
Anbinex

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Anbinex

How to use Anbinex
LEAFLET INCLUDED IN THE PACKAGING: INFORMATION FOR THE USER
Anbinex
50 IU/ml; 500 IU and 1000 IU
Powder and solvent for solution for infusion. Antithrombin III humanum densatum
You should read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor, pharmacist, or nurse
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What is Anbinex and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Anbinex
- 3. How to use Anbinex
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Anbinex
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Anbinex and what is it used for
Anbinex is
an anticoagulant medicine,
belonging to
the class of parenteral anticoagulants.
This medicine is used to treat hereditary antithrombin deficiency, to prevent
the formation of deep vein thrombosis and thromboembolic changes in other blood vessels.
If there are indications for this, it is also administered during surgical procedures and during the postpartum period. In some cases, it may be administered in combination with heparin.
Anbinex is also used in acquired antithrombin deficiency.
2. Important information before using Anbinex
When not to use Anbinex
If the patient is allergic to antithrombin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
You should read the important information at the end of this section.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to use Anbinex, you should discuss it with your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
As with other intravenously administered products, allergic reactions are possible. During infusion, the patient should be closely monitored due to the risk of side effects. If symptoms of hypersensitivity occur, including rash, generalized urticaria, feeling of pressure in the chest, wheezing (difficulty breathing), hypotension, and symptoms of anaphylaxis, the patient should immediately inform their doctor.
In the process of producing medicines from human blood or plasma, certain procedures are used to prevent the transmission of infection to treated patients. These procedures include:
- detailed selection of blood and plasma donors, the purpose of which is to exclude donors who may be a source of infection;
- testing each donation and pool of collected plasma for the presence of viruses/infectious agents;
- including stages in the plasma processing process during which viruses can be inactivated or eliminated.
Despite the use of these preventive measures, it is not possible to completely exclude the possibility of transmitting an infection if medicines produced from human blood or plasma are administered. This also applies to unknown or newly discovered viruses and other pathogens.
It is considered that the preventive measures taken are effective against enveloped viruses, such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, and non-enveloped hepatitis A virus. The above measures may have limited value in the case of non-enveloped viruses, such as parvovirus B19.
Infection with parvovirus B19 can be particularly dangerous for pregnant women (fetal infection) and for people with weakened immunity or suffering from certain types of anemia (e.g., sickle cell anemia, hemolytic anemia).
For patients who regularly receive antithrombin from plasma, the doctor may recommend vaccination against hepatitis A and B.
It is strongly recommended that each time Anbinex is administered to a patient, the patient's name and batch number of the product should be recorded, so that the patient can be linked to the batch of the medicine.
Anbinex and other medicines
You should tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take.
Concomitant administration of antithrombin with therapeutic doses of heparin increases the risk of bleeding. The effect of antithrombin is significantly enhanced by heparin. Concomitant administration of heparin to patients with an increased risk of bleeding should be carefully monitored clinically and biologically.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks she may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, she should consult her doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Anbinex should be used during pregnancy and lactation only if it is clearly indicated. The decision should be made after considering the fact that during pregnancy, there is an increased risk of thromboembolic events.
Driving and using machines
Anbinex has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
Anbinex contains sodium
Anbinex 500 IU contains 1.45 mmol (33.35 mg) of sodium in 10 ml.
Anbinex 1000 IU contains 2.90 mmol (66.7 mg) of sodium in 20 ml.
This should be taken into consideration for patients on a controlled sodium diet.
3. How to use Anbinex
Anbinex for intravenous infusion is prepared by a doctor or nurse.
Use in children and adolescents
Due to the lack of sufficient data, the use of Anbinex in children under 6 years of age is not recommended.
Frequency of administration
The doctor will determine the frequency of administration of Anbinex and the intervals between doses.
Duration of treatment
The doctor will determine the duration of treatment with Anbinex.
In case of overdose of Anbinex
No cases of overdose have been reported.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Anbinex can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
In rare cases, an increase in body temperature and allergic or anaphylactic reactions such as facial flushing, rash, increased or decreased blood pressure, tachycardia (rapid heart rate), chills, wheezing, and swelling, as well as generalized reactions (including chest pain, fever, headache, nausea, and/or vomiting), which in some cases led to the development of severe anaphylactic shock (including shock).
In rare cases, an increase in body temperature has been observed.
A list of side effects in a tabular system.
The frequency of occurrence was assessed using the following criteria:
- very common (> 1/10),
- common (> 1/100, <1>
- uncommon (> 1/1000, <1>
- rare (> 1/10 000, <1>
- very rare (<1>
- frequency not known (frequency cannot be estimated from available data)
| MedDRA System Organ Class (SOC) | Adverse Reaction | Frequency of Occurrence |
| Immune system disorders | Allergic reactions, hypersensitivity | Uncommon |
| Psychiatric disorders | Anxiety | Uncommon |
| Nervous system disorders | Headache, lethargy | Uncommon |
| Cardiovascular disorders | Tachycardia | Uncommon |
| Vascular disorders | Facial flushing, decreased blood pressure, shock | Uncommon |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | Feeling of pressure in the chest and wheezing | Uncommon |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Nausea, vomiting | Uncommon |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Angioedema, generalized urticaria, rash | Uncommon |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | Pain or feeling of burning at the injection site, chills | Uncommon |
| Fever | Rare |
You should inform your doctor if you experience any of these symptoms.
Information on safety measures to prevent the transmission of infectious agents - see section 2.
If you experience any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, you should inform your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
Side effects
can be
reported
directly
to
the Department
of Monitoring
of Adverse
Reactions
of Medicinal
Products,
Medical
Devices,
and Biocidal
Products:
Aleje Jerozolimskie 181C,
02-222 Warsaw,
Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301,
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309,
e-mail: [email protected]
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Anbinex
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date (EXP) stated on the label. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
Do not store above 30°C. Do not freeze.
After reconstitution:
Stability studies indicate a shelf-life of up to 12 hours at 25°C. From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately. If the product is not used after reconstitution, it can be stored for no more than 24 hours at 2°C - 8°C, but only if the user takes responsibility for this and the preparation of the solution was carried out in accordance with the principles of asepsis.
The solution should be clear and slightly opalescent.
Do not use this medicine if you notice particles or sediment.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Anbinex contains
The active substance of the medicine is human antithrombin.
The vial with powder contains 500 IU or 1000 IU of human antithrombin.
After reconstitution, the product contains 50 IU/ml (500 IU/10 ml or 1000 IU/20 ml) of human antithrombin.
The other ingredients are: D-mannitol, sodium chloride, and sodium citrate.
The ampoule-syringe contains 10 ml or 20 ml of water for injections.
For more information on ingredients, see section 2.
What Anbinex looks like and contents of the pack
The packaging contains a vial with a white, hygroscopic, brittle solid substance or powder and an ampoule-syringe with water for injections.
Each Anbinex 500 IU packaging contains a vial with 500 IU of human antithrombin (powder for solution for infusion) and 1 ampoule-syringe with 10 ml of water for injections (solvent).
Each Anbinex 1000 IU packaging contains a vial with 1000 IU of human antithrombin (powder for solution for infusion) and 1 ampoule-syringe with 20 ml of water for injections (solvent).
A set for preparing the solution is attached to each Anbinex packaging, including a connector for the vial and a microfilter.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Instituto Grifols, S.A.
Poligono Levante, c/Can Guasch, 2Parets del Vallès
08150 Barcelona, SPAIN.
To obtain more detailed information, you should contact the representative of the marketing authorization holder.
Grifols Polska Sp. z o. o.
Ul. Grzybowska 87, 00-844 Warsaw
Tel.: +48 22 5040641
Date of last update of the leaflet:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals:
In hereditary deficiency, the dosage and duration of treatment should be adjusted individually for each patient, depending on the family history, including cases of thromboembolic changes, currently occurring clinical risk factors, and laboratory test results.
The dosage and duration of substitution treatment in acquired antithrombin deficiency depend on the level of antithrombin in plasma, the presence of symptoms indicating accelerated consumption, the underlying disease, and the severity of clinical symptoms. The size of the doses and the frequency of their administration should always be adjusted individually for each patient, depending on the clinical effects.
Antithrombin doses are expressed in international units (IU), in accordance with current WHO standards. Antithrombin activity in plasma can be expressed as a percentage (relative to normal plasma activity) or in international units (according to the international standard for plasma antithrombin).
One international unit (IU) of antithrombin activity corresponds to the average amount of antithrombin in 1 ml of normal human plasma. The calculation of the required dose of antithrombin is based on the empirical observation that the administration of 1 IU of antithrombin per kg of body weight increases the antithrombin activity in plasma by approximately 1.1% to 1.6%.
The initial dose is calculated based on the following formula:
Required number of units = body weight (kg) x (100 - initial antithrombin activity (in percent) x 0.8
In the initial phase of treatment, the desired level of antithrombin activity should be determined, depending on the clinical situation. After determining the indications for the use of antithrombin, a dose should be administered to achieve the desired level of antithrombin activity, and then its level should be maintained to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.
The dose should be calculated and monitored based on laboratory measurements of antithrombin activity in plasma. Measurements should be performed at least twice a day, and when the patient's condition stabilizes - once a day; always immediately before the next administration of the medicine. It should be remembered that in the case of severe clinical conditions, such as disseminated intravascular coagulation, the half-life of antithrombin may be significantly shortened. The correction of the dose size should be made, taking into account both the rate of antithrombin consumption, determined based on laboratory measurements, and the clinical course. Antithrombin activity should be maintained above 80% of normal throughout the treatment period or adjusted accordingly, when clinical symptoms indicate that a different level may be more effective.
In the treatment of hereditary deficiency, the initial dose is 30 - 50 IU/kg of body weight.
Then, the size of the dose, the frequency of administration, and the duration of treatment depend on the biological response in a given clinical situation.
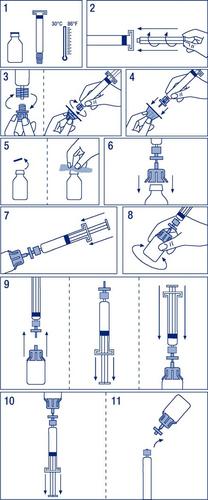
Instructions for preparing the medicine for use
- 1. Warm the vials to a temperature not exceeding 30°C (Figure 1).
- 2. Attach the plunger to the ampoule-syringe with the solvent (Figure 2).
- 3. Remove the filter from the packaging. Remove the plastic cover from the end of the ampoule-syringe and attach the filter (Figure 3).
- 4. Remove the connector for the vial and connect the ampoule-syringe with the filter (Figure 4).
- 5. Remove the plastic cap from the vial and disinfect the exposed rubber stopper with a disinfectant (Figure 5).
- 6. Pierce the stopper in the vial with the needle of the connector (Figure 6).
- 7. Inject the entire solvent into the vial (Figure 7).
- 8. Gently shake the vial until the powder is dissolved (Figure 8).
- 9. Disconnect the ampoule-syringe with the filter from the vial with the connector. Pull the plunger to draw in air in an amount equal to the volume of the solvent. Reconnect the syringe with the attached filter to the vial with the connector (Figure 9).
- 10. Turn the vial upside down and aspirate the solution into the ampoule-syringe (Figure 10).
- 11. Disconnect the ampoule-syringe from the filter and vial and administer slowly intravenously at a rate not exceeding 0.08 ml/kg/min (Figure 11).
Do not leave the unused product for later use.
Do not reuse the administration set.
When using the infusion set, check its compatibility with the ampoule-syringe. Use the appropriate adapters to ensure proper administration of the product.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterInstituto Grifols, S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to AnbinexDosage form: Powder, 1000 IUActive substance: antithrombin IIIManufacturer: Instituto Grifols S.A.Prescription not requiredDosage form: Powder, 50 IU/ml; 500 IUActive substance: antithrombin IIIManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AGPrescription not requiredDosage form: Powder, 50 IU/mlActive substance: antithrombin IIIManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AGPrescription not required
Alternatives to Anbinex in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Anbinex in Ukraine
Alternative to Anbinex in Spain
Online doctors for Anbinex
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Anbinex – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














