
Oftensin

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Oftensin

How to use Oftensin
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Oftensin, 2.5 mg/ml, eye drops, solution
Oftensin, 5 mg/ml, eye drops, solution
Timolol
Read the package leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, please inform your doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Leaflet
- 1. What is Oftensin and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Oftensin
- 3. How to use Oftensin
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Oftensin
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Oftensin and what is it used for
The active substance of Oftensin is timolol. Timolol belongs to a group of medicines called beta-blockers.
Timolol lowers the pressure in the eye by reducing the production of aqueous humor in the eye and increasing its outflow through the uveoscleral tract. Timolol also has a slight effect on episcleral venous pressure.
The medicine does not affect the pupil size or accommodation, which does not disturb vision.
The effect of the medicine starts about 10-30 minutes after administration, and the maximum decrease in intraocular pressure occurs after 1-2 hours. The effect of the medicine lasts up to 24 hours after a single dose.
Indications for use are:
- Treatment of increased intraocular pressure in patients with:
- ocular hypertension,
- chronic open-angle glaucoma.
2. Important information before using Oftensin
When not to use Oftensin:
- if you are allergic to timolol, beta-blockers or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if you have asthma or have had asthma in the past;
- if you have severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (severe lung disease that can cause wheezing, difficulty breathing, and/or prolonged coughing);
- if you have sinus bradycardia;
- if you have sick sinus syndrome;
- if you have second- or third-degree atrioventricular block;
- if you have sinoatrial block;
- if you have cardiogenic shock;
- if you have overt heart failure.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Oftensin, discuss with your doctor the following situations:
- if you experience side effects similar to those observed after oral administration of beta-blockers, as timolol administered topically to the conjunctival sac may be absorbed into the bloodstream;
- if you are already taking an oral beta-blocker. It is also not recommended to use two topical beta-blockers at the same time.
- if you have coronary heart disease (symptoms may include chest pain or tightness, shortness of breath, or choking), heart failure, decreased blood pressure;
- if you have arrhythmias, such as slow heart rate;
- if you have respiratory disorders, asthma, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
- if you have peripheral circulation disorders (e.g., Raynaud's disease or Raynaud's syndrome);
- if you have diabetes (especially unstable) treated with insulin or oral antidiabetic drugs, as timolol may mask the symptoms of low blood sugar;
- if you have angle-closure glaucoma;
- if you have had a filtration surgery;
- if you have hyperthyroidism, as timolol may mask the symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
Risk of anaphylactic reaction
During treatment with timolol, patients with atopic disease or a history of severe anaphylactic reactions to various allergens may exhibit an increased reaction to repeated exposure to these allergens, both accidental and during diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. These patients may not respond to the usual doses of adrenaline used to treat anaphylactic reactions.
Anesthesia during surgical procedures
Before surgical anesthesia, inform your doctor about the use of Oftensin, as timolol may affect the action of some anesthetics.
Children and adolescents
Timolol in the form of eye drops should be used with caution in children and adolescents. In newborns, infants, and small children, timolol should be used with special caution. If coughing, wheezing, abnormal breathing, or abnormal pauses in breathing (apnea) occur, the use of the medicine should be stopped immediately. Contact your doctor as soon as possible. A portable monitor to control apnea may be useful.
Timolol has been studied in infants and children aged 12 days to 5 years who had elevated intraocular pressure or were diagnosed with glaucoma. For more detailed information, consult your doctor.
Oftensin and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take.
Oftensin may affect the action of other medicines or its action may be changed by other medicines, including other eye drops used to treat glaucoma. Inform your doctor if you are using or plan to use medicines that lower blood pressure, heart disease medicines, or diabetes medicines.
Some medicines should not be used at the same time as timolol, and in other cases, your doctor may recommend a change in dosage.
- other beta-blockers;
- adrenaline;
- cimetidine, ranitidine, haloperidol, and amiodarone, phenothiazine derivatives, reserpine;
- antidepressants, including fluoxetine and paroxetine;
- oral calcium channel blockers (e.g., verapamil, diltiazem, nifedipine);
- cardiac glycosides (e.g., digoxin);
- quinidine;
- guanethidine;
- parasympathomimetics;
- inhalation anesthetics: enflurane, halothane, isoflurane, methoxyflurane, chloroform, cyclopropane, or trichloroethylene;
- antidiabetic medicines (insulin or oral antidiabetic medicines).
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Do not use the medicine during pregnancy unless your doctor decides it is necessary.
Do not use the medicine during breastfeeding, as timolol may pass into breast milk.
Driving and using machines
While using timolol in the form of eye drops, visual disturbances and dizziness may occur, which can affect your ability to react. If you experience such side effects, do not drive or operate machinery.
Oftensin contains benzalkonium chloride, phosphates
The medicine contains 0.12 mg of benzalkonium chloride per 1 ml of solution.
Benzalkonium chloride may be absorbed by soft contact lenses and change their color. Remove contact lenses before administration and wait at least 15 minutes before putting them back on. If you have an eye infection, it is not recommended to wear contact lenses.
Benzalkonium chloride may also cause eye irritation, especially in people with dry eye syndrome or disorders affecting the cornea (the transparent layer on the front of the eye). If you experience any abnormal sensations, stinging, or pain in the eye after using the medicine, contact your doctor.
Oftensin 2.5 mg/ml contains 12.72 mg of phosphates per 1 ml of solution.
Oftensin 5 mg/ml contains 11.78 mg of phosphates per 1 ml of solution.
In patients with severe damage to the transparent, anterior part of the eye (cornea), phosphates may rarely cause corneal clouding due to calcium deposits during treatment.
Timolol is well tolerated by patients using hard contact lenses made of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA).
3. How to use Oftensin
Always use this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. If you are not sure, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Children and adolescents
Before recommending the use of timolol, the doctor should perform a thorough medical examination. The doctor will carefully assess the risk-to-benefit ratio of using timolol.
If the benefits outweigh the risks, the medicine should be administered at the lowest available concentration once a day.
In children, a 0.1% solution is usually sufficient to lower intraocular pressure. If this dose does not sufficiently lower intraocular pressure, it may be necessary to administer the medicine twice a day with a 12-hour interval. Children, especially newborns, should be closely monitored for 1 to 2 hours after the first dose and closely monitored for side effects until the surgical procedure is performed.
Treatment period
In children and adolescents, the medicine is used for transitional treatment.
Adults
Recommended dose of the medicine for adults
Initially, one drop of Oftensin 2.5 mg/ml solution into each affected eye twice a day.
If the treatment result is insufficient, the doctor will recommend using one drop of Oftensin 5 mg/ml solution into each affected eye twice a day.
Intraocular pressure should be regularly monitored.
To lower intraocular pressure, Oftensin can be used with other medicines. However, it is not recommended to use two topical beta-blockers at the same time (see section 2. Important information before using Oftensin).
Since in some patients, stabilization of intraocular pressure occurs only after several weeks of treatment with timolol, the assessment of the medicine's effect should be based on intraocular pressure measurements after about 4 weeks of use.
In many cases, if intraocular pressure is stabilized, the doctor may reduce the dose of the medicine, recommending its use once a day.
Changing the current treatment regimen
If you have been using another beta-blocker eye drop previously, you should use the usual dose on the last day of its use. The next day, stop the previous medicine and use Oftensin 2.5 mg/ml - one drop into each affected eye twice a day. If the treatment result is not satisfactory, the doctor may increase the dose to one drop of Oftensin 5 mg/ml into each affected eye twice a day.
If you have been using another anti-glaucoma medicine that is not a beta-blocker, you should continue using it on the same day, adding one drop of Oftensin 2.5 mg/ml into each affected eye twice a day. The next day, stop the previously used anti-glaucoma medicine and continue treatment with Oftensin.
If a higher dose of the medicine is necessary, the doctor will recommend using one drop of Oftensin 5 mg/ml into each affected eye twice a day.
Method of administration:
- 1. Wash your hands and take a comfortable sitting or standing position.
- 2. Unscrew the cap.
- 3. Do not touch the dropper tip to any surface.
- 4. Gently pull the lower eyelid of the affected eye down with your finger.
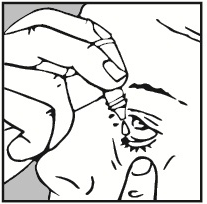
- 5. Hold the upper part of the dropper close to the eye without touching it. Gently squeeze the bottle to release one drop into the eye. Make sure not to squeeze the bottle too hard, so that only one drop gets into the eye.
- 6. Then release the lower eyelid.
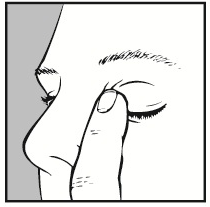
- 7. After using the medicine, close your eyes for as long as possible (3-5 minutes) and press the corner of the affected eye near the nose with your finger. This will prevent the medicine from entering other parts of the body. If the drop did not get into the eye, you should administer a second drop.
- 8. Close the bottle.
Eye drop solutions may become contaminated with bacteria if not stored and used properly, causing eye infections. Using contaminated solutions can lead to serious eye damage and vision loss.
Using a higher dose of Oftensin than recommended
If you use a higher dose of the medicine than recommended, contact your doctor immediately, who will provide appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of overdose may include: decreased blood pressure, slowed heart rate, bronchospasm, and acute heart failure.
Missing a dose of Oftensin
If you miss a dose of the medicine, take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, do not take the missed dose. Do not take a double dose to make up for the missed dose.
If you have any further questions about using this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Oftensin eye drops are generally well tolerated.
Like other locally used eye medicines, timolol is absorbed into the bloodstream. It may cause the same types of side effects as intravenously or orally administered beta-adrenergic blockers. The frequency of systemic side effects after topical administration to the eye is lower than after oral administration or injection.
- Generalized allergic reactions, including angioedema, which may occur in areas such as the face and limbs, may block the airways, causing difficulty swallowing or breathing. Urticaria or itchy rash, localized and generalized rash, itching, severe life-threatening allergic reaction.
- Low blood sugar levels.
- Difficulty sleeping (insomnia), depression, nightmares, memory loss, hallucinations*.
- Fainting, stroke, decreased blood flow to the brain, worsening of myasthenia symptoms (muscle disorder), dizziness, abnormal sensations, such as tingling and numbness, headaches.
- Symptoms of eye irritation (e.g., burning, stinging, itching, tearing, redness), blepharitis, keratitis, blurred vision, and retinal detachment after filtration surgery, which can cause vision disturbances, decreased corneal sensitivity, dry eye, corneal damage and defects (the front layer of the eye), ptosis (the eye is half-closed), double vision.
- Slowed heart rate, chest pain, palpitations, edema (fluid accumulation), changes in heart rhythm and frequency, congestive heart failure (heart disease with shortness of breath and swelling of the feet and legs due to fluid accumulation), arrhythmias, cardiac arrest, heart failure.
- Low blood pressure, Raynaud's phenomenon, cold hands and feet.
- Bronchospasm in the lungs (mainly in patients with pre-existing diseases), difficulty breathing, coughing.
- Taste disorders, nausea, indigestion, diarrhea, dry mouth, abdominal pain, vomiting.
- Hair loss, skin rash with a white-silver color (psoriasis-like rash) or worsening of psoriasis, skin rash.
- Muscle pain not caused by physical activity.
- Sexual disorders, decreased libido.
- Weakness and/or fatigue.
*frequency not known (frequency cannot be estimated from available data)
Other side effects reported in connection with the use of eye drops containing phosphates
In patients with severe damage to the transparent, anterior part of the eye (cornea), phosphates may rarely cause corneal clouding due to calcium deposits during treatment.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, please inform your doctor or pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Aleje Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Oftensin
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Store in a temperature not exceeding 25°C, protected from light.
Shelf life after first opening the container: 28 days.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging after: EXP.
The expiry date refers to the last day of the specified month.
The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP means the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot means the batch number.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Oftensin contains
- The active substance of Oftensin is timolol. Each 1 ml of solution contains 2.5 mg or 5 mg of timolol in the form of timolol maleate.
- Other ingredients are: sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate, disodium phosphate dodecahydrate, benzalkonium chloride, purified water.
What Oftensin looks like and contents of the pack
The pack contains 5 ml of solution.
Marketing authorization holder
Polpharma S.A.
Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
Phone: +48 22 364 61 01
Manufacturer
Polfa Warszawskie Zakłady Farmaceutyczne S.A.
Karolkowa 22/24, 01-207 Warsaw
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterWarszawskie Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLFA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to OftensinDosage form: Drops, 5 mg/mlActive substance: timololManufacturer: SIEGFRIED El Masnou, S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Drops, 5 mg/mlActive substance: timololManufacturer: Warszawskie Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLFA S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Drops, 5 mg/mlActive substance: timololManufacturer: Ursapharm Arzneimittel GmbHPrescription required
Alternatives to Oftensin in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Oftensin in Spain
Alternative to Oftensin in Ukraine
Online doctors for Oftensin
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Oftensin – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














