
FENDIVIA 50 micrograms/HOUR TRANSDERMAL PATCH


How to use FENDIVIA 50 micrograms/HOUR TRANSDERMAL PATCH
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Fendivia 12 micrograms/hour transdermal patch
Fendivia 25 micrograms/hour transdermal patch
Fendivia 50 micrograms/hour transdermal patch
Fendivia 75 micrograms/hour transdermal patch
Fendivia 100 micrograms/hour transdermal patch
fentanyl
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not give it to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack and other information
- What is Fendivia and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Fendivia
- How to use Fendivia
- Possible side effects
- Storing Fendivia
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Fendivia and what is it used for
The name of your medicine is Fendivia
The patches help to relieve very strong and long-lasting pain:
- in adults who need continuous pain treatment
- in children over 2 years of age who are already using opioid medication and who need continuous pain treatment.
Fendivia contains a medicine called fentanyl. It belongs to a group of strong pain-relieving medicines called opioids.
2. What you need to know before you use Fendivia
Do not use Fendivia:
- If you are allergic to fentanyl or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- If you have short-term pain, such as sudden pain or pain after an operation
- If you have breathing difficulties, with slow or weak breathing
Do not use this medicine if you or your child are in any of the above situations. If you are not sure, talk to your doctor or pharmacist before using Fendivia.
Warnings and precautions
- Fendivia can have life-threatening side effects in people who are not regularly using prescribed opioids.
- Fendivia is a medicine that can be life-threatening to children, even if the patches have already been used. Be aware that a sticky patch (used or unused) can be tempting to a child, and if it sticks to the child's skin or if the child puts it in their mouth, it can be fatal.
- Store this medicine in a safe and protected place, where others cannot get to it; see section 5 for more information.
If the patch sticks to another person
The patch should only be used on the skin of the person it has been prescribed for. There have been cases where the patch has stuck accidentally to another family member through close physical contact or sharing the same bed with the person wearing the patch. If the patch sticks accidentally to another person (especially a child), the medicine in the patch can pass through the skin of the other person and can cause serious side effects, such as breathing difficulties, with slow or weak breathing that can be life-threatening. If the patch sticks to someone else's skin, it should be removed immediately and a doctor should be consulted.
Be careful with Fendivia
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist beforeusing this medicine if you are in any of the following situations. Your doctor will need to keep a closer eye on you:
- If you have ever had lung or breathing problems
- If you have ever had heart, liver or kidney problems, or low blood pressure
- If you have ever had a brain tumour
- If you have ever had persistent headaches or a head injury
- If you are an elderly person, as you may be more sensitive to the effects of this medicine.
- If you have a condition called "myasthenia gravis", where the muscles become weak and tire easily.
If you have any of the above conditions (or if you are not sure), talk to your doctor or pharmacist before using Fendivia.
Tell your doctor if you have problems breathing while you are asleep.
Opioids like Fendivia can cause sleep-related breathing disorders, such as sleep apnoea (pauses in breathing during sleep) and sleep-related hypoxemia (low levels of oxygen in the blood). Tell your doctor if you, your partner or your carer notice that you have any of the following symptoms:
- pauses in breathing during sleep
- waking up at night due to difficulty breathing
- difficulty staying asleep
- excessive sleepiness during the day.
Your doctor may decide to change your dose.
Tell your doctor if you notice a change in the pain you feel.If you feel:
- the pain is no longer relieved by the patch
- an increase in pain
- a change in how you feel the pain (for example, you feel pain in a different part of your body)
- pain when something touches your body that you would not expect to hurt.
Do not change the dose yourself. Your doctor may decide to change your dose or treatment.
Side effects and Fendivia
- Fendivia can make you feel unusually drowsy and can slow down your breathing. On rare occasions, these breathing problems can be life-threatening, especially in people who have not used strong opioid painkillers before (such as Fendivia or morphine). If you, or your partner or carer, notice that the person wearing the patch is unusually drowsy, with slow or weak breathing:
- Remove the patch
- Call a doctor or go to the nearest hospital immediately
- Get the person to move and talk as much as possible
- If you have a fever while using Fendivia, talk to your doctor. This can increase the amount of medicine that passes through your skin.
- Fendivia can cause constipation; talk to your doctor or pharmacist for advice on how to prevent or relieve constipation.
You can find a complete list of possible side effects in section 4.
While you are wearing the patch, do not expose it to direct heat, such as heat pads, electric blankets, hot water bottles, water beds, heat lamps or sunlamps. Do not take a hot bath or shower, and do not use saunas or hot tubs. If you do, you may increase the amount of medicine released from the patch.
Long-term use and tolerance
This medicine contains fentanyl, an opioid. Repeated use of opioid painkillers can make the medicine less effective (your body gets used to it, which is known as tolerance). You may also become more sensitive to pain when using Fendivia. This is known as hyperalgesia. Increasing the dose of the patches may continue to reduce the pain for a while, but it can also be harmful. If you notice that the medicine is becoming less effective, talk to your doctor. Your doctor will decide whether it is best for you to increase the dose or to gradually reduce your use of Fendivia.
Dependence and addiction
This medicine contains fentanyl, which is an opioid. It can cause dependence and/or addiction.
Repeated use of Fendivia can also lead to dependence, abuse and addiction, which can result in a potentially life-threatening overdose. The risk of these side effects may be greater with a higher dose and longer use. Dependence or addiction can lead to a feeling of loss of control over the amount of medicine you need to use or how often you need to use it. You may feel a need to keep using the medicine even if it is no longer relieving the pain.
The risk of dependence or addiction varies from person to person. The risk of becoming dependent on or addicted to Fendivia may be greater if:
•You or someone in your family has abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription medicines or illegal drugs ("addiction").
•You are a smoker.
•You have ever had problems with your mood (depression, anxiety or personality disorder) or have been treated by a psychiatrist for another mental health condition.
If you notice any of the following symptoms while using Fendivia, it could be a sign of dependence or addiction.
•You need to use the medicine for longer than your doctor has prescribed.
•You need to use a higher dose than recommended.
- You are using the medicine for reasons other than those prescribed, for example, "to feel calm" or "to help you sleep".
•You have tried to stop using the medicine several times but have been unable to.
- You feel unwell when you stop using the medicine, and you feel better once you start taking it again ("withdrawal symptoms").
If you notice any of these signs, talk to your doctor to determine the best course of treatment for you, when it is appropriate to stop the medicine and how to do it safely.
Withdrawal symptoms when stopping Fendivia
Do not stop using this medicine suddenly. You may experience withdrawal symptoms such as restlessness, difficulty sleeping, irritability, agitation, anxiety, feeling your heartbeat (palpitations), increased high blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, loss of appetite, tremors, shivering, shaking or sweating. If you want to stop using this medicine, talk to your doctor first. Your doctor will tell you how to do it, usually by gradually reducing the dose so that the unpleasant withdrawal symptoms are kept to a minimum.
Using Fendivia with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines. This includes medicines that you buy without a prescription and herbal remedies. You should also tell your pharmacist that you are using Fendivia if you buy any medicines from the pharmacy.
Your doctor will know which medicines can be used safely with Fendivia. You may need to be closely monitored if you are using any of the types of medicines listed below, or if you stop using any of the types of medicines listed below, as this may affect the dose of Fendivia that you need.
In particular, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using:
- Other painkillers, such as other opioid painkillers (e.g. buprenorphine, nalbuphine or pentazocine) and some painkillers for nerve pain (gabapentin and pregabalin).
- Medicines to help you sleep (such as temazepam, zaleplon or zolpidem).
- Medicines to help you calm down (tranquillisers, such as alprazolam, clonazepam, diazepam, hydroxyzine or lorazepam) and medicines for mental health conditions (antipsychotics, such as aripiprazole, haloperidol, olanzapine, risperidone or phenothiazines).
- Medicines to relax your muscles (such as cyclobenzaprine or diazepam).
- Some medicines used to treat depression called SSRIs or SNRIs (such as citalopram, duloxetine, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline or venlafaxine). – see below for more information
- Some medicines used to treat depression or Parkinson's disease called MAOIs (such as isocarboxazid, phenelzine, selegiline or tranylcypromine). You should not use Fendivia in the 14 days after stopping these medicines. – see below for more information
- Some antihistamines, especially those that cause drowsiness (such as chlorphenamine, clemastine, cyproheptadine, diphenhydramine or hydroxyzine).
- Some antibiotics used to treat infections (such as erythromycin or clarithromycin).
- Medicines used to treat fungal infections (such as itraconazole, ketoconazole, fluconazole or voriconazole).
- Medicines used to treat HIV infection (such as ritonavir).
- Medicines used to treat irregular heartbeats (such as amiodarone, diltiazem or verapamil).
- Medicines used to treat tuberculosis (such as rifampicin).
- Some medicines used to treat epilepsy (such as carbamazepine, phenobarbital or phenytoin).
- Some medicines used to treat nausea or vomiting (such as phenothiazines).
- Some medicines used to treat heartburn or stomach ulcers (such as cimetidine).
- Some medicines used to treat angina (chest pain) or high blood pressure (such as nicardipine).
- Some medicines used to treat blood cancer (such as idelalisib).
Using Fendivia with antidepressants
The risk of side effects increases if you are using medicines such as certain antidepressants. Fendivia can interact with these medicines and you may experience changes in your mental state such as agitation, seeing, feeling, hearing or smelling things that are not there (hallucinations) and other effects such as changes in blood pressure, fast heart rate, high body temperature, overactive reflexes, lack of coordination, muscle stiffness, nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea (these can be signs of serotonin syndrome). If they are used together, your doctor may want to keep a close eye on you to detect such side effects, especially when starting treatment or when changing the dose of your medicine.
Using Fendivia with central nervous system depressants, including alcohol and some sedatives
Using Fendivia with sedative medicines, such as benzodiazepines or related medicines, increases the risk of drowsiness, breathing difficulties (respiratory depression), coma and can be life-threatening. Therefore, concomitant use should only be considered when no other treatment options are possible.
However, if your doctor has prescribed Fendivia and sedatives at the same time, the dose and duration of treatment should be limited by your doctor.
Tell your doctor about all sedative medicines you are using, and follow the dose recommended by your doctor.
It may be useful to inform your family and friends about the signs and symptoms mentioned above. Talk to your doctor if you experience any of these symptoms.
Use in athletes
Athletes are informed that this medicine contains a component that may result in a positive doping test.
Operations
If you think you are going to have an anaesthetic, tell your doctor or dentist that you are using Fendivia.
Using Fendivia with alcohol
Do not drink alcohol while you are using Fendivia, unless you have talked to your doctor first.
Fendivia can make you feel drowsy or breathe more slowly. Drinking alcohol can make these effects worse.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
Fendivia should not be used during pregnancy, unless you have talked to your doctor.
Fendivia should not be used during labour, as the medicine can affect the breathing of the newborn baby.
Long-term use of Fendivia during pregnancy can cause withdrawal symptoms in your newborn baby, such as high-pitched crying, irritability, convulsions, poor feeding and diarrhoea, which can be life-threatening if not recognised and treated. Talk to a doctor immediately if you think your baby may have withdrawal symptoms.
Do not use Fendivia if you are breastfeeding. You should not breastfeed for 3 days after removing the Fendivia patch. This is because the medicine can pass into breast milk.
Driving and using machines
Fendivia can affect your ability to drive and use machines or tools, as it can make you feel drowsy or dizzy. If this happens, do not drive or use machines or tools. Do not drive while you are using this medicine until you know how it affects you.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you are unsure whether it is safe for you to drive while using this medicine.
3. How to use Fendivia
Follow your doctor's instructions for administering this medication exactly. If in doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
Your doctor will decide which concentration of Fendivia is most suitable for you, taking into account the intensity of your pain, your general condition, and the type of pain treatment you have received so far.
Before starting treatment and regularly during treatment, your doctor will also explain what you can expect from using Fendivia, when and for how long you should use it, when you should contact your doctor, and when you should stop using it (see also section 2, symptoms of withdrawal when stopping Fendivia).
How to apply and change patches
- Each patch contains a sufficient amount of medication for 3 days (72hours).
- You should change the patch every three days, unless your doctor has instructed you otherwise.
- Always remove the used patch beforeapplying a new one.
- Always change the patch at the same timeof day every 3 days (72 hours).
- If you are using more than one patch, change them all at the same time.
- Write down the day of the week, date, and time each time you apply a patch to remember when you need to change it.
- The following table shows when you should change the patch:
Apply the patch on | Change the patch on | |
Monday | Thursday | |
Tuesday | Friday | |
Wednesday | Saturday | |
Thursday | Sunday | |
Friday | Monday | |
Saturday | Tuesday | |
Sunday | Wednesday |
Where to apply the patch
Adults
- Apply the patch to a flat area of the torso or arm (never over a joint).
Children
- Always apply the patch to the upper back so that your child has difficulty reaching or removing it.
- Check occasionally that the patch is still stuck to the skin.
- It is essential that the child does not remove the patch and put it in their mouth, as this could be life-threatening or fatal.
- Keep your child under close observation for 48 hours after:
- Applying the first patch
- Applying a patch with a higher dose
- The patch may take some time to reach its maximum effect. Therefore, your child may need other pain relievers until the patch is effective. Your doctor will explain this to you.
Adults and children:
Do not apply the patch to
- The same site twice in a row.
- Areas that move a lot (joints), irritated skin, or skin with wounds.
- Areas of skin with a lot of hair. If there is hair, do not shave it (the skin becomes irritated with shaving). Instead, cut it as close to the skin as possible.
How to apply the patch
Step 1: Prepare the skin
- Before applying the patch, check that the skin is completely dry, clean, and fresh
- If you need to wash the skin, use only cold water
- Do not use soap or other cleaners, creams, moisturizers, oils, or talcum powder before applying the patch
- Do not apply the patch immediately after a hot bath or shower
Step 2: Open the envelope
- Each patch is sealed in its own envelope
- Open the envelope by cutting along the dotted line with scissors
- Carefully cut along the edge of the envelope to avoid damaging the patch inside
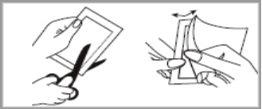
- Hold the two parts of the open envelope and pull to separate them
- Remove the patch and use it immediately
- Save the empty envelope to dispose of the used patch later
- Use each patch only once
- Do not remove the patch from its envelope until you are ready to use it
- Check that the patch is not damaged
- Do not use the patch if it is divided or cut or if it has any damage
- Never divide or cut the patch
Step 3: Peel and press
- Make sure the patch will be covered by loose clothing and do not stick it under tight or elastic fabric
- Carefully peel off one half of the shiny plastic protective layer, starting from the center of the patch. Try not to touch the adhesive part of the patch
- Press this adhesive part of the patch onto the skin
- Remove the other part of the protective layer and press the entire patch onto the skin with the palm of your hand
- Hold it pressed for at least 30 seconds. Make sure the patch is well stuck, especially around the edges
Step 4: Dispose of the patch
- As soon as you remove the patch, fold it firmly in half, so that the adhesive side of the patch sticks to itself
- Put it back in the original envelope and throw it away following the instructions of your pharmacist
- Keep used patches out of sight and reach of children; although they are used, patches contain medication that can harm children and even be fatal
Step 5: Wash your hands
- Always wash your hands with water only after handling patches
More information on using Fendivia
Daily activities during patch use
- Patches are water-resistant
- You can shower or bathe with the patch on, but do not rub it
- If your doctor agrees, you can exercise or play sports with the patch on
- You can also swim with the patch on, but:
- Do not use hot tubs or whirlpools
- Do not cover the patch with tight or elastic fabrics
- When wearing the patch, do not expose it to direct heat, such as heating pads, electric blankets, hot water bottles, waterbeds, or heat lamps or tanning beds. Do not sunbathe or take prolonged hot baths and do not use saunas. If you do, you may increase the amount of medication released from the patch.
How long do patches take to work?
- The first patch may take some time to reach its maximum effect.
- Your doctor may also give you additional pain relievers during the first few days.
- After that, the patch should help relieve pain continuously, so you can stop taking other pain relievers. However, your doctor may prescribe additional pain relievers from time to time.
How long will you need to use the patches?
- Fendivia patches are indicated for prolonged pain. Your doctor will tell you how long you can expect to use the patches.
If your pain worsens
- If your pain worsens suddenly after applying the last patch, you should check your patch. If it is no longer stuck well or has come off, you should replace the patch (see also the section If the patch comes off).
- If your pain worsens over time while using the patches, your doctor may try patches with a higher dose or prescribe additional pain relievers (or both)
- If increasing the patch dose does not help, your doctor may decide to stop using the patches.
If you use too many patches or a patch with the wrong dose
If you have applied too many patches or a patch with the wrong dose, remove them and contact your doctor immediately, go to the hospital, or you can also call the Toxicology Information Service, phone: 91 562 04 20, indicating the medication and the amount applied.
Signs of overdose include breathing problems or weak breathing, fatigue, extreme drowsiness, inability to think clearly or walk or talk normally, and dizziness, dizziness, or confusion. An overdose can also cause a brain disorder known as toxic leukoencephalopathy.
If you forget to change the patch
- If you forget to change the patch, change it as soon as you remember and write down the day and time. Change the patch again after 3 days (72hours), as usual.
- If you are significantly late, you should talk to your doctor, as you may need additional pain relievers, but do notapply additional patches.
If the patch comes off
- If the patch falls off before it is due to be changed, apply a new one immediately and write down the day and time. Choose a new skin area:
- On the torso or arm
- On the upper back of your child
- Tell your doctor about this and leave the patch on for another 3 days (72hours)or for the time your doctor indicates, before changing the patch in the usual way
- If patches tend to fall off, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse
If you want to stop using the patches
- Do not stop using this medication suddenly. If you want to stop using this medication, talk to your doctor first. Your doctor will tell you how to do it, usually by gradually reducing the dose to minimize unpleasant withdrawal effects. See also section 2 “Withdrawal symptoms when stopping Fendivia”.
- If you stop using the patches, do not start using them again without asking your doctor first. You may need a different dose when you restart treatment.
If you have any other questions about using this medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medications, this medication can cause side effects, although not everyone gets them.
If you, your partner, or caregiver notice any of the following signs in the person wearing the patch, remove the patch and call a doctor or go to the nearest hospital immediately. You may need urgent medical treatment.
- Unusual drowsiness, slower or weaker breathing than expected.
Follow the above recommendations and make the person wearing the patch move and talk as much as possible. In very rare cases, these breathing difficulties can be life-threatening or even fatal, especially in people who have not used strong opioid pain relievers before (such as Fendivia or morphine). (Uncommon, may affect up to 1 in 100 patients).
- Sudden swelling of the face or throat, severe irritation, redness, or blisters on the skin.
These can be signs of a severe allergic reaction. (Frequency cannot be estimated from available data).
- Seizures (convulsions). (Uncommon, may affect up to 1 in 100 people).
- Decreased level of consciousness or loss of consciousness. (Uncommon, may affect up to 1 in 100 people).
The following side effects have also been reported
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- Nausea, vomiting, constipation
- Feeling drowsy (drowsiness)
- Feeling dizzy
- Headache
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Allergic reaction
- Loss of appetite
- Difficulty sleeping
- Depression
- Feeling anxious or confused
- Seeing, feeling, hearing, or smelling things that are not there (hallucinations)
- Tremors or muscle spasms
- Strange sensation on the skin, such as tingling or prickling (paresthesia)
- Feeling that everything is spinning (vertigo)
- Fast or irregular heartbeat (palpitations, tachycardia)
- High blood pressure
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Diarrhea
- Dry mouth
- Stomach pain or indigestion
- Excessive sweating
- Itching, rash, or redness of the skin
- Difficulty urinating or emptying the bladder completely
- Extreme fatigue, weakness, or general malaise
- Feeling cold
- Swelling of the hands, ankles, or feet (peripheral edema)
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Feeling agitated or disoriented
- Feeling extremely happy (euphoria)
- Decreased sensation or sensitivity, especially in the skin (hypoesthesia)
- Memory loss
- Blurred vision
- Slow heartbeat (bradycardia) or low blood pressure
- Bluish color of the skin due to decreased oxygen in the blood (cyanosis)
- Loss of intestinal contractions (ileus)
- Skin rash with itching (eczema), allergic reaction, or other skin disorders where the patch is applied
- Flu-like illness
- Feeling of changed body temperature
- Fever
- Muscle contraction
- Difficulty getting or maintaining an erection (impotence) or problems having sex
- Difficulty swallowing
Rare side effects (may affect up to 1 in 1000 people)
- Pupil constriction (miosis)
- Occasional interruption of breathing (apnea)
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from available data)
- Lack of male sex hormones (androgen deficiency)
- Delirium (symptoms may include a combination of agitation, restlessness, disorientation, confusion, fear, seeing or hearing things that are not really there, sleep disturbances, nightmares)
- You may become dependent on Fendivia (see section 2).
You may notice rashes, redness, or mild itching of the skin at the patch application site. It is usually mild and disappears after removing the patch. If it does not, or if the patch irritates your skin a lot, tell your doctor.
Repeated use of patches can cause the medication to lose effectiveness (you get used to it or may become more sensitive to pain), or you may become dependent.
If you switch from another pain reliever to Fendivia or if you stop using Fendivia abruptly, you may experience withdrawal symptoms, such as dizziness, feeling sick, diarrhea, anxiety, or tremors. Tell your doctor if you notice any of these effects.
There have also been reports of newborn babies experiencing withdrawal symptoms after their mothers used Fendivia for a prolonged period during pregnancy.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Medicines Monitoring System for Human Use: www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Storage of Fendivia
Where to store the patches
Keep all patches (used and unused) out of sight and reach of children.
Store this medication in a safe and protected place, where others cannot access it. It can cause serious harm and be fatal for people who use this medication accidentally or intentionally when it has not been prescribed for them.
How long can you store Fendivia
Do not use this medication after the expiration date shown on the box and on the envelope after EXP. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated. If the patches are expired, take them to the pharmacy.
How to dispose of used or unused patches
Accidental exposure of another person to used and unused patches, especially children, can result in a fatal outcome.
Used patches should be folded firmly in half, so that the adhesive side of the patch sticks to itself. Then, they should be thrown away safely by putting them back in the original envelope and keeping them out of sight and reach of others, especially children, until they are disposed of safely.
Medications should not be thrown down the drain or into the trash. Deposit the containers and medications you no longer need at the SIGRE collection point in the pharmacy. If in doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the containers and medications you no longer need. This way, you will help protect the environment.
6. Container Content and Additional Information
Fendivia Composition
The active ingredient is: Fentanyl.
The patches are available in 5 different doses (see table below).
Patch Name | Each patch contains: | Each patch releases a dose of: | The active surface area of each patch is: |
Fendivia 12 micrograms/hour transdermal patch | 1.38 mg | 12 micrograms/hour | 4.2 cm2 |
Fendivia 25 micrograms/hour transdermal patch | 2.75 mg | 25 micrograms/hour | 8.4 cm2 |
Fendivia 50 micrograms/hour transdermal patch | 5.5 mg | 50 micrograms/hour | 16.8 cm2 |
Fendivia 75 micrograms/hour transdermal patch | 8.25 mg | 75 micrograms/hour | 25.2 cm2 |
Fendivia 100 micrograms/hour transdermal patch | 11 mg | 100 micrograms/hour | 33.6 cm2 |
The other components are: Dipropylene glycol, hydroxypropyl cellulose, dimethicone, silicone adhesive (amine-resistant), ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA, release membrane), polyethylene terephthalate (PET, outer plastic laminate), polyester coated with fluoropolymer (protective laminate), and printing ink.
Product Appearance and Container Content
Fendivia is a transparent and rectangular transdermal patch. Each patch is packaged in a heat-sealed, child-resistant envelope made of paper, aluminum, and polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
Each transdermal patch has the trade name, active ingredient, and dose printed in a specific color:
Fendivia 12 micrograms/hour: brown printing
Fendivia 25 micrograms/hour: red printing
Fendivia 50 micrograms/hour: green printing
Fendivia 75 micrograms/hour: light blue printing
Fendivia 100 micrograms/hour: gray printing
The patches are supplied in cardboard containers containing 1, 3, 5, 10, and 20 patches. Only some package sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder
ISTITUTO GENTILI S.r.l.
Via San Giuseppe Cottolengo 15
20143 Milan, Italy
Manufacturer:
LTS Lohmann Therapie-Systeme AG Lohmannstrasse 2D – 56626 Andernach Germany
You can request more information about this medication by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Local Representative:
FERRER FARMA, S.A.
Av. Diagonal, 549, 5th Floor,
08029 Barcelona (Spain)
This medication is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Matrifen: Cyprus
Quatrofen: Sweden
Fendivia: Spain
Date of the last revision of this prospectus: 12-06-2024
Detailed information about this medication is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
- Country of registration
- Average pharmacy price29.25 EUR
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to FENDIVIA 50 micrograms/HOUR TRANSDERMAL PATCHDosage form: TRANSDERMAL PATCH, 12 MCG/HActive substance: fentanylManufacturer: Aristo Pharma Iberia S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: BUCCAL/SUCKING TABLET, 1200 microgramsActive substance: fentanylManufacturer: Ferrer Internacional S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: BUCCAL/SUCKING TABLET, 1600 microgramsActive substance: fentanylManufacturer: Ferrer Internacional S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for FENDIVIA 50 micrograms/HOUR TRANSDERMAL PATCH
Discuss questions about FENDIVIA 50 micrograms/HOUR TRANSDERMAL PATCH, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















