

Phoxilium

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Phoxilium

How to use Phoxilium
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
PHOXILIUM 1.2 mmol/l phosphates
Solution for haemodialysis and haemofiltration
Calcium chloride dihydrate, magnesium chloride hexahydrate, sodium chloride, sodium bicarbonate, potassium chloride, disodium phosphate anhydrous
Read the package leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this package leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this package leaflet, please inform your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. See section 4.
Contents of the package leaflet:
- 1. What is Phoxilium and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Phoxilium
- 3. How to use Phoxilium
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Phoxilium
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Phoxilium and what is it used for
Phoxilium, belonging to the group of solutions for haemofiltration, contains calcium chloride dihydrate, magnesium bicarbonate hexahydrate, sodium chloride, sodium bicarbonate, potassium chloride and disodium phosphate anhydrous.
Phoxilium is used in hospitals in intensive care settings to restore the chemical balance of the blood in patients with kidney damage.
Continuous renal replacement therapy aims to remove accumulated waste products from the blood when the kidneys are not working.
Phoxilium solutionis used to treat critically ill patients with acute kidney injury, characterized by:
- normal potassium levels in the blood (normokalaemia)or
- normal or low phosphate levels in the blood (normo- or hypophosphataemia).
This medicine can also be used in cases of poisoning with substances that can be dialysed or filtered.
2. Important information before using Phoxilium
Do not use Phoxilium in the following three cases:
- if the patient has high potassium levels in the blood (hyperkalaemia);
- if the patient has high bicarbonate levels in the blood (metabolic alkalosis);
- if the patient has high phosphate levels in the blood (hyperphosphataemia).
1/8
Do not use haemodialysis or haemofiltration in the following three cases:
- if haemofiltration cannot alleviate symptoms caused by high urea levels in the blood (uremic symptoms),resulting from kidney damage with significant hypercatabolism (abnormal increase in breakdown processes);
- insufficient arterial pressure in vascular access;
- decreased blood coagulability (systemic anticoagulation)with existing bleeding risk.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Phoxilium, discuss it with your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
Before and during treatment, blood tests will be performed to monitor acid-base balance and electrolyte levels, including the volume of fluids administered (intravenous infusions) and removed (urine output), even if they are not directly related to treatment.
Phoxilium and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take.
This is because the levels of other medicines you are taking may affect Phoxilium treatment.
Your doctor will decide whether to make any changes to your other medicines.
In particular, inform your doctor or pharmacist about:
- phosphates from additional sources (e.g. nutritional fluids), as they may increase the risk of high phosphate levels in the blood (hyperphosphataemia);
- vitamin D and medicines containing calcium chloride or calcium gluconate, due to the potential increased risk of high calcium levels in the blood (hypercalcaemia);
- sodium bicarbonate, as it may increase the risk of excess bicarbonate in the blood (metabolic alkalosis);
- citrate as an anticoagulant, as it may lower calcium levels in the blood.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding and fertility
Pregnancy and breastfeeding:
There are no documented clinical data on the use of this medicine during pregnancy and lactation.
This medicine should only be administered to pregnant or breastfeeding women if clearly necessary.
Fertility:
No effect on fertility is expected, as calcium, sodium, potassium, magnesium, chlorides, phosphates and bicarbonates are normal components of the body.
Driving and using machines
Phoxilium has no effect on the ability to drive and use machines.
3. How to use Phoxilium
Phoxilium is a hospital product administered exclusively by medical personnel.
The volume of Phoxilium and thus the dose depends on the patient's condition.
The dose volume will be determined by the treating physician.
Phoxilium can be administered directly into the bloodstream (intravenously)via a CRRT device or via haemodialysis, when the solution flows on one side of the dialysis membrane and blood on the other side.
2/8
This medicine should always be used exactly as prescribed by your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
In case of doubts, consult your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
The instructions for use are found in the section "The following information is intended for healthcare professionals only".
Overdose of Phoxilium
Phoxilium is intended for hospital use and administration by physicians in a setting of careful monitoring of fluid balance and blood chemistry.
Therefore, it is unlikely that an overdose of Phoxilium will occur.
In the unlikely event of an overdose, the attending physician will take all necessary corrective actions and adjust the dose.
Overdose may lead to fluid overload, decreased bicarbonate levels in the blood (metabolic acidosis) and/or high phosphate levels (hyperphosphataemia) in patients with kidney damage.
It may also lead to serious consequences, such as congestive heart failure and disturbances in blood chemistry.
In case of doubts related to the use of the medicine, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Phoxilium can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
There are three side effects associated with the use of Phoxilium:
- abnormal water content in the body (overhydration or dehydration),
- changes in mineral salt content in the blood (electrolyte imbalance, such ashyperphosphataemia)and
- increased bicarbonate levels in the blood (metabolic alkalosis)or decreased bicarbonate levels in the blood (metabolic acidosis).
There are also certain side effectsthat may be caused by dialysis therapy:
- nausea, vomiting, muscle cramps and low blood pressure (hypotension).
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this package leaflet, please inform your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Pharmacovigilance of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices and Biocidal Products
Aleje Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Tel.: +48 22 4921301
Fax: +48 22 4921309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorisation holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
3/8
5. How to store Phoxilium
Store the medicine in a place out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the label and on the packaging.
The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Store in a temperature range of +4°C to +30°C.
Do not store in a refrigerator or freeze.
Chemical and physical stability of the reconstituted solution has been demonstrated for 24 hours at +22°C.
If the solution is not used immediately, the user is responsible for the storage time and conditions before use, and this time should not exceed 24 hours, including the time of the procedure.
Do not use this medicine if you notice that the solution is cloudy or the outer protective packaging is damaged.
All seams must be intact.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste.
Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required.
These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Phoxilium contains
The active substances before and after mixing (reconstitution) are listed below.
Active substances before mixing:
1000 ml of solution in the small chamber Acontains:
Calcium chloride dihydrate
3.68 g
Magnesium chloride hexahydrate
2.44 g
1000 ml of solution in the large chamber Bcontains:
Sodium chloride
6.44 g
Sodium bicarbonate
2.92 g
Potassium chloride
0.314 g
Disodium phosphate anhydrous
0.225 g
Active substances after mixing:
The solutions in chambers A (250 ml) and B (4750 ml) are mixed to obtain a single reconstituted solution (5000 ml) containing:
mmol/l
calcium, Ca
1.25
magnesium, Mg
0.6
sodium, Na
140
chloride, Cl -
115.9
phosphate, HPO
1.2
bicarbonate, HCO
30
potassium, K
4
Theoretical osmolality: 293 mOsm/l
Other ingredients:
- carbon dioxide (for pH adjustment), E290;
- hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment), E507;
- water for injections.
4/8
What Phoxilium looks like and what the pack contains
Phoxilium is a solution for haemodialysis and haemofiltration packaged in dual-chamber bags.
The final reconstituted solution is obtained after breaking the frangible seal and mixing the two solutions.
The reconstituted solution is clear and colourless.
Each bag (A+B) contains 5000 ml of solution for haemofiltration and haemodialysis.
Each bag is placed in a clear outer packaging.
Each pack contains two bags and an information leaflet.
Marketing Authorisation Holder:
Vantive Belgium SRL
Boulevard d’Angleterre 2
1420 Braine-l’Alleud
Belgium
Manufacturer:
Bieffe Medital S.p.A., Via Stelvio 94, 23035 Sondalo (SO), ITALY
Vantive Manufacturing Limited, Moneen Road, Castlebar, County Mayo, F23 XR63, IRELAND
This medicine is authorised in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Greece, Spain, Netherlands, Ireland, Iceland, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Latvia, Malta, Germany, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Sweden, United Kingdom (Northern Ireland), Italy: Phoxilium
Hungary: Phoxil
Date of last revision of the package leaflet: September 2024
The following information is intended for healthcare professionals only:
Phoxilium 1.2 mmol/l phosphates
Solution for haemodialysis and haemofiltration
Precautions
Strictly follow the instructions for use of the medicinal product Phoxilium.
The solutions from both chambers mustbe mixed before use.
Using a contaminated solution can cause sepsis and shock.
To increase patient comfort, Phoxilium can be warmed to a temperature of +37°C.
Warming the solution before use should be done before reconstitution and only using a dry heat source.
Solutions should not be heated in a water bath or microwave.
Before administration, visually inspect Phoxilium to detect the presence of solid particles and changes in colour.
Do not administer if the solution is not clear and the seal is damaged.
Regularly measure the levels of inorganic phosphates.
Inorganic phosphates must be supplemented in cases of low phosphate levels in the blood.
Additional substitution of sodium bicarbonate may increase the risk of metabolic alkalosis.
In case of fluid balance disorders, carefully monitor the clinical condition and restore fluid balance:
- In case of hypervolaemia, the ultrafiltration rate (net) can be increased in the CRRT device and/or the rate of administration of fluids other than substitution fluid and/or dialysate can be decreased.
5/8
- In case of hypovolaemia, the ultrafiltration rate (net) can be decreased in the CRRT device and/or the rate of administration of fluids other than substitution fluid and/or dialysate can be increased.
Warnings:
Phoxilium should not be used in patients with hyperkalaemia.
Potassium levels in the blood must be monitored before and during haemofiltration and/or haemodialysis.
Since Phoxilium is a potassium-containing solution, transient hyperkalaemia may occur after starting treatment.
The infusion rate should be decreased until the potassium level is within the normal range.
If hyperkalaemia does not resolve, the medicinal product should be discontinued immediately.
If hyperkalaemia occurs during treatment with Phoxilium as a dialysate, it may be necessary to administer a potassium-free dialysate to increase the rate of potassium removal.
Since Phoxilium is a phosphate-containing solution, transient hyperphosphataemia may occur after starting treatment.
The infusion rate should be decreased until the phosphate level is within the normal range.
If hyperphosphataemia does not resolve, the medicinal product should be discontinued immediately.
In patients receiving Phoxilium, regularly monitor electrolytes and acid-base balance.
Phoxilium contains phosphate, a weak acid that can affect the patient's acid-base balance.
If metabolic acidosis develops or worsens during treatment with Phoxilium, it may be necessary to decrease the infusion rate or discontinue the medicinal product.
Since Phoxilium does not contain glucose, its administration may lead to hypoglycaemia.
Regularly monitor blood glucose levels in patients with diabetes (especially those taking insulin or other glucose-lowering medicines); this should also be considered in patients without diabetes, for example, due to the risk of asymptomatic hypoglycaemia during treatment.
In case of hypoglycaemia, consider using a glucose-containing solution.
Other measures may also be necessary to maintain normal blood glucose levels.
Dosage:
The volume and rate of administration of Phoxilium depend on the levels of phosphates and other electrolytes in the blood, acid-base balance, fluid balance and the patient's overall clinical condition.
The volume of substitution fluid and/or dialysate to be administered will also depend on the desired intensity of treatment (dose).
The method of administration (dose, infusion rate and total volume) of Phoxilium should be determined exclusively by a physician with experience in intensive care and continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT).
Therefore, the dose volume depends on the physician's decision and recommendations.
The flow rate ranges for the substitution solution in haemofiltration and haemodiafiltration are:
Adults: 500 to 3000 ml/h.
The flow rate ranges for the dialysate in continuous haemodialysis and continuous haemodiafiltration are:
Adults: 500 to 2500 ml/h.
For adults, the usual total flow rate in CRRT (dialysate and substitution solutions) is around 2000 to 2500 ml/h, which corresponds to a daily fluid volume of around 48 to 60 litres.
6/8
Children and adolescents:
In children, from newborns to adolescents up to 18 years, the flow rate range during use as a substitution fluid in haemofiltration and haemodiafiltration and as a dialysate in continuous haemodialysis and continuous haemodiafiltration is from 1000 to 4000 ml/h/1.73 m².
In adolescents (12-18 years), if the calculated dose for children exceeds the maximum dose for adults, the recommended dose for adults should be used.
Instructions for use:
The solution from the small chamber A is added to the solution from the large chamber B after breaking the frangible seal or tearing the seam directly before use.
The reconstituted solution should be clear and colourless.
During the procedure and administration of the medicinal product to the patient, aseptic technique should be used.
Use only if the outer protective packaging is intact, all seams are intact, the tearable seam is not damaged, and the solution is clear.
Strongly squeeze the bag to check its integrity.
If a leak is detected, the solution should be discarded immediately, as sterility cannot be guaranteed.
The large chamber B has a injection port that allows the addition of other necessary medicinal products after reconstitution.
The user is responsible for assessing the compatibility of the added medicinal product with Phoxilium by detecting any change in colour and/or precipitation, presence of insoluble complexes or crystals.
Before adding another medicinal product, check if it is soluble and stable in Phoxilium and if the pH range of Phoxilium is suitable for it (the pH of the solution after reconstitution is between 7.0-8.5).
Additional components may not be compatible with the solution.
Read the instructions for the added medicinal product.
Remove the fluid from the injection port, hold the inverted bag ("upside down"), inject the medicinal product through the injection port and mix carefully.
Introduction and mixing of additional components must always be performed before connecting the bag to the extracorporeal circuit.
The solution should be administered immediately.
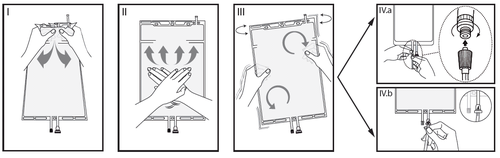
I
Remove the outer packaging immediately before use, discard all remaining packaging.
Open the seam, holding the small chamber with both hands and squeezing until a hole is made in the tearable seam separating the two chambers (see Figure I below).
II
Squeeze the large chamber with both hands until the tearable seam between the two chambers is completely open (see Figure II below).
III
Gently shake the bag to ensure mixing.
The solution is now ready for use and the bag can be hung on a stand (see Figure III below).
IV
Each of the two access ports can be connected to a dialysis or exchange line.
IVaIf using a luer-type access, remove the cap by twisting and pulling, then connect the male luer lock of the dialysis or exchange line to the female luer receptor on the bag, pushing and twisting.
Ensure the connection is fully seated and secure.
The connection is now open.
Check that the fluid flows freely (see Figure IV.a below).
When the dialysis or exchange lines are disconnected from the luer connection, the connection will be closed and fluid flow will be stopped.
The luer port is needle-free and can be disinfected with disinfectants.
IVbWhen using the injection port, first remove the cap by breaking it off.
The injection port can be disinfected with disinfectants.
Then puncture the rubber septum with a needle.
Check that the fluid flows freely (see Figure IV.b below).
7/8
8/8
1. What is Phoxilium and what is it used for
Phoxilium is a solution for hemofiltration, containing calcium chloride dihydrate, magnesium bicarbonate hexahydrate, sodium chloride, sodium bicarbonate, potassium chloride, and disodium phosphate anhydrous. Phoxilium is used in hospitals in intensive care units to restore chemical balance in the blood of patients with kidney damage. Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) aims to remove accumulated waste products from the blood when the kidneys are not working. Treatmentwith Phoxilium is used for critically ill patients with acute kidney injury, characterized by:
- normal potassium levels in the blood (normokalemia)or
- normal or low phosphate levels in the blood (normo- or hypophosphatemia).
This medicine can also be used in cases of poisoning with dialyzable or filterable substances.
2. Important information before using Phoxilium
Do not use Phoxilium in the following three cases:
- if the patient has high potassium levels in the blood (hyperkalemia);
- if the patient has high bicarbonate levels in the blood (metabolic alkalosis);
- if the patient has high phosphate levels in the blood (hyperphosphatemia).
1/8
Do not use hemodialysis or hemofiltration in the following three cases:
- if hemofiltration cannot alleviate symptoms caused by high urea levels in the blood (uremic symptoms),which are the result of kidney damage with significant hypercatabolism (abnormal increase in breakdown processes);
- insufficient arterial pressure in vascular access;
- decreased blood coagulability (systemic anticoagulation)with existing bleeding risk.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Phoxilium, discuss it with your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Before and during treatment, blood will be monitored, i.e., acid-base balance and electrolyte levels will be controlled, including the volume of fluids administered (intravenous infusions) and removed (excreted urine), even those not directly related to CRRT.
Phoxilium and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take. This is because the concentration of other medicines you are taking may affect Phoxilium treatment. Your doctor will decide whether to make any changes to other medicines you are taking. In particular, inform your doctor about:
- phosphates from additional sources (e.g., nutritional fluids), as they may increase the risk of high phosphate levels in the blood (hyperphosphatemia);
- vitamin D and medicines containing calcium chloride or calcium gluconate, due to the possible increased risk of high calcium levels in the blood (hypercalcemia);
- sodium bicarbonate, as it may increase the risk of excess bicarbonate in the blood (metabolic alkalosis);
- citrate as an anticoagulant, as it may lower calcium levels in the blood.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Pregnancy and breastfeeding: There are no clinical data on the use of this medicine during pregnancy and lactation. This medicine should only be given to pregnant or breastfeeding women if clearly necessary. Fertility: No effect on fertility is expected, as calcium, sodium, potassium, magnesium, chloride, phosphate, and bicarbonate are normal components of the body.
Driving and using machines
Phoxilium has no effect on the ability to drive and use machines.
3. How to use Phoxilium
Phoxilium is a hospital product administered exclusively by medical personnel. The volume of Phoxilium and thus the dose depends on the patient's condition. The dose volume will be determined by the treating doctor. Phoxilium can be administered directly into the bloodstream (intravenously)via a CRRT device or via hemodialysis, when the solution flows on one side of the dialysis membrane and blood on the other. This medicine should always be used exactly as prescribed by your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. In case of doubt, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. The instructions for use are in the "Information for healthcare professionals" section. 2/8
Overdose of Phoxilium
Phoxilium is intended for hospital use and administration exclusively by doctors in a situation of careful monitoring of fluid balance and blood chemical composition.
Therefore, it is unlikely that a higher than recommended dose of Phoxilium will be administered.
In the unlikely event of an overdose, the attending physician will take all necessary corrective actions and adjust the dose. Overdose may lead to fluid overload, decreased bicarbonate levels in the blood (metabolic acidosis), and/or high phosphate levels (hyperphosphatemia) in patients with kidney damage. It may also lead to serious consequences, such as congestive heart failure and disturbances in blood chemical composition. In case of doubts about the use of the medicine, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Phoxilium can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. There are three side effects associated with the use of Phoxilium:
- excessive or insufficient water content in the body (overhydration or dehydration),
- changes in mineral salt content in the blood (electrolyte imbalance, such ashyperphosphatemia)and
- increased bicarbonate levels in the blood (metabolic alkalosis)or decreased bicarbonate levels in the blood (metabolic acidosis).
There are also certain side effectsthat may be caused by dialysis therapy:
- nausea, vomiting, muscle cramps, and low blood pressure (hypotension).
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Aleje Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 4921301, Fax: +48 22 4921309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl. Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine. 3/8
5. How to store Phoxilium
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the label and packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month. Store in a temperature range from +4°C to +30°C. Do not store in a refrigerator or freeze. The chemical and physical stability of the reconstituted solution has been demonstrated for 24 hours at +22°C. If the solution is not used immediately, the user is responsible for the storage conditions before use, and this time should not exceed 24 hours, including the time of the procedure. Do not use this medicine if you notice that the solution is cloudy or the outer protective packaging is damaged. All welds must be intact. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Phoxilium contains
The active substances before and after mixing (reconstitution) are presented below.
Active substances before mixing:
1000 ml of solution in the small chamber Acontains: Calcium chloride dihydrate 3.68 g Magnesium chloride hexahydrate 2.44 g 1000 ml of solution in the large chamber Bcontains: Sodium chloride 6.44 g Sodium bicarbonate 2.92 g Potassium chloride 0.314 g Disodium phosphate anhydrous 0.225 g
Active substances after mixing:
The solutions in chambers A (250 ml) and B (4750 ml) are mixed to obtain a single reconstituted solution (5000 ml) containing: mmol/lcalcium, Ca 1.25 magnesium, Mg 0.6 sodium, Na 140 chloride, Cl 115.9 phosphate, HPO 1.2 bicarbonate, HCO 30 potassium, K 4 Theoretical osmolality: 293 mOsm/l
Other ingredients:
- carbon dioxide (to adjust pH), E290;
- hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH), E507;
- water for injections.
4/8
What Phoxilium looks like and what the packaging contains
Phoxilium is a solution for hemodialysis and hemofiltration packaged in a dual-chamber bag. The final reconstituted solution is obtained after breaking the fragile stopper and mixing the two solutions. The reconstituted solution is clear and colorless. Each bag (A+B) contains 5000 ml of hemofiltration and hemodialysis solution. Each bag is placed in a transparent outer packaging. Each packaging contains two bags and an information leaflet.
Marketing authorization holder:
Vantive Belgium SRL, Boulevard d’Angleterre 2, 1420 Braine-l’Alleud, Belgium
Manufacturer:
Bieffe Medital S.p.A., Via Stelvio 94, 23035 Sondalo (SO), ITALY Vantive Manufacturing Limited, Moneen Road, Castlebar, County Mayo, F23 XR63, IRELAND
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Greece, Spain, Netherlands, Ireland, Iceland, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Latvia, Malta, Germany, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Sweden, United Kingdom (Northern Ireland), Italy: Phoxilium Hungary: Phoxil
Date of last revision of the leaflet: September 2024
The following information is intended for healthcare professionals only:
Phoxilium 1.2 mmol/l phosphates
Solution for hemodialysis and hemofiltration
Precautions: The instructions for use and handlingof the Phoxilium medicinal product must be strictly followed. The solutions from both chambers mustbe mixed before use.The use of contaminated solution may cause sepsis and shock. To increase patient comfort, Phoxilium can be warmed to +37°C. Warming of the solution before use should be done before reconstitution and only using a dry heat source. The solutions should not be warmed in a water bath or microwave oven. Before administration, Phoxilium should be visually inspected for the presence of particulate matter and color change. Do not administer if the solution is not clear or the weld is damaged. Electrolytes and acid-base balance should be regularly monitored. Phoxilium contains phosphate, a weak acid that may affect the patient's acid-base balance. If metabolic acidosis develops or worsens during treatment with Phoxilium, it may be necessary to reduce the infusion rate or discontinue the medicinal product. Since Phoxilium does not contain glucose, its administration may lead to hypoglycemia. Blood glucose levels should be regularly monitored in diabetic patients (especially those taking insulin or other glucose-lowering medicines); this should also be considered in non-diabetic patients, for example, due to the risk of asymptomatic hypoglycemia during treatment. In case of hypoglycemia, the use of a glucose-containing solution should be considered. Other measures may also be necessary to maintain adequate blood glucose levels.
Dosage:
The volume and rate of administration of the Phoxilium medicinal product depend on the concentration of phosphates and other electrolytes in the blood, acid-base balance, fluid balance, and the patient's overall clinical condition. The volume of the substitution solution and/or dialysate to be administered will also depend on the desired treatment intensity (dose). The method of administration (dose, infusion rate, and total volume) of the Phoxilium medicinal product should be determined exclusively by a doctor with experience in intensive therapy and continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). Therefore, the dose volume depends on the doctor's decision and recommendations. The flow rate ranges for the substitution solution in hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration are: Adults: 500 to 3000 ml/h. The flow rate ranges for the dialysate in continuous hemodialysis and continuous hemodiafiltration are: Adults: 500 to 2500 ml/h. In adults, the usual total flow rate in CRRT (dialysate and substitution solutions) is approximately 2000 to 2500 ml/h, which corresponds to a daily fluid volume of approximately 48 to 60 liters.
Children and adolescents:
In children, from newborns to adolescents up to 18 years of age, the flow rate range during use as a substitution fluid in hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration and as a dialysate in continuous hemodialysis and continuous hemodiafiltration is from 1000 to 4000 ml/h/1.73 m^2. If the calculated dose for adolescents (12-18 years) exceeds the maximum dose for adults, the recommended dose for adults should be used.
Instructions for use/handling
The solution from the small chamber A is added to the solution from the large chamber B after breaking the fragile stopper or tearing the weld immediately before use. The reconstituted solution should be clear and colorless. During handling and administration of the medicinal product to the patient, aseptic technique should be used. Use only if the outer protective packaging is intact, all welds are intact, the fragile stopper is not damaged, and the solution is clear. Squeeze the bag firmly to check its seal. If a leak is detected, the solution should be discarded immediately, as sterility cannot be guaranteed. The large chamber B has an injection port that allows the addition of other necessary medicinal products after reconstitution of the solution. The user is responsible for assessing the compatibility of the added medicinal product with Phoxilium by detecting any change in color and/or precipitation, presence of insoluble complexes or crystals. Before adding another medicinal product, check if it is soluble and stable in Phoxilium and if the pH range of Phoxilium is suitable for it (the pH of the solution after reconstitution is between 7.0-8.5). Additional components may not be compatible with the solution. Consult the instructions for the added medicinal product. Remove the fluid from the injection port, hold the inverted bag ("upside down"), inject the medicinal product through the injection port, and mix carefully. Introduction and mixing of additional components must always be done before connecting the bag with the solution to the extracorporeal circuit. The solution should be administered immediately.
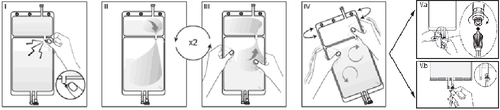
I
Remove the outer packaging immediately before use, discard all remaining packaging. Open the weld between the two chambers of the bag by breaking the fragile stopper. The fragile stopper will remain in the bag (see Figure I below).
II
Ensure that all fluid from the small chamber A has been transferred to the large chamber B (see Figure II below). IIIRinse the small chamber A twice, expressing the mixed solution back into the small chamber A and then again into the large chamber B (see Figure III below).
IV
If the small chamber A is empty: shake the large chamber B to mix its contents thoroughly. The solution is now ready for use, and the bag can be hung on a stand (see Figure IV below).
V
Each of the two access ports can be connected to a dialysis or exchange line. V.aIf using a luer-type access, use aseptic technique, remove the cap, and connect the male luer lock of the dialysis or exchange line to the female luer receptor on the bag; tighten. Using both hands, break the blue fragile stopper at the base and move it back and forth. Do not use tools. Check that the stopper is completely separated and that the fluid flows freely. During treatment, the stopper will remain in the luer port (see Figure V.a below). V.bWhen using the injection port, first remove the cap by breaking it off. The injection port can be disinfected with disinfectants. Then, puncture the rubber septum with a needle. Check that the fluid flows freely (see Figure V.b below). The reconstituted solution should be used immediately. If the reconstituted solution is not used immediately, it should be used within 24 hours of adding solution A to solution B, including the time of the procedure. The reconstituted solution is intended for single use only. Unused solution should be discarded immediately after use. Any unused medicinal product or waste should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations.
8/8
- Country of registration
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterBieffe Medital S.p.A. Vantive Manufacturing Limited
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to PhoxiliumDosage form: Solution, 9 mg/mlActive substance: sodium chloridePrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 100 mg/mlActive substance: dextranManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi Italia S.r.L.Prescription not requiredDosage form: Concentrate, -Active substance: electrolytes in combination with other drugsManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi Norge ASPrescription not required
Alternatives to Phoxilium in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Phoxilium in Ukraine
Alternative to Phoxilium in Spain
Online doctors for Phoxilium
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Phoxilium – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














