How to use Menopur
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
MENOPUR, 600 IU FSH + 600 IU LH, powder and solvent for solution for injection
for injection
Menotropin
You should read the contents of this leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for you.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult your doctor.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor. See section 4.
Contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What Menopur is and what it is used for
- 2. Important information before using Menopur
- 3. How to use Menopur
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Menopur
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Menopur is and what it is used for
Menopur is a powder (in this case, a solid, compact mass) that must be dissolved in a liquid (solvent) before use. The medicine is administered as a subcutaneous or intramuscular injection. Menopur (highly purified menotropin obtained from the urine of postmenopausal women) contains two hormones: follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). FSH and LH are natural hormones produced in the body of a woman and a man. They enable the normal functioning of the reproductive organs. Menopur is used to treat infertility in the following situations: in women who cannot become pregnant because their ovaries do not produce eggs (also in the case of polycystic ovary syndrome). Menopur is used in women who have been treated with clomiphene citrate for infertility, but the medicine has been ineffective; in women participating in assisted reproduction programs, such as in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer, gamete intrafallopian transfer, and intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Menopur stimulates the ovaries to produce multiple follicles in which eggs can develop (development of multiple follicles); in men whose testes produce insufficient sperm due to a lack of gonadotropins (hormones produced by the pituitary gland and affecting the testes).
2. Important information before using Menopur
Before starting treatment with Menopur, it is necessary for the doctor to assess the causes of fertility disorders in both partners. In particular, the following diseases should be checked, which require different, appropriate treatment: hypothyroidism and hypoadrenalism; high levels of the hormone prolactin (hyperprolactinemia); tumors of the pituitary gland (a gland located at the base of the brain); tumors of the hypothalamus (an area located under the part of the brain called the hill). If the patient has any of the above-mentioned diseases, they should inform their doctor before starting treatment with Menopur.
When not to use Menopur
In women and men: if the patient is allergic to menotropin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6); if pituitary or hypothalamic tumors have been diagnosed. In women: if the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding; if the patient has ovarian cysts or ovarian enlargement not caused by polycystic ovary syndrome; if the patient has vaginal bleeding of unknown cause; if the patient has tumors of the uterus, ovaries, or breasts; if the patient has developmental abnormalities of the genital organs that prevent the development of pregnancy; if the patient has uterine fibroids that prevent the development of pregnancy; if the patient has premature menopause. In men: if the patient has prostate cancer; if the patient has testicular tumors.
Warnings and precautions
Caution should be exercised if the patient experiences: abdominal pain; abdominal distension; nausea; vomiting; diarrhea; weight gain; breathing difficulties; decreased frequency or amount of urine passed. The above symptoms should be reported to the doctor immediately, even if they occur several days after the last dose of the medicine. They may be symptoms of excessive ovarian activity, which can be severe. If these symptoms worsen, fertility treatment should be discontinued and appropriate treatment should be initiated in the hospital. Adherence to the prescribed dose and careful monitoring of the treatment course reduces the likelihood of these symptoms. These symptoms may also occur when Menopur is discontinued. If any of these symptoms occur, the doctor should be contacted immediately. During treatment with Menopur, the doctor usually refers the patient for ultrasound examinations (using ultrasound) and sometimes for blood tests to check the response to treatment. Hormone treatment, such as Menopur, may increase the risk of: ectopic pregnancy (outside the uterus) in women with previously diagnosed fallopian tube diseases; miscarriage; multiple pregnancy (twins, triplets, etc.); congenital malformations (physical defects present in the child at birth). In some women treated for infertility, ovarian or other reproductive organ tumors have developed. It is not yet known whether this was caused by hormone treatment such as Menopur. The likelihood of blood clots in veins or arteries is higher in pregnant women. Fertility treatment may increase the likelihood of blood clots, especially if the patient is overweight or if blood clots have occurred previously in the patient or in their family (relatives). The patient should inform their doctor if they think this applies to them. Menopur, in combination with a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), may be administered in the treatment of male infertility.
Children and adolescents
The use of Menopur in children and adolescents is not appropriate.
Menopur and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take. Clomiphene citrate is another medicine used to treat infertility. If Menopur is administered at the same time as clomiphene citrate, the effect on the ovaries may be enhanced. Menopur can be used in combination with Bravelle. See section 3.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Menopur should not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Driving and using machines
It is unlikely that Menopur will affect the ability to drive or use machines.
Menopur contains sodium
Menopur contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per dose, which means that the medicine is considered "sodium-free".
3. How to use Menopur
This medicine should always be used as directed by the doctor. In case of doubts, the doctor should be consulted. Women who do not ovulate (do not produce eggs) Treatment should start within the first 7 days of the menstrual cycle (day 1 is the first day of menstruation). The medicine should be administered daily for at least 7 days. The initial dose is usually 75 IU (International Units) FSH + 75 IU LH to 150 IU FSH + 150 IU LH per day. Depending on the patient's response, the dose may be increased to a maximum of 225 IU FSH + 225 IU LH. The prescribed dose should be administered for at least 7 days before the dose is changed. It is recommended to increase the dose by 37.5 IU FSH + 37.5 IU LH at each change, but not more than 75 IU FSH + 75 IU LH. The treatment cycle should be discontinued if no response is observed after 4 weeks. When a satisfactory response is achieved, the next day after the last injection of Menopur, another hormone - hCG should be administered in a single injection at a dose of 5000 IU to 10,000 IU. It is recommended to have sexual intercourse on the day of administration and the next day after administration of hCG. Alternatively, insemination (administration of semen directly into the uterus) can be performed. The patient remains under close supervision of the doctor for at least 2 weeks after administration of hCG. The doctor will monitor the results of Menopur treatment. Depending on the progress of treatment, the doctor may decide to discontinue Menopur administration and refrain from administering hCG. In such a case, the patient will be instructed to use a mechanical contraceptive method (e.g., condom) or abstain from sexual intercourse until the next menstruation. Women participating in assisted reproduction programs If the patient has also been treated with a GnRH agonist (a medicine that supports the action of gonadotropin-releasing hormone), Menopur administration should start about 2 weeks after the start of GnRH agonist treatment. If the patient has also been treated with a GnRH antagonist, Menopur administration should start on the 2nd or 3rd day of the menstrual cycle (the 1st day of menstruation is the 1st day of the cycle). The medicine should be administered daily for at least 5 days. The initial dose of Menopur is usually 150 IU FSH + 150 IU LH to 225 IU FSH + 225 IU LH per day. Depending on the patient's response to treatment, this dose may be increased to a maximum of 450 IU FSH + 450 IU LH per day. The dose should not be increased by more than 150 IU FSH + 150 IU LH at a time. Treatment usually should not last longer than 20 days. After a sufficient number of follicles of appropriate size have been detected, the patient receives a single injection of hCG at a dose of up to 10,000 IU to induce ovulation (release of the egg). The patient remains under close supervision of the doctor for at least 2 weeks after administration of hCG. The doctor will monitor the results of Menopur treatment. Depending on the progress of treatment, the doctor may decide to discontinue Menopur administration and refrain from administering hCG. In such a case, the patient will be instructed to use a mechanical contraceptive method (e.g., condom) or abstain from sexual intercourse until the next menstruation. Men: Treatment starts with the administration of hCG 3 times a week at a dose of 1000 IU to 3000 IU until a normal testosterone level is achieved in the blood serum. Then, Menopur is administered intramuscularly at a dose of 75 IU FSH + 75 IU LH to 150 IU FSH + 150 IU LH 3 times a week for several months.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
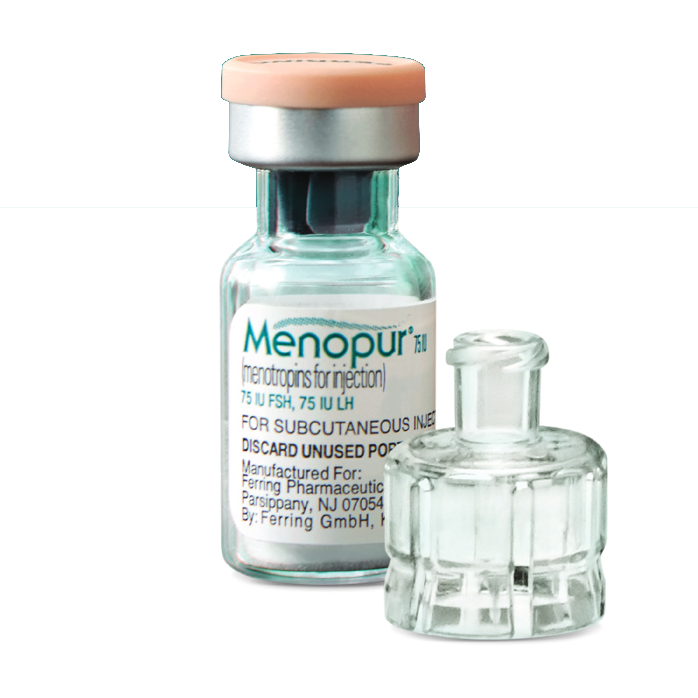
If the doctor has recommended self-injection of Menopur, all instructions provided should be followed. The first injection of Menopur should be performed under the supervision of a doctor. Menopur is a powder in a vial and must be reconstituted (dissolved) before injection. The liquid used to dissolve Menopur is in a pre-filled syringe provided with the vial of powder.
Menopur 600 IU FSH + 600 IU LH must be dissolved before use in the solvent contained in one pre-filled syringe.
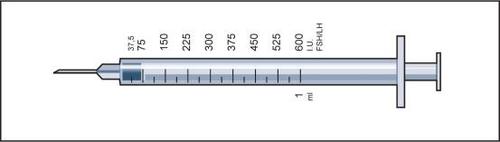
After dissolution, the medicine contained in one vial is administered over several days, and therefore, it should be ensured that only the dose prescribed by the doctor is taken. The doctor prescribes the dose of Menopur in International Units (IU). One of the 9 pre-filled syringes for injection, calibrated in International Units of FSH/LH, which are in the packaging, should be used.
To do this:
1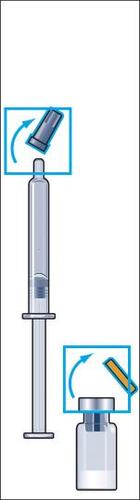 | 2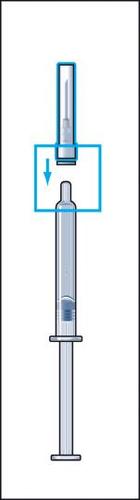 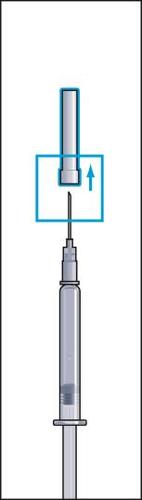 | 3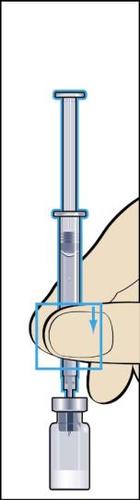 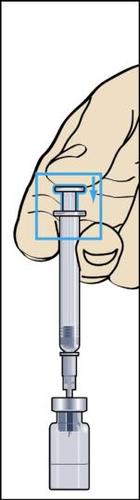 | 4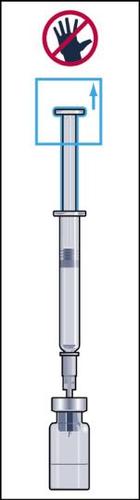 |
- 1. Remove the protective cap from the vial with powder and the rubber cap from the pre-filled syringe with solvent (figure 1).
- 2. Attach the needle (reconstitution needle) to the pre-filled syringe with solvent and remove the protective cap from the needle (figure 2).
- 3. Insert the needle vertically through the center of the rubber stopper of the vial with powder and slowly inject all the solvent into the vial to avoid forming air bubbles (figure 3).
- 4. During injection of the solvent into the vial, a slight overpressure is created. Therefore, after injection of the solvent, the pressure on the plunger should be released for about 10 seconds and allowed to return to the top. This will eliminate the overpressure in the vial (figure 4).
Remove the pre-filled syringe and reconstitution needle.
5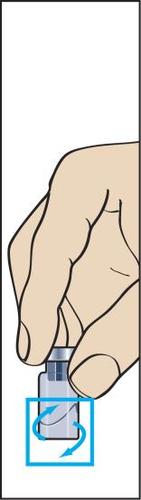 | 6 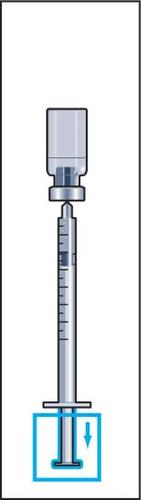 | 7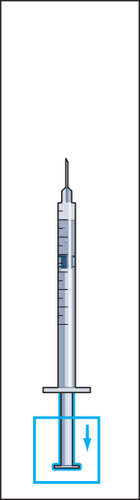 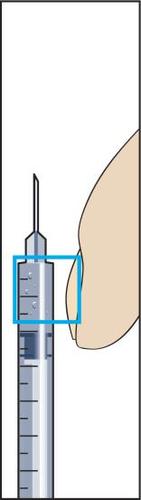 | 8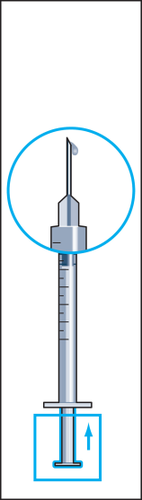 |
- 5. The powder should dissolve quickly (within 2 minutes), forming a clear solution. Although this usually happens after injecting a few drops of solvent, the entire solvent should be injected. To facilitate dissolution of the powder, the vial can be rocked (figure 5). The vial should not be shaken, as this causes the formation of air bubbles.
If the solution is not clear or contains solid particles, it should not be used.
The solution formed after dissolving the powder in the solvent from one pre-filled syringe is now ready for use.
- 6. Remove the pre-filled syringe for injection from the packaging, with the needle attached, and insert the needle vertically through the center of the rubber stopper of the vial. The pre-filled syringe for injection contains a small amount of air, which should be injected into the vial above the solution. Invert the vial and draw up the prescribed dose of Menopur into the pre-filled syringe for injection (figure 6).
NOTE: since the vial contains medicine intended for use over several days, it should be ensured that only the dose prescribed by the doctor is taken.
If the doctor has prescribed Bravelle with Menopur, the two medicines can be mixed. To do this, after reconstituting Menopur, the prescribed dose of Menopur should be injected into the vial with the reconstituted solution of Bravelle. Then, the mixed solution containing both medicines should be drawn up into the syringe and injected subcutaneously. This procedure allows avoiding the injection of each medicine separately.
- 7. Detach the pre-filled syringe from the vial and draw up a small amount of air into the syringe (figure 7).
- 8. Hold the syringe with the needle facing upwards and gently tap the syringe for injection with your finger so that all air bubbles collect at the top (figure 8). Remove the air from the syringe by pressing the plunger gently until the first drop of liquid appears at the tip of the needle.
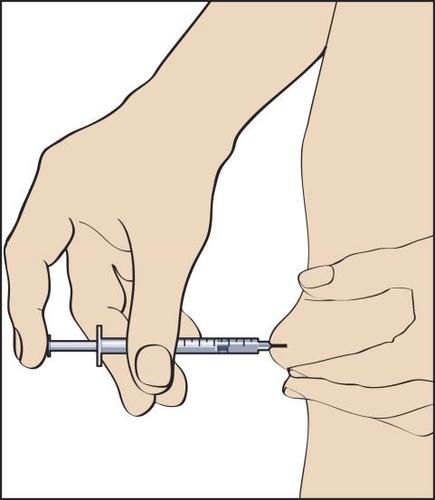
The patient is informed by the doctor or nurse where to inject the medicine (e.g., front of the thigh, abdomen, etc.). Before injection, the skin at the injection site should be disinfected.
9
- 9. To perform the injection, a skin fold should be created between the fingers and the needle inserted at a 90-degree angle (perpendicularly). The solution should be injected by gently pressing the plunger (figure 9), and then the syringe with the needle should be withdrawn.
After withdrawing the syringe with the needle, the injection site should be pressed to prevent any bleeding. Gentle massage at the injection site facilitates the spread of the solution under the skin. Used items should not be thrown into household waste bins but disposed of in an appropriate manner.
- 10. Subsequent injections of the reconstituted Menopur solution are performed by repeating the steps described in points 6 to 9.
Using a higher dose of Menopur than recommended
In case of using a higher dose of Menopur than recommended, the doctor should be informed.
Missing a dose of Menopur
A double dose should not be used to make up for a missed dose. If a dose of Menopur is missed, the doctor should be informed.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Hormones used in fertility treatment, such as Menopur, can cause excessive ovarian activity, leading to a condition called ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), especially in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Symptoms include: abdominal pain; abdominal distension; nausea; vomiting; diarrhea; weight gain; breathing difficulties; decreased frequency or amount of urine passed. In severe cases of OHSS, rare complications have occurred, such as fluid accumulation in the abdominal, pelvic, or pleural cavity, breathing difficulties, and decreased frequency or amount of urine passed, blood clots in blood vessels (thromboembolic disorders), and twisting of the ovaries. If any of these symptoms occur, the doctor should be contacted immediately, even if they occur several days after the last dose of the medicine. During treatment with Menopur, allergic reactions (hypersensitivity) may occur. Symptoms of such reactions may include: rash; itching; swelling of the throat; and breathing difficulties. If any of these symptoms occur, the doctor should be contacted immediately. The following side effects are common(affect 1 to 10 in every 100 patients): abdominal pain; headache; nausea; abdominal distension; pelvic pain; excessive ovarian stimulation causing high activity (ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome); reactions at the injection site, such as pain, redness, bruising, swelling, and/or itching. The following side effects are uncommon(affect 1 to 10 in every 1,000 patients): vomiting; abdominal discomfort; diarrhea; feeling tired; dizziness; fluid-filled blisters in the ovaries (ovarian cysts); breast disorders, including breast pain, breast tenderness, discomfort, nipple pain, and breast swelling; hot flashes. The following side effects are rare(affect 1 to 10 in every 10,000 patients): acne; rash. In addition to the above, the following side effects have been observed after Menopur was made available, and their frequency is unknown: vision disorders; fever; malaise; allergic reactions; weight gain; muscle and joint pain (e.g., back pain, neck pain, and pain in the arms and legs); twisting of the ovary, as a complication of excessive ovarian activity caused by overstimulation; itching; hives; blood clots, as a complication of excessive ovarian activity caused by overstimulation.
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including those not listed in this leaflet, the doctor should be informed. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products: Aleje Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel: +48 22 49 21 301, Fax: +48 22 49 21 309, e-mail: [email protected]. Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder. By reporting side effects, more information can be collected on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Menopur
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children. Before reconstitution, store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C). Do not freeze. Store in the original packaging to protect from light. After reconstitution, the solution can be stored for 28 days at a temperature below 25°C. Do not freeze. The solution should not be administered if it contains solid particles or is not clear. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging after the EXP label. The expiry date refers to the last day of the specified month. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Menopur contains
- The active substance of Menopur is highly purified menotropin (Menotropinum) (human menopausal gonadotropin, hMG) in an amount equivalent to 600 IU FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) and 600 IU LH (luteinizing hormone).
- The other ingredients are: Powder: lactose monohydrate, polysorbate 20, disodium phosphate heptahydrate, phosphoric acid (concentrated) Solvent: water for injections, metacresol (preservative)
What Menopur looks like and contents of the pack
Menopur is a powder and solvent for solution for injection. The pack contains: 1 vial with powder; 1 pre-filled syringe with solvent for reconstitution; 1 reconstitution needle; 9 pre-filled syringes for injection for single use, calibrated in FSH/LH units, with attached needles.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer:
Ferring GmbH, Wittland 11, D-24109 Kiel, Germany. Date of last revision of the leaflet:01/2018. For further information on the medicine, the representative of the marketing authorization holder should be contacted: Ferring Pharmaceuticals Poland Sp. z o.o., ul. Szamocka 8, 01-748 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 246 06 80, Fax: +48 22 246 06 81
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterFerring GmbH
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to MenopurDosage form: Powder, 75 IU FSH + 75 IU LHActive substance: human menopausal gonadotrophinManufacturer: Ferring GmbHPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 1200 IU FSH + 1200 IU LHActive substance: human menopausal gonadotrophinPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 150 IU FSH + 150 IU LHActive substance: human menopausal gonadotrophinManufacturer: Ferring GmbHPrescription required
Alternatives to Menopur in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Menopur in Spain
Alternative to Menopur in Ukraine
Online doctors for Menopur
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Menopur – subject to medical assessment and local rules.