ILARIS 150 mg/mL Injectable Solution

How to use ILARIS 150 mg/mL Injectable Solution
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Ilaris 150mg/ml solution for injection
canakinumab
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
In addition to this leaflet, you will be given a patient card that contains important safety information that you need before and during treatment with Ilaris.
Contents of the pack
- What is Ilaris and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Ilaris
- How to use Ilaris
- Possible side effects
- Storing Ilaris
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Ilaris and what is it used for
What is Ilaris
Ilaris contains the active substance canakinumab, a monoclonal antibody that belongs to a group of medicines called interleukin inhibitors. In the body, it blocks the activity of a substance called interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta), which is found at high levels in inflammatory diseases.
What Ilaris is used for
Ilaris is used to treat the following inflammatory diseases:
- Periodic fever syndromes:
- cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS*)
- tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS*)
- hyperimmunoglobulin D syndrome (HIDS*) / mevalonate kinase deficiency (MKD*)
- familial Mediterranean fever (FMF).
- Still's disease, including adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA)
- Gouty arthritis
(*) by their English language abbreviations
More information about these diseases is provided below.
Periodic fever syndromes
Ilaris is used in adults and children from 2 years of age to treat the following diseases:
- Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS) – this is a group of autoinflammatory diseases, which includes:
- Muckle-Wells syndrome (MWS)
- neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease (NOMID), also known as chronic infantile neurological cutaneous and articular syndrome (CINCA)
- severe manifestations of the cold-induced autoinflammatory syndrome (FCAS) / familial cold urticaria (FCU) that present with signs and symptoms beyond cold-induced urticaria-like rash.
- Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS)
- Hyperimmunoglobulin D syndrome (HIDS) / mevalonate kinase deficiency (MKD)
- Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF): Ilaris is used to treat FMF. Ilaris may be used together with colchicine, if appropriate.
In patients with periodic fever syndromes (CAPS, TRAPS, HIDS/MKD, and FMF), the body produces too much IL-1 beta. This can cause fever, headache, fatigue, skin rash, or joint and muscle pain. By blocking the activity of IL-1 beta, Ilaris can improve these symptoms.
Still's disease
Ilaris is used in adult, adolescent, and pediatric patients from 2 years of age for the treatment of active Still's disease, including adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA) when other treatments have not worked well. Ilaris may be used alone or in combination with methotrexate.
Still's disease, which includes sJIA and AOSD, is an inflammatory disease that can cause pain, swelling, and inflammation of one or more joints, as well as rash and fever. The pro-inflammatory protein IL-1 beta plays an important role in the inflammation of Still's disease. Ilaris can improve the signs and symptoms of Still's disease by blocking the activity of IL-1 beta.
Gouty arthritis
Ilaris is used in adults to treat the symptoms of frequent gouty arthritis attacks if other treatments have not worked well enough.
Gouty arthritis is caused by the formation of urate crystals. These urate crystals cause an overproduction of IL-1 beta, which can lead to sudden severe pain, redness, heat, and swelling of the joints (known as a gout attack). By blocking IL-1 beta, Ilaris can improve these symptoms.
2. What you need to know before you use Ilaris
Do not use Ilaris
- if you are allergic to canakinumab or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- if you have, or suspect you have, a severe and active infection
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor before you start using Ilaris, if you are in any of the following situations:
- if you have any current infection or if you have had repeated infections or suffer from any disease such as a low white blood cell count that makes you more prone to infections
- if you have, or have had, tuberculosis or have been in close contact with someone with active tuberculosis infection. Your doctor may check if you have tuberculosis using a specific test
- if you have signs of liver disorder such as yellowing of the skin and eyes, nausea, loss of appetite, dark-colored urine, and pale-colored stools
- if you need to receive any vaccinations. It is recommended to avoid being vaccinated with a type of vaccine known as a live vaccine while you are being treated with Ilaris (see also "Using Ilaris with other medicines").
- This medicine contains 0.4 mg of polysorbate 80 in each 1 ml of solution for injection. Polysorbates may cause allergic reactions. Inform your doctor if you or your child have any known allergy.
Consult your doctor immediately
- if you have ever had a widespread atypical rash or skin peeling after taking Ilaris.
Rarely, a severe skin reaction, DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms), has been reported with Ilaris treatment, mainly in patients with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA). Seek medical attention immediately if you notice a widespread atypical rash, which may appear together with high fever and enlarged lymph nodes.
Still's disease
- Patient with Still's disease may develop a condition called macrophage activation syndrome (MAS) that can be life-threatening. Your doctor will monitor you for possible triggers of MAS, including infections and re-activation of Still's disease (flare-up).
Traceability
Each time you or your child receive a new pack of Ilaris, it is important that you note the name of the medicine and the batch number and keep this information in a safe place.
Children and adolescents
- CAPS, TRAPS, HIDS/MKD, FMF, and sJIA:Ilaris can be used in children from 2 years of age.
- Gouty arthritis:Ilaris is not recommended for children or adolescents under 18 years of age.
Other medicines and Ilaris
Tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
- Live vaccines: it is recommended to avoid being vaccinated with a live vaccine while you are being treated with Ilaris. Your doctor may need to check your vaccination history and give you any vaccinations you have not had before starting treatment with Ilaris. If you need to receive a live vaccine after starting treatment with Ilaris, discuss this with your doctor. A live vaccine should be given at least 3 months after your last injection of Ilaris and at least 3 months before the next injection.
- Medicines known as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, such as etanercept, adalimumab, or infliximab. These are mainly used in rheumatic and autoimmune diseases. They must not be used with Ilaris because this may increase the risk of infections.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
- You should avoid becoming pregnant and use adequate contraception while you are taking Ilaris and for at least 3 months after the last administration. It is important that you inform your doctor if you are pregnant, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a baby. Your doctor will inform you about the potential risk of using Ilaris during pregnancy.
- If you receive canakinumab while you are pregnant, it is important that you inform the pediatrician or nurse before any vaccinations are given to your baby. Your baby should not receive live vaccines until at least 16 weeks after you received your last dose of canakinumab before delivery.
- It is not known if Ilaris passes into breast milk. Your doctor will inform you about the potential risks of using Ilaris before breastfeeding.
Driving and using machines
Treatment with Ilaris may cause you to feel dizzy or extremely tired. This should be taken into account when assessing your ability to perform tasks that require judgment or motor skills. If you feel dizzy or tired, do not drive or use tools or machines until you feel better.
3. How to use Ilaris
Follow the instructions for administration of this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. If you are unsure, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
Keep your doctor informed about your disease and any symptoms before you use or are given Ilaris (see section 2). Your doctor may decide to postpone or interrupt your treatment, only when necessary.
Ilaris must be used by subcutaneous injection. This means it is injected with a short needle into the fatty tissue just under the skin.
If you have gouty arthritis, a specially trained doctor will supervise your treatment. Ilaris should only be injected by a healthcare professional.
If you have CAPS, TRAPS, HIDS/MKD, FMF, or Still's disease (AOSD or sJIA), you can inject Ilaris yourself after receiving proper training, or it can be injected by a caregiver.
How much Ilaris to use
Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS)
The recommended starting dose of Ilaris is based on body weight:
- Adults and children 4 years of age or older
- 150 mg for patients weighing more than 40 kg
- 2 mg/kg for patients weighing between 15 kg and 40 kg
- 4 mg/kg for patients weighing between 7.5 kg and less than 15 kg
- Children 2 or 3 years of age
- 4 mg/kg for patients weighing 7.5 kg or more
Ilaris is injected every 8 weeks as a single injection.
- If you do not respond sufficiently to treatment after 7 days, your doctor may give you another dose of 150 mg or 2 mg/kg.
- If you respond sufficiently to the second dose, your treatment will continue with 300 mg or 4 mg/kg every 8 weeks.
- If you do not respond sufficiently to the second dose, a third dose of Ilaris may be given at 300 mg or 4 mg/kg.
- If you respond sufficiently to the third dose, your treatment will continue with 600 mg or 8 mg/kg every 8 weeks.
In children who have started with an initial dose of 4 mg/kg and who have not responded sufficiently after 7 days, the doctor may give a second dose of 4 mg/kg. If the child responds sufficiently to this, treatment can continue with a dose of 8 mg/kg every 8 weeks.
Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS), hyperimmunoglobulin D syndrome (HIDS) / mevalonate kinase deficiency (MKD), and familial Mediterranean fever (FMF)
The recommended starting dose of Ilaris is based on body weight:
- Adults and children 2 years of age or older
- 150 mg for patients weighing more than 40 kg
- 2 mg/kg for patients weighing between 7.5 kg and less than 40 kg
Ilaris is injected every 4 weeks as a single injection.
- If you do not respond sufficiently to treatment after 7 days, your doctor may give you another dose of 150 mg or 2 mg/kg.
- If you respond sufficiently to this, your treatment will continue with 300 mg or 4 mg/kg every 4 weeks.
Still's disease (sJIA and AOSD)
The recommended dose of Ilaris for patients with Still's disease weighing 7.5 kg or more is 4 mg/kg (up to a maximum of 300 mg). Ilaris is injected every 4 weeks as a single dose.
Gouty arthritis
Your doctor will discuss with you the need to start or adjust treatment with urate-lowering therapy to reduce the level of uric acid in your blood.
The recommended dose of Ilaris for adult patients with gout is 150 mg given as a single dose during a gout attack.
If you need further treatment with Ilaris, and the last dose provided relief, you should wait at least 12 weeks before the next dose.
Self-injection of Ilaris or injection of Ilaris to a patient
If you are a patient with CAPS, TRAPS, HIDS/MKD, FMF, or Still's disease (AOSD or sJIA), or a caregiver of a patient with one of these diseases, you can administer Ilaris injections yourself after receiving proper training in injection technique.
- The patient or caregiver and the doctor will decide who will give the Ilaris injections.
- Your doctor or nurse will teach you how to give the Ilaris injections.
- You must not try to give yourself an injection if you have not received the necessary training or are not sure how to do it.
- Ilaris 150 mg/ml solution for injection is provided in a single-use vial for individual use.
- Do not reuse leftover solution.
For more information on how to give Ilaris injections, see the "Instructions for use" section at the end of this leaflet. If you have any doubts, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
Duration of treatment with Ilaris
- CAPS, TRAPS, HIDS/MKD, FMF, or Still's disease (AOSD or sJIA):you should continue using Ilaris for as long as your doctor recommends.
- Gouty arthritis:if you have a gout attack, you will be given a single dose of Ilaris. If you experience a new attack, your doctor may consider giving you another dose of Ilaris, but not before 12 weeks have passed since the previous dose was given.
If you use more Ilaris than you should
If you accidentally inject more Ilaris than the recommended dose, it is unlikely to be serious, but you should inform your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse as soon as possible.
If you forget to use Ilaris
If you have CAPS, TRAPS, HIDS/MKD, or FMF, or Still's disease (AOSD or sJIA) and you have forgotten to inject a dose of Ilaris, the next dose should be injected as soon as you remember. Then, talk to your doctor to agree when you should inject the next dose. After that, you should continue with the injections at the recommended intervals as before.
If you stop treatment with Ilaris
Stopping your treatment with Ilaris may cause your disease to worsen. Do not stop treatment with Ilaris unless your doctor tells you to.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
Some adverse effects can be serious. Inform your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following adverse effects:
- Prolonged fever for more than 3 days or any symptom that may suggest a serious infection. This includes tremors, chills, general malaise, loss of appetite, body aches, usually related to the sudden onset of the disease, sore throat or mouth ulcers, cough, phlegm, chest pain, difficulty breathing, ear pain, prolonged headache and redness, heat and localized swelling in the skin or inflammation of the connective tissue (cellulitis). These symptoms may be due to a serious infection, an unusual infection (opportunistic infection) or related to low levels of white blood cells (called leukopenia and neutropenia). If necessary, your doctor may perform regular blood tests.
- Allergic reactions with rash and itching and possibly also hives, difficulty breathing or swallowing, dizziness, unusual awareness of heartbeat (palpitations) and low blood pressure.
Other adverse effects of Ilaris include:
Very common(may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- Infections of any kind. These may include:
- Respiratory infections such as chest infection, flu, throat inflammation, nasal discharge, stuffy nose, sneezing, feeling of pressure or pain in the cheeks or forehead with or without fever (pneumonia, bronchitis, flu-like symptoms, sinusitis, rhinitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis (sore throat), nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection).
- Other infections such as ear infection, skin infection (cellulitis), stomach pain and gastroenteritis and pain and frequent need to urinate with or without fever (urinary tract infection).
- Upper abdominal pain.
- Joint pain (arthralgia).
- Decrease in white blood cell levels (leukopenia).
- Abnormal kidney function test results (decreased renal clearance, proteinuria).
- Reactions at the injection site (such as redness, swelling, heat, and itching).
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Candida - vaginal yeast infection (vulvovaginal candidiasis).
- Feeling dizzy, sensation that everything is spinning (dizziness or vertigo).
- Back or muscle pain.
- Feeling weak or very tired (fatigue, asthenia).
- Decrease in white blood cell levels that help prevent infection (neutropenia).
- Abnormal levels of triglycerides in the blood (lipid metabolism disorder).
- Abnormal liver function test results (elevated transaminases) or elevated bilirubin levels in the blood, with or without yellowing of the skin and eyes (hyperbilirubinemia).
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Heartburn (gastroesophageal reflux disease).
- Decrease in blood cell levels that help prevent bleeding (platelets).
Inform your doctor or your child's doctor immediately if you notice any of these symptoms.
Adverse Effect Reporting
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is a possible adverse effect that is not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the national reporting system included in Appendix V. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Ilaris
- Keep this medicine out of sight and reach of children.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiration date that appears on the label and carton after EXP. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
- Store in a refrigerator (between 2°C and 8°C). Do not freeze.
- Keep the vial in the carton to protect it from light.
- The solution must be used immediately after the first puncture of the vial stopper to prepare the injection.
- Do not use this medicine if you notice that the solution is not transparent to opalescent or contains particles.
- Any unused medicine must be discarded after injecting the dose.
Medicines must not be thrown away through wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Ilaris
- The active ingredient is canakinumab. Each vial contains 150 mg of canakinumab in 1 ml of solution.
- The other ingredients are mannitol, histidine, histidine hydrochloride monohydrate, polysorbate 80 (see section 2), water for injectable preparations.
Appearance of the Product and Package Contents
- Ilaris is presented as an injectable solution in a 2 ml glass vial.
- The solution is a clear to opalescent liquid and colorless to slightly yellowish-brown. Do not use it if the liquid contains easily visible particles, is cloudy, or has a brown color.
- Ilaris is available in packages containing one vial.
Marketing Authorization Holder
Novartis Europharm Limited
Vista Building
Elm Park, Merrion Road
Dublin 4
Ireland
Manufacturer
Novartis Farmacéutica, S.A.
Gran Vía de les Corts Catalanes, 764
08013 Barcelona
Spain
Novartis Pharma GmbH
Roonstrasse 25
90429 Nuremberg
Germany
Lek Pharmaceuticals d.d.
Verovskova Ulica 57
1526 Ljubljana
Slovenia
Novartis Pharma GmbH
Sophie-Germain-Strasse 10
90443 Nürnberg
Germany
You can request more information about this medicine by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Belgium/Belgique/Belgien Novartis Pharma N.V. Tel: +32 2 246 16 11 | Lithuania SIA Novartis Baltics Lietuvos filialas Tel: +370 5 269 16 50 |
Bulgaria Novartis Bulgaria EOOD Tel: +359 2 489 98 28 | Luxembourg/Luxemburg Novartis Pharma N.V. Tel: +32 2 246 16 11 |
Czech Republic Novartis s.r.o. Tel: +420 225 775 111 | Hungary Novartis Hungária Kft. Tel: +36 1 457 65 00 |
Denmark Novartis Healthcare A/S Tel: +45 39 16 84 00 | Malta Novartis Pharma Services Inc. Tel: +356 2122 2872 |
Germany Novartis Pharma GmbH Tel: +49 911 273 0 | Netherlands Novartis Pharma B.V. Tel: +31 88 04 52 111 |
Estonia SIA Novartis Baltics Eesti filiaal Tel: +372 66 30 810 | Norway Novartis Norge AS Tel: +47 23 05 20 00 |
Greece Novartis (Hellas) A.E.B.E. Tel: +30 210 281 17 12 | Austria Novartis Pharma GmbH Tel: +43 1 86 6570 |
Spain Novartis Farmacéutica, S.A. Tel: +34 93 306 42 00 | Poland Novartis Poland Sp. z o.o. Tel: +48 22 375 4888 |
France Novartis Pharma S.A.S. Tel: +33 1 55 47 66 00 | Portugal Novartis Farma - Produtos Farmacêuticos, S.A. Tel: +351 21 000 8600 |
Croatia Novartis Hrvatska d.o.o. Tel: +385 1 6274 220 | Romania Novartis Pharma Services Romania SRL Tel: +40 21 31299 01 |
Ireland Novartis Ireland Limited Tel: +353 1 260 12 55 | Slovenia Novartis Pharma Services Inc. Tel: +386 1 300 75 50 |
Iceland Vistor hf. Tel: +354 535 7000 | Slovakia Novartis Slovakia s.r.o. Tel: +421 2 5542 5439 |
Italy Novartis Farma S.p.A. Tel: +39 02 96 54 1 | Finland Novartis Finland Oy Tel: +358 (0)10 6133 200 |
Cyprus Novartis Pharma Services Inc. Tel: +357 22 690 690 | Sweden Novartis Sverige AB Tel: +46 8 732 32 00 |
Latvia SIA Novartis Baltics Tel: +371 67 887 070 |
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet:
Other Sources of Information
Detailed information about this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency website: https://www.ema.europa.eu
Instructions for Use of Ilaris Injectable Solution
Read these instructions completely before injecting.
- It is essential that you do not attempt to inject yourself until you have been instructed by your healthcare professional.
- Also, consult section 3, "Self-injection of Ilaris or injection of Ilaris in a patient."
Essential Preparations:
- Find a clean site to prepare and administer the injection.
- Wash your hands with water and soap, then dry them with a clean towel.
- After removing the vial from the refrigerator, check the expiration date on the vial. Do not use it after the expiration date that appears on the label and carton. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
- Leave the unopened vial for 10 minutes to bring the contents to room temperature. Do not attempt to heat the vial. Let it warm up on its own.
- Always use new syringes and needles that are in closed packages. Do not touch the needles or the vial stopper.
Gather all the necessary items:
Included in the package
- one vial of Ilaris injectable solution (keep in the refrigerator).
Not included in the package
- a 1.0 ml syringe
- a needle (such as 18 G or 21 G x 2 inches or similar, depending on market availability) to withdraw the solution from the vial ("withdrawal needle").
- a 27 G x 0.5 inch needle (or similar, depending on market availability) for injection ("injection needle")
- alcohol swabs
- dry, clean cotton balls
- a band-aid
- a suitable container for disposing of used needles, syringes, and vials (sharps container)
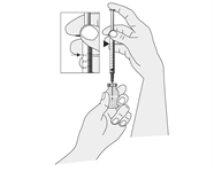
Preparing the Injection
|
Open the packages containing the syringe and the withdrawal needle.
|
|
NOTE: The required amount depends on the dose to be administered. Your healthcare professional will show you the amount to be injected.
|
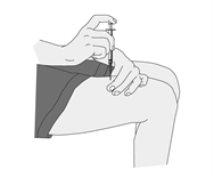
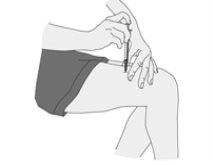
Administering the Injection
|
|
|
|
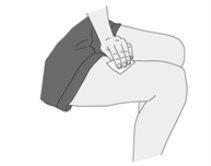
After the Injection
|
|
|
Keep the sharps container out of sight and reach of children. Dispose of it according to the instructions received from your healthcare professional or pharmacist. |
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to ILARIS 150 mg/mL Injectable SolutionDosage form: INJECTABLE, 150 mg/ml of canakinumabActive substance: canakinumabManufacturer: Novartis Europharm LimitedPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 130 mgActive substance: ustekinumabManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 45 mgActive substance: ustekinumabManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription required
Online doctors for ILARIS 150 mg/mL Injectable Solution
Discuss questions about ILARIS 150 mg/mL Injectable Solution, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions