ACTILYSE powder and solvent for injectable solution and for infusion

How to use ACTILYSE powder and solvent for injectable solution and for infusion
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Actilyse, powder and solvent for solution for injection and infusion
alteplase
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or nurse.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack:
- What is Actilyse and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you are given Actilyse
- How Actilyse is given
- Possible side effects
- Storing Actilyse
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Actilyse and what is it used for
The active substance of Actilyse is alteplase. It belongs to a group of medicines called thrombolytics. These medicines work by dissolving blood clots that have formed in the blood vessels.
Actilyse 10 mg, 20 mg or 50 mg is used to treat diseases caused by the formation of blood clots in the blood vessels, including:
- heart attacks caused by blood clots in the heart arteries (acute myocardial infarction)
- blood clots in the lung arteries (massive acute pulmonary embolism)
- stroke caused by a blood clot in a brain artery (acute ischemic stroke)
2. What you need to know before you are given Actilyse
You must not be given Actilyse:
- if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to alteplase or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- if you have or have recently had a disease that increases the risk of bleeding, including:
- bleeding disorder or predisposition to bleeding
- severe or life-threatening bleeding in any part of the body
- bleeding in the brain or skull
- very high blood pressure that is not controlled
- bacterial infection or inflammation of the heart (endocarditis), or inflammation of the membranes that surround the heart (pericarditis)
- inflammation of the pancreas (acute pancreatitis)
- stomach or intestinal ulcers
- varicose veins in the esophagus (esophageal varices)
- blood vessel abnormalities, such as a localized widening of an artery (aneurysm)
- certain tumors
- severe liver disease
- if you are taking medicines to "thin" the blood (oral anticoagulants), unless the appropriate tests do not show clinically relevant activity of the medicine
- if you have ever had surgery on the brain or spinal cord
- if you have had major surgery or a significant injury in the last 3 months
- if you have had a recent puncture of a major blood vessel
- if you have had external cardiac massage in the last 10 days
- if you have had a baby in the last 10 days
Your doctor will not give you Actilyse for the treatment of heart attacks or blood clots in the lung arteries
- if you have or have ever had a stroke caused by bleeding in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke)
- if you have or have ever had a stroke of unknown cause
- if you have had a stroke caused by a blood clot in a brain artery (ischemic stroke) in the last 6 months, unless it is the stroke for which you are being treated now
Additionally, your doctor will not give you Actilyse for the treatment of stroke caused by a blood clot in a brain artery (acute ischemic stroke)
- if your stroke symptoms started more than 4.5 hours ago or if it is possible that your symptoms started more than 4.5 hours ago because you do not know when they started
- if your stroke has only very mild symptoms
- if there are signs of bleeding in the brain
- if you have had a stroke in the last three months
- if your symptoms improve rapidly before you are given Actilyse
- if you have a very severe stroke
- if you had seizures (convulsions) when your stroke started
- if you have an abnormal prothrombin time (a test to check how your blood clots). This test may be abnormal if you have been given heparin (a medicine used to "thin" the blood) in the last 48 hours
- if you are diabetic and have had a stroke
- if you have a very low platelet count (thrombocytopenia)
- if your blood pressure is very high (above 185/110) and can only be lowered with medication
- if your blood sugar levels are very low (less than 50 mg/dl)
- if your blood sugar levels are very high (more than 400 mg/dl)
- if you are under 16 years old. (For adolescents 16 years or older, see section "Your doctor will be particularly careful with Actilyse").
Your doctor will be particularly careful with Actilyse
- if you have had any other allergic reaction other than a sudden and potentially life-threatening allergic reaction (severe hypersensitivity) to the active substance alteplase or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6)
- if you have or have recently had any other disorder that increases the risk of bleeding, such as:
- minor injury
- biopsy (a procedure used to obtain tissue samples)
- puncture of major blood vessels
- intramuscular injection
- external cardiac massage
- if you have been given Actilyse before
- if you are over 65 years old
- if you are over 80 years old, you may have a worse outcome regardless of treatment with Actilyse. However, in general, the benefit-risk with Actilyse in patients over 80 years is positive and age alone is not a barrier to treatment with Actilyse
- if you are an adolescent of 16 years or older, the benefit-risk of treatment for acute ischemic stroke should be carefully evaluated on an individual basis
Other medicines and Actilyse
Tell your doctor if you are using or have recently used other medicines, including those obtained without a prescription. It is especially important that you tell your doctor if you are using or have recently used:
- medicines used to "thin" the blood, including:
- acetylsalicylic acid
- warfarin
- cumarin
- heparin
- certain medicines used to treat high blood pressure (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, ACE inhibitors)
Pregnancy, breastfeeding and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor. Your doctor will only give you Actilyse if the expected benefits outweigh the risks for your baby.
3. How Actilyse is given
Actilyse will be prepared and given to you by your doctor or a healthcare professional. It is not intended for self-administration.
Treatment with Actilyse should be started as soon as possible after the onset of symptoms.
There are three diseases for which Actilyse is indicated:
Heart attack (acute myocardial infarction)
The dose you will be given will depend on your body weight. The maximum dose of Actilyse is 100 mg but will be lower if you weigh less than 65 kg.
It can be given in two different ways:
- 90-minute dosing regimen, for patients treated within 6 hours after the onset of symptoms. This consists of:
- an initial injection of part of the Actilyse dose into a vein
- infusion of the rest of the dose over the next 90 minutes.
- 3-hour dosing regimen, for patients treated between 6-12 hours after the onset of symptoms. This consists of:
- an initial injection of part of the Actilyse dose into a vein
- infusion of the rest of the dose over the next 3 hours.
In addition to Actilyse, your doctor will give you another medicine to prevent the formation of blood clots. This medicine will be given to you as soon as possible after the start of chest pain.
Blood clots in the lung arteries (massive acute pulmonary embolism)
The dose you will be given will depend on your body weight. The maximum dose of Actilyse is 100 mg but will be lower if you weigh less than 65 kg.
The medicine is usually given as follows:
- an initial injection of part of the dose into a vein
- infusion of the rest of the dose over the next 2 hours.
After treatment with Actilyse, your doctor will start (or continue) treatment with heparin (a medicine used to "thin" the blood).
Stroke caused by a blood clot in a brain artery (acute ischemic stroke)
Actilyse should be given within 4.5 hours after the onset of the first symptoms. The sooner you receive Actilyse, the more you can benefit from treatment and the lower the risk of harmful side effects. The dose you will be given will depend on your body weight. The maximum dose of this medicine is 90 mg but will be lower if you weigh less than 100 kg. Actilyse is given as follows:
- an initial injection of part of the dose into a vein
- infusion of the rest of the dose over the next 60 minutes.
You should not take acetylsalicylic acid during the first 24 hours after being treated for a stroke with Actilyse. Your doctor may give you an injection of heparin if necessary.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or a healthcare professional.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following side effects have been observed in patients given Actilyse:
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- heart failure - may require interruption of treatment
- bleeding in the brain (cerebral hemorrhage) after treatment of a stroke caused by a blood clot in a brain artery (acute ischemic stroke) - may require interruption of treatment
- fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema)
- bleeding into the damaged blood vessel (such as hematoma)
- low blood pressure (hypotension)
- chest pain (angina pectoris)
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- more heart attacks
- bleeding in the brain (cerebral hemorrhage) after treatment of a heart attack (myocardial infarction) - may require interruption of treatment
- stop of heart beats (cardiac arrest) - may require interruption of treatment
- shock (very low blood pressure) due to heart failure - may require interruption of treatment
- bleeding in the throat
- bleeding in the stomach or intestine, including blood in vomit (hematemesis) or blood in stool (melena or rectal bleeding), bleeding in the gums
- bleeding into body tissues causing purple spots (ecchymosis)
- bleeding in the urinary tract or reproductive organs, which can cause blood in the urine (hematuria)
- bleeding or bruising at the injection site
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- bleeding related to the lung, such as coughing up blood (hemoptysis) or bleeding in the respiratory tract - may require interruption of treatment
- nosebleeds (epistaxis)
- irregular heartbeats after blood flow to the heart has been restored
- heart valve problems (mitral regurgitation) or problems with the walls that separate the heart chambers (ventricular septal defect) - may require interruption of treatment
- sudden blockage of an artery in the lungs (pulmonary embolism), brain (cerebral embolism), and other areas of the body (systemic embolism)
- bleeding in the ear
- low blood pressure
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
- bleeding in the membrane surrounding the heart (hemopericardium) - may require interruption of treatment
- internal bleeding in the back of the abdomen (retroperitoneal hemorrhage) - may require interruption of treatment
- formation of blood clots in blood vessels that can travel to other organs in the body (embolism). The symptoms will depend on the affected organ
- allergic reactions, for example, hives (urticaria) and rash, difficulty breathing up to asthma (bronchospasm), fluid under the skin and mucous membranes (angioedema), low blood pressure or shock - may require interruption of treatment
- bleeding in the eye (ocular hemorrhage)
- upset stomach (nausea)
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
- severe allergic reactions (e.g. anaphylaxis that is life-threatening) - may require interruption of treatment
- events that affect the nervous system, such as:
- seizures (convulsions, fits)
- difficulty speaking
- confusion or delirium (severe confusion)
- anxiety with restlessness (agitation)
- depression
- altered thoughts (psychosis)
These disorders usually occur in association with a stroke caused by a blood clot or bleeding in the brain.
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data)
- bleeding in internal organs, for example, bleeding in the liver (hepatic hemorrhage) - may require interruption of treatment
- formation of cholesterol crystals that can travel to other organs in the body (cholesterol crystal embolization). The symptoms will depend on the affected organ - may require interruption of treatment
- bleeding that may require a blood transfusion
- vomiting
- increase in body temperature (fever)
Patients who have had bleeding in the brain or other serious bleeding events may die or suffer permanent disability.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or nurse, even if it is possible that the side effects are not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly to the Spanish Medicines Agency at www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storing Actilyse
It is not usual for you to store Actilyse as it will be given to you by your doctor.
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not store above 25°C. Store in the original package to protect from light.
Do not use Actilyse after the expiry date which is stated on the label and carton. The expiry date is the last day of the month stated.
Reconstituted solution
The reconstituted solution has been shown to be stable for 24 hours at 2-8°C and for 8 hours at 25°C.
From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately after reconstitution. If not used immediately, the storage time and conditions before use will be the responsibility of the user and should not exceed 24 hours at 2-8°C.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Actilyse
- The active ingredient is alteplase. Each vial contains 10 mg (equivalent to 5,800,000 IU), 20 mg (equivalent to 11,600,000 IU), or 50 mg (equivalent to 29,000,000 IU) of alteplase.
Alteplase is produced using recombinant DNA technology, utilizing a Chinese hamster ovary cell line. The other components are arginine, phosphoric acid (for pH adjustment), and polysorbate 80.
- The solvent is water for injectable preparations.
Appearance of the Product and Container Contents
Actilyse is a powder and solvent for injectable solution and perfusion. Each container contains a vial with powder and a vial with solvent.
Actilyse is available in the following container sizes:
- a vial of powder with 10 mg of alteplase and a vial with 10 ml of solvent.
- a vial of powder with 20 mg of alteplase, a vial with 20 ml of solvent, and a transfer cannula.
- a vial of powder with 50 mg of alteplase, a vial with 50 ml of solvent, and a transfer cannula.
Only some container sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
55216 Ingelheim am Rhein
Germany
Local Representative:
Boehringer Ingelheim España, S.A.
Prat de la Riba, 50
08174 Sant Cugat del Vallès (Barcelona)
Spain
Manufacturer
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG
Birkendorfer Strasse 65
88397 Biberach/Riss
Germany
Boehringer Ingelheim France
100-104 avenue de France
75013 Paris
France
Date of Last Revision of this Prospectus:09/2024
Detailed and updated information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
Traceability
In order to improve the traceability of biological medicinal products, the name and batch number of the administered medicinal product must be clearly recorded.
The 2 mg alteplase vials are not intended for use in the indications of acute myocardial infarction, massive pulmonary embolism, or acute ischemic stroke (due to the risk of massive underdosing). Only the 10 mg, 20 mg, and 50 mg vials are intended for use in these indications.
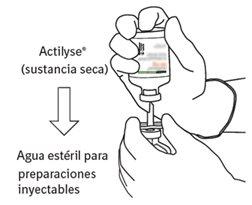
Reconstitution
To obtain a final concentration of 1 mg of alteplase per ml after reconstitution, the entire volume of the provided solvent should be transferred to the vial containing the Actilyse powder. For this purpose, the transfer cannula included in the 20 mg and 50 mg container sizes should be used. For the 10 mg presentation, a syringe should be used.
To obtain a final concentration of 2 mg of alteplase per ml after reconstitution, only half of the provided solvent should be used (according to the table below). In these cases, a syringe should always be used to transfer the necessary amount of solvent to the vial containing the Actilyse powder.
The contents of a vial of Actilyse (10 mg, 20 mg, or 50 mg) should be dissolved under aseptic conditions with water for injectable preparations, according to the following table, to obtain a final concentration of alteplase of 1 mg/ml or 2 mg/ml:
Actilyse dry substance | 10 mg | 20 mg | 50 mg |
(a) Volume of sterile water for injectable preparations to be added to the dry substance | 10 ml | 20 ml | 50 ml |
Final concentration: | 1 mg alteplase/ml | 1 mg alteplase/ml | 1 mg alteplase/ml |
(b) Volume of sterile water for injectable preparations to be added to the dry substance | 5 ml | 10 ml | 25 ml |
Final concentration: | 2 mg alteplase/ml | 2 mg alteplase/ml | 2 mg alteplase/ml |
The reconstituted solution should be administered intravenously. The reconstituted solution of 1 mg/ml may be further diluted with a sterile sodium chloride 9 mg/ml (0.9%) injectable solution to a minimum concentration of 0.2 mg/ml, as the appearance of turbidity in the reconstituted solution cannot be excluded. Further dilution of the reconstituted solution of 1 mg/ml with sterile water for injectable preparations or, in general, the use of carbohydrate perfusion solutions, e.g., dextrose, is not recommended due to the increased formation of turbidity in the reconstituted solution. Actilyse should not be mixed with other medicinal products in the same perfusion vial (not even with heparin).
For storage conditions, please see section 5 of the prospectus.
The reconstituted solution is for single use. Any unused fraction of the solution should be discarded.
Instructions for reconstituting Actilyse
1 | Reconstitute immediately before administration. |
|
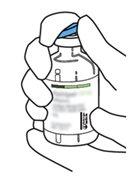
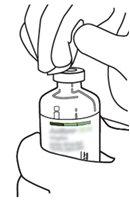
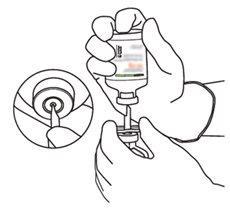
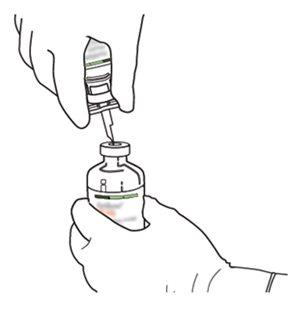
2 | Remove the protective caps from the two vials containing sterile water and Actilyse dry substance, respectively, by pulling them upwards with a finger. |
|
3 | Clean the rubber stopper of each vial with an alcohol swab. |
|
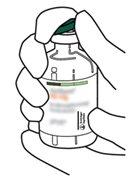
4 | Remove the transfer cannula* from its packaging. Do not disinfect or sterilize the transfer cannula; it is sterile. Remove the cap. |
|
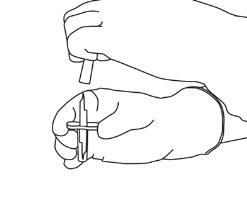
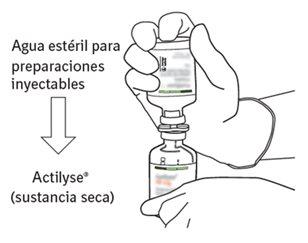
5 | Hold the vial of sterile water vertically on a stable surface. Directly from above, pierce the rubber stopper vertically in the center of the stopper with the transfer cannula, pressing carefully but firmly, without twisting. |
|
6 | Hold the vial of sterile water and the transfer cannula firmly with one hand using the two lateral flaps. Remove the remaining cap from the top of the transfer cannula. |
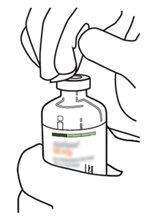
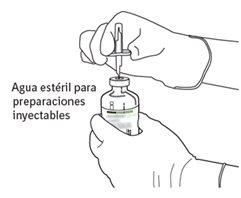
|
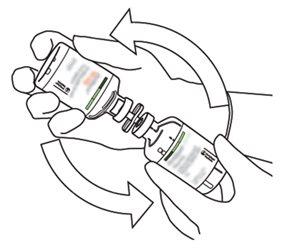
7 | Hold the vial of sterile water and the transfer cannula firmly with one hand using the two lateral flaps. Hold the vial with Actilyse dry substance vertically above the transfer cannula and position the tip of the transfer cannula just in the center of the stopper. Press the vial with the dry substance downwards with the transfer cannula directly from above, piercing the rubber stopper vertically and carefully but firmly, without twisting. |
|
8 | Invert the two vials and allow the water to drain completely into the dry substance. |
|
9 | Remove the empty water vial along with the transfer cannula. They can be discarded. |
|
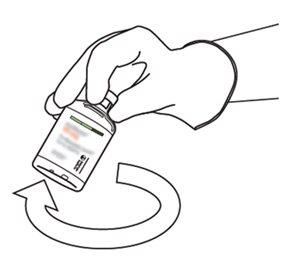
10 | Take the vial with reconstituted Actilyse and gently turn it to dissolve any remaining powder, but do not shake, as this will produce foam. If there are bubbles, keep the solution still for a few minutes to allow them to disappear. |
|
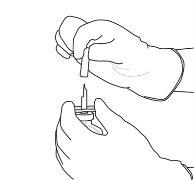
11 | The reconstituted solution contains 1 mg/ml of alteplase. It should be clear and colorless to light yellow and should not contain any particles. | |
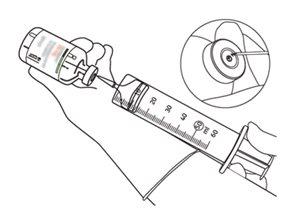
12 | Withdraw the required amount using only a needle and a syringe. Do not use the puncture area of the transfer cannula to avoid losses. |
|
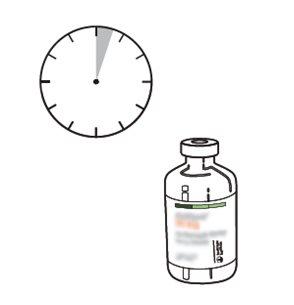
13 | Use immediately. Discard the unused solution. |
(* If a transfer cannula is included in the kit. Reconstitution can also be performed with a syringe and a needle.)
Dosage and Administration
Acute Myocardial Infarction
Dosage
- 90-minute dosing regimen (accelerated) for patients with acute myocardial infarction, in whom treatment can be initiated within 6 hours after the onset of symptoms.
In patients with a body weight ≥ 65 kg:
Volume to be administered based on alteplase concentration | ||
1 mg/ml | 2 mg/ml | |
15 mg as an intravenous bolus, immediately followed by | 15 ml | 7.5 ml |
50 mg as an intravenous infusion at a constant rate over the first 30 minutes, immediately followed by | 50 ml | 25 ml |
35 mg as an intravenous infusion at a constant rate over 60 minutes, up to a maximum total dose of 100 mg | 35 ml | 17.5 ml |
In patients with a body weight <65 kg, the total dose should be adjusted according to weight as follows:< p>
Volume to be administered based on alteplase concentration | ||
1 mg/ml | 2 mg/ml | |
15 mg as an intravenous bolus, immediately followed by | 15 ml | 7.5 ml |
0.75 mg/kg body weight (bw) as an intravenous infusion at a constant rate over the first 30 minutes, immediately followed by | 0.75 ml/kg bw | 0.375 ml/kg bw |
0.5 mg/kg body weight (bw) as an intravenous infusion at a constant rate over 60 minutes | 0.5 ml/kg bw | 0.25 ml/kg bw |
- 3-hour dosing regimen for patients with acute myocardial infarction in whom treatment can be initiated between 6 and 12 hours after the onset of symptoms.
In patients with a body weight ≥ 65 kg:
Volume to be administered based on alteplase concentration | ||
1 mg/ml | 2 mg/ml | |
10 mg as an intravenous bolus, immediately followed by | 10 ml | 5 ml |
50 mg as an intravenous infusion at a constant rate over the first hour, immediately followed by | 50 ml | 25 ml |
40 mg as an intravenous infusion at a constant rate over 2 hours, up to a maximum total dose of 100 mg | 40 ml | 20 ml |
In patients with a body weight <65 kg:< p>
Volume to be administered based on alteplase concentration | ||
1 mg/ml | 2 mg/ml | |
10 mg as an intravenous bolus, immediately followed by | 10 ml | 5 ml |
an intravenous infusion at a constant rate over 3 hours, up to a maximum total dose of 1.5 mg/kg bw | 1.5 ml/kg bw | 0.75 ml/kg bw |
Concomitant treatment: Concomitant antithrombotic treatment is recommended in accordance with current international guidelines for the treatment of patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction.
Method of administration
The reconstituted solution should be administered intravenously and is for immediate use.
The 2 mg alteplase vials are not intended for use in this indication.
Massive Pulmonary Embolism
Dosage
In patients with a body weight ≥ 65 kg:
A total dose of 100 mg of alteplase should be administered over 2 hours. The following dosing regimen is the one with which there is most experience:
Volume to be administered based on alteplase concentration | ||
1 mg/ml | 2 mg/ml | |
10 mg as an intravenous bolus over 1-2 minutes, immediately followed by | 10 ml | 5 ml |
90 mg as an intravenous infusion at a constant rate over 2 hours, up to a maximum total dose of 100 mg | 90 ml | 45 ml |
In patients with a body weight <65 kg:< p>
Volume to be administered based on alteplase concentration | ||
1 mg/ml | 2 mg/ml | |
10 mg as an intravenous bolus over 1-2 minutes, immediately followed by | 10 ml | 5 ml |
an intravenous infusion at a constant rate over 2 hours, up to a maximum total dose of 1.5 mg/kg bw | 1.5 ml/kg bw | 0.75 ml/kg bw |
Concomitant treatment: After treatment with Actilyse, heparin treatment should be initiated (or resumed) if aPTT values are below twice the upper limit of normal. The infusion should be adjusted to maintain aPTT values in the range of 50-70 seconds (1.5-2.5 times the reference value).
Method of administration
The reconstituted solution should be administered intravenously and is for immediate use.
The 2 mg alteplase vials are not intended for use in this indication.
Acute Ischemic Stroke
Treatment should only be performed under the responsibility and supervision of a trained physician with experience in neurovascular care, see Summary of Product Characteristics section 4.3 contraindications and 4.4 special warnings and precautions for use.
Treatment with Actilyse should be initiated as soon as possible within 4.5 hours after the onset of stroke symptoms (see Summary of Product Characteristics section 4.4). Beyond 4.5 hours after the onset of stroke symptoms, there is a negative benefit-risk ratio associated with treatment with Actilyse, and it should not be administered (see Summary of Product Characteristics section 5.1).
Dosage
The recommended total dose is 0.9 mg of alteplase per kg of body weight (up to a maximum of 90 mg), starting with 10% of the total dose as an initial intravenous bolus, immediately followed by the remaining total dose infused intravenously over 60 minutes.
TABLE OF DOSAGE FOR ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Using the recommended standard concentration of 1 mg/ml, the volume (ml) to be administered is equal to the recommended dose value (mg) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Weight (kg) | Total Dose (mg) | Bolus Dose (mg) | Infusion Dose* (mg) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
40 | 36.0 | 3.6 | 32.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
42 | 37.8 | 3.8 | 34.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
44 | 39.6 | 4.0 | 35.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
46 | 41.4 | 4.1 | 37.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
48 | 43.2 | 4.3 | 38.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
50 | 45.0 | 4.5 | 40.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
52 | 46.8 | 4.7 | 42.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
54 | 48.6 | 4.9 | 43.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
56 | 50.4 | 5.0 | 45.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
58 | 52.2 | 5.2 | 47.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
60 | 54.0 | 5.4 | 48.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
62 | 55.8 | 5.6 | 50.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
64 | 57.6 | 5.8 | 51.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
66 | 59.4 | 5.9 | 53.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
68 | 61.2 | 6.1 | 55.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
70 | 63.0 | 6.3 | 56.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
72 | 64.8 | 6.5 | 58.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
74 | 66.6 | 6.7 | 59.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
76 | 68.4 | 6.8 | 61.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
78 | 70.2 | 7.0 | 63.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
80 | 72.0 | 7.2 | 64.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
82 | 73.8 | 7.4 | 66.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
84 |
75.6 | 7.6 | 68.0 | |
86 | 77.4 | 7.7 | 69.7 |
88 | 79.2 | 7.9 | 71.3 |
90 | 81.0 | 8.1 | 72.9 |
92 | 82.8 | 8.3 | 74.5 |
94 | 84.6 | 8.5 | 76.1 |
96 | 86.4 | 8.6 | 77.8 |
98 | 88.2 | 8.8 | 79.4 |
100+ | 90.0 | 9.0 | 81.0 |
*administered at a concentration of 1mg/ml for 60 minutes at a constant infusion rate.
Adjuvant treatment:the safety and efficacy of this regimen with concomitant administration of heparin or platelet aggregation inhibitors such as acetylsalicylic acid during the first 24 hours after symptom onset have not been sufficiently investigated. Therefore, the administration of intravenous heparin or platelet aggregation inhibitors such as acetylsalicylic acid should be avoided in the first 24 hours after treatment with Actilyse due to an increased risk of bleeding. If heparin is required for other indications (e.g. prevention of deep vein thrombosis), the dose should not exceed 10,000 IU per day, administered subcutaneously.
Method of administration
The reconstituted solution should be administered intravenously and is for immediate use.
The 2 mg alteplase vials are not indicated for use in this indication.
Pediatric population
Experience with the use of Actilyse in children and adolescents is limited. Actilyse is contraindicated in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke in children and adolescents under 16 years of age (see Summary of Product Characteristics section 4.3). The dose in adolescents between 16 and 17 years is the same as for adults (see Summary of Product Characteristics section 4.4 for recommendations on imaging techniques to be used beforehand).
Adolescents 16 years of age or older should be treated according to the instructions for use in the adult population after obtaining images using appropriate techniques to rule out false strokes and confirm the arterial occlusion corresponding to the neurological deficit.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to ACTILYSE powder and solvent for injectable solution and for infusionDosage form: INJECTABLE, 1500 IUActive substance: apadamtase alfa and cinaxadamtase alfaManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AgPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 500 IUActive substance: apadamtase alfa and cinaxadamtase alfaManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AgPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLEActive substance: protein CManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AgPrescription required
Online doctors for ACTILYSE powder and solvent for injectable solution and for infusion
Discuss questions about ACTILYSE powder and solvent for injectable solution and for infusion, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions