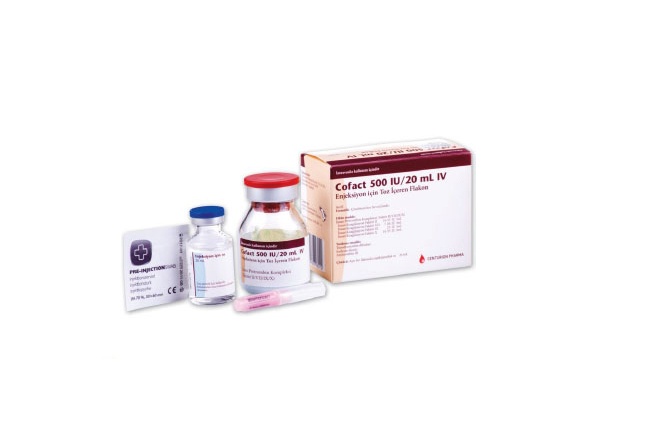
COFACT 500 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION

How to use COFACT 500 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Cofact 500UI powder and solvent for solution for injection.
Human prothrombin complex
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the package leaflet
- What is Cofact and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Cofact
- How to use Cofact
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Cofact
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Cofact and what is it used for
Cofact contains as active substances, factors II, VII, IX, and X, which are blood coagulation factors of human blood.
These factors are natural components of human blood and are commonly referred to as prothrombin complex. They are dependent on vitamin K. If there is a deficiency of one or more of these factors, blood coagulation disorders may occur. As a result, there is a greater tendency to bleed. The administration of Cofact helps to supplement this deficiency, by combating or preventing hemorrhages.
Cofact can be used for:
Treatment or prevention of bleeding, due to
- acquired deficiency of the coagulation factors of the prothrombin complex. For example, in the case of deficiency caused by treatment with vitamin K antagonists or in the case of overdose of vitamin K antagonists, when rapid correction of this deficiency is required.
- congenital deficiencies of one of the vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors, when purified specific coagulation factor products are not available.
2. What you need to know before you use Cofact
Do not use Cofact
- if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to any of the active substances or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor specializing in coagulation disorders before receiving this medicine.
- If you have an acquired deficiency of the vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors (e.g., caused by treatment with vitamin K antagonist medications), Cofact should only be used when rapid correction of prothrombin complex levels is necessary, such as in the case of severe bleeding or emergency surgery. In other cases, it is usually sufficient to reduce the dose of the vitamin K antagonist medication and/or administer vitamin K.
- If you are receiving a vitamin K antagonist medication, you may have a higher risk of clot formation. In this case, treatment with Cofact may potentiate this risk.
- If you are born with a deficiency of one of the vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors (congenital deficiency), specific products for the coagulation factor should be used when available.
- If an allergic reaction or anaphylactic-type reaction occurs, the infusion with Cofact should be discontinued immediately.
There is a risk of thrombosis or disseminated intravascular coagulation (i.e., formation of blood clots in blood vessels) when receiving this medicine, especially when receiving it repeatedly.
- Your doctor will check if the administration of this medicine represents a risk of thrombosis (see section 4). The following people have a higher probability of suffering a thrombosis:
- people who have suffered a myocardial infarction or who have had (or still have) other heart artery diseases
- people with liver diseases
- newborns (neonates)
- people who are about to undergo surgery or who have recently undergone surgery
- people with a higher probability of suffering coagulation complications (e.g., history of thromboembolic events or disseminated intravascular coagulation)
Your doctor will carefully consider the benefit of treatment with this medicine compared to the risk of these complications.
Viral safety
When medicines are prepared from human blood or plasma, certain measures are taken to prevent the transmission of infections to patients. These measures include:
- careful selection of blood and plasma donors to ensure that people at risk of being carriers of infections are excluded,
- testing of each donation and of plasma pools for the presence of signs of viruses/infections,
- inclusion of stages in the processing of blood or plasma that can inactivate or eliminate viruses.
Despite these measures, when medicines prepared from human blood or plasma are administered, the possibility of transmission of infections cannot be totally excluded. This also applies to any emerging or unknown virus and to other types of infections.
The measures taken are considered effective against enveloped viruses such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), and hepatitis C virus (HCV), and against the non-enveloped hepatitis A virus (HAV). The measures taken may have limited value against other non-enveloped viruses such as parvovirus B19. Parvovirus B19 infection can be severe in pregnant women (fetal infection) and in people whose immune system is depressed or who have some type of anemia (e.g., sickle cell disease or hemolytic anemia).
It is strongly recommended that each time you are administered a dose of this medicine, the name and batch number of the product be recorded, in order to have a record of the batches used.
Children and adolescents
No data are available on the use of this medicine in children or adolescents.
Other medicines and Cofact
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines, including those obtained without a prescription.
No information is available on the possible interactions between Cofact and other medicines, except for anticoagulants.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, your doctor will only administer Cofact if it is clearly indicated.
Driving and using machines
No studies have been performed on the effects on the ability to drive or use machines.
Cofact contains sodium
Cofact contains up to 448 mg of sodium (a major component of cooking salt) per 100 ml. This is equivalent to up to 22% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium for an adult. Take this into account if you are on a controlled sodium diet.
3. How to use Cofact
Your treatment should be initiated, administered, and monitored by a doctor with experience in the treatment of coagulation disorders. Your doctor will determine the amount of Cofact you need for the treatment or prevention of hemorrhages due to the use of anticoagulants or in the case of congenital deficiency of one of the vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors.
The exact dose depends on:
- the severity of your disease
- your weight
- the coagulation factors you need
- the amount of these factors in your blood (your blood level).
In the case of congenital deficiency of the coagulation factors, it is important to periodically determine the blood levels of the coagulation factors.
Information for healthcare professionals can be found at the end of the package leaflet.
If you use more Cofact than you should
Your doctor should regularly check the state of your clots during treatment. High doses of prothrombin complex concentrate have been associated with cases of myocardial infarction, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and increased clot formation in a blood vessel in patients at risk of suffering these complications.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following side effects have been observed:
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- there is a risk of blood clot formation (see section 2)
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- there is a risk of decreased blood pressure
The frequency of the following side effects is unknown(the frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- Allergic or hypersensitivity reactions (see section 2)
- Heart attack
- Nausea, vomiting
- Redness at the infusion site, irritation at the infusion site, swelling at the infusion site, discomfort
- Temporary increase in liver test results
- Stroke, dizziness
- Pulmonary embolism, difficulty breathing
- Excessive sweating, itching of the skin, hives, rash
Patients with a deficiency of one of the coagulation factors II, VII, IX, or X may develop antibodies against these factors as a result of using Cofact. In this case, the activity of the product will not be optimal.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are not listed in this package leaflet. You can also report side effects directly to the Spanish Medicines Agency: https://www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Cofact
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and on the label of the vial after EXP. The expiry date is the last day of the month stated.
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C). Do not freeze. Keep the vial in the outer packaging to protect it from light.
Cofact can be stored at or below 25°C for up to six months. The date on which the medicine has reached room temperature should be noted on the packaging. If it is not used within six months of storage at room temperature, the product should be discarded.
Once the product has been removed from the refrigerator, it must not be put back.
The stability of the reconstituted product has been demonstrated for up to 3 hours at 15°C - 25°C. However, to prevent contamination, the reconstituted product should be used immediately.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
Composition of Cofact
- The active substances are coagulation factors II, VII, IX, and X, and other active substances are proteins C and S.
- One vial of Cofact 500 UI contains 500 UI of factor IX; 280-700 UI of factor II; 140-400 UI of factor VII; and 280-700 UI of factor X; 222-780 UI of protein C; 20-160 UI of protein S.
After dissolution in the water for injections supplied, the solution for injection ready for use contains:
- not less than 14 UI and not more than 35 UI of factor II per ml;
- not less than 7 UI and not more than 20 UI of factor VII per ml;
- 25 UI of factor IX per ml;
- not less than 14 UI and not more than 35 UI of factor X per ml;
- not less than 11 UI and not more than 39 UI of protein C per ml;
- not less than 1 UI and not more than 8 UI of protein S per ml.
The other ingredients are sodium citrate, sodium chloride, and antithrombin.
Appearance and packaging of the product
Cofact is supplied as a powder and solvent for solution for injection.
Cofact powder for injection is a blue-colored powder. The solvent is a clear, colorless liquid without visible particles. The reconstituted solution ready for injection is a blue-colored solution.
Contents of the 500 UI pack
1 vial of 500 UI powder
1 vial of 20 ml water for injections
1 nextaro v transfer device
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Prothya Biosolutions Netherlands B.V.
Plesmanlaan 125
NL-1066 CX Amsterdam
Netherlands
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Austria, Belgium, Finland, France, Germany, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, and Spain: Cofact.
Sweden: Thyaplex
Date of last revision of this leaflet: August 2024
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended exclusively for healthcare professionals:
Qualitative and Quantitative Composition
Cofact is presented as a powder and solvent for solution for injection containing human prothrombin complex. The product nominally contains the following IU of human coagulation factors:
Cofact 500 IU | After reconstitution*(IU/ml) | ||
Active substances | |||
Coagulation Factor II | 280 – 700 | 14 – 35 | |
Coagulation Factor VII | 140 – 400 | 7 – 20 | |
Coagulation Factor IX | 500 | 25 | |
Coagulation Factor X | 280 – 700 | 14 – 35 | |
Other active substances | |||
Protein C | 222 – 780 | 11 – 39 | |
Protein S | 20 – 160 | 1 – 8 | |
*After reconstitution with 20ml of water for injections.
The total protein content per vial of 500 IU is 260 – 700 mg. The specific activity of the product is ≥ 0.6 IU/mg, expressed as Factor IX activity.
The activity of all coagulation factors, as well as proteins C and S (antigens), has been determined according to current WHO or European Pharmacopoeia standards.
After reconstitution, this medicinal product contains 125 – 195 mmol of sodium/l, up to 89.6 mg of sodium per vial of 500 IU.
Posology and Method of Administration
Posology
Only general dosage guidelines are provided below. Treatment should be initiated under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of coagulation disorders. The dose and duration of replacement therapy depend on the severity of the disorder, the location and intensity of bleeding, and the patient's clinical condition.
The dosage and frequency of administration must be individualized for each patient. Dosage intervals should be adapted to the different circulating half-lives of the various coagulation factors in the prothrombin complex. Individual dosage requirements can only be calculated based on periodic determination of individual plasma levels of the relevant coagulation factors or global analysis of prothrombin complex levels (prothrombin time, INR) and continuous monitoring of the patient's clinical condition.
In the case of major surgical interventions, precise monitoring of replacement therapy is essential, using coagulation analysis (specific coagulation factor assays and/or global prothrombin complex level analysis).
Bleeding and Perioperative Prophylaxis of Bleeding during Treatment with Vitamin K Antagonists:
The dose will depend on the INR before treatment, the desired INR, and body weight. The following tables provide approximate doses required to normalize INR to different initial INR levels.
The dosage tables only represent general dosage guidelines, which cannot replace individual dose assessment for each patient and strict control of INR and other coagulation parameters during treatment.
Recommended Doses of Cofact in ml to Achieve a Desired INR ≤ 2.1
Initial INR Body Weight | 7.5 | 5.9 | 4.8 | 4.2 | 3.6 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 2.8 | 2.6 | 2.5 | 2.3 | 2.2 |
50kg | 40 | 40 | 40 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 20 | 20 | X | X | X | X |
60kg | 50 | 50 | 40 | 40 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 20 | X | X | X | X |
70kg | 60 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 40 | 40 | 30 | 30 | X | X | X | X |
80kg | 60 | 60 | 60 | 50 | 50 | 40 | 40 | 30 | X | X | X | X |
90kg | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 50 | 50 | 40 | 30 | X | X | X | X |
100kg | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 50 | 40 | 40 | X | X | X | X |
Recommended Doses of Cofact in ml to Achieve a Desired INR ≤ 1.5
Initial INR Body Weight | 7.5 | 5.9 | 4.8 | 4.2 | 3.6 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 2.8 | 2.6 | 2.5 | 2.3 | 2.2 |
50kg | 60 | 60 | 60 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 40 | 40 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
60kg | 80 | 70 | 70 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 50 | 50 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 30 |
70kg | 90 | 80 | 80 | 70 | 70 | 70 | 60 | 60 | 50 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
80kg | 100 | 100 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 80 | 80 | 70 | 60 | 50 | 50 | 40 |
90kg | 100 | 100 | 100 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 80 | 80 | 70 | 60 | 50 | 40 |
100kg | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 90 | 90 | 80 | 70 | 70 | 60 | 50 |
The doses are calculated based on the Factor IX concentration in Cofact, due to its relatively short half-life and low yield after infusion compared to the other coagulation factors in Cofact. It is assumed that a mean plasma Factor IX concentration of ≥ 30% is sufficient to achieve an INR of ≤ 2.1 and ≥ 60% to achieve an INR of ≤ 1.5. The calculated amounts are rounded to multiples of 10 ml and an upper limit of 60 or 100 ml in total (see tables above). The desired INR values are recommended by the Dutch Federation of Thrombosis Services and are of the same order as the English and German recommendations.
The correction of the hemostasis disorder induced by vitamin K antagonists persists for about 6-8 hours. However, the effects of vitamin K, if administered at the same time, are usually achieved within 4-6 hours. Therefore, it is normally not necessary to repeat treatment with human prothrombin complex when vitamin K has been administered.
Since these recommendations are empirical and recovery and duration of effect may vary, monitoring of INR during treatment is mandatory.
Bleeding and Perioperative Prophylaxis of Bleeding due to Congenital Deficiency of any Vitamin K-Dependent Coagulation Factor, when the Specific Coagulation Factor Product is not Available:
The calculation of the required dose for treatment is based on the empirical data that approximately 1 IU of Factor VII or Factor IX per kg body weight increases the plasma activity of Factor VII or IX, respectively, by 0.01 IU/ml; and 1 IU of Factor II or X per kg body weight increases the plasma activity of Factor II or X by 0.02 and 0.017 IU/ml, respectively.
The dose of a specific factor administered is expressed in International Units (IU), which are related to the current WHO standard for each factor. The plasma activity of a specific coagulation factor is expressed either as a percentage (relative to normal plasma) or in International Units (relative to the international standard for the specific coagulation factor).
One International Unit (IU) of coagulation factor activity is equivalent to the amount contained in 1 ml of normal human plasma.
For example, the calculation of the required dose of Factor X is based on the empirical data that 1 International Unit (IU) of Factor X per kg body weight increases the plasma activity of Factor X by 0.017 IU/ml. The required dose is determined using the following formula:
Required Units = body weight (kg) x desired increase in Factor X (IU/ml) x 60
Where 60 (ml/kg) is the reciprocal value of the estimated recovery.
If the individual recovery is known, this value should be used for the calculation.
Pediatric Population
The safety and efficacy of Cofact in pediatric patients have not been established.
Method of Administration
For instructions on reconstitution of the medicinal product before administration, see section 6.6. "Special Precautions for Disposal and Other Handling". Cofact should be administered intravenously.
It is recommended to administer the reconstituted product at a rate of approximately 2 ml per minute.
Incompatibilities
This medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal products.
Cofact is compatible with polypropylene material. Treatment may fail due to adsorption of the coagulation factor to the inner surface of other injection/infusion equipment.
Shelf Life
3 years.
After reconstitution, physicochemical stability has been demonstrated for 3 hours at 15 – 25°C. From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately after reconstitution. If not used immediately, the in-use storage times and conditions are the responsibility of the user.
Special Precautions for Disposal and Other Handling
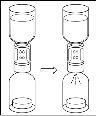
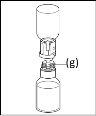
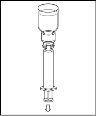
General instructions for use of a nextaro transfer devicev
- The dried protein fraction must be dissolved with 20 ml of water for injectable preparations. If the closed vials of powder and solvent (water for injectable preparations) are stored at 2°C - 8°C, it is necessary to allow them to reach room temperature (15°C - 25°C) before dissolving the preparation. This temperature should be maintained during reconstitution. If a water bath is used for heating, care should be taken to avoid getting water in contact with the rubber stoppers or flip-off caps of the vial. The temperature of the water bath should not exceed 37°C.
- During the procedure described below, an aseptic technique should be applied. Before opening the package of the transfer device, make sure to remove the flip-off caps from the vials of powder and solvent, and disinfect the neck edge and rubber stoppers with an antiseptic solution and let them dry. Do not touch the rubber stoppers of the solvent vial or the powder vial.
- As a result of the vacuum in the powder vial, the solvent is automatically transferred to the powder vial.
- As a general rule, the powder should be completely dissolved within 10 minutes to form a blue-colored solution. The solution should be transparent or slightly opalescent. Do not use cloudy solutions or those with deposits. The solution should be visually inspected for particles and discoloration before administration.
- Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations.
- Procedure for using a nextaro transfer devicev
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
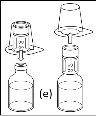
Note: The transfer device should be attached first to the solvent vial and then to the powder vial. Otherwise, a loss of vacuum will occur and the transfer of the solvent will not be possible. |
|
Wait until the solvent has been completely transferred. Continue holding the complete unit formed by the solvent vial, the transfer device, and the powder vial, and make sure it remains on a flat surface throughout the transfer process. Once the solvent has been transferred, with both vials still connected, gently shake the powder vial until the product is completely dissolved. To avoid foam formation, do not shake the vial. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to COFACT 500 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 1000 IU/vialActive substance: coagulation factor IX, II, VII and X in combinationManufacturer: Csl Behring GmbhPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 500 IUActive substance: coagulation factor IX, II, VII and X in combinationManufacturer: Csl Behring GmbhPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 250 IUActive substance: coagulation factor IX, II, VII and X in combinationManufacturer: Prothya Biosolutions Netherlands B.V.Prescription required
Online doctors for COFACT 500 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Discuss questions about COFACT 500 IU POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions