

Regiocit

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Regiocit

How to use Regiocit
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: information for the user
Regiocit, solution for hemofiltration
Citrate, sodium, chloride ions
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains
important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
- In case of any doubts, you should consult a doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- If the patient experiences any adverse reactions, including any adverse reactions not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Regiocit and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Regiocit
- 3. How to use Regiocit
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Regiocit
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Regiocit and what is it used for
This medicine is a solution for hemofiltration, preventing blood clotting during continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT), a type of dialysis procedure. The medicine is used in critically ill patients, especially when the use of a medicine usually used to prevent blood clotting (heparin) is not appropriate. Citrate ions provide an anticoagulant effect by binding calcium present in the blood.
2. Important information before using Regiocit
This medicine should not be used in the case of:
- allergy to the active substances or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6),
- severe liver dysfunction,
- severe blood flow disorder in the muscles.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to use this medicine, you should discuss it with your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This medicine is not intended for direct intravenous infusion. It should only be used with a device that allows continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) to be performed, a type of dialysis used in critically ill patients with renal failure. The CRRT device must be adapted to citrate ions as an anticoagulant.
Regiocit can be warmed to a temperature of 37°C to increase patient comfort. Warming the solution before use should only be done using a dry heat source. The solution should not be warmed in water or in a microwave oven. Before administration, Regiocit should be visually inspected for the presence of solid particles and changes in color. It should only be used if the solution is clear, free from visible solid particles, and the seal is intact.
If the protective cap or the bag with the solution is damaged, the solution may be contaminated and should not be used. Treatment also involves the administration of other fluids by infusion. To ensure compatibility with the medicine, it may be necessary to adjust the composition or rate of administration of these fluids.
The doctor will closely monitor the patient's hemodynamic status, fluid balance, glucose level, electrolyte balance, and acid-base balance before starting the procedure and during it.
The concentration of sodium, magnesium, potassium, phosphates, and calcium will be closely monitored.
Any necessary corrections will be made in the treatment.
Regiocit does not contain calcium. The use of Regiocit may lead to a decrease in blood calcium levels (hypocalcemia).
Regiocit does not contain magnesium. The use of Regiocit may cause a decrease in blood magnesium levels (hypomagnesemia). Blood magnesium levels will be closely monitored and magnesium infusion may be necessary.
Regiocit does not contain glucose. The administration of Regiocit may lead to a decrease in blood glucose levels (hypoglycemia). Blood glucose levels should be regularly monitored.
Regiocit does not contain potassium. The potassium level in the serum must be monitored before and during treatment.
The doctor will pay particular attention to the rate of citrate ion infusion. Too high a dose of citrate ions can cause a decrease in blood calcium levels and an increase in blood pH, which can lead to neurological and cardiac complications.
A high blood pH value can be corrected by adjusting the dialysis settings and infusing 0.9% sodium chloride solution after the filter or changing the composition of the CRRT solution. Low calcium levels can be corrected by infusing calcium ions.
The doctor should pay particular attention to patients with liver failure or shock.
In these patients, there may be a significant decrease in citrate metabolism, leading to citrate accumulation and a decrease in blood pH. The doctor will decide whether the patient's treatment needs to be changed. In the case of an increased ratio of total calcium to ionized calcium above 2.3, the rate of citrate buffer administration should be reduced or discontinued.
In the case of using Regiocit in patients with liver dysfunction, it is essential to frequently monitor pH, electrolytes, the ratio of total calcium to ionized calcium, and systemic ionized calcium to avoid electrolyte and acid-base balance disorders. The medicine should not be used in patients with severe liver dysfunction.
In the case of excessive fluid volume in the body (hypervolemia), the net ultrafiltration rate prescribed for the CRRT device can be increased and/or the rate of administration of other fluids can be reduced.
In the case of insufficient fluid volume in the body (hypovolemia), the net ultrafiltration rate prescribed for the CRRT device can be reduced and/or the rate of administration of other fluids can be increased.
Regiocit is hypo-osmolar/hypotonic compared to standard CRRT substitution fluids and should be used with caution in patients with traumatic brain injury, brain edema, or increased intracranial pressure.
It is essential to follow the instructions for use. Improper use of access ports or other fluid restriction devices can lead to improper weight loss in the patient and trigger device alarms. Continuing treatment without removing the cause of these events can cause patient injury or death.
Regiocit and other medicines
You should tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse about all medicines the patient is currently taking or has recently taken, including those available without a prescription. This is because during dialysis therapy, the levels of other medicines may decrease. The attending doctor will decide whether changes in the dosing of medicines taken by the patient are necessary.
In particular, you should inform your doctor about the use of medicines containing any of the following ingredients:
- vitamin D and other medicines containing calcium, as well as medicines containing calcium chloride or calcium gluconate, as they may increase the risk of high blood calcium levels (hypercalcemia) and reduce the anticoagulant effect;
- sodium bicarbonate, as it may increase blood bicarbonate levels.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Fertility:
It is not expected that the medicine will affect fertility, as sodium, chloride, and citrate occur naturally in the body.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding:
There are no documented clinical data on the use of this medicine during pregnancy and breastfeeding. This medicine should only be administered to pregnant and breastfeeding women if there is a clear need.
Driving and using machines
It is not known whether the medicine affects the ability to drive and use machines.
3. How to use Regiocit
For intravenous use. This medicine is intended for use in hospitals and should only be administered by healthcare professionals. The administered volume, and thus the dose of the medicine, depends on the patient's condition. The volume of the dose will be determined by the attending doctor.
Recommended flow rates of the medicine in adult and adolescent patients:
- in continuous veno-venous hemofiltration at 1-2.5 l/h with a blood flow rate of 100 to 200 ml/min.
- in continuous veno-venous hemodiafiltration at 1-2 l/h with a blood flow rate of 100 to 200 ml/min.
Use in elderly patients:
The recommended flow rates are the same as for adult and adolescent patients.
Use in children:
In newborns and small children (from birth to 23 months), the target dose of Regiocit should be 3 mmol of citrate ions per liter of blood flowing in continuous hemofiltration or hemodiafiltration. In children (from 2 to 11 years), the dose should be adjusted according to the patient's body weight and blood flow rate.
Liver dysfunction or shock:
In liver dysfunction or shock, the initial dose of citrate ions should be reduced.
Instructions for use
Regiocit will be administered to the patient in a hospital. The doctor is familiar with the administration of Regiocit. The instructions for use are attached at the end of this leaflet.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although they may not occur in everyone.
The doctor or nurse will regularly monitor the patient's blood parameters to detect any adverse reactions. The use of this solution may cause the following side effects:
Common: may occur in up to 1 in 10 people
- acid-base balance disorder in the blood,
- electrolyte balance disorders in the blood (e.g., decreased levels of calcium, sodium, magnesium, potassium, and/or phosphates in the blood or increased levels of calcium in the blood).
Unknown: frequency cannot be determined from available data
- fluid balance disorders in the body (dehydration, fluid retention in the body);
- decreased blood pressure*;
- nausea*, vomiting*;
- muscle cramps*.
* Adverse reactions more related to dialysis therapy than to the medicine itself.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, you should inform your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, more information can be collected on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Regiocit
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
There are no special recommendations for storing the medicine.
Do not freeze.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the label and packaging.
The expiry date refers to the last day of the stated month.
Do not use this medicine if you notice damage to the product or the presence of solid particles in the solution.
The solution can be disposed of in the sewage system without harm to the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Regiocit contains
Composition:
Sodium chloride
5.03 g/l
Sodium citrate
5.29 g/l
The active substances of the medicine are:
Sodium ions, Na
140 mmol/l
Chloride ions, Cl
86 mmol/l
Citrate ions, C6H5O7
18 mmol/l
Theoretical osmolality: 244 mOsm/l
pH ≈ 7.4
Other ingredients are:
Diluted hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment) E 507
Water for injections
What Regiocit looks like and what the packaging contains
This medicine is a clear and colorless hemofiltration solution in a single-chamber bag made of multi-layered film containing polyolefins and elastomers. The solution is sterile and free from bacterial endotoxins. Each bag contains 5000 ml of solution and is placed in a transparent protective bag. Each box contains two bags and one patient leaflet.
Marketing authorization holder
Vantive Belgium SRL
Boulevard d’Angleterre 2
1420 Braine-l’Alleud
Belgium
Manufacturer
Bieffe Medital S.p.A.
Via Stelvio 94
23035 Sondalo (SO)
Italy
or
Vantive Manufacturing Limited,
Moneen Road,
Castlebar
County Mayo
F23 XR63
Ireland
To obtain more detailed information, you should contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder.
This medicine is authorized for distribution in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Austria, Belgium, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, United Kingdom (Northern Ireland): Regiocit
Bulgaria: Regiocit (Региоцит)
Date of last revision of the leaflet: September 2024
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Dosing
The rate of Regiocit administration depends on the target citrate dose and the prescribed blood flow rate. When prescribing Regiocit, the rates of fluid removal and other therapeutic fluids, the requirements for fluid removal from the patient, additional fluid administration, and the desired acid-base and electrolyte balance should be taken into account. Regiocit should only be prescribed and its administration (dose, infusion rate, and total volume) should be determined by a doctor with experience in intensive care and CRRT.
The rate of Regiocit infusion before the filter should be adjusted in relation to the blood flow rate to achieve a target citrate concentration in the blood of 3 to 4 mmol/l. When prescribing Regiocit, the rates of fluid removal and other therapeutic fluids, the requirements for fluid removal from the patient, additional fluid administration, and the desired acid-base and electrolyte balance should be taken into account.
Citrate acts as a buffer source (due to its conversion to bicarbonate). The rate of Regiocit infusion must take into account the rate of buffer administration from other sources (e.g., dialysate and/or substitution fluid). Regiocit must be used with a dialysate/substitution fluid with an appropriate bicarbonate concentration.
A separate calcium infusion is always required. Calcium infusion should be adjusted or discontinued according to the doctor's recommendation in case of anticoagulation.
Monitoring of ionized calcium (iCa) levels after filtration, iCa in systemic blood, and total calcium levels in blood, in combination with other laboratory and clinical parameters, is necessary to determine the appropriate dosing of Regiocit based on the desired degree of anticoagulation.
The levels of sodium, magnesium, potassium, and phosphates should be regularly monitored and supplemented if necessary.
Regiocit flow rates in adults and adolescents:
- in continuous veno-venous hemofiltration at 1-2.5 l/h with a blood flow rate of 100 to 200 ml/min;
- in continuous veno-venous hemodiafiltration at 1-2 l/h with a blood flow rate of 100 to 200 ml/min.
Children and adolescents:
In newborns and small children (from birth to 23 months), the target dose of Regiocit should be 3 mmol of citrate ions per liter of blood flowing in continuous hemofiltration or hemodiafiltration. In children (from 2 to 11 years), the dose should be adjusted according to the patient's body weight and blood flow rate.
Special patient groups:
There is no need for special dose modification in elderly patients compared to adult patients.
Liver dysfunction or shock:
Dose reduction may be necessary in patients with mild or moderate liver dysfunction (e.g., ≤12 on the Child-Pugh scale).
In the case of liver dysfunction (including, for example, liver cirrhosis), the initial citrate dose should be reduced due to the risk of inadequate metabolism. Frequent monitoring of citrate accumulation is recommended. Regiocit should not be administered to patients with severe liver dysfunction or shock with hypoperfusion (e.g., septic shock and lactic acidosis), due to reduced citrate metabolism.
Overdose
Inadequate administration of too large a volume of substitution fluid may lead to overdose, which can be life-threatening. Overdose may result in pulmonary edema and congestive heart failure due to excess fluid in the body, as well as hypocalcemia and metabolic alkalosis due to excess citrate in relation to blood flow. These disorders should be immediately corrected by discontinuing the substitution fluid and administering calcium intravenously. Cautious calcium supplementation may reverse the effects of overdose. The risk can be minimized by close monitoring during treatment.
In patients with impaired citrate metabolism (liver dysfunction or shock), overdose may manifest as citrate accumulation, metabolic acidosis, total hypercalcemia, and hypocalcemia with a decreased ionized calcium level, along with an increased ratio of total calcium to ionized calcium.
Regiocit administration should be discontinued or reduced.
To correct metabolic acidosis, bicarbonate should be supplemented. Continuous renal replacement therapy can be continued without anticoagulation or alternative anticoagulation methods can be considered.
Preparation and/or use
The solution can be disposed of in the sewage system without harm to the environment.
You should follow the instructions for use below:
In the entire process of preparing and administering the medicine to the patient, aseptic technique should be used.
The medicine should be removed from the protective packaging immediately before use. Use only if the protective packaging is not damaged, all seals are intact, and the solution is clear. Squeeze the bag firmly to check its integrity. If a leak is detected, the solution should be discarded immediately, as its sterility cannot be guaranteed. The solution should be used immediately after opening the packaging to avoid microbial contamination.
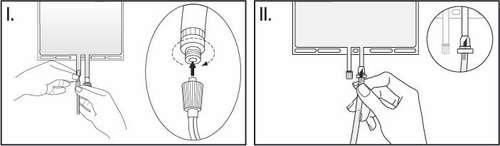
- I. When using luer-type connectors, the cap should be removed by twisting and pulling. Connect the male luer lock on the pre-filter line to the female luer on the bag by pushing and twisting. Ensure that the connectors are fully seated, then tighten. The connector is now open. Ensure that the fluid flows freely (see Figure I below).
When the pre-filter line is disconnected from the luer connector, the connector will close, stopping the flow of solution. The luer connector is needle-free and can be disinfected with disinfectants.
II. When using an injection port (or spike), the sliding cap should be removed.
The injection port can be disinfected with disinfectants. Insert the spike through the rubber septum. Ensure that the fluid flows freely (see Figure II below).
Before adding any substances or medicines, ensure that they are soluble and stable in Regiocit and that the pH range is suitable for them. Do not add any components with known or suspected incompatibility.
Read the instructions for the use of the added medicine and other relevant literature.
Do not use if, after addition, a change in color or precipitation occurs or if insoluble complexes or crystals are detected. After adding additional components, the solution should be thoroughly mixed. Additional components must always be introduced and mixed before connecting the bag with the solution to the extracorporeal circuit.
The solution is intended for single use only. Any unused solution should be discarded.
- Country of registration
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterBieffe Medital S.p.A. Vantive Manufacturing Limited
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to RegiocitDosage form: Solution, 9 mg/mlActive substance: sodium chloridePrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 100 mg/mlActive substance: dextranManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi Italia S.r.L.Prescription not requiredDosage form: Concentrate, -Active substance: electrolytes in combination with other drugsManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi Norge ASPrescription not required
Alternatives to Regiocit in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Regiocit in Ukraine
Alternative to Regiocit in Spain
Online doctors for Regiocit
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Regiocit – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














