
DUODOPA 240 mg/mL + 12 mg/mL SOLUTION FOR INFUSION


How to use DUODOPA 240 mg/mL + 12 mg/mL SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Duodopa 240mg/ml + 12mg/ml solution for infusion
foslevodopa/foscarbidopa
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What Duodopa solution for infusion is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use Duodopa solution for infusion
- How to use Duodopa solution for infusion
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Duodopa solution for infusion
- Contents of the pack and further information
- Instructions for use of Duodopa solution for infusion with the Vyafuser pump
1. What Duodopa solution for infusion is and what it is used for
This medicine contains two active substances, foslevodopa and foscarbidopa, and is used to treat Parkinson's disease.
How Duodopa solution for infusion works
- Foslevodopa is converted into "dopamine" in the body. This adds to the dopamine already present in your brain and spinal cord. Dopamine helps to transmit signals between nerve cells.
- Low levels of dopamine are the cause of the symptoms of Parkinson's disease, such as tremors, feelings of stiffness, slow movement, and balance disorders.
- Treatment with foslevodopa increases the amount of dopamine in your body. This means it reduces these symptoms.
- Foscarbidopa improves the effect of foslevodopa. It also reduces the side effects of foslevodopa.
2. What you need to know before you use Duodopa solution for infusion
Do not use Duodopa solution for infusion if
- you are allergic to foslevodopa, foscarbidopa, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- you have a eye disorder called "narrow-angle glaucoma"
- you have severe heart problems
- you have severe irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia)
- you have had a recent stroke
- you are taking medicines for depression called selective MAO-A inhibitors and non-selective MAO inhibitors such as moclobemide and phenelzine. You must stop treatment with these medicines at least two weeks before starting to take Duodopa solution for infusion
- you have a tumor in the adrenal gland (pheochromocytoma)
- you have hormonal problems such as an overproduction of cortisol (Cushing's syndrome) or your thyroid hormones are too high (hyperthyroidism)
- you have ever had skin cancer or have any suspicious moles or marks on your skin that have not been checked by your doctor.
Do not use Duodopa solution for infusion in any of the above cases. If you are not sure, consult your doctor before using this medicine.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before starting treatment with Duodopa solution for infusion and during treatment if:
- you have ever had a heart attack, blood vessel obstruction, or any other heart disease, including irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia),
- you have a lung problem (such as asthma),
- you have ever had a hormonal disease,
- you have ever had depression with suicidal thoughts or any other mental illness,
- you have a eye disorder called "open-angle glaucoma",
- you have ever had a stomach ulcer,
- you have ever had seizures (convulsions),
- you have kidney or liver disease,
- you are on a controlled sodium diet (see "Duodopa solution for infusion contains sodium"),
- you experience any changes in the skin at the infusion site, such as redness, heat, swelling, pain, or color change when pressure is applied to the area,
- you have progressive weakness, pain, numbness, or loss of sensation in your fingers or toes (polyneuropathy). Your doctor will examine these signs and symptoms before you start treatment with Duodopa solution for infusion and periodically thereafter. Inform your doctor if you already have neuropathy or a health problem associated with neuropathy.
If you are in any of the above situations or if you are not sure, consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting treatment with Duodopa solution for infusion.
Tell your doctor if you notice involuntary and uncontrollable movements in your limbs, back, neck, or chin (dyskinesias) or an increase in stiffness or slowing of movements. It may be necessary to adjust the daily dose or the device may be blocked.
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
Do not stop using Duodopa solution for infusion unless your doctor tells you to. Stopping treatment or suddenly lowering the dose of Duodopa solution for infusion can cause a serious disorder called "neuroleptic malignant syndrome". The signs may include:
- rapid heartbeat, changes in blood pressure, and sweating, followed by fever,
- faster breathing, muscle stiffness, decreased consciousness, and coma,
- higher levels of a protein in the blood (an enzyme called "creatine phosphokinase"). Your doctor will measure this.
Impulse Control Disorders (changes in behavior)
Tell your doctor if you, your family, or caregiver notice that you develop impulses or cravings to behave in an unusual way for you, or you cannot resist the impulse, urge, or temptation to carry out certain activities that may be harmful to you or others. These behaviors are called "impulse control disorders" and include:
- gambling addiction,
- eating or spending excessively,
- abnormal increase in sexual desire or increase in sexual thoughts or feelings.
Your doctor may need to review your treatments. They will talk to you about methods to control or reduce these symptoms (see section 4 "Impulse Control Disorders - changes in behavior").
Dopamine Dysregulation Syndrome
Tell your doctor if you, your family, or caregiver notice that you develop symptoms similar to addiction, leading to a desire for high doses of Duodopa solution for infusion and other medicines used to treat Parkinson's disease.
Infections at the infusion site
Tell your doctor if you notice any changes in the skin at the infusion site, such as redness, heat, swelling, pain, or color change when pressure is applied to the area. You should always follow aseptic (sterile) techniques while using this medicine and change the infusion site regularly (at least every three days) using new infusion equipment. Make sure the new infusion site is at least 2.5 cm away from the site used in the last 12 days. You may need to change the infusion site more frequently than every 3 days if you notice any of the above changes.
Duodopa solution for infusion and cancer
In the body, foscarbidopa (a component of Duodopa solution for infusion) breaks down into a substance called "hydrazine". It is possible that hydrazine may cause damage to genetic material, which can cause cancer. However, it is not known if the amount of hydrazine produced with normal doses of Duodopa solution for infusion can cause this.
Children and adolescents
Duodopa solution for infusion is not recommended for children and adolescents under 18 years of age. This is because the medicine has not been studied in this age group.
Other medicines and Duodopa solution for infusion
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines. This includes those bought without a prescription and herbal medicines.
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting treatment with Duodopa solution for infusion if you are taking other medicines for:
- tuberculosis, such as isoniazid;
- anxiety, such as benzodiazepines;
- nausea or vomiting, such as metoclopramide;
- high blood pressure, such as antihypertensives;
- blood vessel spasms, such as papaverine;
- seizures or epilepsy, such as phenytoin;
- psychiatric disorders, such as antipsychotics, including phenothiazines, butyrophenones, and risperidone;
- Parkinson's disease, such as tolcapone, entacapone, opicapone, and amantadine;
- depression, such as tricyclic antidepressants, including amoxapine and trimipramine.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking a COMT inhibitor (catechol-O-methyltransferase), as it may increase the amount of levodopa in your blood. Your doctor may need to adjust the dose of these medicines.
Tell your doctor if you are taking medicines called sympathomimetic drugs, such as salbutamol, phenylephrine, isoproterenol, dobutamine to treat low blood pressure. Sympathomimetic drugs and levodopa may increase the risk of high blood pressure (hypertension) or irregular heartbeats (arrhythmia).
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking medicines that are eliminated by the action of an enzyme called 'CYP1A2'. For example:
- caffeine (helps to keep you alert)
- melatonin (helps to regulate sleep)
- fluvoxamine, duloxetine (antidepressants that improve mood)
- clozapine (to control schizophrenia)
- theophylline (helps with asthma)
Certain medicines (such as selegiline) that you may be taking may lower your blood pressure, which can make you feel dizzy when standing up from a chair or bed (orthostatic hypotension). Duodopa solution for infusion may worsen this feeling of dizziness. Moving slowly when getting up from a lying or sitting position can make you feel less dizzy.
Do not use Duodopa solution for infusion if you are taking
- medicines for depression called selective MAO-A inhibitors and non-selective MAO inhibitors, such as moclobemide or phenelzine.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before taking this medicine.
This medicine should not be used during pregnancy or in women of childbearing age unless the benefits to the mother outweigh the possible risks to the fetus.
It is not known if Duodopa solution for infusion is excreted in breast milk. Breastfeeding should be discontinued during treatment with Duodopa solution for infusion.
Driving and using machines
Do not drive or use tools or machines until you are sure how Duodopa solution for infusion affects you.
- Duodopa solution for infusion may make you feel very sleepy, or you may find yourself falling asleep suddenly (sudden sleep attacks).
- Duodopa solution for infusion may lower your blood pressure, which can make you feel dizzy or lightheaded.
Do not drive or use any tools or machines until you feel fully alert or no longer feel dizzy or lightheaded.
Duodopa solution for infusion contains sodium
Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you need 9 ml or more of Duodopa solution for infusion per day for a prolonged period, especially if you have been advised to follow a low-sodium diet.
3. How to use Duodopa solution for infusion
Follow the instructions for administration of this medicine exactly as indicated by your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist. If you are unsure, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
How to use Duodopa solution for infusion
- Before starting treatment, you or your caregiver will receive training on how to handle the product and the infusion pump.
- Duodopa solution for infusion is a solution that is administered under the skin (called "subcutaneous infusion"), most often in the abdomen, using an infusion pump. You should avoid using the infusion pump in a circular area of 5 cm around the navel.
- Your doctor or nurse will adjust the pump settings to adjust the dose to your needs.
- The pump will continuously administer the medicine to you over 24 hours. You may need to refill the pump with a new syringe within a 24-hour period to ensure that it administers enough medicine into your blood to control your symptoms.
How much medicine to use
- Follow the instructions for administration of this medicine exactly as indicated by your doctor.
- Your doctor will decide how much Duodopa solution for infusion you will receive and for how long. You will usually receive a continuous maintenance dose.
- If needed, you may receive extra doses (an option available on your pump) to treat sudden "OFF" symptoms that may appear during continuous infusion; this will be decided by your doctor.
- In case of interruptions of more than 3 hours, you should also self-administer a loading dose (an option available on your pump) before resuming continuous infusion to rapidly restore symptom control.
Consult section 7, "Instructions for use of Duodopa solution for infusion with the Vyafuser pump" before using Duodopa solution for infusion.
If you use more Duodopa solution for infusion than you should
If you have been administered a higher dose of Duodopa solution for infusion than you should, stop the infusion immediately and contact your doctor, call the Toxicology Information Service, phone 91 562 04 20, indicating the medicine and the amount administered, or go to a hospital immediately. Bring the medicine with you. The following effects may occur:
- unusual rapid, slow, or irregular heartbeats (arrhythmia).
- low blood pressure (hypotension).
If you forget to use or interrupt treatment with Duodopa solution for infusion
If you forget to use Duodopa solution for infusion, turn on your pump with your usual dose as soon as possible.
The administration of Duodopa solution for infusion may be interrupted for short periods of time, for example, when showering. Make sure to change the infusion equipment (tubes and cannula) and change to a different administration site if you interrupt the infusion for more than 1 hour. In case of interruptions of more than 3 hours, you should also self-administer a loading dose to rapidly restore symptom control. The loading dose option is available on your pump as set by your doctor or nurse.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine may cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
Stop using Duodopa solution for infusion and inform your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following serious adverse effects. You may need urgent medical treatment:
- narrow-angle glaucoma (acute pain in the eyes, headache, blurred vision, nausea, and vomiting),
- swelling of the face, tongue, or throat that may make it difficult to swallow or breathe, or a skin rash like hives. These may be signs of a severe allergic reaction (anaphylactic reaction). Frequency not known. Cannot be estimated from available data.
Your doctor will decide if you can continue using Duodopa solution for infusion.
Other Adverse Effects
Tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse if you notice any of the following adverse effects.
Very Common:may affect more than 1 in 10 patients
- infection at the infusion site (cellulitis at the infusion site) (see section 2),
- anxiety,
- seeing, hearing, or perceiving things that do not exist (hallucinations),
- depression,
- reactions at the infusion site (redness, swelling, and pain),
- falls,
- urinary tract infections.
Common:may affect up to 1 in 10 patients
- reactions at the infusion site (hematoma, skin peeling, drug leakage, bleeding, inflammation, irritation, swelling, lump, itching, rash),
- abscesses at the infusion site,
- loss of appetite,
- confusion,
- delusions,
- paranoia,
- thoughts of self-harm (suicidal thoughts),
- problems with thinking, learning, and memory (cognitive disorder),
- involuntary movements (dyskinesia),
- uncontrolled muscle spasms that affect the eyes, head, neck, or body (dystonia)
- headache,
- reduced sense of touch, tingling, or numbness, burning or prickling sensation in the hands, arms, legs, or feet (hypoesthesia, paresthesia),
- progressive weakness or pain or numbness or loss of sensation in the fingers or toes (polyneuropathy),
- sudden appearance or worsening of Parkinson's disease symptoms, this is called "ON/OFF phenomenon",
- sudden sleepiness, excessive drowsiness, sleep disorders,
- high or low blood pressure,
- feeling of dizziness,
- dizziness when standing up or changing posture (orthostatic hypotension) due to a drop in blood pressure. Always change posture slowly, do not stand up quickly,
- fainting,
- abdominal pain,
- constipation,
- dry mouth,
- nausea, diarrhea, or vomiting,
- inability to control urine (incontinence),
- difficulty urinating (urinary retention),
- lack of energy, feeling of weakness (fatigue),
- swelling of the ankles and hands due to excess fluid (peripheral edema)
- psychotic disorder,
- very low levels of vitamin B6 in the body,
- very low levels of vitamin B12 in the body,
- increase in the number of amino acids, small molecules that form the body's proteins,
- increase in the amount of homocysteine in the blood, which contributes to the formation of proteins in the body,
- sore throat,
- weight gain,
- weight loss,
- difficulty sleeping (insomnia),
- rash, itching, increased sweating,
- muscle spasms,
- difficulty breathing,
- feeling of general discomfort,
- anemia,
- abnormal dreams,
- agitation,
- having a swollen stomach (abdominal distension), gas (flatulence), indigestion (dyspepsia)
- having pain,
- having neck pain,
- difficulty swallowing or change in taste (bitter taste),
- irregular heartbeats.
Impulse Control Disorders (changes in behavior)These are common, may affect 1 in 10 patients.
Some people are unable to resist the impulse to perform an action that could be harmful to themselves or others. This may include
- a strong impulse to gamble excessively despite serious personal or family consequences,
- altered or increased interest and sexual behavior with great concern for you or others. This could include an increased sexual impulse,
- uncontrolled or excessive shopping or spending,
- eating excessively (eating large amounts of food in a short period) or compulsive eating (eating more food than normal and more than necessary to satisfy hunger).
Tell your doctor if you, your family, or caregiver notice any of these behaviors. Your doctor may need to review your treatment. They will discuss with you methods to control or reduce these symptoms.
Uncommon:may affect up to 1 in 100 patients
- desire for large doses of Duodopa solution for infusion beyond those required to control motor symptoms, known as dopamine dysregulation syndrome,
- dark urine,
- hoarse voice, chest pain,
- hair loss, red skin, hives,
- excessive salivation,
- change in gait,
- attempting to end or ending one's own life, suicide,
- low white blood cell count or changes in blood cell counts, which may cause bleeding,
- elevated mood (euphoric mood), increased sexual interest, dementia, feeling of fear,
- problems controlling movements and making sudden uncontrolled movements
- problems opening the eyes, double vision, blurred vision, damage to the optic nerve (ischemic optic neuropathy),
- irregular heartbeats that you can feel (palpitations),
- confusion,
- nightmares,
- swelling of a vein.
Rare:may affect up to 1 in 1,000 patients
- grinding of teeth
- painful erection that does not disappear,
- suspicious marks or spots on the skin that appear or worsen, or skin tumors (malignant melanoma),
- dark saliva or sweat, burning sensation on the tongue, hiccups,
- unusual thoughts,
- abnormal breathing.
Reporting Adverse Effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is an adverse effect that is not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting adverse effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Duodopa Solution for Infusion
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Store the vials in the outer packaging to prevent them from breaking.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date that appears on the label of the vial and on the packaging. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
- Do not freeze.
- Store and transport refrigerated (between 2°C and 8°C).
- The vials can be stored at room temperature, up to a maximum of 30°C, for a single period of up to 28 days.
- The packaging includes a space to record the day the medicine was removed from the refrigerator.
- After storing the medicine at room temperature, do not return it to the refrigerator.
- Discard the medicine if it is not used during the 28-day period at room temperature.
- Transfer the entire contents of the vial to the syringe at once for administration.
- Do not reuse an opened vial; vials are for single use.
- Once opened: use immediately. Use Duodopa solution for infusion within 24 hours once transferred from the vial to the syringe.
- Medicines should not be thrown away through wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of packaging and medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
- Discard the vial after transferring the medicine to the syringe.
- Discard the syringe and any unused medicine that remains in the syringe after the medicine has been in the syringe for 24 hours.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Duodopa Solution for Infusion
- The active ingredients are foslevodopa and foscarbidopa. 1 ml contains 240 mg of foslevodopa and 12 mg of foscarbidopa.
- 1 vial of 10 ml contains 2,400 mg of foslevodopa and 120 mg of foscarbidopa.
- The other components are sodium hydroxide 10 N (for pH adjustment), concentrated hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment), and water for injectable preparations.
Appearance of the Product and Container Contents
Duodopa solution for infusion is a clear to slightly opalescent solution, free of particles, provided in a clear, colorless glass vial with a gray rubber stopper and a turquoise plastic cap. The color of the solution may vary from colorless to yellow or brown and may have a purple or red tint. Color variations are expected and do not affect the quality of the medication. The solution may darken after the vial stopper is pierced or while it is in the syringe.
Each container contains 7 vials of 10 ml each.
The sterile, single-use infusion components (syringe, infusion set, and vial adapter) suitable for use are provided separately; consult your doctor or pharmacist. The Vyafuser pump is supplied separately.
Marketing Authorization Holder
AbbVie Spain, S.L.U.
Avenida de Burgos 91,
28050 Madrid, Spain
Manufacturers
AbbVie S.r.I
S.R. 148 Pontina Km 52 snc
04011 Campoverde di Aprilia (LT)
Italy
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet: December 2023
Other Sources of Information
Detailed information on this medication is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) (http://www.aemps.gob.es/)
- Instructions for Use of Duodopa Solution for Infusion with the Vyafuser Pump
Read the entire following section before using Duodopa solution for infusion.
Important Information
Read the following instructions carefully: these instructions explain how to prepare and use Duodopa solution for infusion.
- Duodopa solution for infusion is administered by subcutaneous infusion with the help of the Vyafuser pump and its infusion components (syringe, infusion set, and vial adapter).
- You can obtain the infusion components separately by consulting your doctor or pharmacist.
- You must also read the complete instructions carefully before using Duodopa solution for infusion.
- Instructions for use of the vial adapter
- Instructions for use of the infusion set
- Instructions for use of the Vyafuser pump for patients.
- Your doctor or nurse will configure the pump for you so that you always receive the correct dose.
- Your doctor or nurse will tell you how to administer the medication and how to handle the pump before starting treatment.
- If in doubt, consult your doctor or nurse.
How to Prepare Your Medication
- Do not dilute the Duodopa solution for infusion or fill the syringe with any other solution.
- The medication must be at room temperature before infusion. If it is refrigerated before use, remove the vial from the refrigerator and let it stand at room temperature, away from direct sunlight, for 30 minutes. If the medication is refrigerated, do not heat it (either in the vial or in the syringe) in any way other than letting it stand at room temperature. For example, do not heat it in the microwave or in hot water.
- Preparation
Follow these steps each time you need to refill your pump with Duodopa solution for infusion.
- Wash your hands with water and soap and dry them.
- Make sure the smooth surface is clean. This will help prevent contamination when preparing the syringe.
- On a smooth surface, place
- Syringe (inside its container)
- Vial of Duodopa solution for infusion
- Vial adapter (in its container). A new vial adapter must be used with each new vial of Duodopa solution for infusion.
- Alcohol wipes (not provided with the medication)
- Check the expiration date of the vial, the vial adapter, and the syringe, and that the containers are not damaged.
- Do notuse the vial, the vial adapter, or the syringe if their respective sterile containers are damaged.
- Do notuse the Duodopa solution for infusion, the vial adapter, or the syringe if the expiration date has passed.
- Do notuse it if the Duodopa solution for infusion is cloudy or contains flakes or particles.
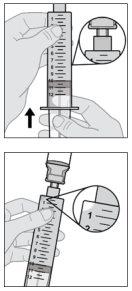
- Prepare the vial of solution
|
|
|
Your vial adapter may be different from the one shown in this section.
To obtain detailed information, consult the instructions for use of the vial adapter. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
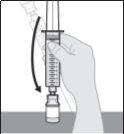
Do not shake or tap the syringe to remove air bubbles.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Prepare the subcutaneous infusion of Duodopa solution for infusion
|
|
|
- Choose and prepare the infusion site
For more information, consult the infusion set instructionsand the instructions for use of the Vyafuser pump for patients. |
|
- Start the subcutaneous infusion of Duodopa solution for infusion
| ||||||||||||
|
- After use
- Used solution vials with the vial adapter still connected must be discarded according to local regulations or as indicated by your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to DUODOPA 240 mg/mL + 12 mg/mL SOLUTION FOR INFUSIONDosage form: TABLET, 10 mg/100 mgActive substance: levodopa and decarboxylase inhibitorManufacturer: Fairmed Healthcare GmbhPrescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 12.5 mg/50 mgActive substance: levodopa and decarboxylase inhibitorManufacturer: Fairmed Healthcare GmbhPrescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 25 mg/100 mgActive substance: levodopa and decarboxylase inhibitorManufacturer: Fairmed Healthcare GmbhPrescription required
Online doctors for DUODOPA 240 mg/mL + 12 mg/mL SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
Discuss questions about DUODOPA 240 mg/mL + 12 mg/mL SOLUTION FOR INFUSION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions





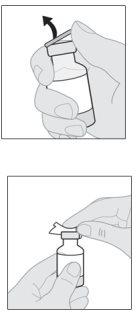
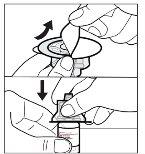
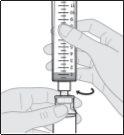
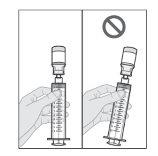
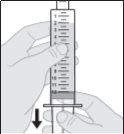
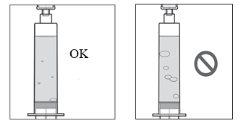
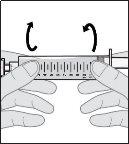
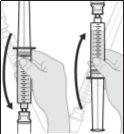
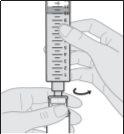
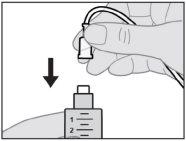 Connect the infusion set to the new syringe.
Connect the infusion set to the new syringe.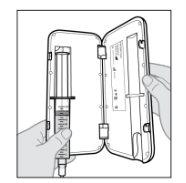
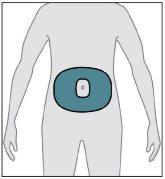 From the area shown (on the abdomen), choose a site at least 5 cm away from the navel.
From the area shown (on the abdomen), choose a site at least 5 cm away from the navel.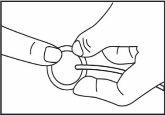 to the body and the infusion set to the cannula.
to the body and the infusion set to the cannula.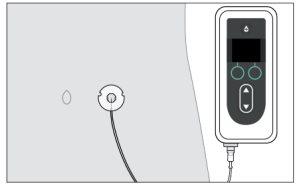 Start the pump. For more information, consult the instructions for use of the Vyafuser pump.
Start the pump. For more information, consult the instructions for use of the Vyafuser pump.


