
GAMUNEX 100 mg/mL SOLUTION FOR INFUSION

How to use GAMUNEX 100 mg/mL SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Gamunex 100mg/ml solution for infusion
human normal immunoglobulin (IgIV)
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack and other information
- What Gamunex is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use Gamunex
- How to use Gamunex
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Gamunex
Contents of the pack and further information
1. What Gamunex is and what it is used for
What isGamunex
Gamunex contains human normal immunoglobulin (antibodies) as a highly purified protein extracted from human plasma (part of the blood from donors). This medicine belongs to a group of medicines called intravenous immunoglobulins, which are used to treat diseases in which the body's defense system that fights diseases does not work properly.
What Gamunex is used for
Treatment in adults, children, and adolescents (0-18 years) who lack sufficient antibodies (replacement therapy) such as:
- Patients with primary immunodeficiency syndrome (PIDS), a congenital deficiency of antibodies.
- Patients with acquired immunodeficiency (AIDS) with severe or recurrent infections, ineffective antibiotic treatment, and demonstrated specific antibody deficiency or serum IgG level <4 g l.< li>
Treatment in adults, children, and adolescents (0-18 years) who are susceptible and have been exposed to measles or are at risk of future exposure to measles and in whom active immunization against measles is contraindicated or not recommended.
Treatment in adults, children, and adolescents (0-18 years) with certain autoimmune diseases (immunomodulation). These are classified into five groups:
- Primary immune thrombocytopenia, a condition in which the number of platelets in the bloodstream is drastically reduced. Platelets are an important part of the blood clotting process, and a reduced number of platelets can cause bleeding and unwanted bruising. This medicine is also used in patients with a high risk of bleeding or before surgery, to correct the platelet count.
- Guillain-Barré syndrome, a condition in which the immune system attacks the nerves and prevents them from functioning properly.
- Kawasaki disease (in this case, together with acetylsalicylic acid), a childhood disease in which the blood vessels (arteries) in the body become enlarged.
- Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP), a rare and progressive disease that causes weakness in the limbs, numbness, pain, and fatigue.
- Multifocal motor neuropathy (MMN), a rare disease that causes weakness in the limbs in a slow and progressive manner without sensory loss.
Treatment in adults 18 years or older with:
Severe acute exacerbations of myasthenia gravis. Myasthenia gravis is a disease that causes muscle weakness; exacerbations mainly affect swallowing, speech, and breathing.
2. What you need to know before you use Gamunex
Do not useGamunex
- if you are allergic to human normal immunoglobulins or to any of the other components of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if you do not have sufficient immunoglobulins of the IgA type in your blood and have developed antibodies against IgA.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before starting treatment with Gamunex.
Infusion reactions and hypersensitivity
Certain adverse reactions may be related to the infusion rate. Therefore, the recommended infusion rate should be followed (see "Information intended for healthcare professionals" at the end of this leaflet).
Certain adverse effects may occur more frequently:
- in case of high infusion rate;
- in patients with complete absence of gammaglobulins or low levels of gammaglobulin (agammaglobulinemia or hypogammaglobulinemia) with or without IgA deficiency;
- in patients who receive human normal immunoglobulin for the first time or, in rare cases, when changing the immunoglobulin medicine or after a prolonged treatment-free interval.
Possible complications can often be avoided by ensuring that:
- you are not hypersensitive to human immunoglobulin by administering the initial infusion of Gamunex slowly,
- you are closely monitored for any symptoms during the infusion period. Especially if it is the first time you receive a human immunoglobulin, if you have been switched from another immunoglobulin or if you have been without treatment for some time, you should be monitored for possible adverse effects during the first infusion and for one hour after it.
In case of adverse effects, the infusion rate should be reduced or the infusion should be stopped until the symptoms disappear. If the symptoms persist even after stopping the infusion, appropriate treatment should be initiated. In case of a severe hypersensitivity reaction with a drop in blood pressure and shortness of breath to the point of presenting a severe generalized allergic reaction (anaphylactic shock), treatment with this medicine should be stopped immediately and adequate measures should be taken.
Patients with kidney problems and other risk factors
There have been reports of kidney function disorders and acute kidney failure associated with the intravenous administration of immunoglobulins. You are at special risk if you have certain risk factors such as pre-existing kidney function impairment (renal insufficiency), diabetes (diabetes mellitus), or reduced blood volume (hypovolemia). Other circumstances considered risk factors are being overweight or receiving simultaneous treatment with medicines that have harmful effects on the kidneys and/or being over 65 years old. In any case, you should take the following precautions:
- drink plenty of fluids to ensure adequate fluid intake before starting treatment;
- your doctor should monitor your urine output and measure your kidney function;
- do not use certain medicines that increase urine production (loop diuretics) at the same time.
The infusion rate in your case should be as slow as possible, and the immunoglobulin should be used at the lowest possible concentration. If a kidney function disorder occurs, your doctor will consider stopping treatment with immunoglobulin.
Hemolysis (abnormal destruction of red blood cells)
It is commonly reported that immunoglobulins increase the risk of red blood cell destruction (hemolysis) in adults and children. If you are given high doses of IgIV on the same day or over several days and your blood group is A, B, or AB and/or you have an underlying inflammatory condition, you may be at higher risk of red blood cell destruction (hemolysis).
In post-marketing reports, it has been observed that high-dose IgIV indications in children, especially Kawasaki disease, are associated with a higher number of reports of hemolytic reactions than other IgIV indications in children.
You should see a doctor if you develop paleness (pale skin), lethargy (feeling of weakness), dark urine, shortness of breath, or palpitations (rapid heartbeat).
There have been isolated cases of kidney failure associated with hemolysis with a fatal outcome.
Information on safety with respect to infections
When medicines are manufactured from human blood or plasma, certain measures are taken to prevent the transmission of infections to patients. These measures include:
- careful selection of blood or plasma donors to ensure that those who may transmit infections are excluded,
- testing of each donation and of plasma pools for potential viruses or infections,
- inclusion of steps in the processing of blood or plasma that can inactivate or eliminate viruses.
Despite these measures, when medicines prepared from human blood or plasma are administered, the possibility of transmitting infections cannot be completely excluded. This also applies to unknown or emerging viruses and other types of infections.
The measures taken are considered effective for enveloped viruses such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C virus. The measures taken may have limited value for non-enveloped viruses such as hepatitis A virus and/or parvovirus B19. Immunoglobulins have not been associated with infections caused by hepatitis A virus or parvovirus B19, possibly because the antibodies against these infections contained in the product are protective.
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per single dose (up to a maximum of 2 g/kg); this is essentially "sodium-free".
It is strongly recommended that, each time you are administered a dose of this medicine, a note be taken of the name and batch number of the product, in order to maintain a record of the batches used.
Other medicines and Gamunex
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
You should avoid concomitant use of medicines that increase water elimination from your body (loop diuretics) during treatment with Gamunex.
Effects on vaccines: Gamunex may reduce the effectiveness of certain types of vaccines (live attenuated vaccines). In the case of rubella, mumps, and varicella, a period of up to 3 months should elapse between administration of this medicine and administration of these vaccines. In the case of measles, the period may be up to 1 year.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Dizziness or other reactions may occur that could affect your ability to drive or use machines. If this happens, wait until the symptoms have passed before driving or using machines.
3. How to use Gamunex
Your doctor will inject Gamunex into your veins (intravenous administration).
The dose you receive will depend on your disease and body weight, and will be determined by your doctor (see the section "Information intended for healthcare professionals only" at the end of this leaflet).
At the start of the infusion, you will receive Gamunex at a slow rate. Then, depending on how you feel, your doctor may gradually increase the infusion rate.
If you stop treatment withGamunex
If you stop treatment with this medicine, your clinical condition may worsen. Talk to the doctor in charge of your treatment if you want to stop treatment with this medicine prematurely.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
In rare and isolated cases, the following side effects have been reported with immunoglobulin preparations. Seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of the following side effects during or after the infusion:
- Sudden drop in blood pressure and, in isolated cases, anaphylactic shock (whose signs are rash, low blood pressure, rapid or irregular heartbeat, wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath, among others), even if you have not shown any allergic reaction in a previous administration.
- Cases of temporary non-infectious meningitis (whose signs are headache, fear or intolerance to light, stiffness in the neck).
- Cases of transient decrease in the number of red blood cells in the blood (hemolytic anemia/reversible hemolysis).
- Cases of transient skin reactions.
- Increased serum creatinine level (a test that measures kidney function) and/or acute kidney failure (whose signs are lower back pain, fatigue, decreased urine output).
- Thromboembolic reactions such as, for example, myocardial infarction (pressure around the chest with a feeling that the heart is beating too fast), stroke (muscle weakness in the face, arm, or leg, problems speaking or understanding what others are saying), pulmonary embolism (shortness of breath, chest pain, and fatigue), deep vein thrombosis (pain and swelling in a limb).
- Cases of transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) that cause hypoxia (lack of oxygen), shortness of breath, rapid breathing, bluish discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes, fever, and low blood pressure.
In clinical trials conducted with Gamunex, the following side effects have been observed:
The following side effects were frequent (may affect up to 1 in 10 infusions):
- headache
- fever
The following side effects were uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 infusions):
- dizziness
- urticaria (hives, redness, itching of the skin)
- pruritus (itching)
- rash
- nausea
- vomiting
- high blood pressure
- throat inflammation
- cough
- stuffy nose
- wheezing
- joint pain
- back pain
- pseudo-flu syndrome
- fatigue
- chills
- asthenia (weakness)
- muscle pain
The following side effects were rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 infusions):
- hemolytic anemia
- difficulty breathing
- sinusitis
- skin peeling
- anxiety
- decreased hemoglobin
- heavy digestion
- bruising
- flushing
- musculoskeletal stiffness
- palmar erythema (redness of the palms of the hands)
- aphonia (loss of voice)
- decreased white blood cell count
- dermatitis (skin inflammation) or contact dermatitis
- abdominal pain
- diarrhea
- low blood pressure
- neck pain
- musculoskeletal pain
- chest pain
- general malaise
- injection site reaction
- urethritis (pain or difficulty urinating)
- upper respiratory tract viral infection (disease caused by an acute infection affecting the upper respiratory tract, including the nose, paranasal sinuses, and throat)
- lymphocytosis (increase in the number of a specific type of white blood cell)
- hypersensitivity (allergic reaction)
- photosensitivity
- hypertensive crises (sudden increase in blood pressure)
- hyperemia (increased blood flow)
- hemoglobinuria (abnormally high concentrations in the urine of the protein that carries oxygen in the blood)
- increased blood pressure
- presence of free hemoglobin (hemoglobin circulating outside of red blood cells)
- increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (increased settling rate of red blood cells in a test tube)
What measures should be taken in case of side effects
If side effects occur, the infusion rate should be reduced or the infusion should be stopped until the signs of the side effects have disappeared. If the signs persist even after stopping the infusion, appropriate treatment should be administered.
In the case of a severe hypersensitivity reaction with a drop in blood pressure and shortness of breath to the point of presenting a severe generalized allergic reaction (anaphylactic shock), treatment with this medicine should be stopped immediately and adequate measures should be taken.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly through the Spanish Medicines Surveillance System for Human Use: www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Gamunex
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and vial. The shelf life is 3 years.
Store in a refrigerator (2 - 8°C). Do not freeze. Keep the vial in the outer carton.
The medicine can be stored in its outer carton for a single period of up to 6 months at room temperature (maximum 25°C). In this case, the shelf life of the medicine expires at the end of these 6 months, regardless of the original expiry date. The new expiry date should be written on the outer carton. However, the new expiry date should not be later than the expiry date printed on the carton. The medicine should not be refrigerated again.
Once the individual container is opened, the contents should be used immediately. Any remaining amount should be discarded. It is not allowed to store the medicine further, even in the refrigerator, due to the possible invasion of germs.
6. Container Content and Additional Information
Composition of Gamunex
The active ingredient is normal human immunoglobulin (IgIV). One ml of this medicine contains 100 mg of protein with an IgG content of at least 98% in water for injectable preparations.
A 10 ml vial contains: 1 g of normal human immunoglobulin
A 50 ml vial contains: 5 g of normal human immunoglobulin
A 100 ml vial contains: 10 g of normal human immunoglobulin
A 200 ml vial contains: 20 g of normal human immunoglobulin
A 400 ml vial contains: 40 g of normal human immunoglobulin
The percentage of IgG subclasses is approximately 62.8% (IgG1), 29.7% (IgG2), 4.8% (IgG3), and 2.7% (IgG4).
The maximum content of IgA is 84 micrograms/ml.
The other components are glycine and water for injectable preparations.
Product Appearance and Container Content
Gamunex is a solution for infusion. The solution is transparent to slightly opalescent and colorless to pale yellow.
Gamunex is available in container sizes of 10 ml, 50 ml, 100 ml, 200 ml, and 400 ml. The box contains a vial made of glass with a stopper (chlorobutyl), a label with a detachable part that becomes a handle, and a package leaflet.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder:
Grifols Deutschland GmbH Colmarer Straße 22 60528 Frankfurt Germany
Tel.: +49 69/660 593 100
Manufacturer:
Grifols Institute, S.A.
Can Guasc, 2 – Parets del Vallès
08150 Barcelona
Spain
Local Representative:
Grifols Institute, S.A.
Can Guasc, 2 – Parets del Vallès
08150 Barcelona
Spain
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Germany, Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Ireland, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, United Kingdom (Northern Ireland): Gamunex 10% 100 mg/ml
Denmark, Slovakia, Spain, Finland, France, Hungary, Italy, Norway, Czech Republic, Sweden: Gamunex 100 mg/ml
Greece: Gaminex 10% 100 mg/ml
Date of the last revision of this package leaflet:September 2022.
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) (http://www.aemps.gob.es/)
? ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended for healthcare professionals only:
Use only clear or slightly opalescent and colorless or pale yellow solutions for infusion that are free of particles – do not shake. Before infusion, allow Gamunex to reach room temperature or body temperature (e.g., by means of a water bath at a maximum temperature of 37°C).
The vials are supplied with a label with a detachable handle (Fig. 1). After introducing the infusion equipment (Fig. 2), invert the vial and fold back the part of the label corresponding to the handle (Fig. 3). Press firmly with your fingerto create a foldon each side where the handle is attached to the rest of the label (Fig. 4). Hang the vial from the infusion stand using the resulting handle (Fig. 5).
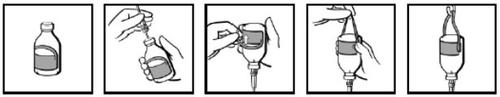
Fig. 1 Fig. 2 Fig. 3 Fig. 4 Fig. 5
Dosage and Administration
The dose and dosage regimen depend on the indication.
It may be necessary to individualize the dose for each patient based on the clinical response. The dose based on body weight may need to be adjusted in patients with low weight or overweight. The following dosage regimens are indicated for guidance purposes.
The recommended dosage is summarized in the following table:
Indication | Dose | Frequency of Infusions |
Replacement Therapy | ||
Primary Immunodeficiency Syndromes | Initial dose: 0.4-0.8 g/kg Maintenance dose: 0.2-0.8 g/kg | Every 3-4 weeks |
Secondary Immunodeficiencies | 0.2-0.4 g/kg | Every 3-4 weeks |
Pre-/Post-Exposure Prophylaxis to Measles: | ||
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis in Susceptible Patients | 0.4 g/kg | As soon as possible and within 6 days of exposure, and may be repeated once after 2 weeks to maintain serum antibody levels against measles > 240 mIU/ml |
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis in Patients with PID/IDS | 0.4 g/kg | In addition to maintenance therapy, administered as an extra dose within 6 days of exposure |
Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis in Patients with PID/IDS | 0.53 g/kg | If a patient receives a maintenance dose of less than 0.53 g/kg every 3-4 weeks, this dose should be increased once to at least 0.53 g/kg |
Immunomodulation: | ||
Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia | 0.8-1 g/kg or 0.4 g/kg/day | On day 1, may be repeated once in the next 3 days For 2 to 5 days |
Guillain-Barré Syndrome | 0.4 g/kg/day | For 5 days |
Kawasaki Disease | 2 g/kg | In a single dose with acetylsalicylic acid |
Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP) | Initial dose: 2 g/kg Maintenance dose: 1 g/kg | In divided doses over 2 to 5 days Every 3 weeks in divided doses over 1 to 2 days |
Multifocal Motor Neuropathy (MMN) | Initial dose: 2 g/kg Maintenance dose: 1 g/kg or 2 g/kg | In divided doses over 2 to 5 consecutive days Every 2 to 4 weeks or Every 4 to 8 weeks in divided doses over 2 to 5 days |
Severe Acute Exacerbations of Myasthenia Gravis | 2 g/kg | Divided over 2 consecutive days (1 g/kg per day) |
Form of Administration
Intravenous route.
Normal human immunoglobulin should be administered intravenously at an initial rate of 0.6-1.2 ml/kg/h for 0.5 hours. In case of an adverse reaction, the rate of administration should be reduced or the infusion interrupted. If well tolerated, the rate of administration can be gradually increased to a maximum of 4.8-8.4 ml/kg/h.
Pediatric Population
The dosage in children and adolescents (0-18 years) is not different from that in adults, as the dosage for each indication is calculated based on body weight and adjusted to the clinical outcome of the aforementioned diseases.
Gamunex should not be mixed with other infusion solutions or with other medicines. If dilution is necessary before infusion, a 50 mg/ml glucose solution can be used. Do not dilute with saline solutions.
Concomitant administration of Gamunex and heparin through a single-lumen administration device should be avoided.
The infusion lines through which Gamunex is administered can be flushed with a 50 mg/ml glucose solution or with a sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) and should not be flushed with heparin.
The heparinized line through which Gamunex has been administered should be flushed with a 50 mg/ml glucose solution or with a sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) and should not be flushed with heparin.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to GAMUNEX 100 mg/mL SOLUTION FOR INFUSIONDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 100 mg/mlActive substance: immunoglobulins, normal human, for intravascular adm.Manufacturer: Instituto Grifols S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 100 mg/mlActive substance: immunoglobulins, normal human, for intravascular adm.Manufacturer: Instituto Grifols S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE PERFUSION, 100 mg/mlActive substance: immunoglobulins, normal human, for intravascular adm.Manufacturer: Instituto Grifols S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for GAMUNEX 100 mg/mL SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Discuss questions about GAMUNEX 100 mg/mL SOLUTION FOR INFUSION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















