
GLIADEL 7.7 mg IMPLANT

How to use GLIADEL 7.7 mg IMPLANT
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
GLIADEL 7.7 mg implant
Carmustine
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, even if they are not mentioned in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack:
- What GLIADEL implant is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use GLIADEL implant
- How to use GLIADEL implant
- Possible side effects
- Storage of GLIADEL implant
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What GLIADEL implant is and what it is used for
GLIADEL implant is a delivery system for the anticancer active substance carmustine directly into the site where the brain tumor was located, after its surgical removal. Carmustine belongs to a group of anticancer substances that allow combating the growth of tumor cells localized in the brain.
GLIADEL implant can be used in combination with radiotherapy for the treatment of brain tumors.
It has been shown that GLIADEL implant prolongs the survival of patients with brain tumors.
2. What you need to know before you use GLIADEL implant
Do not use GLIADEL implant
- if you are allergic to the active substance or to any of the other components of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions
After the surgery to remove the brain tumor and introduce GLIADEL implant, your doctor or surgeon will closely monitor you for any complications. In some cases, the surgeon may need to re-operate (due to complications or recurrence of the tumor). Complications include:
- Seizures (crises)
- Brain infections (infections inside the skull)
- Brain inflammation due to fluid accumulation
- Cerebrospinal fluid leakage
- Wound healing problems
Your doctor will closely monitor you if you are taking steroids due to inflammation or increased fluid pressure in the brain.
Before introducing the implants, the surgeon may need to close a channel in the brain to prevent the implants from passing through it, which could cause fluid accumulation inside the skull.
After the introduction of GLIADEL implant, imaging techniques can detect brain inflammation due to fluid accumulation and inflammation caused by GLIADEL implant or tumor progression.
Other medicines and GLIADEL implant
Tell your doctor if you are using or have recently used other medicines, including those obtained without a prescription.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor before using this medicine. GLIADEL implant has not been studied in pregnant women. The active substance, carmustine, has been shown to negatively affect fetal development. GLIADEL implant should not be used in pregnant or breastfeeding women. Women of childbearing age are advised to use effective contraceptive methods during 6 months after receiving GLIADEL implant. Men with a female partner of childbearing age should use contraceptive methods for 90 days after receiving GLIADEL implant.
Driving and using machines
Driving is not recommended after treatment. Consult your doctor before driving or using tools or machines.
3. How to use GLIADEL implant
GLIADEL implant should only be used in adults.
The surgeon or pharmacist will ensure that the medicine is available for your operation. After the removal of the brain tumor, the surgeon will introduce up to eight implants into the space that the tumor occupied. Your surgeon will decide the number of implants to introduce into the cavity created after the removal of the brain tumor. The implants are placed to cover as much of the surface of this cavity as possible. After the operation, the implants dissolve slowly over two to three weeks, releasing carmustine directly to the surrounding cells.
If you have any further questions about the use of this product, ask your surgeon.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, GLIADEL can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If you think any of the side effects you are experiencing are serious or if you notice any side effects not mentioned in this leaflet, tell your doctor.
The following are the most common side effects observed during clinical trials in patients with newly diagnosed malignant glioma (brain tumor) (120 patients) or recurrent malignant glioma (110 patients).
The following four categories of side effects may be associated with the use of GLIADEL implant:
|
During clinical trials, the following side effects were observed in patients, which were similar to those observed in patients undergoing brain tumor surgery without GLIADEL implant placement.
Very common: may affect more than 1 in 10 patients
- Psychiatric disorders
Depression
- Nervous system disorders
Weakness, especially on one side of the body; seizures (spasms); confusion; headache, skull inflammation; somnolence; speech disorders
- Vascular disorders
Vascular inflammation
- Gastrointestinal disorders
Nausea; vomiting; constipation
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Rash; hair loss
- Renal and urinary disorders
Urinary tract infection
- General disorders and administration site conditions
General health deterioration; infection; headache; feeling of weakness; fever or pain, abnormal (slow) wound healing.
Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 patients
- Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Anemia (reduced red blood cell count), which can cause pale skin, fatigue, and shortness of breath; reduced platelet count, which increases the risk of bleeding; increased white blood cell count
- Endocrine disorders (hormonal problems)
Diabetes mellitus
- Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Peripheral edema (excess fluid in the arms or legs); low sodium levels in the blood, which can cause fatigue and confusion, muscle twitching, spasms, and coma; high blood sugar levels, low potassium levels in the blood, which can cause weakness and muscle twitching, and abnormal heart rhythm
- Psychiatric disorders
Personality changes, excessive anxiety, abnormal thinking, hallucinations, insomnia (little sleep)
- Nervous system disorders
Amnesia (memory loss); increased intracranial pressure due to excess fluid; facial paralysis; lack of coordination; reduced sensitivity to stimulation; abnormal burning and itching sensations; difficulty walking; dizziness; epileptic seizure (spasms); tremors; meningitis; abscess (localized collection of pus); loss of consciousness
- Eye disorders
Blurred or abnormal vision; eye contour inflammation; eye pain
- Vascular disorders
Bleeding; high or low blood pressure
- Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders
Lung infection or pneumonia causing shortness of breath, cough, and fever
- Gastrointestinal disorders
Oral microbial infection; diarrhea; constipation; fecal incontinence (uncontrolled fecal loss); difficulty swallowing; gastric or intestinal bleeding
- Epithelial and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Rash
- Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
General infection
- Renal and urinary disorders
Urinary incontinence, urinary tract infections
- General disorders and administration site conditions
Abdominal pain, from back to chest; facial inflammation; abscess (localized collection of pus); accidental injury; allergic reaction; neck pain; blood infection
Uncommon side effects (between 1 and 10 patients in 1000)
Traumatic injuries, poisonings, and complications of therapeutic procedures
Pneumocephalus (air accumulation in the implant area)
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, even if they are not mentioned in this leaflet.
You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of GLIADEL implant
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Store in a freezer at a temperature of -20°C or lower.
Unopened outer pouches can be stored at a temperature below 22°C for a maximum of 6 hours. The pouches can be re-frozen once if they have not been opened and have been stored for a maximum of 6 hours at a temperature below 22°C. After re-freezing, the medicine should be used within 30 days.
Do not use GLIADEL implant after the expiry date stated on the packaging and/or on the pouch after EXP. The expiry date is the last day of the month indicated.
Your surgeon or hospital pharmacist will check the expiry date before using the implants.
6. Contents of the pack and additional information
Composition of GLIADEL implant
- The active ingredient is carmustine. Each implant contains 7.7 mg of carmustine
- The other component is polifeprosan 20.
Appearance of the product and pack contents
GLIADEL implant is available in boxes of eight circular implantable wafers. These wafers are disk-shaped implants that are white to off-white in color. Each implant is individually packaged in a foil pouch.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
CLINIGEN HEALTHCARE B.V.
Schiphol Boulevard 359
WTC Schiphol Airport, D Tower 11th floor
1118BJ Schiphol
Netherlands
Manufacturer
ALMAC PHARMA SERVICES (IRELAND) LIMITED
Finnabair Industrial Estate
Dundalk
Co. Louth A91 P9KD
Ireland
Tel: +353 42 932 0718
Fax: +353 42 932 0718
ALMAC PHARMA SERVICES LIMITED
20 Seagoe Industrial Estate
Craigavon, BT63 5QD,
United Kingdom
Tel: +44 (0)28 3836 3363
Fax: +44 (0)28 3836 3300
Date of last revision of this leaflet: 04/2021
Detailed and up-to-date information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
INFORMATION LEAFLET FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS
- NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
GLIADEL 7.7 mg implant
- QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each implant contains 7.7 mg of carmustine.
To consult the complete list of excipients, see section 6.1.
- PHARMACEUTICAL FORM
Implant.
Disk-shaped implant that is white to off-white in color.
- CLINICAL PARTICULARS
4.1Therapeutic indications
GLIADEL implant is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with newly diagnosed high-grade malignant glioma as an adjuvant therapy to surgery and radiation.
GLIADEL implant is indicated as an adjuvant therapy to surgery for the treatment of patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme, histologically diagnosed, in whom surgical resection is indicated.
4.2Posology and method of administration
Posology
Intralesional use only.
Each GLIADEL implant contains 7.7 mg of carmustine, so that after placement of eight implants in the tumor resection cavity, a dose of 61.6 mg is released.
Pediatric population
The safety and efficacy of GLIADEL implant in children under 18 years of age have not been established. No data are available.
Method of administration
It is recommended to place a maximum of eight implants if the size and shape of the resection cavity allow it. Halved implants may be used, but implants fractured into more than two parts should be eliminated in containers suitable for biohazardous waste (see section 6.6).
It is recommended to proceed with the placement of the implants directly from the inner sterile packaging of the product to the resection cavity. Oxycellulose pads may be placed over the implants to fix them to the surface of the cavity (see section 6.6).
4.3Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1.
4.4Special warnings and precautions for use
Patient monitoring is required to detect possible complications of craniotomy, including seizures, intracranial infections, abnormal wound healing, cerebral edema, and pneumocephalus (see section 4.8). In patients treated with GLIADEL implant, cases of intracerebral mass effect not responsive to corticosteroids have been described, including one case that resulted in brain herniation. Patients treated with GLIADEL implant should be closely monitored for the development of cerebral edema/intracranial hypertension after corticosteroid use (see section 4.8). Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks were more frequent in patients treated with GLIADEL implant. Special care is recommended for the impermeable closure of the dura mater and in the treatment of local wounds (see section 4.8).
Changes in the walls of cerebral blood vessels located near the Gliadel wafer have been described, including cases of aneurysm causing cerebral bleeding several months after Gliadel wafer implantation. The implantation of Gliadel wafers adjacent to large cerebral vessels should be avoided.
The development of cerebral edema with mass effect (due to tumor recurrence, intracranial infection, or necrosis) may require reoperation and, in some cases, removal of GLIADEL implant or its remnants.
Communication between the surgical resection cavity and the ventricular system should be avoided to prevent the implants from displacing into the ventricular system and potentially causing obstructive hydrocephalus. If there is a communication pathway larger than the diameter of the implant, it should be closed prior to the implantation of GLIADEL implant.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging may show an increase in the density of the brain tissue surrounding the resection cavity after the placement of GLIADEL implants. This increased density may reflect edema or inflammation caused by the GLIADEL implants or tumor progression.
Women of childbearing age should use effective contraceptive methods during at least 6 months after receiving GLIADEL implant.
Male patients with female partners of childbearing age should be advised to use effective contraceptive methods during at least 90 days after receiving GLIADEL implant.
4.5Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Interactions between GLIADEL implant and other medicinal products or chemotherapy have not been formally studied.
4.6Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy:
There are no studies of GLIADEL implant in pregnant women, nor studies evaluating the toxicity of GLIADEL implant on reproduction.
When administered systemically, carmustine, the active substance of GLIADEL implant, may have genotoxic effects and negatively affect fetal development (see section 5.3). Therefore, the use of GLIADEL implant is not recommended during pregnancy, nor in women of childbearing age who are not using contraceptive methods. Women of childbearing age should use effective contraceptive methods during at least 6 months after receiving GLIADEL implant.
Male patients with female partners of childbearing age should be advised to use effective contraceptive methods during at least 90 days after receiving GLIADEL implant. However, if the use of GLIADEL implant is still considered necessary during pregnancy, the patient should be informed of the potential risks to the fetus. In the event that the patient becomes pregnant after receiving GLIADEL implant, genetic counseling should be sought.
Breast-feeding:
It is unknown whether the components of GLIADEL implant are excreted in breast milk. Since some medicinal products are eliminated in breast milk and due to the potential risk of serious adverse reactions from carmustine in infants, breast-feeding is contraindicated.
Fertility:
No fertility studies have been conducted with GLIADEL implant.
4.7Effects on ability to drive and use machines
GLIADEL implant does not affect the ability to drive vehicles and use machinery. However, craniotomy and GLIADEL implant may cause alterations in vision and the nervous system. Therefore, the patient should be aware of the potential effect of these reactions on the ability to drive or use machines.
4.8Undesirable effects
The spectrum of undesirable effects observed in patients with newly diagnosed high-grade malignant glioma and recurrent malignant glioma was consistent with that observed in patients undergoing craniotomy for malignant glioma.
The following undesirable effects are listed below, which were observed in patients treated with GLIADEL implant during clinical trials.
These undesirable effects are listed in decreasing order of severity within each frequency.
Primary Surgery
The following data correspond to the undesirable effects most frequently observed in 5% or more of the 120 patients with newly diagnosed malignant glioma treated with GLIADEL implant in the clinical trial.
Undesirable effects observed in ≥ 5% of patients treated with GLIADEL implant in primary surgery
System organ class | Undesirable effects | |
Endocrine disorders | Common* | Diabetes mellitus |
Psychiatric disorders | Very common | Depression |
Common | Personality disorder, anxiety, abnormal thinking, hallucinations, insomnia | |
Nervous system disorders | Very common | Hemiplegia, seizures, confusion, cerebral edema, aphasia, somnolence, speech disorders |
Common | Amnesia, increased intracranial pressure, personality disorders, anxiety, facial paralysis, neuropathy, ataxia, hypesthesia, paresthesia, abnormal thinking, abnormal gait, dizziness, grand mal seizures, hallucinations, insomnia | |
Eye disorders | Common | Conjunctival edema, abnormal vision, visual field defects |
Vascular disorders | Very common | Thrombophlebitis |
Common | Hemorrhage | |
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | Common | Pulmonary embolism |
Infections and infestations Gastrointestinal disorders | Common | Pneumonia |
Very common | Nausea, vomiting, constipation | |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Common | Diarrhea |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Very common | Rash, alopecia |
Renal and urinary disorders | Common | Urinary tract infection, urinary incontinence |
General disorders and administration site conditions | Very common | Worsening, headache, asthenia, infection, fever, pain, abnormal wound healing |
Common | Abdominal pain, back pain, facial edema, chest pain, abscess, accidental injury, peripheral edema |
Intracranial hypertension was reported more frequently in patients treated with GLIADEL implant than in those who received placebo (9.2% vs 1.7%), being a late finding coinciding with tumor recurrence, and was considered unlikely to be associated with the use of GLIADEL implant (see section 4.4).
CSF leaks were more frequent in patients treated with GLIADEL implant than in patients who received placebo. However, intracranial infections or other wound healing abnormalities did not increase (see section 4.4).
Surgery for recurrent disease
The following undesirable effects were observed after surgery in 4% or more of patients treated with GLIADEL implant in repeat surgery. Only reactions that were more frequent in the group that received GLIADEL implant than in the placebo group are listed, with the exception of effects on the nervous system, which may have been caused by the placebo implants. These undesirable effects either were not present before surgery or worsened after surgery during the follow-up period. The follow-up period was up to 71 months.
Undesirable effects observed in ≥ 4% of patients treated with GLIADEL implant in repeat surgery
System organ class | Undesirable effects | |
Blood and lymphatic system disorders | Common | Anemia |
Metabolism and nutrition disorders | Common | Hyponatremia |
Nervous system disorders | Very common | Seizure, hemiplegia, headache, somnolence, confusion |
Common | Aphasia, stupor, cerebral edema, increased intracranial pressure, meningitis or abscess | |
Vascular disorders | Common | Thrombophlebitis |
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | Common | Pulmonary embolism |
Gastrointestinal disorders | Common | Nausea, vomiting |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Common | Rash |
Renal and urinary disorders | Very common | Urinary tract infection |
General disorders and administration site conditions | Very common | Abnormal wound healing |
Common | Infection, pain |
The following adverse effects, which are not included in the table below, were reported in patients treated with GLIADEL implant in all studies. These effects either were not present before surgery or worsened after surgery during the follow-up period. It was not possible to establish whether GLIADEL implant was the cause of these effects.
Adverse effects in patients receiving GLIADEL implant
System organ class | Undesirable effects | |
Blood and lymphatic system disorders | Common | Thrombocytopenia, leukocytosis |
Metabolism and nutrition disorders | Common | Hyponatremia, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia |
Nervous system disorders | Common | Hydrocephalus, ataxia, dizziness, hemiplegia, coma, amnesia, diplopia |
Uncommon | Cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral infarction | |
Psychiatric disorders | Common | Depression, abnormal thinking, insomnia, paranoid reaction |
Eye disorders | Common | Visual disturbance, eye pain |
Cardiac disorders | Common | Hypertension, hypotension |
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | Common | Infection, pneumonia by aspiration |
Gastrointestinal disorders | Common | Diarrhea, constipation, dysphagia, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, fecal incontinence |
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Common | Rash |
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | Common | Infection |
Renal and urinary disorders | Common | Urinary incontinence |
General disorders and administration site conditions | Common | Peripheral edema, neck pain, accidental injury, back pain, allergic reaction, asthenia, chest pain, sepsis |
Injury, poisoning, and procedural complications | Uncommon | Pneumocephalus |
Cases of air accumulation in the area of the GLIADEL implant have been reported, sometimes associated with neurological symptoms (hemiplegia, aphasia, seizures).
The following four categories of undesirable effects are possibly related to treatment with GLIADEL implant.
Seizures:
In the primary surgery clinical trial, the incidence of seizures in the first five days after implantation was 2.5% in the GLIADEL implant group.
In the clinical trial for surgery in recurrent disease, the incidence of seizures after surgery was 19% in patients treated with GLIADEL implant. In this trial, 12/22 (54%) of patients treated with GLIADEL implant experienced the onset of seizures or worsening of existing seizures during the first five days after surgery. The median time to the onset of seizures or worsening of existing seizures after surgery was 3.5 days in patients treated with GLIADEL implant.
Cerebral edema:
The development of cerebral edema with mass effect (due to tumor recurrence, intracranial infection, or necrosis) may require reoperation and, in some cases, removal of GLIADEL implant or its remnants (see section 4.4).
Wound healing abnormalities:
The following wound healing abnormalities have been reported in clinical trials of GLIADEL implant: wound dehiscence, delayed wound healing, subdural, subgaleal, or suture-line effusions, and CSF leaks.
In the primary surgery trial, CSF leaks occurred in 5% of patients who received GLIADEL implant. During surgery, an impermeable closure of the dura mater should be ensured to minimize the risk of CSF leak (see section 4.4).
Infections:
Intracranial action:
In the initial surgery clinical trial, the incidence of brain abscess or meningitis was 5% in patients treated with GLIADEL implant.
In surgery for recurrent disease, the incidence of brain abscess or meningitis was 4% in patients treated with GLIADEL implant.
In a published clinical trial, the formation of cysts has been reported after treatment with GLIADEL implant. This reaction occurred in 10% of the patients observed in the trial. However, cyst formation is possible after resection of a malignant glioma.
Notification of suspected adverse reactions
It is important to report any suspected adverse reactions to the medication after its authorization. This allows for continuous monitoring of the benefit-risk relationship of the medication. Healthcare professionals are invited to report suspected adverse reactions through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaram.es.
4.9Overdose
Not applicable.
- PHARMACEUTICAL PROPERTIES
5.1Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Antineoplastic agents, alkylating agents, nitrosoureas, ATC code: L01AD01
Preclinical data
GLIADEL implant releases carmustine directly into the surgical cavity created after tumor resection. As they are exposed to the aqueous medium of the cavity, the anhydride bonds of the copolymer are hydrolyzed, releasing carmustine, carboxyphenoxipropano, and sebacic acid. The carmustine released from GLIADEL implant diffuses into the surrounding brain tissue and exerts an antineoplastic effect by alkylating DNA and RNA.
Carmustine is degraded and metabolized spontaneously, creating the alkylating group, presumably a chloroethyl carbonium ion, which leads to the formation of irreversible cross-links in DNA.
The antitumor activity of GLIADEL implant depends on the release of carmustine into the tumor cavity in sufficient quantities for effective cytotoxicity.
Within 3 weeks, more than 70% of the copolymer is degraded. The monomers have different metabolism and elimination. Carboxyphenoxipropano is mainly eliminated by the kidneys, and sebacic acid, an endogenous fatty acid, is metabolized by the liver and exhaled as CO2 in animals.
Clinical efficacy and safety
Initial surgery
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial in 240 adults with newly diagnosed high-grade malignant glioma undergoing initial craniotomy for tumor resection, the median survival increased from 11.6 months with placebo to 13.9 months with GLIADEL implant (p = 0.079, log-rank test not stratified) in the initial follow-up phase of the trial. The most common tumor type was glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) (n = 207), followed by anaplastic oligoastrocytoma (n = 11), anaplastic oligodendroglioma (n = 11), and anaplastic astrocytoma (n = 2). The hazard ratio for GLIADEL implant was 0.77 (95% CI: 0.57 - 1.03). In the long-term follow-up phase, patients who were still alive at the end of the initial follow-up phase were followed up for at least three years or until their death. The median survival increased from 11.6 months with placebo to 13.9 months with GLIADEL implant (p <0.05, log-rank test). The hazard ratio for GLIADEL implant treatment was 0.73 (95% CI: 0.56 - 0.95).
Surgery for recurrent disease
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial in 145 adults with recurrent glioblastoma (GBM), GLIADEL implant prolonged the survival of these patients. 95% of the patients treated with GLIADEL implant received 7 to 8 implants.
The survival rate with placebo at 6 months was 36% (26/73), compared to 56% (40/72) with GLIADEL implant treatment. The median survival of patients with GBM was 20 weeks with placebo, compared to 28 weeks with GLIADEL implant treatment.
5.2Pharmacokinetic properties
The absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination of the copolymer in humans are not known. The concentrations of carmustine released by GLIADEL implant in human brain tissue have not been determined. It is not possible to determine the plasma levels of carmustine after GLIADEL implant implantation. Carmustine is not detected in blood or cerebrospinal fluid in rabbits with carmustine implants at 3.85%.
After intravenous perfusion of carmustine with doses between 30 and 170 mg/m2, the mean terminal elimination half-life, clearance, and steady-state volume of distribution are, respectively, 22 minutes, 56 ml/min/kg, and 3.25 l/kg. Approximately 60% of an intravenous dose of 200 mg/m2 of 14C-carmustine is excreted in the urine within 96 hours, and 6% is exhaled as CO2.
GLIADEL implants are biodegradable in the human brain when placed in the cavity after tumor resection. The rate of biodegradation varies from patient to patient. During the biodegradation process, implant remnants can be observed using brain imaging techniques or during subsequent surgery, even if extensive degradation of all components has occurred.
5.3Preclinical safety data
No carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, embryofetal toxicity, pre- and postnatal toxicity, and fertility impairment studies have been conducted with GLIADEL implant.
Carmustine, the active ingredient of GLIADEL implants, when administered systemically, has embryotoxic, teratogenic, genotoxic, and carcinogenic effects and can cause testicular degeneration in various animal models.
- PHARMACEUTICAL DATA
6.1List of excipients
Polifeprosan 20
6.2Incompatibilities
Not applicable.
6.3Shelf life
4 years.
6.4Special precautions for storage
Store in freezer. Do not store at a temperature above -20°C.
Unopened outer envelopes can be stored at a temperature below 22°C for a maximum of 6 hours.
The medication can be refrozen once if the envelopes have not been opened and have been stored for a maximum of 6 hours at a temperature below 22°C. After refreezing, the medication must be used within 30 days.
6.5Nature and content of the packaging
GLIADEL implant is available in a box containing 8 implants. Each implant is individually packaged in 2 laminated aluminum envelopes.
6.6Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Implants must be handled by personnel wearing surgical gloves, as exposure to carmustine can cause severe burns and skin hyperpigmentation. The use of double gloves is recommended, and after use, the outer gloves must be discarded in a biohazardous waste container. During implant placement, a dedicated surgical instrument must be used. If repeat neurosurgical intervention is indicated, any implant or implant remnants must be handled as potential cytotoxic agents. Disposal of unused medication and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out in accordance with local regulations for cytotoxic agents.
GLIADEL implants must be handled with caution. The envelopes containing the GLIADEL implants must be delivered to the operating room and must remain closed until the time of implant placement in the resection cavity. Only the outer surface of the outer envelope is non-sterile. In any case, if an implant is accidentally dropped, it must be disposed of properly.
Instructions for opening the envelopes containing the implant:
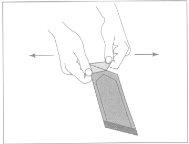
Figure 1:To open the outer envelope, locate the folded corner and gently pull it outward.
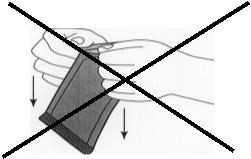
Figure 2:Do not pull downward by twisting the knuckles on the envelope. This could exert pressure on the implant and break it.
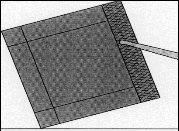
Figure 3:Remove the inner envelope with the help of forceps and pull it upward.
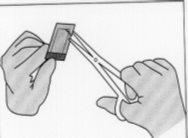
Figure 4:To open the inner envelope, hold it gently and cut it circularly around the implant.
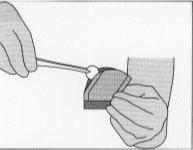
Figure 5:To remove the implant, gently grasp it with the help of forceps and place it in the resection cavity.
In any case, if an implant is dropped, it must be disposed of properly.
Once the tumor has been resected, the tumor diagnosis has been confirmed by pathology, and hemostasis has been achieved, up to 8 implants can be placed to cover the resection cavity as much as possible. A slight overlap between the implants is considered acceptable. Halved implants can be used, but if they are fragmented into more than two parts, they must be eliminated in biohazardous waste containers.
Oxicelulosa dressing strips can be placed over the implants to fix them to the surface of the cavity. After implant placement, the resection cavity must be irrigated, and the dura mater must be closed in a watertight manner.
Disposal of unused medication and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out in accordance with local regulations for biohazardous waste.
- MARKETING AUTHORIZATION HOLDER
CLINIGEN HEALTHCARE B.V.
Schiphol Boulevard 359
WTC Schiphol Airport, D Tower 11th floor
1118BJ Schiphol
Netherlands
- MARKETING AUTHORIZATION NUMBER(S)
Reg. A.E.M.P.S. n° 62.745
- DATE OF FIRST AUTHORIZATION/RENEWAL OF AUTHORIZATION
Date of first authorization: 19/10/1999
Date of last renewal: 10/12/2008
- DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
April 2021
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to GLIADEL 7.7 mg IMPLANTDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 100 mgActive substance: carmustineManufacturer: Zentiva K.S.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 100 mgActive substance: carmustineManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 300 mgActive substance: carmustineManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription required
Online doctors for GLIADEL 7.7 mg IMPLANT
Discuss questions about GLIADEL 7.7 mg IMPLANT, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions






