
DZUVEO 30 micrograms sublingual tablet


How to use DZUVEO 30 micrograms sublingual tablet
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Dzuveo 30micrograms sublingual tablet
sufentanil
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is Dzuveo and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Dzuveo
- How to use Dzuveo
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Dzuveo
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Dzuveo and what is it used for
The active substance of Dzuveo is sufentanil, which belongs to a group of powerful pain-relieving medicines called opioids.
Sufentanil is used to treat moderate to severe acute pain in adults in a medically controlled setting, such as a hospital.
2. What you need to know before you use Dzuveo
Do not use Dzuveo
- If you are allergic to sufentanil or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- If you have severe lung or breathing problems.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor or nurse before you start using Dzuveo. Tell your doctor or nurse before treatment if:
- You have any disorder that affects your breathing (such as asthma, wheezing, or difficulty breathing). As Dzuveo may affect your breathing, your doctor or nurse will check your breathing during treatment.
- You have had a head injury or brain tumor.
- You have heart and circulation problems, especially slow heart rate, irregular heartbeat, low blood volume, or low blood pressure.
- You have moderate to severe liver problems or severe kidney problems, as these organs affect how your body breaks down and eliminates the medicine; you have abnormally slow bowel movements.
- You have a gallbladder or pancreas disease.
- You or any family member has ever abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription medicines, or illegal drugs ("addiction").
- You are a smoker.
- You have had mood problems (depression, anxiety, or personality disorder) or have been treated by a psychiatrist for other mental illnesses.
This medicine contains sufentanil, which is an opioid. Repeated use of opioid painkillers can make the medicine less effective (your body gets used to them). It can also lead to dependence and abuse, which can result in a potentially life-threatening overdose. It is important that you talk to your doctor if you are concerned about becoming dependent on Dzuveo.
Talk to your doctor DURING use of Dzuveo if:
- You feel pain or increased sensitivity to pain (hyperalgesia) that does not respond to a higher dose of the medicine as prescribed by your doctor.
What you need to know before you use Dzuveo
Sleep-related breathing disorders
- Dzuveo may cause sleep-related breathing disorders such as sleep apnea (pauses in breathing during sleep) and sleep-related hypoxemia (low oxygen level in the blood). These symptoms may include pauses in breathing during sleep, waking up at night due to difficulty breathing, difficulty staying asleep, or excessive sleepiness during the day. If you or someone else notices these symptoms, contact your doctor. Your doctor may consider reducing the dose.
Children and adolescents
Dzuveo should not be used in children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
Other medicines and Dzuveo
Tell your doctor if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines. In particular, tell your doctor if you are taking any of the following:
- Ketoconazole, used to treat fungal infections, this medicine may affect how your body breaks down sufentanil.
- Any medicine that may make you drowsy (has a sedative effect), such as sleeping pills, medicines to treat anxiety (e.g., benzodiazepines), tranquilizers, or other opioid medicines, as they may increase the risk of serious breathing problems, coma, and death.
- Medicines for the treatment of depression, known as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). These medicines should not be taken in the 2 weeks prior to, or concomitantly with, the administration of Dzuveo.
- Medicines for the treatment of epilepsy, nerve pain, or anxiety (gabapentin and pregabalin), as they increase the risk of opioid overdose and respiratory depression and may put the patient's life at risk.
- Medicines for the treatment of depression known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). It is not recommended to use these medicines concomitantly with Dzuveo.
- Other medicines that are also taken sublingually (medicines that are placed under the tongue, where they dissolve) or medicines that have an effect in your mouth (such as nystatin, a liquid or tablets that are kept in the mouth to treat fungal infections), as the effect on Dzuveo has not been studied.
- Commonly prescribed opioids (e.g., morphine, codeine, fentanyl, hydromorphone, oxycodone).
- Medicines used to treat high blood pressure or angina (chest pain), known as calcium channel blockers or beta-blockers, such as diltiazem and nifedipine.
Using Dzuveo with alcohol
Do not drink alcohol while using Dzuveo. It may increase the risk of serious breathing problems.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor before taking this medicine.
Dzuveo should not be used during pregnancy or in women of childbearing potential who are not using effective contraceptive methods.
Dzuveo passes into breast milk and may cause side effects in the breastfed child. Breastfeeding is not recommended if you are taking Dzuveo.
Driving and using machines
Dzuveo affects your ability to drive or use machines, as it may cause drowsiness, dizziness, or visual disturbances. You should not drive or use machines if you experience any of these symptoms during or after treatment with sufentanil. You should only drive or use machines if a sufficient time has elapsed after the last administration of Dzuveo.
Dzuveo contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per tablet; this is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to use Dzuveo
This medicine should be administered by a doctor or nurse using the single-dose administration device. You should not administer this medicine yourself.
Dzuveo should only be used in a medically controlled setting, such as a hospital. It can only be prescribed by doctors with experience in the use of powerful painkillers like sufentanil and who are aware of the effects it may have on you, particularly on your breathing (see "Warnings and precautions" above).
The recommended dose is one 30 microgram sublingual tablet as needed, administered at least 1 hour apart. A healthcare professional will administer the sublingual tablet using the disposable single-dose applicator. The applicator will help the healthcare professional place a tablet under your tongue. The tablets dissolve under the tongue and should not be chewed or swallowed because they will not work to relieve pain unless they can dissolve under the tongue. You should not eat or drink anything and should speak as little as possible in the 10 minutes following administration of each dose.
After receiving a dose, you will not be given another dose for at least 1 hour. The maximum daily dose is 720 micrograms per day (24 tablets per day).
Dzuveo should not be used for more than 48 hours.
After your treatment, the medical staff will dispose of the applicator as appropriate.
If you use more Dzuveo than you should
Symptoms of overdose include serious breathing problems, such as slow and shallow breathing, loss of consciousness, very low blood pressure, collapse, and muscle stiffness. If these symptoms start to appear, inform a doctor or nurse immediately.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Serious side effects
The most serious side effects are serious breathing problems, such as slow and shallow breathing, which can even make you stop breathing.
If you experience any of the above side effects, inform your doctor or nurse immediately.
Very common side effects(may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
Nausea, vomiting, or feeling sick and feeling of warmth in general.
Common side effects (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Difficulty sleeping, anxiety, or confusion, dizziness.
- Headache, drowsiness, feeling sleepy.
- Increased heart rate, high blood pressure, low blood pressure.
- Low oxygen levels in the blood, feeling of pain in the lower throat, slow and shallow breathing.
- Dry mouth, flatulence (gas), constipation, indigestion, or reflux.
- Allergic reactions, itching of the skin.
- Muscle contractions and spasms.
- Difficulty urinating.
- This medicine may also cause changes in red blood cell, white blood cell, calcium, albumin, potassium, and sodium levels in the blood, which can only be detected by a blood test. If you are going to have a blood test, make sure your doctor knows you are taking this medicine.
Uncommon side effects (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- Lung inflammation, eye redness and inflammation, throat inflammation.
- Fat accumulation under the skin.
- Difficulty controlling blood sugar levels (diabetes), increased cholesterol.
- Agitation, lack of interest or emotion, lack of energy, disorientation, euphoria, hallucinations, or seeing things that do not exist, nervousness.
- Problems with muscle movement coordination, muscle contractions, tremors, or excessive agitation, exaggerated reflex responses, burning sensation, feeling of fainting, abnormal skin sensation (tingling), numbness in general, tiredness, forgetfulness, migraine, tension headache.
- Vision disorders, eye pain.
- Slow heart rate, irregular heartbeat, angina, or other chest discomfort.
- High or low blood pressure when standing up, skin redness.
- Slow or difficult breathing (even when sleeping), nosebleeds, hiccups.
- Chest pain and difficulty breathing caused by a blood clot in the lung, fluid in the lungs, wheezing.
- Diarrhea, belching, stomach lining inflammation or gastritis, gas, acid reflux, retching, stomach pain or discomfort.
- Blistering, excessive sweating, skin rash, dry skin, numbness of the mouth or face.
- Back pain, chest, or other parts of the body, pain in the limbs.
- Difficulty urinating, strong-smelling urine, pain when urinating, kidney failure.
- Swelling, uncomfortable feelings in the chest, chills, and weakness (lack of energy).
This medicine may also cause changes in platelet (which help blood to clot), magnesium, protein, sugar, fat, phosphate, and plasma levels in the blood, which can only be detected by a blood test. If you are going to have a blood test, make sure your doctor knows you are taking this medicine.
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- Severe allergic reactions (anaphylactic shock), seizures, coma, small pupil size, skin redness.
- Withdrawal syndrome, which may include symptoms such as agitation, anxiety, muscle pain, insomnia, sweating, and yawning.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly via the national reporting system listed in Appendix V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Dzuveo
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Your doctor or nurse will make sure that:
- this medicine is not used after the expiry date stated on the label and on the carton after EXP. The expiry date is the last day of the month stated.
- it is stored in the original packaging to protect it from light and oxygen.
- you do not use this medicine if you notice signs of deterioration.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Your healthcare professional will dispose of the packaging and any unused medicine in accordance with hospital regulations. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
Composition of Dzuveo
- The active substance is sufentanil. Each sublingual tablet contains 30 micrograms of sufentanil (as citrate).
- The other ingredients are mannitol (E421), dicalcium phosphate, hypromellose, sodium croscarmellose, indigo carmine (E132), stearic acid, and magnesium stearate.
Appearance and packaging
Dzuveo is a flat, blue, sublingual tablet with rounded edges. It is 3 mm in diameter and is supplied in a single-dose applicator (labeled as [sublingual tablet]). The applicator, with the tablet inside, is packaged in a pouch.
Each pouch contains one applicator and one sufentanil 30 microgram tablet. Each pack contains 5 or 10 pouches.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Laboratoire Aguettant
1, rue Alexander Fleming
69007 Lyon
France.
Date of last revision of this leaflet:
<------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------>
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
Instructions for use of the single-dose applicator (SDA)
Single-use product / Do not reuse
Do not use if the pouch seal is broken
Do not use if the single-dose applicator (SDA) is damaged
The patient should be instructed not to chew or swallow the tablet.
The patient should be instructed not to eat or drink anything and to speak as little as possible in the 10 minutes following administration of the tablet.
- When ready to administer the medicine, open the pouch by tearing along the perforation at the top. The pouch contains a transparent plastic SDA with a single blue tablet housed in the tip and a packet with an oxygen absorber. The packet with the oxygen absorber should be discarded.
The following shows the contents of the pouch:

Plunger
Locking system
- Remove the white locking system from the green plunger by pressing on both sides at the same time to release it from the plunger. Discard the locking system.
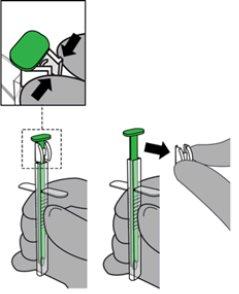
- Instruct the patient to, if possible, touch the palate with their tongue.
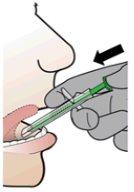
- Gently place the SDA against the patient's teeth or lips.
- Place the tip of the SDA under the patient's tongue and facing the floor of the mouth. NOTE: Avoid direct contact between the mucosa and the tip of the SDA.
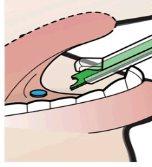
- Press the green plunger to release the tablet into the patient's sublingual space and confirm correct placement of the tablet.
The single-dose applicator (SDA) should be disposed of in accordance with hospital policies and local requirements.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to DZUVEO 30 micrograms sublingual tabletDosage form: INJECTABLE, 5 micrograms/mlActive substance: sufentanilManufacturer: Medochemie LimitedPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 50 micrograms/mlActive substance: sufentanilManufacturer: Medochemie LimitedPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 5 micrograms/mLActive substance: sufentanilManufacturer: Altan Pharmaceuticals SaPrescription required
Online doctors for DZUVEO 30 micrograms sublingual tablet
Discuss questions about DZUVEO 30 micrograms sublingual tablet, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















