastic bottles containing 250 ml, 500 ml, or 1000 ml, available in packs of 1 or 10 bottles
- Plastic bags containing 250 ml, 500 ml, or 1000 ml, available in packs of 1 or 20 bags (250 ml and 500 ml) or 1 or 10 bags (1000 ml)
- Glass bottles containing 250 ml, 500 ml, or 1000 ml, available in packs of 1 or 10 bottles (250 ml and 500 ml) or 1 or 6 bottles (1000 ml).
Marketing authorization holder
B|BRAUN
- Braun Melsungen AG
Carl-Braun-Strasse, 1 Postal address:
34212 Melsungen 34209 Melsungen
Germany
Tel.: + 49-5661-71-0
Fax.: +49-5661-71-4567
Manufacturer
B.Braun Melsungen AG
Carl-Braun-Strasse, 1
34212 Melsungen
Germany
- Braun Medical, S.A.
Ctra. de Terrassa, 121
08191-Rubí (Barcelona)
Spain
- Braun Avitum AG
Schwarzenberger Weg 73-79
34212 Melsungen
Germany
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Austria | Sterofundin ISO Infusionslösung |
Belgium | Sterofundin ISO oplossing voor infusie |
Bulgaria | Sterofundin ISO |
Cyprus | Sterofundin ISO |
Czech Republic | Ringerfundin B.Braun |
Denmark | Ringerfundin |
Estonia | Sterofundin ISO |
Finland | Ringerfundin infuusioneste, liuos |
France | Isofundine, solution pour perfusion |
Germany | Sterofundin ISO Infusionslösung |
Greece | Sterofundin ISO |
Hungary | Ringerfundin B. Braun infúzio |
Italy | Sterofundin |
Latvia | Sterofundin ISO |
Lithuania | Sterofundin ISO infuzinis tirpalas |
Luxembourg | Sterofundin Iso solution pour perfusion |
Malta | Sterofundin ISO |
Netherlands | Sterofundin ISO |
Norway | Ringerfundin infusjonsvaeske |
Poland | Sterofundin ISO |
Portugal | Isofundin, solução para perfusão |
Romania | Sterofundin ISO solutie perfuzabila |
Slovenia | Sterofundin ISO raztopina za infundiranje |
Slovakia | Ringerfundin |
Spain | Isofundin, solución para perfusión |
Sweden | Ringerfundin infusionsvästka, lösning |
United Kingdom | Sterofundin ISO solution for infusion |
Date of last revision of this leaflet: February 2018
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Healthcare Products (AEMPS) (http://www.aemps.gob.es/)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
Symptoms associated with excessive overdose of individual components of the solution:
- Symptoms of hyperkalemia:
Paresthesia in the limbs, muscle weakness, paralysis, cardiac arrhythmia, asystole, and mental confusion.
- Symptoms of hypermagnesemia:
Loss of tendon reflexes and respiratory depression, nausea, vomiting, skin flushing, thirst, decreased blood pressure, drowsiness, confusion, muscle weakness, bradycardia, coma, and cardiac arrest.
- Symptoms of hyperchloremia:
Loss of bicarbonate and acidosis.
- Symptoms of hypercalcemia:
Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, constipation, abdominal pain, muscle weakness, mental disorders, polydipsia, polyuria, nephrocalcinosis, and, in severe cases, cardiac arrhythmias and coma. The intravenous injection of calcium salts too quickly can cause a chalky taste and flushing.
- Symptoms of excessive overdose of acetate and malate:
Metabolic alkalosis, which can cause mood changes, fatigue, shortness of breath, muscle weakness, and cardiac arrhythmia, and, in the presence of low calcium levels, also spasms and cramps.
Handling
The solution should be administered with sterile equipment using aseptic technique. The equipment should be prepared with the solution to prevent air from entering the system.
If plastic bags are used, only the outer bag should be removed immediately before use.
If administration is by rapid infusion under pressure, all air should be eliminated from the plastic container and infusion equipment before infusion, as otherwise there is a risk of producing gas embolism during infusion.
During administration, fluid balance, plasma electrolyte concentrations, and pH should be monitored. Isofundin can be administered as long as fluid replacement is indicated.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to ISOFUNDIN SOLUTION FOR INFUSIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 1361 mgActive substance: electrolytesManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi España, S.A.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE INFUSION, 2% Sodium Chloride / 100 mlActive substance: electrolytesManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi España, S.A.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 33 mg / 30 mg / 860 mgActive substance: electrolytesManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi España, S.A.U.Prescription required
Online doctors for ISOFUNDIN SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Discuss questions about ISOFUNDIN SOLUTION FOR INFUSION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















