
Zibor

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Zibor

How to use Zibor
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Zibor 25,000 anti-Xa IU/mL solution for injection in a pre-filled syringe
Bemiparin sodium
Read the package leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Leaflet
- 1. What is Zibor and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Zibor
- 3. How to use Zibor
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Zibor
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Zibor and what is it used for
Zibor 25,000 anti-Xa IU/mL containing bemiparin sodium (Bemiparinum natricum) as the active substance, belongs to the group of anticoagulant medicines, low molecular weight heparins, which prevent blood clotting in blood vessels. Zibor is used to treat blood clots in the legs and/or lungs (deep vein thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism).
2. Important information before using Zibor
When not to use Zibor:
- If the patient is allergic to bemiparin sodium, heparin, or similar products (such as enoxaparin, dalteparin, nadroparin) or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- If the patient has had an allergic reaction after administration of any heparin-containing medicine.
- If the patient is allergic to any substance of porcine origin.
- If the patient has heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) - a condition in which the number of platelets decreases and they clump together after administration of Zibor or disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) with a decrease in platelet count.
- If the patient has a condition known as endocarditis (inflammation of the heart lining and heart valves).
- If the patient has a tendency to bleed excessively.
- If the patient has severe liver and/or kidney failure.
- If the patient has any changes with a high risk of bleeding (e.g., active gastric ulcer, vascular malformations, and aneurysms of the brain).
- If the patient has had bleeding into the brain.
- If the patient has had a head, spine, eye, or ear injury or surgery is planned.
and/or ear.
- During treatment with Zibor, spinal or epidural anesthesia should not be used, as it is dangerous. Therefore, the doctor should be informed about the treatment with Zibor before undergoing surgery.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Zibor, discuss it with your doctor.
- If liver dysfunction occurs.
- In case of kidney function disorders. The doctor may decide to monitor the patient closely. If the patient has severe kidney disease, the doctor may recommend special dosing rules.
- If the patient has uncontrolled high blood pressure.
- If the patient has had gastric or duodenal ulcers in the past, which are no longer present.
- If the patient has thrombocytopenia - a disorder in which there is a small number of platelets, making it easy to bruise and bleed.
- If the patient has kidney or urinary stones.
- If the patient has any other organic changes associated with an increased risk of bleeding complications.
- If the patient has eye diseases (related to blood vessels).
- If the patient has diabetes.
- If blood tests show an increased potassium level in the blood.
- Make sure the doctor is properly informed about the planned lumbar puncture (puncture of the lower back to collect cerebrospinal fluid for laboratory tests).
Zibor and other medicines
Inform the doctor if the patient is taking any of the following medicines:
- any medicine administered intramuscularly, as Zibor should be avoided during treatment with intramuscularly administered medicines.
- other anticoagulant medicines, such as warfarin and/or acenocoumarol (vitamin K antagonists) used to treat or prevent clotting disorders.
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen, used to treat arthritis.
- corticosteroids, such as prednisolone, used to treat inflammatory diseases, such as arthritis.
- platelet aggregation inhibitors, such as acetylsalicylic acid, ticlopidine, or clopidogrel, used to prevent clotting disorders.
- medicines that increase potassium levels in the blood, such as diuretics (urinary medicines) and antihypertensive medicines (used to lower blood pressure).
- medicines that increase blood volume, such as dextran.
- intravenous nitroglycerin used to treat heart diseases.
Tell the doctor or pharmacist about all medicines the patient is taking, has recently taken, or plans to take.
Laboratory tests
- In some patients, it may be necessary to determine the platelet count. The doctor will decide if it is necessary (e.g., before starting treatment, on the first day of therapy, and then regularly every 3 to 4 days, and at the end of treatment).
- In case of certain diseases (diabetes, kidney diseases) or if the patient is taking potassium-sparing medicines, the doctor may recommend determining the potassium level in the blood.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult a doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Zibor does not affect the ability to drive or use machines.
3. How to use Zibor
This medicine should always be used exactly as prescribed by the doctor. In case of doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
Recommended dose:
Adults (18-64 years)
The daily dose of Zibor will be determined based on the patient's body weight.
- for patients with a body weight below 50 kg, the dose is 0.2 mL (5000 anti-Xa IU).
- for patients with a body weight between 50 kg and 70 kg, the dose is 0.3 mL (7500 anti-Xa IU).
- for patients with a body weight between 71 kg and 100 kg, the dose is 0.4 mL (10,000 anti-Xa IU).
- for patients with a body weight above 100 kg, the daily dose is determined based on body weight using the conversion factor: 115 anti-Xa IU/kg body weight/day.
Activity is expressed in international units of anti-Xa factor inhibition (IU)
of the First International Standard for Low Molecular Weight Heparin.
Zibor is usually injected under the skin, usually into the fatty tissue of the abdomen or the upper part of the thigh. In the hospital, the medicine is administered by a doctor or nurse. After discharge from the hospital, it may be necessary to continue treatment with Zibor at home.
- Zibor should not be injected intramuscularly or mixed with other intramuscularly administered medicines.
- The medicine is usually administered once a day.
- The doctor will inform the patient about the duration of treatment (usually for about 5-9 days).
- If the doctor has recommended self-administration of the medicine, the patient should strictly follow the doctor's instructions (see below: "How to inject Zibor?").
Use in elderly patients (65 years and older):usually, there is no need to change the dosing recommended for other adult patients. In case of liver function disorders, the doctor should be informed, who may decide to monitor the patient closely. In case of kidney function disorders, the doctor should be informed, who may decide to monitor the patient closely. If the patient has severe kidney disease, the doctor may recommend special dosing rules.
Use in children and adolescents (under 18 years):Zibor is not recommended for use in children.
How to inject Zibor?
Zibor should never be injected intramuscularly, as it may cause bleeding into the muscles.
Before the first self-administration of the injection, the patient should receive detailed instructions on the proper injection technique. The instructions should be provided to the patient by a doctor or qualified medical staff.
Follow the instructions below:
- Wash your hands thoroughly and sit or lie down in a comfortable position.
- Choose a place on the abdomen, avoiding the area around the navel and any areas with scars or bruising, and clean the skin thoroughly.
- For each injection, choose a different place, e.g., alternating between the left and right sides.
- Remove the cap from the Zibor pre-filled syringe.
- To maintain the sterility of the needle, do not touch it to any surface.
- The pre-filled syringe is ready for use.
- Before injecting, do not press the plunger to remove air bubbles, as this may cause loss of medicine.
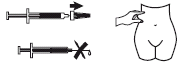
- Holding the pre-filled syringe in one hand, use your thumb and index finger of the other hand to gently hold the cleaned skin area, creating a skin fold.
- Insert the entire length of the needle into the thick part of the skin fold at a 90-degree angle.
- Press the plunger while holding the skin fold throughout the injection.
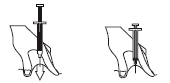
- Remove the needle by pulling it straight up and release the skin fold.
- Do not rub the injection site. This will help avoid bruising.
- Do not replace the cap on the pre-filled syringe. Dispose of it (first the needle) in a sharps container, close it tightly, and keep it out of the reach of children.
- If you feel that the effect of the medicine is too strong (e.g., if unexpected bleeding occurs) or too weak (no improvement), inform your doctor or pharmacist.
Using a higher dose of Zibor than recommended
Administering too high a dose of the medicine may cause bleeding. If bleeding occurs, immediately inform your doctor or go to the nearest hospital with this leaflet.
Missing a dose of Zibor
Do not use a double dose to make up for a missed dose. Contact your doctor as soon as possible to find out what to do.
Stopping treatment with Zibor
Before stopping treatment with Zibor, always consult your doctor.
In case of any further doubts about the use of this medicine, consult your doctor.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Zibor can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
In case of the following side effects, stop using Zibor and inform your doctor or nurse (or go to the nearest hospital emergency department immediately):
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Bleeding complications, such as blood in the urine and/or stool, which may cause bleeding anemia.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1000 people):
- Severe decrease in platelet count (severe thrombocytopenia type II) leading to bruising, bleeding in the mouth, gums, and nose, and rash.
- Dark, painful changes at the injection site (skin necrosis).
- Spinal hematoma after spinal or epidural anesthesia, leading to neurological damage of varying severity, including transient or long-term paralysis.
- Severe allergic reactions (fever, chills, shortness of breath, swelling of the larynx, feeling of loss of consciousness, sweating, hives, itching, decreased blood pressure, heat strokes, loss of consciousness, bronchospasm, laryngeal edema).
Other side effects:
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- Bruising, skin discoloration, itching, and pain at the injection site.
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Mild and transient increase in liver enzymes visible in laboratory tests.
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Mild and transient decrease in platelet count (thrombocytopenia type I) visible in laboratory tests.
- Mild skin allergic reactions: rash, hives, skin streaks.
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- Increased potassium levels in the blood visible in laboratory tests.
Long-term use of Zibor or similar medicines may cause osteoporosis. The frequency of occurrence is not known.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, inform your doctor. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring, Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, PL-02 222 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, Fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl.
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help gather more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Zibor
Keep the medicine out of sight and reach of children.
Do not store above 25°C. Do not freeze.
Do not use this medicine if you notice:
- that the protective packaging has been opened.
- that the protective packaging has been damaged.
- that the contents of the pre-filled syringe are cloudy.
- that it contains small particles.
After opening the packaging containing the Zibor pre-filled syringe, use it immediately.
Expiration date
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date stated on the carton after "Expiration date".
The expiration date refers to the last day of the given month.
Disposal
Single-dose container.
Used pre-filled syringes should be disposed of in a sharps container.
Used pre-filled syringes should not be kept.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Zibor contains
- The active substance is bemiparin sodium.
- The other ingredient is water for injections.
What Zibor looks like and contents of the pack
Zibor is a colorless or slightly yellowish, clear solution, without visible impurities.
Zibor 25,000 anti-Xa IU/mL is available in packs containing 2, 10, 30, and 100 pre-filled syringes containing 0.2 mL, 0.3 mL, or 0.4 mL of the solution for injection.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Each 0.2 mL pre-filled syringe contains a dose of 5,000 anti-Xa IU bemiparin sodium.
Each 0.3 mL pre-filled syringe contains a dose of 7,500 anti-Xa IU bemiparin sodium.
Each 0.4 mL pre-filled syringe contains a dose of 10,000 anti-Xa IU bemiparin sodium.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
GINELADIUS, S.L.
Rufino González 50,
28037 Madrid, Spain
+(34) 91 375 62 30
Manufacturer
Laboratorios Farmacéuticos ROVI, S.A.
Julián Camarillo, 35
28037 Madrid, Spain
ROVI Pharma Industrial Services, S.A.
Julián Camarillo Nº 35
28037 Madrid, Spain
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Ivor:Italy, Portugal.
Zibor:Czech Republic, Estonia, Ireland, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, United Kingdom.
Phivor:Spain.
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterLaboratorios Farmaceuticos Rovi, S.A. Rovi Pharma industrial Services, S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to ZiborDosage form: Powder, 500 IUActive substance: antithrombin IIIManufacturer: Instituto Grifols S.A.Prescription not required
Alternatives to Zibor in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Zibor in Spain
Alternative to Zibor in Ukraine
Online doctors for Zibor
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Zibor – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














