
INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml EMULSION FOR INFUSION


How to use INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml EMULSION FOR INFUSION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Prospective: Information for the User
INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml Emulsion for Infusion
Purified Soybean Oil
Read the entire prospectus carefully before starting to use the medication:
If you consider that any of the adverse effects you are suffering from is serious or if you notice any adverse effect not mentioned in this prospectus, inform your doctor or pharmacist.
|
In this prospectus:
- What INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml is and what it is used for
- Before using INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml
- How to use INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml
- Possible side effects
- Storage of INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml
- Additional information for the healthcare professional
1. What INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml is and what it is used for
INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml is a lipid emulsion for intravenous infusion. It is presented in plastic bags with an overbag of 100 ml, 250 ml, and 500 ml. It belongs to the group of medications called intravenous solutions for parenteral nutrition.
INTRALIPID is indicated in patients who need intravenous nutrition for energy and essential fatty acid intake. INTRALIPID is also indicated in patients with essential fatty acid deficiency (EFAD) who cannot maintain or restore a normal pattern of essential fatty acids through oral intake.
2. Before using INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml
Do not use INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml:
INTRALIPID is contraindicated in patients with acute shock and in patients with severe hyperlipemia. Severe liver failure. Hemophagocytic syndrome.
Hypersensitivity (allergy) to egg protein, soy, or peanut or to any of the active ingredients or excipients.
Be careful with INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml:
INTRALIPID should be administered with caution in cases of lipid metabolism disorders such as renal insufficiency, uncompensated diabetes mellitus, pancreatitis, liver function disorders, hypothyroidism (if hypertriglyceridemia is present), and sepsis. If INTRALIPID is administered to patients in these situations, strict control of serum triglyceride concentration is mandatory.
This product contains soybean oil and egg phospholipids, which can very rarely cause allergic reactions. Cross-allergic reactions have been observed between soy and peanut.
INTRALIPID should be administered with caution to neonates and premature infants with hyperbilirubinemia and in cases of possible pulmonary hypertension. In neonates, and particularly in premature infants, with long-term parenteral nutrition, platelet count, liver function tests, and serum triglyceride concentration should be monitored.
INTRALIPID may interfere with certain laboratory tests (bilirubin, lactate dehydrogenase, oxygen saturation, Hb, etc.), if the blood sample is taken before the lipids have been adequately eliminated from the bloodstream. Lipids are eliminated after a lipid-free period of 5-6 hours, in most patients.
When used in newborns and children under 2 years, the solution (in bags and administration equipment) should be protected from light exposure until administration is completed (see section 2).
Use of other medications:
Certain medications, such as insulin, may interfere with the body's lipase system. However, this type of interaction has only minor clinical importance.
Heparin, at therapeutic doses, produces a transient increase in plasma lipolysis, resulting in a transient decrease in triglyceride clearance due to depletion of lipoprotein lipase.
Soybean oil contains vitamin K1, which should be taken into account in patients treated with coumarin derivatives, as they interfere with vitamin K1.
This medication should not be mixed with other products unless compatibility data are available.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using or have recently used any other medication, including those purchased without a prescription.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding:
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before using any medication.
No adverse effects have been reported during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Driving and using machines:
No effects on the ability to drive and use machines are expected.
3. How to use INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml
Follow the administration instructions for Intralipid 200 mg/ml exactly as indicated by your doctor. Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you have doubts.
Due to the risk of microbiological contamination, an opened container should be infused within a maximum of 24 hours.
When used in newborns and children under 2 years, the solution (in bags and administration equipment) should be protected from light exposure until administration is completed (see section 2).
Dosage and administration method
The ability to eliminate INTRALIPID should determine the dosage and infusion rate. See later, Lipid elimination.
DOSAGE
1 g of triglycerides corresponds to 5 ml of INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml.
Adults. The recommended maximum dose is 3 g of triglycerides/kg body weight/day. Administering this upper limit, INTRALIPID provides 70% of energy requirements, even in patients with highly increased energy requirements. The infusion rate for INTRALIPID should not exceed 500 ml in 5 hours.
Neonates and children. The recommended dose range in neonates and children is 0.5-4 g of triglycerides/kg body weight/day. The infusion rate should not exceed 0.17 g of triglycerides/kg body weight/hour (4 g in 24 hours). In premature infants and low-birth-weight neonates, INTRALIPID should be infused continuously over 24 hours. The initial dose should be 0.5-1 g/kg body weight/day, followed by a successive increase of 0.5-1 g/kg body weight/day up to 2 g/kg body weight/day. The dose can be increased up to 4 g/kg body weight/day, only under close monitoring of serum triglyceride concentration, liver function tests, and oxygen saturation. The indicated rates are the maximum rates and should not be exceeded to compensate for missed doses.
Essential fatty acid deficiency (EFAD). To prevent or correct an essential fatty acid deficiency, 4-8% of non-protein energy should be provided as INTRALIPID to provide sufficient amounts of linoleic and linolenic acid. If EFAD is associated with stress, the amount of INTRALIPID required to correct the deficiency may be substantially higher.
LIPID ELIMINATION
Adults. The ability to eliminate lipids should be closely monitored in patients with the conditions mentioned in the section "Before using INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml", and in patients who receive INTRALIPID for more than one week. This is done by collecting a blood sample after a lipid-free period of 5-6 hours. The blood cells are then separated from the plasma by centrifugation. If the plasma is opalescent, the infusion should be postponed. The sensitivity of this method may cause hypertriglyceridemia to go unnoticed. Therefore, it is recommended that serum triglyceride concentrations be determined in patients who are likely to have altered lipid tolerance.
Neonates and children. The ability to eliminate lipids should be regularly monitored in neonates and children. Determining serum triglyceride levels is the only reliable method.
If you use more INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml than you should:
See the section "Possible side effects", "Lipid overload syndrome". Severe overdose of lipid emulsions containing triglycerides can, especially if carbohydrates are not administered simultaneously, lead to acidosis.
If you have any other doubts about the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medications, INTRALIPID can cause side effects, although not everyone will experience them.
Infusion of INTRALIPID may cause an increase in body temperature and, less frequently, chills, tremors, and nausea/vomiting (incidence <1%).
Reports of other adverse reactions related to INTRALIPID infusions are extremely rare, less than one adverse report per million infusions.
Classification of organ systems according to WHO | Frequency | Symptom |
General disorders at the body level | Uncommon (more than 1 in 1,000, less than 1 in 100) Rare (less than 1 in 10,000) | Headache, increased body temperature, chills, tremors, fatigue Anaphylactic reaction (allergic reaction) |
Cardiovascular disorders | Rare (less than 1 in 10,000) | Circulatory effects e.g. hyper/hypotension (high or low blood pressure) |
Gastrointestinal disorders | Uncommon (more than 1 in 1,000, less than 1 in 100) | Abnormal pain, Nausea, vomiting |
Hepatobiliary disorders | Rare (less than 1 in 10,000) | Transient increase in liver function tests |
Musculoskeletal, connective tissue, and bone disorders | Rare (less than 1 in 10,000) | Abdominal pain |
Blood and lymphatic system disorders | Rare (less than 1 in 10,000) | Thrombocytopenia (decreased platelet count) |
Red blood cell disorders | Rare (less than 1 in 10,000) | Hemolysis (red blood cell breakdown), reticulocytosis (increased reticulocytes) |
Male reproductive system disorders | Rare (less than 1 in 10,000) | Priapism (prolonged erection) |
Skin disorders | Rare (less than 1 in 10,000) | Rash (skin eruption), urticaria |
Thrombocytopenia associated with prolonged treatment with INTRALIPID has been reported in children. A transient increase in liver function tests has also been detected after prolonged intravenous nutrition with or without INTRALIPID. Increased cholesterol has been observed in children after prolonged treatment with INTRALIPID. The reasons are not clear at present.
Lipid overload syndrome. An altered ability to eliminate INTRALIPID can lead to a lipid overload syndrome as a result of overdosing. However, this syndrome can also occur at recommended infusion rates associated with sudden changes in the patient's clinical situation, such as altered renal function or infection. The lipid overload syndrome is characterized by hyperlipemia, fever, lipid infiltration, alterations in various organs, and coma. All symptoms are generally reversible if the infusion of INTRALIPID is stopped.
If you consider that any of the side effects you are experiencing is serious or if you notice any side effect not mentioned in this prospectus, inform your doctor or pharmacist.
5. Storage of INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml
Store at a temperature below 25°C. Do not freeze.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Do not use INTRALIPID after the expiration date stated on the packaging after the letters EXP. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Do not use INTRALIPID if you notice that the packaging is damaged. For the bag: after inspecting the integrity indicator, the overbag should be removed.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your doctor how to dispose of the packaging and any unused medication. This will help protect the environment.
When used in newborns and children under 2 years, the solution (in bags and administration equipment) should be protected from light exposure until administration is completed (see section 2).
6. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Composition of INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml
1 ml of emulsion contains:
The active ingredient is:
Purified soybean oil 200 mg
The other components are: purified egg phospholipids, glycerol (anhydrous), water for
injectable preparations.
Appearance of the product and packaging content
Infusion bag: the bag consists of an inner bag (primary packaging) with an overbag. Between the inner bag and the overbag, an oxygen absorber and an integrity indicator (Oxalert) are placed
The overbag, oxygen absorber, and integrity indicator must be discarded after opening the overbag. The integrity indicator (OxalertTM) reacts with free oxygen and changes color in case of alteration of the overbag.
Package sizes: bags of 100 ml, 250 ml, and 500 ml.
10 bags of 250 ml
12 bags of 500 ml
Only some types or sizes of packaging may be marketed.
All components of the packaging materials are latex-free and
PVC-free.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Holder: Fresenius Kabi España S.A.U
C/ Marina 16-18, Torre Mapfre 08005 Barcelona
Manufacturer:
Fresenius Kabi AB
Rapsgatan 7, 751 82 Uppsala
Sweden
This leaflet was approved in October 2019.
Detailed and updated information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the
Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for doctors or healthcare professionals
Instructions for use/manipulation
Use only if the packaging remains intact. For the bag: after inspecting the integrity indicator, the overbag must be removed.
Additions must be made aseptically. The isolated addition of electrolyte solutions to INTRALIPID should not be carried out. Only medicinal, nutritional, or electrolyte solutions whose compatibility has been documented may be added directly. Compatibility data are available from the manufacturer for several mixtures. The remaining content of opened bags must be discarded and not kept for later use.
When used in newborns and children under 2 years, the solution (in bags and administration equipment) must be protected from light exposure until administration is completed.
Special precautions for storage
After adding other nutritional elements
Mixture in plastic bag (phthalate-free film): mixtures prepared aseptically in a controlled and validated aseptic area must be used within 7 days after preparation. Mixtures can be stored for up to 6 days under refrigeration (2-8°C), followed by a maximum perfusion period of 24 hours.
Exposure to light of intravenous parenteral nutrition solutions, especially after mixing with trace elements or vitamins, may have adverse effects on the clinical outcome of newborns due to the generation of peroxides and other degradation products. When used in newborns and children under 2 years, INTRALIPID must be protected from ambient light until administration is completed.
Special precautions for disposal and other manipulations:
When used in newborns and children under 2 years, it must be protected from light exposure until administration is completed. Exposure of INTRALIPID to ambient light, especially after mixing with trace elements or vitamins, generates peroxides and other degradation products that can be reduced if the product is protected from light exposure.
Instructions for use
Fresenius Kabi infusion bags
- Inspect the integrity indicator (Oxalert TM ) A before removing the overbag. If the
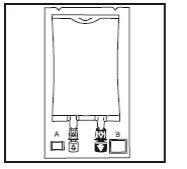 indicator is black, oxygen has entered the overbag and the product should be rejected.
indicator is black, oxygen has entered the overbag and the product should be rejected.
- Remove the overbag by tearing along the notch and pulling downwards along the packaging. The
Oxalert A bag and oxygen absorber B should be discarded.
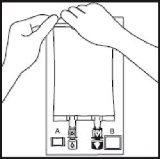
- If the use of additives is required, break the white addition port by the arrow-shaped mark (A). If no
additives are required, proceed to step 5.
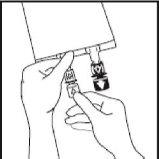
- Insert the needle horizontally through the center of the addition port membrane and
inject the additives (of known compatibility). Use syringes with 18-23 gauge needles and a maximum length of 40 mm.
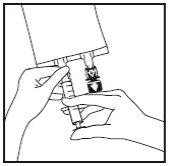
- Use a perfusion equipment without air intake or close the air intake of the perfusion equipment. Follow the instructions for use of the perfusion equipment. Use a tip with the specified diameter according to ISO standard 8536-4, 5,6 +/- 0.1 mm.
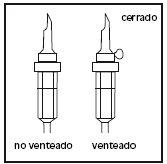
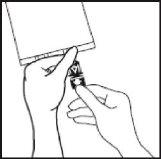
- Break the blue perfusion port by the arrow-shaped mark
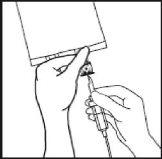
- Hold the base of the perfusion port. Insert the tip through the perfusion port by means of a slight wrist rotation until the tip is fully inserted.
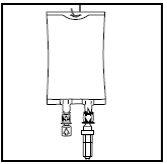
- Hang the bag on the hanger by the perforated notch and start the perfusion.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml EMULSION FOR INFUSIONDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 200 mg/mlActive substance: fat emulsionsManufacturer: Baxter S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSIONActive substance: fat emulsionsManufacturer: B Braun Medical S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSIONActive substance: fat emulsionsManufacturer: B Braun Medical S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml EMULSION FOR INFUSION
Discuss questions about INTRALIPID 200 mg/ml EMULSION FOR INFUSION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















