INFANRIX HEXA powder and suspension for injectable suspension

How to use INFANRIX HEXA powder and suspension for injectable suspension
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Infanrix hexa,Powder and suspension for suspension for injection in a pre-filled syringe
Vaccine against diphtheria (D), tetanus (T), pertussis (acellular component) (Pa), hepatitis B (recombinant DNA) (HBV), poliomyelitis (inactivated) (IPV), and Haemophilus influenzaetype b (Hib) conjugate (adsorbed).
Read all of this leaflet carefully before your child is given this vaccine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This vaccine has been prescribed for your child. Do not pass it on to others.
- If your child experiences any side effects, consult your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What Infanrix hexa is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before your child is given Infanrix hexa
- How Infanrix hexa is given
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Infanrix hexa
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Infanrix hexa is and what it is used for
Infanrix hexa is a vaccine that is used to protect your child against six diseases:
- Diphtheria: a serious bacterial disease that mainly affects the respiratory tract and, sometimes, the skin, causing severe respiratory problems and, sometimes, suffocation. The bacteria also release a toxin that can cause nerve damage, heart problems, and even death.
- Tetanus: the tetanus bacteria, commonly found in soil, dust, horse manure, and wood splinters, enter the body through cuts, scratches, or wounds in the skin and release a toxin. This can cause muscle stiffness, painful muscle spasms, convulsions, and even death.
- Pertussis (whooping cough): a highly contagious bacterial infection that affects the respiratory tract, causing a prolonged cough that often has a characteristic "whoop" sound. It can also cause ear infections, chest infections (bronchitis), lung infections (pneumonia), convulsions, brain damage, or even death.
- Hepatitis B: caused by the hepatitis B virus, which attacks the liver. The virus can cause a lifelong infection and may lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer.
- Poliomyelitis: an infection caused by a virus that can sometimes cause nerve damage and permanent damage, making muscles unable to move (paralysis), including the muscles needed for breathing and walking. It can cause permanent damage or even death.
- Haemophilus influenzaetype b (Hib): a bacterial infection. It can cause meningitis (inflammation of the brain), which can cause mental retardation (delay), cerebral palsy, deafness, epilepsy, or partial blindness. It can also cause throat swelling, leading to death by suffocation. It can also infect the blood, heart, lungs, bones, joints, and tissues of the eyes and mouth.
How Infanrix hexa works
- Infanrix hexa helps the body to develop its own protection (antibodies). This will protect your child against these diseases.
- As with all vaccines, Infanrix hexa may not completely protect all vaccinated children.
- The vaccine cannot cause the diseases it protects your child against.
2. What you need to know before your child is given Infanrix Hexa
Infanrix hexa must not be given
- if your child is allergic to:
- Infanrix hexa or any of the other components of this vaccine (listed in section 6).
- Formaldehyde.
- Neomycin or polymyxin (antibiotics).
Signs of an allergic reaction may include skin itching, rash, decreased breathing, and swelling of the face or tongue.
- if your child has had an allergic reaction to any vaccine against the diseases: diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B, polio, or Haemophilus influenzaetype b.
- if your child has had neurological problems in the 7 days following previous administration of a pertussis vaccine.
- if your child has a severe infection with fever (over 38 °C). A minor infection, such as a cold, should not be a problem for vaccination, but tell your doctor first.
Infanrix hexa must not be given if any of the above situations apply to your child. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before your child is given Infanrix hexa.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before your child is given Infanrix hexa:
- if, after a previous administration of Infanrix hexa or another pertussis vaccine, your child has had any problems, especially:
- fever (over 40 °C) in the 48 hours following vaccination
- collapse or shock-like state in the 48 hours following vaccination
- prolonged, inconsolable crying lasting 3 hours or more, occurring within 48 hours of vaccination
- seizures (with or without fever) in the 3 days following vaccination
- if your child has an undiagnosed or progressive brain disease or uncontrolled epilepsy. The vaccine can be given once the disease is under control
- if your child has any bleeding problems or bruises easily
- if your child tends to have seizures when they have a fever, or if there is a family history.
- if your child stops responding or has seizures (fits) after vaccination, contact your doctor immediately. See also section 4 Possible side effects.
- if your baby was born very prematurely (at 28 weeks of gestation or less) they may experience longer pauses between breaths than usual during the 2-3 days following vaccination. These babies may require respiratory monitoring for 48-72 hours after administration of the first two or three doses of Infanrix hexa.
If any of the above situations apply to your child (or you are not sure), talk to your doctor or pharmacist before your child is given Infanrix hexa.
Using Infanrix hexa with other medicines
Your doctor may ask you to give your child a medicine that reduces fever (such as paracetamol) before or immediately after administration of Infanrix hexa. This may help reduce some of the side effects (febrile reactions) of Infanrix hexa.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if your child is taking, has recently taken, or might take any other medicines or has recently received any other vaccine.
Infanrix hexa contains neomycin, polymyxin, para-aminobenzoic acid, phenylalanine, sodium, and potassium
This vaccine contains neomycin and polymyxin (antibiotics). Tell your doctor if your child has had an allergic reaction to these components.
Infanrix Hexa contains para-aminobenzoic acid. It may cause allergic reactions (possibly delayed) and, exceptionally, bronchospasm.
This vaccine contains 0.0298 micrograms of phenylalanine per dose. Phenylalanine may be harmful in case of phenylketonuria (PKU), a rare genetic disorder in which phenylalanine accumulates because the body cannot eliminate it properly.
This vaccine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per dose; this is, essentially, “sodium-free”.
This vaccine contains potassium, less than 1 mmol (39 mg) per dose; this is, essentially, “potassium-free”.
3. How Infanrix Hexa is given
How much is given
- Your child will receive a total of two or three injections with an interval of at least 2 or 1 month(s) between each injection.
- The doctor or nurse will tell you when your child needs to come back for the next injections.
- The doctor will inform you if additional injections (booster doses) are needed.
How the vaccine is given
- Infanrix hexa is injected into a muscle.
- The vaccine must never be injected into a blood vessel or into the skin.
If your child misses a dose
- If your child misses a scheduled injection, it is important that you schedule another appointment.
- Make sure your child completes the full vaccination series. Otherwise, your child may not be fully protected against the diseases.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this vaccine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following side effects can occur with this vaccine:
Allergic reactions
If your child has an allergic reaction, see a doctor immediately. The signs may include:
- rashes that can be itchy or blistering
- swelling of the eyes and face
- difficulty breathing or swallowing
- a sudden drop in blood pressure and loss of consciousness.
These signs usually start soon after receiving the injection. Talk to a doctor immediately if this happens when leaving the clinic.
See your doctor immediately if your child has any of the following serious side effects:
- collapse
- loss of consciousness
- seizures (with or without fever).
These side effects have occurred very rarely with Infanrix hexa and other pertussis vaccines. They usually occur within 2 or 3 days of vaccination.
Other side effects include:
Very common(may affect more than 1 in 10 doses of the vaccine): drowsiness, loss of appetite, elevated temperature of 38 °C or more, swelling, pain, redness at the injection site, abnormal crying, feeling irritable or restless.
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 doses of the vaccine): diarrhea, vomiting, elevated temperature over 39.5 °C, swelling or hardness more than 5 cm at the injection site, feeling nervous.
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 doses of the vaccine): upper respiratory tract infection, fatigue, cough, extensive swelling of the limb where the vaccine was administered.
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 doses of the vaccine): bronchitis, rash, swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck, armpit, and groin, bleeding or bruising more easily than usual (thrombocytopenia), in premature infants (born at 28 weeks of gestation or less) pauses between breaths may be longer than usual during the 2-3 days following vaccination, temporary stop in breathing (apnea), swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue, or throat which can cause difficulty swallowing or breathing (angioedema), swelling of the entire limb where the vaccine was administered, blisters.
Very rare(may affect up to 1 in 10,000 doses of the vaccine): itching (dermatitis).
Experience with the hepatitis B vaccine
In extremely rare cases, the following side effects have been reported with the hepatitis B vaccine: paralysis, numbness or weakness of the arms and legs (neuropathy), inflammation of some nerves, possibly with tingling or loss of sensation or movement (Guillain-Barré syndrome), inflammation or infection of the brain (encephalopathy, encephalitis), infection around the brain (meningitis).
No causal relationship has been established with the vaccine.
Bleeding or bruising more easily than usual (thrombocytopenia) has been reported with hepatitis B vaccines.
Reporting of side effects
If your child experiences any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly through the national reporting system listed in Appendix V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Infanrix Hexa
- Keep this vaccine out of the sight and reach of children.
- Do not use this vaccine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton. The expiry date is the last day of the month stated.
- Store in a refrigerator (between 2 °C and 8 °C).
- Store in the original package to protect from light.
- Do not freeze. Freezing destroys the vaccine.
- Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Container contents and additional information
Composition of Infanrix hexa
The active substances are:
Diphtheria toxoid1 at least 30 International Units
Tetanus toxoid1 at least 40 International Units
Bordetella pertussisantigens
Pertussis toxoid1 25 micrograms
Filamentous hemagglutinin1 25 micrograms
Pertactin1 8 micrograms
Hepatitis B surface antigen2,3 10 micrograms
Inactivated poliovirus
type 1 (Mahoney strain)4 40 D antigen units
type 2 (MEF-1 strain)4 8 D antigen units
type 3 (Saukett strain)4 32 D antigen units
Haemophilus influenzaetype b polysaccharide 10 micrograms
(polyribosylribitol phosphate)3
conjugated with tetanus toxoid as a carrier protein approx. 25 micrograms
1adsorbed on hydrated aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3) 0.5 milligrams Al3+
2produced in yeast cells (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) by recombinant DNA technology
3adsorbed on aluminum phosphate (AlPO4) 0.32 milligrams Al3+
4propagated in VERO cells
The other components are:
Hib powder: anhydrous lactose
DTPa-VHB-VPI suspension: sodium chloride (NaCl), 199 medium (containing amino acids (including phenylalanine), mineral salts (including sodium and potassium), vitamins (including para-aminobenzoic acid) and other substances) and water for injections.
Appearance of the product and container contents
- The diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B, and inactivated poliomyelitis (DTPa-VHB-VPI) component is a white, slightly milky liquid and is presented in a pre-filled syringe (0.5 ml).
- The Hib component is a white lyophilized powder and is presented in a glass vial.
- Both components are mixed just before your child receives the injection. The appearance of the mixture is a white, slightly milky liquid.
- Infanrix hexa is available in a vial of 1 dose + pre-filled syringe, pack sizes of 1 and 10 with and without separate needles, and a multipack of 5 packs, each containing 10 vials (1 dose) and 10 pre-filled syringes (1 dose), without separate needles.
- Only some pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals s.a.
Rue de l'Institut 89
B-1330 Rixensart
Belgium
You can request more information about this medicinal product by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
België/Belgique/Belgien GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals SA/NV Tél/Tel: + 32 10 85 52 00 | Lietuva GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA Tel: +370 80000334 |
| Luxembourg/Luxemburg GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals SA/NV Tél/Tel: + 32 10 85 52 00 |
Ceská republika GlaxoSmithKline s.r.o. Tel: + 420 22 2 00 11 11 | Magyarország GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA Tel.: +36 80088309 |
Danmark GlaxoSmithKline Pharma A/S Tlf.: + 45 36 35 91 00 | Malta GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA Tel: +356 80065004 |
Deutschland GlaxoSmithKline GmbH & Co. KG Tel: + 49 (0)89 360448701 | Nederland GlaxoSmithKline BV Tel: + 31 (0)33 2081100 |
Eesti GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA Tel: +372 8002640 | Norge GlaxoSmithKline AS Tlf: + 47 22 70 20 00 |
Ελλάδα GlaxoSmithKline Μονοπρ?σωπη A.E.B.E. Τηλ: + 30 210 68 82 100 | Österreich GlaxoSmithKline Pharma GmbH. Tel: + 43 (0)1 97075 0 |
España GlaxoSmithKline, S.A. Tel: + 34 900 202 700 | Polska GSK Services Sp. z o.o. Tel.: + 48 (22) 576 9000 |
France Laboratoire GlaxoSmithKline Tél: + 33 (0) 1 39 17 84 44 Hrvatska GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA Tel: +385 800787089 | Portugal Smith Kline & French Portuguesa, Produtos Farmacêuticos, Lda. Tel: + 351 21 412 95 00 România GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA Tel: +40 800672524 |
Ireland GlaxoSmithKline (Ireland) Ltd Tel: + 353 (0)1 495 5000 | Slovenija GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA Tel: +386 80688869 |
Ísland Vistor hf. Sími: +354 535 7000 | Slovenská republika GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA. Tel: +421 800500589 |
Italia GlaxoSmithKline S.p.A. Tel:+ 39 (0)45 7741 111 | Suomi/Finland GlaxoSmithKline Oy Puh/Tel: + 358 (0)10 30 30 30 |
Κ?προς GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA Τηλ: +357 80070017 | Sverige GlaxoSmithKline AB Tel: + 46 (0)8 638 93 00 |
Latvija GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA Tel: +371 80205045 | United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA Tel: +44(0)800 221441 |
Date of last revision of this leaflet:
Other sources of information
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the European Medicines Agency website: https://www.ema.europa.eu/
The leaflet for this medicinal product is available in all EU/EEA languages on the European Medicines Agency website.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
After storage, a clear liquid and a white deposit may be observed in the pre-filled syringe containing the DTPa-VHB-VPI suspension. This is a normal observation.
The pre-filled syringe should be shaken well to obtain a white, turbid, and homogeneous suspension.
The vaccine is reconstituted by adding the entire contents of the pre-filled syringe to the vial containing the lyophilized powder. The mixture should be shaken well until the lyophilized powder is completely dissolved before administration.
The reconstituted vaccine appears as a slightly more turbid suspension than the liquid component alone. This is a normal observation.
The vaccine suspension should be visually examined before and after reconstitution for any foreign particles and/or changes in physical appearance. If any of these circumstances are observed, do not administer the vaccine.
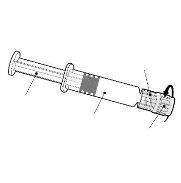
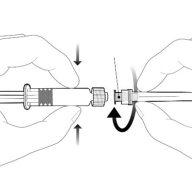
Instructions for the pre-filled syringe
| Hold the syringe by the body, not by the plunger. Remove the syringe cap by twisting it counterclockwise. |
| To insert the needle, attach the base to the Luer-Lock adapter and turn it one-quarter turn clockwise until it clicks. Reconstitute the vaccine as indicated above. Do not remove the plunger from the syringe body. If this happens, do not administer the vaccine. |
Disposal of waste
Disposal of unused medicinal products and all materials that have come into contact with them should be done in accordance with local regulations.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to INFANRIX HEXA powder and suspension for injectable suspensionDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.5 mLManufacturer: Sanofi Winthrop IndustriePrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.5 mlManufacturer: Sanofi Winthrop IndustriePrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.5 mlManufacturer: Sanofi Winthrop IndustriePrescription required
Online doctors for INFANRIX HEXA powder and suspension for injectable suspension
Discuss questions about INFANRIX HEXA powder and suspension for injectable suspension, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions