
Kalium hloratum Vzf 15%

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Kalium hloratum Vzf 15%

How to use Kalium hloratum Vzf 15%
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
POTASSIUM CHLORIDE WZF 15%
150 mg/ml, concentrate for solution for infusion
Potassium chloride
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Potassium chloride WZF 15% and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Potassium chloride WZF 15%
- 3. How to use Potassium chloride WZF 15%
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Potassium chloride WZF 15%
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Potassium chloride WZF 15% and what is it used for
Potassium chloride WZF 15% contains potassium, which is one of the main cations of cellular fluid and one of the most important elements in the composition of body fluids.
It participates in many enzymatic reactions and physiological processes, including the proper functioning of the nervous and muscular systems. It affects the body's water management, participates in maintaining acid-base balance and osmotic pressure.
Potassium chloride WZF 15% concentrate for solution for infusion is intended exclusively for intravenous administration in infusion and must be diluted before administrationin a large volume of infusion solution.
Potassium chloride WZF 15% is used:
- in the treatment of hypokalemia,
- in the treatment of digitalis glycoside poisoning,
- as an electrolyte additive to infusion fluids for hydration or parenteral nutrition.
Potassium chloride WZF 15% is intended for patients in whom the use of oral potassium medications is not possible.
2. Important information before using Potassium chloride WZF 15%
When not to use Potassium chloride WZF 15%
- if the patient is allergic to potassium chloride;
- if the patient has hyperkalemia (excess potassium in the blood).
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Potassium chloride WZF 15%, discuss it with your doctor or pharmacist.
Potassium chloride should not be used in people with atrial fibrillation, atrioventricular block, intraventricular conduction disorders, Addison's disease, adrenogenital syndrome, aldosterone deficiency states.
Use with caution in conditions with acute dehydration, extensive mechanical tissue damage, extensive burns, concurrent internal bleeding, after transfusion of a large volume of red blood cell concentrate, in patients receiving chemotherapy, in rare neurological syndromes (familial periodic hyperkalemic paralysis).
Do not administer intravenously to patients with normal or slightly decreased potassium levels if they have renal failure or other conditions that may lead to potassium retention and hyperkalemia.
Using Potassium chloride WZF 15% in patients with renal impairment
Particular caution should be exercised when using the drug in patients with renal impairment, as hyperkalemia and toxic effects on the heart may occur. The drug should not be used in renal failure, in conditions with oliguria or anuria, in kidney diseases with impaired function of the distal tubules (sickle cell anemia, systemic lupus erythematosus).
Potassium chloride WZF 15% and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the medicines you are taking, have recently taken, or plan to take.
Medicines that increase potassium levels:
- angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (medicines used in hypertension);
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (anti-inflammatory and analgesic medicines);
- heparin (anticoagulant medicine);
- cyclosporine, tacrolimus (immunosuppressive medicines used after transplants);
- amiloride, spironolactone, triamterene (diuretic medicines);
- trimethoprim (chemotherapeutic agent used in urinary tract infections);
- pentamidine (medicine used in infections caused by protozoa);
- digoxin (cardiac glycoside);
- propranolol, nadolol, timolol (non-selective beta-adrenergic blockers).
Medicines that decrease potassium levels:
- insulin (used in diabetes);
- bicarbonates;
- beta-adrenergic medicines.
Potassium weakens the effect of digitalis glycosides.
Calcium salts administered intravenously normalize ECG changes typical of hyperkalemia.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
The medicine may be used during pregnancy only if, in the doctor's opinion, the expected benefits to the mother outweigh the potential risk to the fetus. Both hypokalemia and hyperkalemia are harmful to the mother and fetus.
The medicine passes into breast milk, so caution should be exercised when using it in breastfeeding women.
Driving and using machines
The medicine does not affect the ability to drive and use machines.
3. How to use Potassium chloride WZF 15%
This medicine should always be used in accordance with the doctor's or pharmacist's recommendations. If you have any doubts, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
The medicine must be diluted before administration.
After dilution, the medicine is administered in intravenous drip infusion.
Potassium chloride WZF 15% does not contain preservatives.
The dose and infusion rate are adjusted by the doctor according to the patient's condition.
For detailed dosing and administration, see "Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals" at the end of the leaflet.
Using a higher dose of Potassium chloride WZF 15% than recommended
In the event of disruption of excretion mechanisms or too rapid intravenous administration of potassium, hyperkalemia may occur, which can potentially be fatal.
Mild (5-6 mmol/l) or moderate (6-7 mmol/l) hyperkalemia is asymptomatic; an increased potassium level can be detected in serum and characteristic ECG changes can be observed. With significant hyperkalemia (above 7-8 mmol/l), weakness, paresthesia, bradycardia, conduction disorders, hypotension, spastic paralysis of skeletal and respiratory muscles, loss of reflexes, impaired consciousness, cardiac arrest, and death may occur. Appropriate action is taken by medical personnel.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Due to the form and route of administration of the medicine, the following may occur: fever, infection at the infusion site, venous thrombosis or phlebitis at the injection site, extravasation, increased blood volume (hyperolemia), and excess potassium in the blood.
During too rapid intravenous administration, pain at the injection site may occur, and less frequently, irritation or phlebitis. Infusion of potassium chloride through a central venous catheter (especially too rapid or at high concentration) can lead to cardiac arrest and death.
Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and side effects resulting from potassium overdose may occur.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Potassium chloride WZF 15%
Store at a temperature below 25°C. Do not freeze.
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the specified month.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Potassium chloride WZF 15% contains
- The active substance of the medicine is potassium chloride. Each ml of concentrate contains 150 mg of potassium chloride.
- The other ingredient is water for injections.
What Potassium chloride WZF 15% looks like and what the pack contains
A 10 ml ampoule contains 1.5 g of potassium chloride, which corresponds to 20 mmol (20 mEq) of potassium.
A 20 ml vial contains 3.0 g of potassium chloride, which corresponds to 40 mmol (40 mEq) of potassium.
50 ampoules of 10 ml; 10 vials of 20 ml
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Pharmaceutical Works POLPHARMA S.A.
ul. Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
phone: +48 22 364 61 01
Date of last update of the leaflet:November 2024
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals:
Method of administration
Potassium chloride WZF 15% must be diluted before administration.
Potassium chloride WZF 15% does not contain preservatives.
After the first dose of concentrate has been drawn from the vial, the remainder can be stored for up to 24 hours at a temperature below 25°C.
Potassium chloride WZF 15% concentrate for solution for infusion is intended exclusively for intravenous administration in infusion and must be diluted before administration in a large volume of infusion solution.
Potassium chloride WZF 15% concentrate for solution for infusion can be diluted with:
5% glucose solution, 0.9% sodium chloride solution, Ringer's solution, Ringer's solution with sodium lactate, or Hartmann's solution.
The sodium content from the diluent should be taken into account when calculating the total sodium content in the prepared dilution of the medicine. To obtain accurate information about the sodium content in the solution used to dilute the medicine, refer to the patient information leaflet for the diluent used.
10 ml of concentrate containing 20 mmol of potassium (ampoule content) should be diluted to 500 ml of infusion solution.
20 ml of concentrate containing 40 mmol of potassium (vial content) should be diluted to 1000 ml of infusion solution.
The resulting solution should be thoroughly mixed. The potassium concentration in the resulting solution is 40 mmol/l.
Potassium chloride WZF 15% and infusion solutions used to dilute the concentrate do not contain preservatives. Therefore, the infusion solution should be prepared immediately before administration and used within 6 hours. Unused solution should be discarded.
Warning:
Do not mix the medicine with solutions of: mannitol, amikacin, amphotericin B, amoxicillin, benzylpenicillin, diazepam, dobutamine, ergotamine, methylprednisolone, phenytoin, promethazine, streptomycin, sodium nitroprusside, etoposide with cisplatin and mannitol, as incompatibilities may occur.
The list of medicines that may exhibit incompatibilities with Potassium chloride WZF 15% may be incomplete, so if there is a need to administer the medicine with other medicines in one infusion, compatibility should be checked in each case.
Before mixing Potassium chloride WZF 15% with parenteral nutrition solutions, compatibility should be checked in each case.
Instructions for opening the ampoule
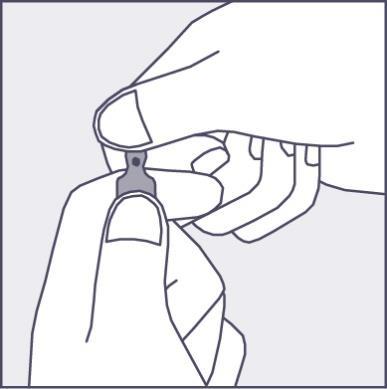
Before opening the ampoule, make sure that the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule.
You can gently shake the ampoule or tap it with your finger to facilitate the flow of the solution.
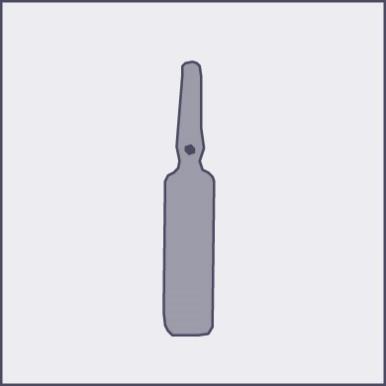
A colored dot has been placed on each ampoule (see Figure 1) as a mark indicating the location of the break point below it.
- To open the ampoule, hold it vertically, with both hands, with the colored dot facing you - see Figure 2. The upper part of the ampoule should be grasped in such a way that the thumb is above the colored dot.
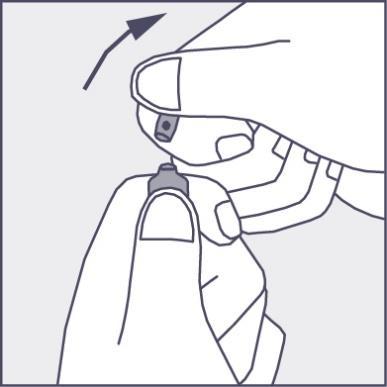
- Press in the direction of the arrow shown in Figure 3. The ampoules are intended for single use only and should be opened immediately before use. The remaining contents of the unused product should be discarded in accordance with applicable regulations.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
- The dose and infusion rate depend on the patient's condition. Even in the case of significant hypokalemia, the medicine cannot be administered without dilution.
- In simplified terms, it can be assumed that 10 mmol of potassium chloride leads to an increase in serum potassium concentration by 0.1 mmol/l. The actual effect of the administered dose on kaliemia depends on many factors, such as: volemic status, acid-base balance, hormonal balance, renal function, concomitant diseases, and medications taken. The need for potassium in a given patient can only be determined empirically based on repeated measurements of serum potassium levels.
the factors such as: volemic status, acid-base balance, hormonal balance, renal function, concomitant diseases, and medications taken. The need for potassium in a given patient can only be determined empirically based on repeated measurements of serum potassium levels.
- The potassium concentration in the infusion should not exceed 40 mmol/l, and the infusion rate should not exceed 20 mmol/hour. The dose depends on the individual patient's condition, usually the daily dose should not exceed 200 mmol.
In specific conditions, the serum potassium concentration may not reflect the actual potassium stores in the body. This is due to the redistribution of potassium ions between intracellular and extracellular spaces. A typical example is hyperkalemia in a patient with uncontrolled diabetes and metabolic acidosis. Such a patient has a systemic potassium deficiency due to its loss as a result of osmotic diuresis. Acidosis causes potassium to escape from cells into the extracellular space and hyperkalemia. It should be remembered to supplement potassium during hydration and correction of metabolic acidosis. - Local symptoms (pain) may prevent infusion, and in such cases, the infusion should be administered into two veins or into a large vein, e.g., the femoral vein.
- The potassium chloride solution should not be administered too quickly through a central catheter (inserted into the subclavian, jugular, or femoral vein), as this can lead to cardiac arrest. Administration through a central catheter should be avoided.
- During intravenous infusion (especially with rapid potassium administration), ECG and serum potassium and other electrolyte levels should be monitored. Dehydrated patients should be given 1000 ml of fluid without potassium before administering fluids containing potassium, unless hypokalemia occurs. Potassium deficiency is often accompanied by magnesium deficiency; this deficiency should be supplemented simultaneously.
Dosing Adults
In patients with a serum potassium level above 3 mmol/l, the infusion rate should not exceed 10 mmol/hour. The potassium concentration in the infusion solution should not exceed 40 mmol/l. The daily dose should not exceed 200 mmol.
If the serum potassium level is below 3 mmol/l, especially if ECG changes or muscle weakness are observed, potassium should be administered at a rate of 20 mmol/hour (and in justified cases 40 mmol/hour). The potassium concentration in the infusion solution should not exceed 40 mmol/l. Only in justified cases can the daily dose exceed 200 mmol.
Children
The recommended dose is 0.25-0.5 mmol/kg body weight. The infusion rate should not exceed 10 mmol/hour. The dose should not exceed 1 mmol/kg body weight/hour.
ECG and serum potassium and other electrolyte levels should be closely monitored.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterZakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Kalium hloratum Vzf 15%Dosage form: Concentrate, 150 mg/mlActive substance: potassium chlorideManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi Espana S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Concentrate, -Active substance: electrolytes in combination with other drugsManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi Norge ASPrescription not requiredDosage form: Concentrate, (170.1 mg + 133.5 mg + 14 mg)/mlActive substance: electrolytes in combination with other drugsPrescription not required
Alternatives to Kalium hloratum Vzf 15% in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Kalium hloratum Vzf 15% in Ukraine
Alternative to Kalium hloratum Vzf 15% in Spain
Online doctors for Kalium hloratum Vzf 15%
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Kalium hloratum Vzf 15% – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














