BENEPALI 25 mg SOLUTION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE

How to use BENEPALI 25 mg SOLUTION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Benepali 25 mg solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
etanercept
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- Your doctor will also give you a Patient Alert Card, which contains important safety information that you need to know before and during treatment with Benepali.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is Benepali and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Benepali
- How to use Benepali
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Benepali
- Contents of the pack and other information
- Instructions for use (see back)
1. What is Benepali and what is it used for
Benepali contains the active substance etanercept.
Benepali is a medicine that is made from two human proteins. It blocks the action of another protein, which is found in the body, that causes inflammation. Benepali works by reducing inflammation associated with certain diseases.
Benepali can be used in adults aged 18 years and older to:
- treat moderate or severe rheumatoid arthritis;
- psoriatic arthritis;
- severe axial spondyloarthritis, including ankylosing spondylitis;
- moderate or severe plaque psoriasis.
Benepali is usually used when other treatments have not been effective enough or are not suitable for you.
In the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, Benepali is normally used in combination with methotrexate, although it can also be used as a single medicine if treatment with methotrexate is not suitable for you. Benepali can slow down the damage caused by rheumatoid arthritis to your joints and improve your ability to perform daily activities, whether used alone or in combination with methotrexate.
In patients with psoriatic arthritis with multiple joint involvement, Benepali can improve your ability to perform normal daily activities.
In patients with multiple symmetric joints that are swollen or painful (e.g. in hands, wrists, and feet), Benepali can delay the progression of structural damage to these joints caused by the disease.
Benepali is also indicated for the treatment of children and adolescents with the following diseases:
- For the following types of juvenile idiopathic arthritis when treatment with methotrexate has not worked adequately, or is not suitable for them:
- Polyarthritis (with positive or negative rheumatoid factor) and extended oligoarthritis in patients aged 2 years and older and weighing 62.5 kg or more.
- Psoriatic arthritis in patients aged 12 years and older and weighing 62.5 kg or more.
- For enthesitis-related arthritis in patients aged 12 years and older and weighing 62.5 kg or more, for whom the use of other commonly used treatments has not worked adequately, or is not suitable for them.
- Severe plaque psoriasis in patients aged 6 years and older and weighing 62.5 kg or more who have had an inadequate response to (or are unable to take) phototherapies or other systemic therapies.
2. What you need to know before you use Benepali
Do not use Benepali
- if you or the child in your care are allergic to etanercept or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6). If you or the child experience allergic reactions, such as chest tightness, wheezing, dizziness, or rash, do not inject more Benepali and contact your doctor immediately.
- if you or the child are at risk of developing a severe blood infection called sepsis. If you are not sure, consult your doctor.
- if you or the child have any type of infection. If you are not sure, consult your doctor.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor before starting treatment with Benepali.
- Allergic reactions:If you or the child experience allergic reactions, such as chest tightness, wheezing, dizziness, or rash, do not inject more Benepali and contact your doctor immediately.
- Infections/surgery:If you or the child develop a new infection or are about to undergo major surgery, your doctor may want to monitor your treatment with Benepali.
- Infections/diabetes:Inform your doctor if you or the child have a history of recurrent infections or have diabetes or other disorders that increase the risk of infection.
- Infections/monitoring:Inform your doctor of any recent travel outside the European region. If you or the child develop symptoms of an infection such as fever, chills, or cough, notify your doctor immediately. Your doctor will decide whether to continue monitoring you or the child for the presence of infections after you or the child stop treatment with Benepali.
- Tuberculosis:Since cases of tuberculosis have been reported in patients treated with Benepali, your doctor will examine the signs and symptoms of tuberculosis before starting Benepali. This may include a thorough medical history, chest X-ray, and a tuberculosis test. The performance of these tests should be recorded on the Patient Alert Card. It is very important that you tell your doctor if you or the child have had tuberculosis, or if you or the child have been in close contact with someone who has had tuberculosis. If symptoms of tuberculosis (such as persistent cough, weight loss, apathy, moderate fever) or any other infection appear during or after treatment, inform your doctor immediately.
- Hepatitis B:Inform your doctor if you or the child have or have had hepatitis B. Your doctor will perform a hepatitis B test before you or the child start treatment with Benepali. Treatment with Benepali may reactivate hepatitis B in patients who have previously been infected with the hepatitis B virus. If this occurs, you or the child must stop using Benepali.
- Hepatitis C:Inform your doctor if you or the child have hepatitis C. Your doctor may want to monitor treatment with Benepali in case the infection worsens.
- Blood disorders:Inform your doctor immediately if you or the child have signs or symptoms such as persistent fever, sore throat, bruising, bleeding, or paleness. These symptoms may indicate a serious blood problem that requires discontinuation of treatment with Benepali.
- Nervous system and vision disorders:Inform your doctor if you or the child have multiple sclerosis, optic neuritis (inflammation of the optic nerves), or transverse myelitis (inflammation of the spinal cord). Your doctor will decide whether Benepali is a suitable treatment.
- Congestive heart failure:Inform your doctor if you or the child have a history of congestive heart failure, because Benepali needs to be used with caution in these circumstances.
- Cancer:Inform your doctor if you have or have had lymphoma (a type of blood cancer) or any other cancer before you are given Benepali. Patients with severe rheumatoid arthritis who have had the disease for a long time may be at a higher than average risk of developing lymphoma. Children and adults taking Benepali may have an increased risk of developing lymphoma or other cancers. Some adolescent and child patients who have received etanercept or other medicines that work in the same way as etanercept have developed cancers, including unusual types, which sometimes had a fatal outcome. Some patients taking Benepali have developed skin cancers. Inform your doctor if you or the child develop any changes in the appearance of the skin or growths on the skin.
- Chickenpox:Inform your doctor if you or the child are exposed to chickenpox while using Benepali. Your doctor will determine whether preventive treatment for chickenpox is appropriate.
- Alcoholism: Benepali should not be used to treat hepatitis related to alcoholism. Please inform your doctor if you or the child in your care have a history of alcoholism.
- Wegener's granulomatosis:Benepali is not recommended for the treatment of Wegener's granulomatosis, a rare inflammatory disease. If you or the child in your care have Wegener's granulomatosis, discuss this with your doctor.
- Anti-diabetic medicines:Inform your doctor if you or the child have diabetes or are taking medicines to treat diabetes. Your doctor may decide whether you or the child need less anti-diabetic medicine while taking Benepali.
- Vaccines:Some vaccines, such as oral polio vaccine, should not be given while using Benepali. Consult your doctor before you or the child receive any vaccine.
Children and adolescents
The use of Benepali is not indicated in children and adolescents with a body weight below 62.5 kg.
- Vaccinations:If possible, children should have all vaccinations up to date before using Benepali. Some vaccines, such as oral polio vaccine, should not be given while using Benepali. Consult your doctor before you or the child receive any vaccine.
Benepali should not normally be used in children under 2 years of age or with a body weight below 62.5 kg with polyarthritis or extended oligoarthritis, in children under 12 years of age or with a body weight below 62.5 kg with enthesitis-related arthritis or psoriatic arthritis, or in children under 6 years of age or with a body weight below 62.5 kg with plaque psoriasis.
Using Benepali with other medicines
Inform your doctor or pharmacist if you or the child are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines (including anakinra, abatacept, or sulfasalazine).
Do not useBenepali with medicines that contain the active substance anakinra or abatacept.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
Women of childbearing potential should be advised to use adequate contraception during treatment with Benepali and for 3 weeks after stopping treatment to prevent pregnancy.
Benepali should only be used during pregnancy if clearly necessary.
If you have received Benepali during pregnancy, your baby may have a higher risk of getting an infection. Additionally, in one study, more birth defects were observed when the mother had received etanercept during pregnancy, compared to mothers who had not received etanercept or other similar medicines (TNF antagonists), but there was no pattern in the types of birth defects reported. Another study did not find an increased risk of congenital malformations when the mother had received etanercept during pregnancy. Your doctor will help you decide whether the benefits of treatment outweigh the potential risk to your baby. If you want to breastfeed while being treated with Benepali, ask your doctor. It is important that you inform the pediatrician and other healthcare professionals about the use of Benepali during pregnancy and breastfeeding before your baby receives any vaccine.
Driving and using machines
There is no information to suggest that the use of Benepali affects the ability to drive and use machines.
Benepali contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per 25 mg; this is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to use Benepali
Follow exactly the instructions for administration of this medicine given by your doctor. If you are not sure, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
If you think that the action of Benepali is too strong or too weak, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Use in adult patients (aged 18 years and older)
Rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and axial spondyloarthritis, including ankylosing spondylitis
The usual dose is 25 mg administered twice a week or 50 mg once a week, given as an injection under the skin.
However, your doctor may decide on an alternative frequency for injecting Benepali.
Plaque psoriasis
The usual dose is 25 mg twice a week or 50 mg once a week.
Alternatively, 50 mg may be administered twice a week for up to 12 weeks, followed by 25 mg twice a week or 50 mg once a week.
Your doctor will decide how long you should use Benepali and whether you need to repeat treatment based on your response. If Benepali has no effect on your disease after 12 weeks, your doctor may advise you to stop using this medicine.
Use in children and adolescents
The dose and frequency of administration will depend on the child's or adolescent's body weight and disease. Your doctor will determine the suitable dose for the child and prescribe the most appropriate presentation of etanercept.
The dose for pediatric patients with a body weight of 62.5 kg or more is 25 mg administered twice a week or 50 mg administered once a week with a pre-filled syringe or pre-filled pen.
Other etanercept medicines are available with doses suitable for children.
For polyarthritis or extended oligoarthritis in patients aged 2 years and older and weighing 62.5 kg or more, or enthesitis-related arthritis or psoriatic arthritis in patients aged 12 years and older and weighing 62.5 kg or more, the usual dose is 25 mg administered twice a week or 50 mg administered once a week.
For plaque psoriasis in patients aged 6 years and older and weighing 62.5 kg or more, the usual dose is 50 mg administered once a week. If Benepali has no effect on the child's disease after 12 weeks, your doctor may advise you to stop using this medicine.
Your doctor will give you precise instructions for preparing and calculating the correct dose.
Method and route of administration
Benepali is given as an injection under the skin (subcutaneous use).
In section 7, "Instructions for use", you will find detailed instructions for injecting Benepali.
The Benepali solution should not be mixed with any other medicine.
To help you remember, it may be useful to note down the day(s) of the week you should use Benepali in a diary.
If you use more Benepali than you should
If you use more Benepali than you should (either by injecting too much at one time or by using it too frequently), you should talk to a doctor or pharmacist immediately. Always carry the medicine pack with you, even if it is empty.
If you forget to use Benepali
If you miss a dose, you should inject it as soon as you remember, unless the next dose is scheduled for the next day, in which case you should omit the missed dose. Then continue injecting the medicine on the usual day(s). If you do not remember until the day you are due to take the next dose, do not inject a double dose (two doses on the same day) to make up for the missed dose.
If you stop treatment with Benepali
Your symptoms may return after stopping treatment.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine may cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
Allergic Reactions
If you observe any of the following reactions, do not inject more Benepali. Inform your doctor immediately or go to the Emergency Service of the nearest hospital.
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Swelling of the face, throat, hands, and feet
- Feeling of nervousness or anxiety, palpitations, sudden reddening of the skin and/or feeling of heat
- Severe rash, itching, or hives (prominent red or pale skin rashes, often accompanied by itching)
Severe allergic reactions are rare. However, any of the above symptoms may be a sign of an allergic reaction to Benepali, so you should seek urgent medical attention immediately.
Severe Adverse Effects
If you notice any of the following effects, you or the child may need urgent medical attention.
- Signs of severe infections(including pneumonia, non-superficial skin infections, joint infections, and blood infections), such as high fever that may be accompanied by cough, shortness of breath, chills, weakness, or a painful, sensitive, red, and hot area on the skin or joints;
- Signs of blood disorders,such as bleeding, bruising, or paleness;
- Signs of nervous system disorders, such as numbness or tingling, vision changes, eye pain, or weakness in an arm or leg;
- Signs of heart failureor worsening of heart failure, such as fatigue or shortness of breath with activity, swelling of the ankles, feeling of fullness in the neck or abdomen, shortness of breath at night, or cough, blue discoloration of the nails or around the lips;
- Signs of cancer:cancer can affect any part of the body, including the skin and blood, and the possible signs will depend on the type and location of the cancer. These signs may include weight loss, fever, swelling (with or without pain), persistent cough, presence of lumps or thickening of the skin;
- Signs of autoimmune reactions(in which antibodies that can damage normal body tissues develop) such as pain, itching, weakness, and abnormal breathing, thinking, feeling, or vision;
- Signs of lupus or lupus-like syndrome, such as weight changes, persistent rash, fever, muscle or joint pain, or fatigue;
- Signs of inflammation of the blood vesselssuch as pain, fever, redness, or heat of the skin, or itching.
These adverse effects are rare or infrequent, but they are serious conditions (some of which can be life-threatening). If any of them occur, inform your doctor immediately or go to the Emergency Service of the nearest hospital.
Other Adverse Effects
The following are the known adverse effects of Benepali, listed in decreasing order of frequency:
- Very Common(may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
Infections (including colds, sinusitis, bronchitis, urinary tract infections, and skin infections); injection site reactions (including bleeding, bruising, redness, itching, pain, and swelling) (do not occur as frequently after the first month of treatment; some patients have developed an injection site reaction that they had recently used); and headache.
- Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
Allergic reactions; fever; rash; itching; antibodies directed against normal tissues (formation of autoantibodies).
- Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
Severe infections (including pneumonia, non-superficial skin infections, joint infections, blood infections, and generalized infections); worsening of congestive heart failure; low red blood cell count, low white blood cell count, low neutrophil count (a type of white blood cell); low platelet count; skin cancer (excluding melanoma); localized skin swelling (angioedema); hives (prominent red or pale skin rashes, often accompanied by itching); eye inflammation; psoriasis (new or worsening); inflammation of the blood vessels affecting multiple organs; increased liver enzymes in blood tests (in patients who also receive treatment with methotrexate, the increase in liver enzymes is common); abdominal cramps and pain, diarrhea, weight loss, or blood in the stool (signs of intestinal problems).
- Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
Severe allergic reactions (including severe localized skin swelling and wheezing); lymphoma (a type of blood cancer); leukemia (cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow); melanoma (a type of skin cancer); combined low red blood cell count, white blood cell count, and platelet count; nervous system disorders (with severe muscle weakness and symptoms similar to those of multiple sclerosis or optic nerve or spinal cord inflammation); tuberculosis; new-onset congestive heart failure; seizures; lupus or lupus-like syndrome (symptoms may include persistent rash, fever, joint pain, and fatigue); skin rash that can lead to severe blistering and peeling of the skin; liver inflammation caused by the immune system (autoimmune hepatitis; in patients who also receive treatment with methotrexate, the frequency is uncommon); immune disorder that can affect the lungs, skin, and lymph nodes (sarcoidosis); inflammation or scarring of the lungs (in patients who also receive treatment with methotrexate, the frequency of inflammation or scarring of the lungs is uncommon); lichenoid reactions (pruritic reddish-purple skin rash and/or thick white-gray lines on the mucous membranes); opportunistic infections (such as tuberculosis and other infections that occur when disease resistance decreases); erythema multiforme (inflammatory rash); cutaneous vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels in the skin); nerve damage, including Guillain-Barré syndrome (a severe disease that can affect breathing and damage organs); damage to the small filters within the kidneys, leading to impaired kidney function (glomerulonephritis).
- Very Rare(may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
Failure of the bone marrow to produce crucial blood cells; toxic epidermal necrolysis (a potentially life-threatening skin disease).
- Frequency Not Known(cannot be estimated from the available data):
Merkel cell carcinoma (a type of skin cancer); Kaposi's sarcoma (a rare cancer related to human herpesvirus 8 infection. Kaposi's sarcoma usually manifests more frequently as purple-colored skin lesions); excessive activation of white blood cells associated with inflammation (macrophage activation syndrome); reactivation of hepatitis B (a liver infection); worsening of a disease called dermatomyositis (inflammation and weakness of the muscles accompanied by skin rash); listeriosis (a bacterial infection).
Adverse Effects in Children and Adolescents
The adverse effects observed in children and adolescents, as well as their frequencies, are similar to those described above.
Reporting of Adverse Effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if it is a possible adverse effect that is not listed in this prospectus. You can also report them directly through the national reporting system included in Appendix V. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Benepali
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date that appears on the packaging and the label of the pre-filled syringe after "EXP". The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Store in a refrigerator (between 2°C and 8°C). Do not freeze.
Keep the pre-filled syringes in the outer packaging to protect them from light.
After removing the syringe from the refrigerator, wait approximately 30 minutes for the Benepali solution in the syringe to reach room temperature.Do not heat it in any other way. Then, it is recommended to use it immediately.
Benepali can be stored outside the refrigerator at a maximum temperature of 30°C, and for a single period of up to 31 days; after which, the medicine cannot be refrigerated again. Benepali should be discarded if it has not been used within 31 days of being removed from the refrigerator. It is recommended that you note the date on which Benepali was removed from the refrigerator and the date from which Benepali should be discarded (no later than 31 days from the removal of the packaging from the refrigerator).
Observe the solution in the syringe. It should be between transparent and slightly opalescent, colorless or pale yellow and may contain small white or almost transparent protein particles. This is the normal appearance of Benepali. Do not use this medicine if you observe that the solution is more yellowish or cloudy, or if it has particles different from those described above. If you are concerned about the appearance of the solution, contact your pharmacist for any assistance you may need.
Medicines should not be thrown away through wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medicines that you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Benepali
- The active substance is etanercept. Each pre-filled syringe contains 25 mg of etanercept.
- The other components are sucrose, sodium chloride, sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate, and disodium hydrogen phosphate heptahydrate, and water for injectable preparations (see section 2 "Benepali contains sodium").
Appearance and Container Contents of the Product
Benepali is presented as a pre-filled syringe, containing a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless or pale yellow injectable solution.
Benepali is available in packs containing 4 pre-filled syringes, multipacks containing 2 packs, each with 4 pre-filled syringes, and multipacks containing 6 packs, each with 4 pre-filled syringes. Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder
Samsung Bioepis NL B.V.
Olof Palmestraat 10
2616 LR Delft
Netherlands
Manufacturer
Biogen Netherlands B.V.
Prins Mauritslaan 13
1171 LP Badhoevedorp
Netherlands
Samsung Bioepis NL B.V.
Olof Palmestraat 10
2616 LR Delft
Netherlands
For further information on this medicinal product, please contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Belgium/Belgique/Belgien Biogen Belgium NV/S.A Tel: + 32 2 219 1218 | Lithuania Biogen Lithuania UAB Tel: + 370 5 259 61 |
| Luxembourg/Luxemburg Biogen Belgium NV/SA Tel: + 32 2 219 121 |
Czech Republic Biogen (Czech Republic) s.r.o. Tel: + 420 255 706 200 | Hungary Biogen Hungary Kft. Tel: + 36 1 899 9880 |
Denmark Biogen (Denmark) A/S Tel: + 45 77 41 57 57 | Malta Pharma.MT Ltd Tel: + 356 2133 7008 |
Germany Biogen GmbH Tel: + 49 (0) 89 99 6170 | Netherlands Biogen Netherlands B.V. Tel: + 31 20 542 2000 |
Estonia Biogen Estonia OÜ Tel: + 372 618 9551 | Norway Biogen Norway AS Tel: + 47 23 40 01 00 |
Greece Genesis Pharma S.A. Tel: + 30 210 877 1500 | Austria Biogen Austria GmbH Tel: + 43 1 484 46 13 |
Spain Biogen Spain, S.L. Tel: + 34 91 310 7110 | Poland Biogen Poland Sp. z o.o. Tel: + 48 22 351 51 00 |
France Biogen France SAS Tel: + 33 (0)1 776 968 14 | Portugal Biogen Portugal Sociedade Farmacêutica, Unipessoal, Lda Tel: + 351 21 318 8450 |
Croatia Ewopharma d.o.o Tel: + 385 (0)1 6646 563 | Romania Ewopharma România SRL Tel: + 40 212 601 344 |
Ireland Biogen Idec (Ireland) Ltd. Tel: + 353 (0)1 463 7799 | Slovenia Biogen Pharma d.o.o. Tel: + 386 1 511 02 90 |
Iceland Icepharma hf. Tel: + 354 540 8000 | Slovakia Biogen Slovakia s.r.o. Tel: + 421 2 323 340 08 |
Italy Biogen Italia s.r.l. Tel: + 39 02 584 99 010 | Finland Biogen Finland Oy Tel: + 358 207 401 200 |
Cyprus Genesis Pharma (Cyprus) Ltd Tel: + 357 22 76 57 15 | Sweden Biogen Sweden AB Tel: + 46 8 594 113 60 |
Latvia Biogen Latvia SIA Tel: + 371 68 688 158 |
Date of Last Revision of this Leaflet: 03/2025
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the European Medicines Agency website: http://www.ema.europa.eu.
- Instructions for Use
Read the instructions for use before starting to use Benepali and each time you are given a new prescription. They may contain new information.
- Do notattempt to administer an injection until your doctor or nurse has taught you how to do it.
A single-use pre-filled syringe contains a dose of 25 mg of Benepali.
Find a well-lit and clean surface and gather the components you need:
- A new Benepali pre-filled syringe
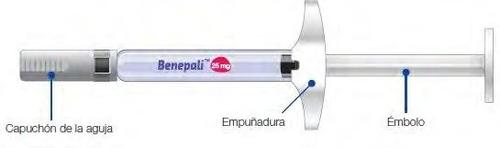
- Do notshake the pre-filled syringe.
The pack does not include:
- 1 alcohol swab, gauze, and plaster

- Sharps disposal container

- Before You Start
- Inspect the Pre-filled Syringe:
Check the expiration date on the pre-filled syringe label.
- Do notuse the pre-filled syringe after the expiration date.
- Do notuse the pre-filled syringe if it has been dropped onto a hard surface. The internal components may be broken.
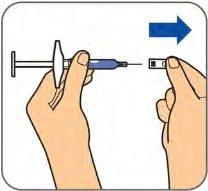
- Do notuse the pre-filled syringe if the needle cap is not in place or is not firmly attached.
- Check the Solution:
Look at the medicine in the pre-filled syringe.
The medicine should be clear to slightly opalescent, colorless or pale yellow, and may contain small white or almost transparent protein particles.
- Do notuse the solution if it is more yellow or cloudy, or if it contains particles other than those described above.
- Wait Until the Medicine Reaches Room Temperature:
Take one of the pre-filled syringes out of the refrigerator and let it sit at room temperature for at least 30 minutes before injecting the solution.
This makes the injection easier and more comfortable for you.
- Do notremove the needle cap until you are ready to inject.
- Do notuse heat sources such as a microwave or hot water to warm up Benepali.
- Choose an Injection Site:
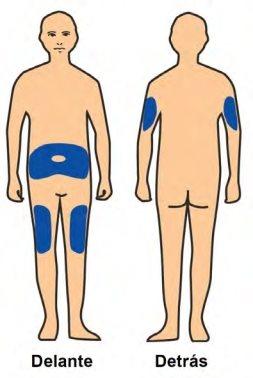
The Benepali pre-filled syringe is intended for subcutaneous injection. It should be injected into the thigh, abdomen, or the upper back of the arm(see the image on the left).
You must use a different site for each new injection.
If you inject into the abdomen, choose a site that is at least 5 cm away from the navel.
- Do notinject into areas of skin that are red, hard, bruised, or sensitive.
- Avoidareas with scars or stretch marks.
- If you have psoriasis, do notinject the medicine into any raised, thick, red, or scaly skin patches or lesions.
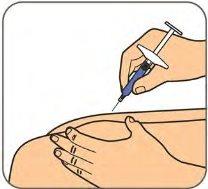
- Injection Steps
Step 1:
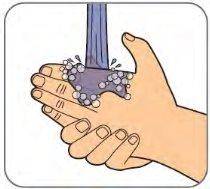
| Wash your hands with soap and water. |
Step 2: | Clean the injection site with an alcohol swab. See "Choose an injection site" for how to choose the injection site.
|
Step 3:
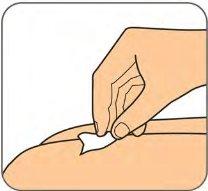
| Remove the needle cap by pulling it straight off and dispose of it in the trash or in the sharps disposal container. See the instructions for choosing an injection site in "Choose an injection site".
|
Step 4:
| Gently pinch the cleaned skin to make a fold. Hold the pre-filled syringe at a 45-degree angle to the skin. With a quick, short motion, push the needle all the way into the skin. You can release the skin fold when the needle is fully inserted. |
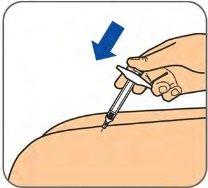
Step 5:
| Slowly push the plunger to inject all of the Benepali solution. |
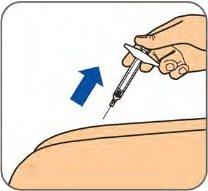
Step 6:
| When the syringe is empty, pull the needle out of the skin at the same angle you inserted it.
|
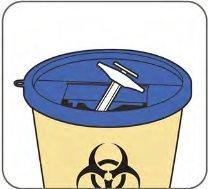
Disposal:
| Dispose of the entire syringe in an authorized sharps disposal container. Ask your doctor how to properly dispose of a full sharps disposal container. You can purchase sharps disposal containers at your pharmacy.
|
- Care of the Injection Site
If bleeding occurs at the injection site, press the area with a gauze.
- Do notrub the injection site.
If necessary, you can cover the injection site with a plaster.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to BENEPALI 25 mg SOLUTION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGEDosage form: INJECTABLE, 50 mgActive substance: etanerceptManufacturer: Samsung Bioepis Nl B.V.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 50mgActive substance: etanerceptManufacturer: Samsung Bioepis Nl B.V.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 10 mgActive substance: etanerceptManufacturer: Pfizer Europe Ma EeigPrescription required
Online doctors for BENEPALI 25 mg SOLUTION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE
Discuss questions about BENEPALI 25 mg SOLUTION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions