
PRISMASOL 2 mmol/l POTASSIUM, SOLUTION FOR HEMODIALYSIS AND HEMOFILTRATION


How to use PRISMASOL 2 mmol/l POTASSIUM, SOLUTION FOR HEMODIALYSIS AND HEMOFILTRATION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Leaflet: information for the user
Prismasol 2 mmol/lPotassium solution for hemodialysis and hemofiltration.
Calcium chloride, dihydrate / Magnesium chloride hexahydrate / Glucose monohydrate / 90% lactic acid solution / Sodium chloride / Potassium chloride / Sodium hydrogen carbonate
Read the entire leaflet carefully before starting to use this medication, as it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, as you may need to read it again.
- If you have any doubts, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- If you experience side effects, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the leaflet:
- What is Prismasol and what is it used for.
- What you need to know before starting to use Prismasol.
- How to use Prismasol
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Prismasol
- Package contents and additional information
1. What is Prismasol and what is it used for
Prismasol contains the following active ingredients: calcium chloride, dihydrate; magnesium chloride, hexahydrate; glucose monohydrate, 90% lactic acid solution; sodium chloride; potassium chloride; and sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Prismasol is used in the treatment of renal insufficiency as a solution for hemofiltration or continuous hemodiafiltration (as a replacement for fluid loss produced by the passage of blood through the filter) and continuous hemodialysis or hemodiafiltration (the blood passes through one side of the dialysis membrane while the dialysis solution passes through the other side of the same membrane).
Prismasol can also be used in cases of poisoning with dialyzable or filterable substances.
Prismasol 2 mmol/l potassium is especially indicated in patients with a tendency to hyperpotasemia (high potassium levels in the blood)
2. What you need to know before starting to administer Prismasol
Do not use Prismasol 2 mmol/l potassium in case of:
- allergy to any of the active ingredients or to any of the other components (listed in section 6),
- low potassium levels in the blood (hypokalemia),
- high bicarbonate concentration in the blood (metabolic alkalosis).
The presence of corn-derived antigen in Prismasol cannot be excluded.
Do not use hemofiltration or dialysis treatment in case of:
- renal insufficiency with pronounced hypercatabolism (abnormally increased catabolism), if uremic symptoms (symptoms caused by high urea levels in the blood) cannot be corrected with hemofiltration.
- insufficient blood pressure in the vascular access.
- systemic anticoagulation (reduced blood coagulation) if there is a high risk of bleeding.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before starting to use Prismasol.
The solution can only be used under the supervision of a competent doctor in renal insufficiency treatments using hemofiltration, hemodiafiltration, and continuous hemodialysis techniques.
Before and during treatment, your blood condition will be monitored, for example, acid-base balance and electrolyte concentrations (salts in the blood) will be monitored, as well as all fluids administered (intravenous perfusion) and produced (diuresis), including those not directly related to treatment.
Potassium levels in the blood should be closely monitored, especially if you are diabetic.
Other medications and Prismasol
Inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or may have taken other medications.
The blood concentration of some other medications may be reduced during treatment. Your doctor will decide if your medication needs to be changed.
In particular, inform your doctor in the following cases:
- digitalis medications (for the treatment of certain heart failures), as the risk of cardiac arrhythmias (irregular or rapid heartbeats) induced by these medications increases during hypokalemia (low potassium levels in the blood).
- Vitamin D and calcium-containing medications, as they may increase the risk of hypercalcemia (elevated calcium levels in the blood).
- any sodium hydrogen carbonate supplement (or other buffered source), as it may increase the risk of metabolic alkalosis (excess bicarbonate in the blood).
- when citrate is used as an anticoagulant (as a protector in dialysis equipment), it may reduce plasma calcium levels.
Pregnancy and Lactation
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medication.
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, your doctor will decide if you should be administered Prismasol.
Driving and using machines
There is no data to suggest that Prismasol affects the ability to drive or use machines.
3. How to use Prismasol
Follow the administration instructions for this medication exactly as indicated by your doctor or pharmacist. If in doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
The volume of Prismasol to be administered will depend on your clinical conditions and the desired fluid balance. Therefore, the dose volume will depend on your doctor's judgment.
Route of administration: intravenous and hemodialysis.
If you think you have used more Prismasol than you should:
Your fluid, acid-base, and electrolyte balance must be carefully monitored.
In the unlikely event of an overdose, your doctor will take the necessary corrective measures to adjust the dose.
An overdose may cause:
- fluid overload in the blood,
- increased bicarbonate levels in the blood (metabolic alkalosis),
- and/or reduced salt levels in the blood (hypophosphatemia, hypokalemia).
Overdose could lead to serious consequences such as congestive heart failure, electrolyte or acid-base imbalance.
For instructions on use, see the section "This information is intended only for healthcare professionals".
If you have any further questions on the use of this medication, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medications, this medication can cause side effects, although not everyone will experience them.
The following side effects have been reported:
Unknown: frequency cannot be estimated from available data
- changes in blood salt levels (electrolyte imbalances such as hypophosphatemia or hypokalemia)
- elevated plasma bicarbonate concentration (metabolic alkalosis) or reduced plasma bicarbonate concentration (metabolic acidosis)
- abnormally high or low water volume in the body (hyper or hypovolemia)
- abnormally high glucose levels in the blood (hyperglycemia)
- nausea
- vomiting
- muscle cramps
- hypotension (low blood pressure)
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are not listed in this leaflet.
You can also report them directly through the Spanish Medication Monitoring System for Human Use: www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Storage of Prismasol
Keep this medication out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not store at a temperature below +4°C.
Do not use this medication after the expiration date indicated on the label and packaging after CAD. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
The chemical and physical stability of the reconstituted solution has been demonstrated for 24 hours at a temperature of +22°C. If the solution is not used immediately, the storage time and conditions before use are the responsibility of the user and should not exceed 24 hours, including the duration of treatment.
Medications should not be disposed of through wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medications you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
(PVC FORMAT WITH BREAKABLE VALVE)
What PRISMASOL contains
The active principles are:
Before reconstitution:
1000 ml of Electrolyte Solution (Small Compartment A) contains:
Calcium chloride dihydrate 5.145 g
Magnesium chloride hexahydrate 2.033 g
Glucose 22.000 g
(S)-Lactic acid 5.400 g
1000 ml of buffer solution (Large Compartment B) contains:
Sodium chloride 6.450 g
Sodium hydrogen carbonate 3.090 g
Potassium chloride 0.157 g
After reconstitution:
The solution from Compartment A (250 ml) and Compartment B (4750 ml) is mixed to produce a reconstituted solution (5000 ml) with the following composition:
mmol/l | mEq/l | |
Calcium Ca2+ | 1.75 | 3.50 |
Magnesium Mg2+ | 0.50 | 1.00 |
Sodium Na+ | 140.00 | 140.00 |
Chloride Cl- | 111.50 | 111.50 |
Lactate | 3.00 | 3.00 |
Hydrogen carbonate HCO3- | 32.00 | 32.00 |
Potassium K+ | 2.00 | 2.00 |
Glucose | 6.10 | |
Theoretical osmolality: | 297 mOsm/l |
The other components are:carbon dioxide (E-290), water for injectable preparations.
pH of the reconstituted solution: 7.0 – 8.5
Product appearance and container contents
Prismasol is presented in a bicompartmental bag, containing the small compartment A with the electrolyte solution and the large compartment B with the buffer solution. The final reconstituted solution is obtained after breaking the breakable valve and mixing both solutions. The reconstituted solution is transparent and slightly yellow. Each bag (A+B) contains 5000 ml of solution for hemodialysis and hemofiltration. The bag is covered by a transparent overbag.
Each box contains two bags and a leaflet.
Marketing authorization holder:
Vantive Belgium SRL
Boulevard d´Angleterre 2
1420 Braine-l´Alleud
Belgium
Manufacturer:
Bieffe Medital S.p.A.
Via Stelvio 94
23035 Sondalo (SO)
Italy
Or
Vantive Manufacturing Limited
Moneen Road,
Castlebar
County Mayo
F23 XR63
Ireland
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Germany, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Slovakia, Slovenia, Estonia, Spain, Finland, France, Greece, Netherlands, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Sweden, United Kingdom (Northern Ireland): Prismasol 2
Further information about this medicinal product can be obtained from the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Vantive Health, S.L.
Polígono industrial sector 14
C/ Pouet de Camilo nº2
46394 Ribarroja del Turia
Valencia
Spain
Date of last revision of this leaflet: 03/2018
Detailed and updated information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.es
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals
Prismasol 2 mmol/l Potassium solution for hemodialysis and hemofiltration
Precautions
The instructions for use and handling of Prismasol must be followed accurately.
The solutions from the two compartments must be mixed before use.
The use of contaminated hemofiltration and hemodialysis solutions can cause sepsis, shock, and conditions that can lead to death.
Prismasol can be heated to 37 °C to improve patient comfort. The heating of the solution before use must be done before reconstitution, only with dry heat. The solutions must not be heated in water or in the microwave. The solution must be visually inspected before administration to detect the presence of particles and any possible color change, when the solution and container allow it. Do not administer if the solution is not transparent or if the seal is not intact.
Prismasol is a solution that contains potassium. Before and during hemofiltration and hemodialysis, the blood potassium concentration must be monitored. Depending on the potassium concentration in the blood before treatment, hypo- or hyperkalemia may develop.
If hypokalemia occurs, it may be necessary to add potassium and/or administer a dialysate with a higher potassium concentration.
If hyperkalemia occurs once treatment has started, the addition of potassium sources that affect concentrations should be assessed. When the solution is used as a replacement solution, the perfusion rate should be reduced and it should be confirmed that the desired potassium concentration has been achieved. If hyperkalemia is not resolved, perfusion should be stopped immediately.
If hyperkalemia develops when the solution is used as a dialysate, it may be necessary to administer a potassium-free dialysate to increase potassium elimination.
The concentration of inorganic phosphates should be measured regularly. In the event that the levels of inorganic phosphate in the blood are low, it should be restored. A phosphate concentration of up to 1.2 mmol/l can be added to the solution. If potassium phosphate is added, the total potassium concentration should not exceed 4 mEq/l (4 mmol/l).
Although no cases of severe hypersensitivity reactions to corn with Prismasol have been reported, solutions containing glucose derived from hydrolyzed corn starch should not be used in patients with a known allergy to corn or corn-derived products.
If signs or symptoms of a suspected hypersensitivity reaction develop, administration should be stopped immediately. Appropriate compensatory therapeutic measures should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Due to the glucose and lactate content of the solution, it may cause hyperglycemia, especially in diabetic patients. Blood glucose levels should be monitored regularly. In the event of hyperglycemia, it may be necessary to administer a dextrose-free replacement solution or dialysate. Other corrective measures may be necessary to maintain the desired blood glucose control.
Prismasol contains sodium hydrogen carbonate (bicarbonate) and lactate (a precursor to bicarbonate), which can affect acid-base balance. If metabolic alkalosis develops or worsens during treatment with the solution, it may be necessary to reduce the administration rate or stop administration.
Before and during treatment, close monitoring of electrolyte and acid-base balance should be performed throughout the procedure.
In the event of fluid imbalance, the clinical situation should be carefully controlled and fluid balance should be corrected as necessary.
Method of administration
Intravenous and for hemodialysis. Prismasol, when used as a replacement solution, is administered within the circuit before the hemofilter (pre-dilution) or after the hemofilter (post-dilution)
Posology
The volume and rate of use of Prismasol will depend on the electrolyte concentration in the blood, acid-base balance, and the patient's overall clinical condition. The administration schedule (dose, perfusion rate, and cumulative volume) of Prismasol should be established by a doctor.
The flow rates used for the replacement solution in hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration are:
Adults: 500 – 3000 ml/hour
The flow rates used for the dialysis solution (dialysate) in continuous hemodialysis and continuous hemodiafiltration are:
Adults: 500 - 2500 ml/hour
Normally, the flow rates used in adults are approximately 2000 to 2500 ml/h, which corresponds to a daily fluid volume of approximately 48 to 60 liters.
Pediatric population
The flow rate ranges for the replacement solution in hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration and for the dialysis solution (dialysate) in continuous hemodialysis are:
Children (from neonates to adolescents up to 18 years of age): 1000 to 2000 ml/h/1.73 m2.
Flow rates of up to 4000 ml/h/1.73 m2 may be necessary, especially in small children (≤10 kg). The absolute flow rate (in ml/h) in the pediatric population should not generally exceed the maximum flow rate in adults.
Handling instructions
The electrolyte solution (small compartment A) is added to the buffer solution (large compartment B) after breaking the breakable valve just before use to obtain the reconstituted solution.
Use only with suitable extracorporeal renal replacement equipment.
Aseptic technique should be followed throughout the handling and administration process to the patient.
Use only if the overbag is intact, all seals are intact, the breakable valve is not broken, and the solution is transparent. Squeeze the bag firmly to ensure there are no leaks. If leaks are observed, discard the solution immediately, as sterility cannot be guaranteed.
The large compartment (B) is equipped with an injection port for adding other medications that may be necessary once the solution is reconstituted. It is the responsibility of the doctor to assess the compatibility of a medication added to Prismasol by checking for any color change and/or precipitation, insoluble complexes, or crystals. Before adding a medication, verify that it is soluble and stable in water at the pH of Prismasol (the pH of the reconstituted solution is between 7.0 and 8.5). Additives may not be compatible. The instructions for use of the added medication should be consulted.
Remove any liquid from the injection port, put the bag in an inverted position, add the medication through the injection port, and mix perfectly. The solution should be administered immediately.The introduction and mixing of additives should always be done before connecting the solution bag to the extracorporeal circuit.
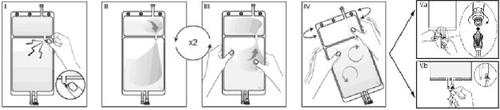
IRemove the overbag from the bag immediately before use and discard any other packaging material. Open the seal by breaking the breakable valve located between the two compartments of the bag. The valve will remain inside the bag. (See figure I below).
IIEnsure that all the liquid from the small compartment A is transferred to the large compartment B. (See figure II below).
IIIRinse twicethe small compartment A by forcing the mixed solution to return to this compartment and then again to the large compartment B (See figure III below).
IVOnce the small compartment A is empty, shake the large compartment B to mix its contents completely. The solution is now ready to use and can be hung on the equipment. (See figure IV below).
VThe dialysis or replacement line can be connected to either of the two access ports.
V.aIf the luer connector is used, remove the plug by a twisting and pulling motion and connect the luer male connector of the dialysis or replacement line to the luer female receptor of the bag by a pressing and twisting motion. Ensure that the connection is secure and tightened. The connection will open. Check that the liquid circulates freely. (See figure Va below).
If the dialysis or replacement line is disconnected from the luer connector, the connector will close and the flow of the solution will stop. The luer port is a needle-free port that can be cleaned.
V.bIf the injection access is used, first remove the cap. The injection port is a port that can be disinfected with a swab. Introduce the spike through the rubber wall. Verify that the solution circulates freely. (See figure Vb below).
The solution should be used immediately after removing the overbag. If not, the reconstituted solution should be used within 24 hours, including the duration of treatment after adding the electrolyte solution to the buffer solution.
The reconstituted solution is for single use. Discard any unused solution immediately.
The disposal of unused medicinal products and all materials that have been in contact with them should be done in accordance with local regulations.
(PVC FORMAT WITH BREAKABLE VALVE)
What PRISMASOL contains
The active principles are:
Before reconstitution:
1000 ml of Electrolyte Solution (Small Compartment A) contains:
Calcium chloride dihydrate 5.145 g
Magnesium chloride hexahydrate 2.033 g
Glucose 22.000 g
(S)-Lactic acid 5.400 g
1000 ml of buffer solution (Large Compartment B) contains:
Sodium chloride 6.450 g
Sodium hydrogen carbonate 3.090 g
Potassium chloride 0.157 g
After reconstitution:
The solution from Compartment A (250 ml) and Compartment B (4750 ml) is mixed to produce a reconstituted solution (5000 ml) with the following composition:
mmol/l | mEq/l | |
Calcium Ca2+ | 1.75 | 3.50 |
Magnesium Mg2+ | 0.50 | 1.00 |
Sodium Na+ | 140.00 | 140.00 |
Chloride Cl- | 111.50 | 111.50 |
Lactate | 3.00 | 3.00 |
Hydrogen carbonate HCO3- | 32.00 | 32.00 |
Potassium K+ | 2.00 | 2.00 |
Glucose | 6.10 | |
Theoretical osmolality: | 297 mOsm/l |
The other components are:carbon dioxide (E-290), water for injectable preparations.
pH of the reconstituted solution: 7.0 – 8.5
Product appearance and container contents
Prismasol is presented in a bicompartmental bag, containing the small compartment A with the electrolyte solution and the large compartment B with the buffer solution. The final reconstituted solution is obtained after breaking the breakable valve and mixing both solutions. The reconstituted solution is transparent and slightly yellow. Each bag (A+B) contains 5000 ml of solution for hemodialysis and hemofiltration. The bag is covered by a transparent overbag.
Each box contains two bags and a leaflet.
Marketing authorization holder:
Vantive Belgium SRL
Boulevard d´Angleterre 2
1420 Braine-l´Alleud
Belgium
Manufacturer:
Bieffe Medital S.p.A.
Via Stelvio 94
23035 Sondalo (SO)
Italy
Or
Vantive Manufacturing Limited
Moneen Road,
Castlebar
County Mayo
F23 XR63
Ireland
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Germany, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Slovakia, Slovenia, Estonia, Spain, Finland, France, Greece, Netherlands, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Sweden, United Kingdom (Northern Ireland): Prismasol 2
Further information about this medicinal product can be obtained from the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Vantive Health, S.L.
Polígono industrial sector 14
C/ Pouet de Camilo nº2
46394 Ribarroja del Turia
Valencia
Spain
Date of last revision of this leaflet: 03/2018
Detailed and updated information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.es
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals
Prismasol 2 mmol/l Potassium solution for hemodialysis and hemofiltration
Precautions
The instructions for use and handling of Prismasol must be followed accurately.
The solutions from the two compartments must be mixed before use.
The use of contaminated hemofiltration and hemodialysis solutions can cause sepsis, shock, and conditions that can lead to death.
Prismasol can be heated to 37 °C to improve patient comfort. The heating of the solution before use must be done before reconstitution, only with dry heat. The solutions must not be heated in water or in the microwave. The solution must be visually inspected before administration to detect the presence of particles and any possible color change, when the solution and container allow it. Do not administer if the solution is not transparent or if the seal is not intact.
Prismasol is a solution that contains potassium. Before and during hemofiltration and hemodialysis, the blood potassium concentration must be monitored. Depending on the potassium concentration in the blood before treatment, hypo- or hyperkalemia may develop.
If hypokalemia occurs, it may be necessary to add potassium and/or administer a dialysate with a higher potassium concentration.
If hyperkalemia occurs once treatment has started, the addition of potassium sources that affect concentrations should be assessed. When the solution is used as a replacement solution, the perfusion rate should be reduced and it should be confirmed that the desired potassium concentration has been achieved. If hyperkalemia is not resolved, perfusion should be stopped immediately.
If hyperkalemia develops when the solution is used as a dialysate, it may be necessary to administer a potassium-free dialysate to increase potassium elimination.
The concentration of inorganic phosphates should be measured regularly. In the event that the levels of inorganic phosphate in the blood are low, it should be restored. A phosphate concentration of up to 1.2 mmol/l can be added to the solution. If potassium phosphate is added, the total potassium concentration should not exceed 4 mEq/l (4 mmol/l).
Although no cases of severe hypersensitivity reactions to corn with Prismasol have been reported, solutions containing glucose derived from hydrolyzed corn starch should not be used in patients with a known allergy to corn or corn-derived products.
If signs or symptoms of a suspected hypersensitivity reaction develop, administration should be stopped immediately. Appropriate compensatory therapeutic measures should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Due to the glucose and lactate content of the solution, it may cause hyperglycemia, especially in diabetic patients. Blood glucose levels should be monitored regularly. In the event of hyperglycemia, it may be necessary to administer a dextrose-free replacement solution or dialysate. Other corrective measures may be necessary to maintain the desired blood glucose control.
Prismasol contains sodium hydrogen carbonate (bicarbonate) and lactate (a precursor to bicarbonate), which can affect acid-base balance. If metabolic alkalosis develops or worsens during treatment with the solution, it may be necessary to reduce the administration rate or stop administration.
Before and during treatment, close monitoring of electrolyte and acid-base balance should be performed throughout the procedure.
In the event of fluid imbalance, the clinical situation should be carefully controlled and fluid balance should be corrected as necessary.
Method of administration
Intravenous and for hemodialysis. Prismasol, when used as a replacement solution, is administered within the circuit before the hemofilter (pre-dilution) or after the hemofilter (post-dilution)
Posology
The volume and rate of use of Prismasol will depend on the electrolyte concentration in the blood, acid-base balance, and the patient's overall clinical condition. The administration schedule (dose, perfusion rate, and cumulative volume) of Prismasol should be established by a doctor.
The flow rates used for the replacement solution in hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration are:
Adults: 500 – 3000 ml/hour
The flow rates used for the dialysis solution (dialysate) in continuous hemodialysis and continuous hemodiafiltration are:
Adults: 500 - 2500 ml/hour
Normally, the flow rates used in adults are approximately 2000 to 2500 ml/h, which corresponds to a daily fluid volume of approximately 48 to 60 liters.
Pediatric population
The flow rate ranges for the replacement solution in hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration and for the dialysis solution (dialysate) in continuous hemodialysis are:
Children (from neonates to adolescents up to 18 years of age): 1000 to 2000 ml/h/1.73 m2.
Flow rates of up to 4000 ml/h/1.73 m2 may be necessary, especially in small children (≤10 kg). The absolute flow rate (in ml/h) in the pediatric population should not generally exceed the maximum flow rate in adults.
Handling instructions
The electrolyte solution (small compartment A) is added to the buffer solution (large compartment B) after breaking the breakable valve just before use to obtain the reconstituted solution.
Use only with suitable extracorporeal renal replacement equipment.
Aseptic technique should be followed throughout the handling and administration process to the patient.
Use only if the overbag is intact, all seals are intact, the breakable valve is not broken, and the solution is transparent. Squeeze the bag firmly to ensure there are no leaks. If leaks are observed, discard the solution immediately, as sterility cannot be guaranteed.
The large compartment (B) is equipped with an injection port for adding other medications that may be necessary once the solution is reconstituted. It is the responsibility of the doctor to assess the compatibility of a medication added to Prismasol by checking for any color change and/or precipitation, insoluble complexes, or crystals. Before adding a medication, verify that it is soluble and stable in water at the pH of Prismasol (the pH of the reconstituted solution is between 7.0 and 8.5). Additives may not be compatible. The instructions for use of the added medication should be consulted.
Remove any liquid from the injection port, put the bag in an inverted position, add the medication through the injection port, and mix perfectly. The solution should be administered immediately.The introduction and mixing of additives should always be done before connecting the solution bag to the extracorporeal circuit.
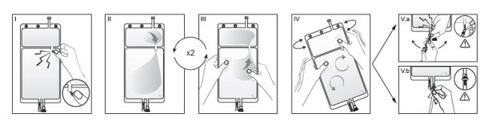
IRemove the overbag from the bag immediately before use and discard any other packaging material. Open the seal by breaking the breakable valve located between the two compartments of the bag. The valve will remain inside the bag. (See figure I below).
IIEnsure that all the liquid from the small compartment A is transferred to the large compartment B. (See figure II below).
IIIRinse twicethe small compartment A by forcing the mixed solution to return to this compartment and then again to the large compartment B (See figure III below).
IVOnce the small compartment A is empty, shake the large compartment B to mix its contents completely. The solution is now ready to use and can be hung on the equipment. (See figure IV below).
VThe dialysis or replacement line can be connected to either of the two access ports.
V.aIf the luer connector is used, remove the plug by a twisting and pulling motion and connect the luer male connector of the dialysis or replacement line to the luer female receptor of the bag by a pressing and twisting motion. Ensure that the connection is secure and tightened. The connection will open. Check that the liquid circulates freely. (See figure Va below).
If the dialysis or replacement line is disconnected from the luer connector, the connector will close and the flow of the solution will stop. The luer port is a needle-free port that can be cleaned.
V.bIf the injection access is used, first remove the cap. The injection port is a port that can be disinfected with a swab. Introduce the spike through the rubber wall. Verify that the solution circulates freely. (See figure Vb below).
The solution should be used immediately after removing the overbag. If not, the reconstituted solution should be used within 24 hours, including the duration of treatment after adding the electrolyte solution to the buffer solution.
The reconstituted solution is for single use. Discard any unused solution immediately.
The disposal of unused medicinal products and all materials that have been in contact with them should be done in accordance with local regulations.

Hypokalemia or hyperkalemia may occur.
If hypokalemia occurs, potassium addition and/or administration of a dialysate with a higher potassium concentration may be necessary.
If hyperkalemia occurs once treatment has started, the addition of potassium sources affecting concentrations should be assessed. When the solution is used as a replacement solution, the perfusion rate should be decreased and it should be confirmed that the desired potassium concentration has been reached. If hyperkalemia is not resolved, perfusion should be stopped immediately.
If hyperkalemia develops when the solution is used as a dialysate, it may be necessary to administer a potassium-free dialysate to increase potassium elimination.
The concentration of inorganic phosphates should be measured regularly. In the event that blood inorganic phosphate levels are low, they should be restored. A phosphate concentration of up to 1.2 mmol/l can be added to the solution. If potassium phosphate is added, the total potassium concentration should not exceed 4 mEq/l (4 mmol/l).
Although no cases of severe hypersensitivity reactions to corn with Prismasol have been reported, solutions containing glucose derived from hydrolyzed corn starch should not be used in patients with known allergy to corn or corn-derived products.
If signs or symptoms of suspected hypersensitivity reactions develop, administration should be interrupted immediately. Appropriate therapeutic compensatory measures that are clinically indicated should be instituted.
Due to the glucose and lactate content of the solution, it may lead to hyperglycemia, especially in diabetic patients. Blood glucose levels should be monitored regularly. In case of hyperglycemia, it may be necessary to administer a dextrose-free replacement or dialysis solution. Other corrective measures may be necessary to maintain desired glycemic control.
Prismasol contains sodium hydrogen carbonate (bicarbonate) and lactate (precursor of bicarbonate) that can affect acid-base balance. If metabolic alkalosis develops or worsens during treatment with the solution, it may be necessary to reduce the administration rate or stop administration.
Before and during treatment, close monitoring of electrolyte and acid-base balance should be performed throughout the procedure.
In case of fluid imbalance, the clinical situation should be carefully controlled and fluid balance should be corrected as necessary.
Administration Method
Intravenous and for hemodialysis. Prismasol, when used as a replacement solution, is administered within the circuit before the hemofilter (pre-dilution) or after the hemofilter (post-dilution)
Posology
The volume and rate of use of Prismasol will depend on the concentration of electrolytes in the blood, acid-base balance, and the patient's overall clinical condition. The administration schedule (dose, perfusion rate, and cumulative volume) of Prismasol should be established by a physician.
The flow rates used for the replacement solution in hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration are:
Adults: 500 - 3000 ml/h
The flow rates used for the dialysis solution (dialysate) in continuous hemodialysis and continuous hemodiafiltration are:
Adults: 500 - 2500 ml/h
Normally, the flow rates used in adults are approximately 2000 to 2500 ml/h, which corresponds to a daily fluid volume of approximately 48 to 60 liters.
Pediatric Population
The flow rate intervals for the replacement solution in hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration and for the dialysis solution (dialysate) in continuous hemodialysis are:
Children (from neonates to adolescents up to 18 years of age): 1000 to 2000 ml/h/1.73 m2.
Flow rates of up to 4000 ml/h/1.73 m2 may be necessary, especially in small children (≤10 kg). The absolute flow rate (in ml/h) in the pediatric population should not generally exceed the maximum flow rate in adults.
Handling Instructions
The electrolyte solution (small compartment A) is added to the buffer solution (large compartment B) after breaking the breakable seal just before use to obtain the reconstituted solution.
Use only with suitable extracorporeal renal replacement therapy equipment.
Aseptic technique should be followed throughout the handling and administration process to the patient.
Use only if the overbag is intact, all seals are intact, the breakable seal is not broken, and the solution is transparent. Squeeze the bag firmly to ensure there are no leaks. If leaks are observed, discard the solution immediately as sterility cannot be guaranteed.
The large compartment (B) is equipped with an injection port for adding other medications that may be necessary once the solution has been reconstituted. It is the physician's responsibility to assess the compatibility of a medication added to Prismasol by checking for any change in color and/or precipitation, insoluble complexes, or crystals. Before adding a medication, verify that it is soluble and stable in water at the pH of Prismasol (the pH of the reconstituted solution is between 7.0 and 8.5). Additives may not be compatible. The instructions for use of the added medication should be consulted.
Remove any liquid from the injection port, put the bag in an inverted position, add the medication through the injection port, and mix perfectly. The solution should be administered immediately. The introduction and mixing of additives should always be performed before connecting the solution bag to the extracorporeal circuit.
IRemove the overbag from the bag immediately before use and discard any other packaging material. Open the seal by breaking the breakable seal located between the two compartments of the bag. The seal will remain inside the bag. (See figure I below).
IIEnsure that all liquid from the small compartment A is transferred to the large compartment B. (See figure II below).
IIIRinse twicethe small compartment A by forcing the mixed solution to return to this compartment and then again to the large compartment B (See figure III below).
IVOnce the small compartment A is empty, shake the large compartment B to mix its contents completely. The solution is now ready to use and can be hung on the equipment. (See figure IV below).
VThe dialysis or replacement line can be connected to either of the two access ports.
V.aIf the luer access is used, remove the plug and connect the luer lock male connector on the dialysis or replacement line to the luer female receptor on the bag: do it firmly. Using your thumb and fingers, break the blue breakable seal at its base and move it back and forth. Do not use tools. Verify that the seal is completely separated and that the solution circulates freely. The seal will remain in the luer access during treatment. (See figure Va below).
V.bIf the injection access is used, remove the cap first. The injection port is a port that can be disinfected with a swab. Insert the spike through the rubber wall. Verify that the solution circulates freely. (See figure Vb below).
The solution should be used immediately after removing the overbag. If not, the reconstituted solution should be used within 24 hours, including the duration of treatment after adding the electrolyte solution to the buffer solution.
The reconstituted solution is for single use. Discard any unused solution immediately.
The disposal of unused medication and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
(POLYOLEFIN FORMAT WITH VALVE)
What PRISMASOL contains
The active ingredients are:
Before reconstitution:
1000 ml of electrolyte solution (small compartment A) contains:
Calcium chloride dihydrate 5.145 g
Magnesium chloride hexahydrate 2.033 g
Glucose 22.000 g
(S)-Lactic acid 5.400 g
1000 ml of buffer solution (large compartment B) contains:
Sodium chloride 6.450 g
Sodium hydrogen carbonate 3.090 g
Potassium chloride 0.157 g
After reconstitution:
The solution from compartment A (250 ml) and compartment B (4750 ml) is mixed to produce a reconstituted solution (5000 ml) with the following composition:
mmol/l | mEq/l | |
Calcium Ca2+ | 1.75 | 3.50 |
Magnesium Mg2+ | 0.50 | 1.00 |
Sodium Na+ | 140.00 | 140.00 |
Chloride Cl- | 111.50 | 111.50 |
Lactate | 3.00 | 3.00 |
Hydrogen carbonate HCO3- | 32.00 | 32.00 |
Potassium K+ | 2.00 | 2.00 |
Glucose | 6.10 | |
Theoretical osmolality: | 297 mOsm/l |
The other components are:carbon dioxide (E-290), water for injectable preparations.
pH of the reconstituted solution: 7.0 – 8.5
Appearance of the product and packaging content
Prismasol is presented in a bicompartmental bag, containing the small compartment A with the electrolyte solution and the large compartment B with the buffer solution. The final reconstituted solution is obtained after breaking the sealed wall and mixing both solutions. The reconstituted solution is transparent and slightly yellow. Each bag (A+B) contains 5000 ml of solution for hemodialysis and hemofiltration. The bag is covered by a transparent overbag.
Each box contains two bags and a leaflet.
Marketing authorization holder:
Vantive Belgium SRL
Boulevard d´Angleterre 2
1420 Braine-l´Alleud
Belgium
Manufacturer:
Bieffe Medital S.p.A.
Via Stelvio 94
23035 Sondalo (SO)
Italy
Or
Vantive Manufacturing Limited Moneen Road,
Castlebar
County Mayo
F23 XR63
Ireland
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Germany, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Slovakia, Slovenia, Estonia, Spain, Finland, France, Greece, Netherlands, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Sweden, United Kingdom (Northern Ireland): Prismasol 2
For further information on this medicinal product, please contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Vantive Health, S.L.
Polígono industrial sector 14
C/ Pouet de Camilo nº2
46394 Ribarroja del Turia
Valencia
Spain
Date of last revision of this leaflet: 03/2018
Detailed and updated information on this medicinal product is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.es
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended for healthcare professionals only
Prismasol 2 mmol/l Potassium solution for hemodialysis and hemofiltration
Precautions
The instructions for use and handling of Prismasol should be followed accurately.
The solutions from the two compartments must be mixed before use.
The use of contaminated hemofiltration and hemodialysis solutions can cause sepsis, shock, and conditions that can lead to death.
Prismasol can be heated to 37 °C to improve patient comfort. Heating of the solution before use should be done before reconstitution using only dry heat. The solutions should not be heated in water or in the microwave. The solution should be visually inspected before administration to detect the presence of particles and any possible change in color, when the solution and packaging allow. Do not administer if the solution is not transparent or if the seal is not intact.
Prismasol is a solution that contains potassium. Before and during hemofiltration and/or hemodialysis, blood potassium concentration should be monitored. Depending on the potassium concentration in the blood before treatment, hypokalemia or hyperkalemia may develop.
If hypokalemia occurs, potassium addition and/or administration of a dialysate with a higher potassium concentration may be necessary.
If hyperkalemia occurs once treatment has started, the addition of potassium sources affecting concentrations should be assessed. When the solution is used as a replacement solution, the perfusion rate should be decreased and it should be confirmed that the desired potassium concentration has been reached. If hyperkalemia is not resolved, perfusion should be stopped immediately.
If hyperkalemia develops when the solution is used as a dialysate, it may be necessary to administer a potassium-free dialysate to increase potassium elimination.
The concentration of inorganic phosphates should be measured regularly. In the event that blood inorganic phosphate levels are low, they should be restored. A phosphate concentration of up to 1.2 mmol/l can be added to the solution. If potassium phosphate is added, the total potassium concentration should not exceed 4 mEq/l (4 mmol/l).
Although no cases of severe hypersensitivity reactions to corn with Prismasol have been reported, solutions containing glucose derived from hydrolyzed corn starch should not be used in patients with known allergy to corn or corn-derived products.
If signs or symptoms of suspected hypersensitivity reactions develop, administration should be interrupted immediately. Appropriate therapeutic compensatory measures that are clinically indicated should be instituted.
Due to the glucose and lactate content of the solution, it may lead to hyperglycemia, especially in diabetic patients. Blood glucose levels should be monitored regularly. In case of hyperglycemia, it may be necessary to administer a dextrose-free replacement or dialysis solution. Other corrective measures may be necessary to maintain desired glycemic control.
Prismasol contains sodium hydrogen carbonate (bicarbonate) and lactate (precursor of bicarbonate) that can affect acid-base balance. If metabolic alkalosis develops or worsens during treatment with the solution, it may be necessary to reduce the administration rate or stop administration.
Before and during treatment, close monitoring of electrolyte and acid-base balance should be performed throughout the procedure.
In case of fluid imbalance, the clinical situation should be carefully controlled and fluid balance should be corrected as necessary.
Administration Method
Intravenous and for hemodialysis. Prismasol, when used as a replacement solution, is administered within the circuit before the hemofilter (pre-dilution) or after the hemofilter (post-dilution)
Posology
The volume and rate of use of Prismasol will depend on the concentration of electrolytes in the blood, acid-base balance, and the patient's overall clinical condition. The administration schedule (dose, perfusion rate, and cumulative volume) of Prismasol should be established by a physician.
The flow rates used for the replacement solution in hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration are:
Adults: 500 - 3000 ml/h
The flow rates used for the dialysis solution (dialysate) in continuous hemodialysis and continuous hemodiafiltration are:
Adults: 500 - 2500 ml/h
Normally, the flow rates used in adults are approximately 2000 to 2500 ml/h, which corresponds to a daily fluid volume of approximately 48 to 60 liters.
Pediatric Population
The flow rate intervals for the replacement solution in hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration and for the dialysis solution (dialysate) in continuous hemodialysis are:
Children (from neonates to adolescents up to 18 years of age): 1000 to 2000 ml/h/1.73 m2.
Flow rates of up to 4000 ml/h/1.73 m2 may be necessary, especially in small children (≤10 kg). The absolute flow rate (in ml/h) in the pediatric population should not generally exceed the maximum flow rate in adults.
Handling Instructions
The electrolyte solution (small compartment A) is added to the buffer solution (large compartment B) after breaking the sealed wall just before use to obtain the reconstituted solution.
Use only with suitable extracorporeal renal replacement therapy equipment.
Aseptic technique should be followed throughout the handling and administration process to the patient.
Use only if the overbag is intact, all seals are intact, the sealed wall is not broken, and the solution is transparent. Squeeze the bag firmly to ensure there are no leaks. If leaks are observed, discard the solution immediately as sterility cannot be guaranteed.
The large compartment (B) is equipped with an injection port for adding other medications that may be necessary once the solution has been reconstituted. It is the physician's responsibility to assess the compatibility of a medication added to Prismasol by checking for any change in color and/or precipitation, insoluble complexes, or crystals. Before adding a medication, verify that it is soluble and stable in water at the pH of Prismasol (the pH of the reconstituted solution is between 7.0 and 8.5). Additives may not be compatible. The instructions for use of the added medication should be consulted.
Remove any liquid from the injection port, put the bag in an inverted position, add the medication through the injection port, and mix perfectly. The solution should be administered immediately. The introduction and mixing of additives should always be performed before connecting the solution bag to the extracorporeal circuit.
To verify if it is soluble and stable in water at the pH of Prismasol (the pH of the reconstituted solution is between 7.0 and 8.5). Additives may not be compatible. The Instructions for use of the added medication should be consulted.
Remove any liquid from the injection port, put the bag in an inverted position, add the medication through the injection port, and mix perfectly. The solution should be administered immediately. The introduction and mixing of additives should always be performed before connecting the solution bag to the extracorporeal circuit.
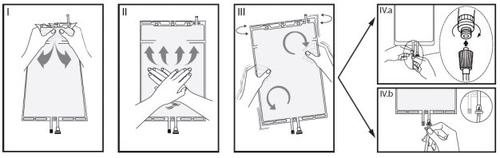
IRemove the overbag from the bag immediately before use and mix the solutions from the two different compartments. Hold the small compartment with both hands and squeeze until the peelable sealed wall between the two compartments opens. (See figure I below).
IIPress the large compartment with both hands until the sealed wall between the two compartments is completely open. (See figure II below).
IIIMake sure the solutions are completely mixed by gently shaking the bag. The solution is now ready to use and the bag can be hung on the equipment. (See figure III below).
IVThe dialysis or substitution line can be connected to either of the two access ports.
IV.aIf the luer connector is used, remove the plug by a twisting and pulling movement and connect the male luer connector of the dialysis or substitution line to the female luer receptor of the bag by a pressing and twisting movement. Make sure the connection is secure and tightened. The connection will open. Check that the liquid circulates freely. (See figure IVa below).
If the dialysis or substitution line is disconnected from the luer connector, the connector will close and the flow of the solution will stop. The luer port is a needle-free port that can be cleaned.
IV.bIf the injection access is used, first remove the capsule. The injection port is a port that can be disinfected with a swab. Introduce the spike through the rubber wall. Verify that the solution circulates freely. (See figure IVb below).
The solution should be used immediately after removing the overbag. If not, the reconstituted solution should be used within 24 hours, including the duration of treatment after adding the electrolyte solution to the buffer solution.
The reconstituted solution is for single use. Discard any unused solution immediately.
The disposal of unused medication and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to PRISMASOL 2 mmol/l POTASSIUM, SOLUTION FOR HEMODIALYSIS AND HEMOFILTRATIONDosage form: HEMOFILTRATION, 2 mmol potassium/lActive substance: HemofiltratesManufacturer: Nikkiso BelgiumPrescription requiredDosage form: HEMOFILTRATION, 4 mmol potassium/lActive substance: HemofiltratesManufacturer: Nikkiso BelgiumPrescription requiredDosage form: HEMOFILTRATION, -Active substance: HemofiltratesManufacturer: Nikkiso BelgiumPrescription required
Online doctors for PRISMASOL 2 mmol/l POTASSIUM, SOLUTION FOR HEMODIALYSIS AND HEMOFILTRATION
Discuss questions about PRISMASOL 2 mmol/l POTASSIUM, SOLUTION FOR HEMODIALYSIS AND HEMOFILTRATION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















