
Haemate P 1000 i.m. Fviii/2400 i.m. Vvf

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Haemate P 1000 i.m. Fviii/2400 i.m. Vvf

How to use Haemate P 1000 i.m. Fviii/2400 i.m. Vvf
INFORMATION LEAFLET - INFORMATION FOR THE USER
HaemateP 250 IU FVIII/600 IU VWF
HaemateP 500 IU FVIII/1200 IU VWF
HaemateP 1000 IU FVIII/2400 IU VWF
Powder and solvent for solution for injection or infusion
Human coagulation factor VIII (FVIII) / Human von Willebrand factor (VWF)
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, please inform your doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What is Haemate P and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Haemate P
- 3. How to use Haemate P
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Haemate P
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. WHAT IS HAEMATE P AND WHAT IS IT USED FOR
What is Haemate P
Haemate P is supplied as a powder and solvent. The reconstituted solution is administered intravenously by injection or infusion.
Haemate P is produced from human plasma (the liquid part of the blood) and contains human von Willebrand factor and human coagulation factor VIII.
What is Haemate P used for
Haemate P contains both human coagulation factor VIII (FVIII) and von Willebrand factor (VWF), which is important for the patient to need more. If the patient has hemophilia A, the doctor will prescribe Haemate P with the specified number of FVIII units. If the patient has von Willebrand disease, the doctor will prescribe Haemate P with the specified number of VWF units.
Von Willebrand disease (VWD)
Haemate P is used for the prevention and treatment of bleeding, including bleeding during surgical procedures, caused by a lack of von Willebrand factor, when desmopressin (DDAVP) therapy is ineffective or contraindicated.
Hemophilia A (congenital factor VIII deficiency)
Haemate P is used for the prevention or control of bleeding caused by a lack of factor VIII in the blood.
It can also be used for the treatment of acquired factor VIII deficiency and for the treatment of patients with antibodies to factor VIII.
2. IMPORTANT INFORMATION BEFORE USING HAEMATE P
The following sections contain information that should be considered before using Haemate P
When not to use Haemate P:
- In case of hypersensitivity (allergy) to human von Willebrand factor or human coagulation factor VIII or to any of the other components of this medicine (listed in section 6).
In case of allergy to any medicine or food, inform your doctor.
Warnings and precautions
Identifiability
It is particularly recommended that each administration of Haemate P to the patient be recorded, including the name and batch number, in order to maintain a record of the batches used.
Before starting treatment with Haemate P, discuss the following with your doctor or pharmacist:
- In case of allergic reactions or anaphylactic reactions(severe allergic reaction that causes severe breathing difficulties or dizziness). As with any protein injection, it is possible for allergic hypersensitivity reactions to occur. The doctor should inform the patient about the early signs of hypersensitivity reactions such as hives, generalized rash, chest tightness, wheezing, low blood pressure, and anaphylaxis (severe allergic reaction that causes severe breathing difficulties or dizziness). If such symptoms occur, administration of the medicine should be stopped immediately and a doctor should be consulted.
- Formation of inhibitors(antibodies) is a known complication that can occur during treatment with all factor VIII-containing medicines. These inhibitors, especially at high levels, can disrupt proper treatment and the patient will be closely monitored for the development of these inhibitors. If bleeding in the patient is not properly controlled with Haemate P, the doctor should be informed immediately.
- In case of existing heart disease or risk of its occurrence, inform your doctor or pharmacist.
- If the administration of Haemate P requires a central venous access device (CVAD), the doctor should consider the risk of complications associated with CVAD, including local infections, bacteremia, and thrombosis at the catheter site.
Von Willebrand disease
- In case of known risk of thrombosis (thrombotic events, including pulmonary embolism), especially in patients with clinical or morphological risk factors (e.g. postoperative periods without antithrombotic prophylaxis, prolonged immobilization, obesity, overdose, cancer). In such cases, the patient should be monitored for early signs of thrombosis. Antithrombotic prophylaxis should be initiated, in accordance with current guidelines.
The doctor will carefully weigh the benefits of Haemate P treatment against the risk of these complications.
Safety of use in terms of the possibility of transmitting viruses
In the case of medicines prepared from human blood or plasma, precautions are taken to prevent the transmission of viruses to patients. These include:
- careful selection of blood and plasma donors to ensure that donors at risk of transmitting infections are excluded.
- testing of each donation and plasma pool for the presence of viruses/infections, and
- inclusion in the processing of blood or plasma of procedures that can inactivate or remove viruses.
Despite their use, when administering medicines prepared from human blood or plasma, it is not possible to completely rule out the possibility of transmitting an infection. This applies to both previously unknown or newly discovered viruses and other types of infections.
The procedures used are recognized as effective against enveloped viruses, such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV, the virus that causes AIDS), hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C virus (inflammation of the liver), as well as against the non-enveloped hepatitis A virus (inflammation of the liver).
Against non-enveloped viruses, such as parvovirus B19, the procedures used may have limited effectiveness.
Parvovirus B19 infections can be serious:
- for pregnant women (infection of the unborn child) and
- for people with impaired immune systems or increased red blood cell production due to certain types of anemia (e.g. sickle cell anemia or hemolytic anemia).
When regularly/repeatedly taking products made from human plasma containing von Willebrand factor and factor VIII, the doctor may recommend considering vaccination against hepatitis A and B.
Haemate P and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken, including those available without a prescription
- Haemate P should not be mixed with other medicines, solvents, or diluents.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
- If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
- Since hemophilia A is rare in women, there are no data available on the use of factor VIII during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- In the case of von Willebrand disease, women are more at risk than men due to the additional risk of bleeding associated with menstruation, pregnancy, childbirth, and gynecological complications. Based on experience gained from post-marketing studies, substitution of von Willebrand factor (VWF) is recommended for the prevention and treatment of acute bleeding. Clinical studies on VWF substitution therapy in pregnant and lactating women are not available.
- During pregnancy and breastfeeding, Haemate P should only be used if there are justified indications.
Driving and using machines
There are no reports that Haemate P impairs the ability to drive or operate machines.
Haemate P contains sodium
Haemate 250 IU FVIII/600 IU VWF contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per vial, so it can be considered "sodium-free".
Haemate 500 IU FVIII/1200 IU VWF contains 26 mg of sodium (main component of common salt) per vial, which corresponds to 1.3% of the recommended maximum daily intake of sodium for an adult.
Haemate 1000 IU FVIII / 2400 IU VWF contains 52.5 mg of sodium (main component of common salt) per vial, which corresponds to 2.6% of the recommended maximum daily intake of sodium for an adult.
3. HOW TO USE HAEMATE P
Treatment should be initiated and conducted under the supervision of a doctor experienced in the treatment of this type of disease.
Dosage
The required amount of von Willebrand factor and factor VIII and the duration of treatment depend on several factors, such as body weight, severity of the disease, location and intensity of bleeding, or the need to prevent bleeding during surgery or examination (see section "Information intended for healthcare professionals only"). If Haemate P has been prescribed for use at home, the patient is instructed by the doctor on how to perform the injection and dosing.
Follow the guidelines provided by your doctor or nurse from the hemophilia treatment center.
Using a higher dose of Haemate P than recommended
Symptoms of VWF or FVIII overdose are not known. However, the risk of thrombosis (thrombosis) cannot be ruled out in case of exceptionally high doses, especially with VWF products with high FVIII content.
Reconstitution and administration General information
- The powder must be mixed (reconstituted) with the solvent (liquid part) and drawn from the vial under aseptic conditions.
- The solution should be clear or slightly opalescent. After filtration/drawing (see below), the reconstituted product should be visually inspected for particles and discoloration before administration. Even if the reconstitution procedure guidelines are followed carefully, the presence of a few clumps or particles is not uncommon. The filter included with the Mix2Vial device completely removes these particles. Filtration does not affect dose calculations.
- Do not use solutions that are visibly cloudy or contain clumps or particles after filtration.
- Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations and the doctor's recommendations.
Reconstitution
Without opening either vial, warm the Haemate P powder and solvent to room temperature, leaving the vials at this temperature for about an hour or holding them in your hand for a few minutes. DO NOT expose the vials to direct heat. Do not heat the vials above body temperature (37°C).
Carefully remove the protective caps from the solvent vial and Haemate P vial. Clean the exposed rubber stoppers of both vials with an alcohol swab and let them dry. The solvent can then be transferred to the Haemate P vial using the provided Mix2Vial device. Follow the instructions below.
1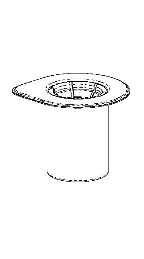 |
|
2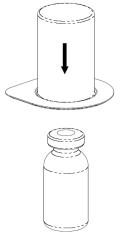 |
|
3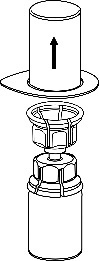 |
|
4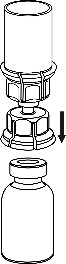 |
|
5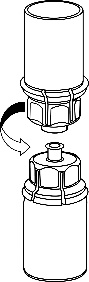 |
|
6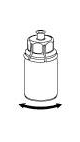 |
|
7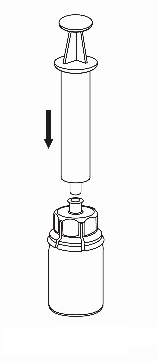 |
|
Withdrawal and administration
8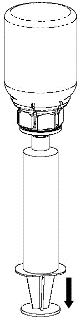 |
|
9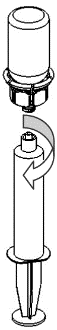 |
|
Method of administration
For the injection of Haemate P, it is recommended to use plastic, single-use syringes, as solutions of this type tend to stick to the surface of all glass syringes.
The solution should be administered slowly intravenously, at a rate not exceeding 4 ml per minute. Care should be taken to prevent blood from entering the syringe filled with the product. After drawing the product into the syringe, it should be used immediately.
If it is necessary to administer a larger amount of factor, this can also be done by infusion. For this purpose, the reconstituted product should be transferred to an approved infusion system. The infusion should be performed according to the doctor's instructions. Attention should be paid to the occurrence of any immediate reaction. In case of any reaction that may be related to the administration of Haemate P, the injection/infusion should be stopped (see also section 2).
If you have any further questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS
Like all medicines, Haemate P can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following adverse reactions have occurred very rarely (in less than 1 in 10,000 patients):
- Acute allergic reaction (such as angioedema, burning and stinging at the injection site, chills, flushing, generalized rash, headache, skin allergic reaction (hives), low blood pressure, lethargy, nausea, anxiety, tachycardia, chest tightness, tingling, vomiting, wheezing), which has occurred very rarely and in some cases may lead to severe anaphylaxis (including shock).
- Increased body temperature (fever).
Von Willebrand disease
- Very rarely, there is a risk of thrombotic events, including pulmonary embolism (the risk of forming and moving blood clots to the vascular system (veins/arteries) with potential impact on organs),
- In patients receiving VWF products, sustained elevated levels of FVIII:C in plasma may increase the risk of thrombosis (see also section 2)
- In patients with VWD, very rarely, inhibitors (neutralizing antibodies) against VWF may occur. If such inhibitors occur, they will manifest as an inadequate clinical response leading to prolonged bleeding. This is particularly the case in patients with type 3 VWD. Such antibodies can be associated with anaphylactic reactions. Therefore, patients who have experienced an anaphylactic reaction should be tested for the presence of an inhibitor. In such cases, it is recommended to contact a specialized hemophilia treatment center.
Hemophilia A
- In previously untreated children, inhibitors (antibodies) against factor VIII may occur very frequently (in more than 1 in 10 patients). However, in patients who have previously been treated with factor VIII (more than 150 days of treatment), the risk is not very common (less than 1 in 100 patients). If this happens, the patient's medicines may stop working properly and the patient may experience persistent bleeding. If this happens, the doctor should be informed immediately.
Side effects in children and adolescents
The frequency, type, and severity of adverse reactions in children are comparable to those in adults.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, please inform your doctor or pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocides:
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
tel.: +48 22 49 21 301
fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. HOW TO STORE HAEMATE P
- Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the label and carton (after the EXP abbreviation)
- Do not store above 25 oC.
- Do not freeze.
- Store the vials in the outer packaging to protect from light.
- Haemate P does not contain a preservative, so the reconstituted solution should be used immediately.
- If the reconstituted solution is not administered immediately, it should be used within 3 hours.
- After drawing the product into the syringe, it should be used immediately.
- The batch number is printed on the label and carton after the Lot abbreviation.
6. CONTENTS OF THE PACK AND OTHER INFORMATION
What Haemate P contains The active substances of Haemate P are:
Human von Willebrand factor and human coagulation factor VIII
The other ingredients (excipients) are:
Human albumin, glycine, sodium chloride, sodium citrate, sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid (in small amounts to adjust the pH)
Solvent: Water for injections
What Haemate P looks like and what the pack contains
Haemate P is supplied as a white or pale yellow powder, or a brittle, solid mass, and water for injections as a solvent. The reconstituted solution should be clear or slightly opalescent, i.e., it may shine when held up to the light, but it must not contain any visible particles.
Pack sizes
The pack containing 250 IU FVIII/600 IU VWF includes:
1 vial of powder
1 vial of 5 ml water for injections
1 20/20 transfer system with filter,
Administration set (inner packaging)
1 single-use syringe of 5 ml capacity,
1 infusion set,
2 alcohol swabs,
1 non-sterile plaster
The pack containing 500 IU FVIII/1200 IU VWF includes:
1 vial of powder
1 vial of 10 ml water for injections
1 20/20 transfer system with filter
Administration set (inner packaging)
1 single-use syringe of 10 ml capacity,
1 infusion set,
2 alcohol swabs,
1 non-sterile plaster
The pack containing 1000 IU FVIII/2400 IU VWF includes:
1 vial of powder
1 vial of 15 ml water for injections
1 20/20 transfer system with filter,
Administration set (inner packaging)
1 single-use syringe of 20 ml capacity,
1 infusion set,
2 alcohol swabs,
1 non-sterile plaster
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
CSL Behring GmbH
Emil-von-Behring-Strasse 76
35041 Marburg
Germany
Date of approval of the leaflet:
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Dosage Von Willebrand disease:
It is important to calculate the dose using the specified number of international units (IU) of VWF: RCo
1 IU/kg VWF: RCo usually increases the level of circulating VWF: RCo by about 0.02 IU/ml (2%).
The required dose should be calculated using the following formula:
Required dose = body weight [kg] x desired increase in VWF: RCo level [% or IU/ml] x 0.5.
The dose and frequency of administration should always be individually tailored based on clinical efficacy.
- 40 – 80 IU/kg of von Willebrand factor (VWF: RCo) and 20 – 40 IU FVIII: C/kg body weight (bw) are usually recommended to achieve hemostasis.
A higher initial dose of von Willebrand factor of 80 IU/kg may be required, especially in patients with type 3 von Willebrand disease, where maintaining adequate levels may require higher doses than in other types of the disease.
Prevention of bleeding during surgical procedures or major trauma:
To prevent massive bleeding during or after surgical procedures, the injection should be started 1 to 2 hours before the procedure.
An appropriate dose should be administered every 12 – 24 hours. The dose and duration of treatment depend on the patient's clinical condition, the type and intensity of bleeding, and the levels of VWF: RCo and FVIII: C.
When using von Willebrand factor preparations containing FVIII, the treating physician should be aware that prolonged therapy may cause excessive increase in FVIII: C levels. After 24 – 48 hours of treatment, to avoid uncontrolled increase in FVIII: C levels, it is recommended to consider reducing the dose and/or extending the interval between administrations.
Children and adolescents
Dosage in children is based on body weight, so the dose is determined on the same basis as for adults. The frequency of administration should always be determined individually based on clinical efficacy.
Hemophilia A:
Monitoring of treatment
During treatment, it is essential to properly determine the levels of factor VIII to measure the correct dose to be administered to the patient and the frequency of repeated infusions. The response of individual patients to factor VIII may vary, considering different recovery levels and half-lives. Dosing based on body weight may require adjustment in patients with overweight or underweight. Especially in the case of major surgical procedures, it is necessary to closely monitor substitution therapy through coagulation tests (factor VIII activity level in plasma).
Patients should be monitored for the development of factor VIII inhibitors. See also section 2.
Dosage and duration of substitution therapy depend on the degree of factor VIII deficiency, the location and intensity of bleeding, and the patient's clinical condition.
It is essential to calculate the dose using the specified number of international units (IU) of FVIII: RCo
The number of units of factor VIII administered is expressed in international units (IU), which refer to the current WHO standard for factor VIII concentrates. Factor VIII activity in plasma is expressed as a percentage (relative to normal human plasma) or, preferably, in IU (relative to the International Standard for factor VIII in plasma).
One IU of factor VIII activity is equal to the amount of factor VIII contained in 1 ml of normal human plasma.
Acute treatment
The calculation of the required dose of factor VIII is based on the empirical finding that 1 IU of factor VIII per kg of body weight increases the plasma factor VIII activity by about 2% (2 IU/dl). The required dose is calculated using the following formula:
Required dose = body weight [kg] x desired increase in factor VIII level [% or IU/dl] x 0.5.
The dose and frequency of administration should always be individually tailored based on clinical efficacy.
In case of the following types of bleeding or surgical procedures, factor VIII activity should not fall below the specified values for plasma activity (in % or IU/dl) during the corresponding period:
| Type of bleeding/surgical procedure | Therapeutic level of factor VIII activity in plasma (% or IU/dl) | Dosing frequency (hours) / treatment duration (days) |
| Bleeding | ||
| Mild hemarthrosis, muscle bleeding, or bleeding from the mouth | 20-40 | Repeat infusion every 12 to 24 hours for at least 1 day until pain and bleeding have resolved or healed |
| Extensive hemarthrosis; bleeding into muscle or hematoma | 30-60 | Repeat infusion every 12-24 hours for 3 to 4 days or more until pain and acute dysfunction have resolved |
| Life-threatening bleeding: | 60-100 | Repeat infusion every 8 to 24 hours until the risk has resolved |
| Surgical procedures | ||
| Minor procedures, including tooth extraction | 30-60 | Every 24 hours, for at least 1 day, until healing |
| Major surgical procedures | 80-100 (pre- and post-operative) | Repeat infusion every 8 – 24 hours until adequate wound healing, then therapeutically for at least 7 days to achieve 30% to 60% (IU/dl) factor VIII activity. |
Prophylaxis
In long-term prophylactic treatment of patients with severe hemophilia A, usually 20 to 40 IU of factor VIII per kg of body weight are administered at intervals of 2 to 3 days.
In some cases, especially in younger patients, more frequent administration of this factor or the use of higher doses may be necessary.
Children and adolescents
There are no data from clinical studies on the dosing of Haemate P in children.
Special warnings and precautions for use
When using VWF preparations, the treating physician should be aware that prolonged therapy may cause excessive increase in FVIII: C levels. In patients receiving VWF preparations containing FVIII, it is recommended to monitor plasma FVIII: C levels to avoid sustained, excessive increase in FVIII: C levels, which may increase the risk of thrombosis, and to consider the use of antithrombotic agents.
Side effects
When high or frequently repeated doses are administered, when inhibitors are present, or in the case of pre- and post-operative care, all patients should be monitored for signs of hypervolemia. Additionally, patients with blood groups A, B, and AB should be monitored for signs of intravascular hemolysis and/or decreasing hematocrit values.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterCSL Behring GmbH
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Haemate P 1000 i.m. Fviii/2400 i.m. VvfDosage form: Powder, 50 IU/ml; 500 IU + 60 IU/ml; 600 IUActive substance: von Willebrand factor and coagulation factor VIII in combinationManufacturer: Instituto Grifols S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 25 IU/ml; 250 IU + 30 IU/ml; 300 IUActive substance: von Willebrand factor and coagulation factor VIII in combinationManufacturer: Instituto Grifols S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 100 IU/ml; 1000 IU + 120 IU/ml; 1200 IUActive substance: von Willebrand factor and coagulation factor VIII in combinationManufacturer: Instituto Grifols S.A.Prescription required
Alternatives to Haemate P 1000 i.m. Fviii/2400 i.m. Vvf in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Haemate P 1000 i.m. Fviii/2400 i.m. Vvf in Ukraine
Alternative to Haemate P 1000 i.m. Fviii/2400 i.m. Vvf in Spain
Online doctors for Haemate P 1000 i.m. Fviii/2400 i.m. Vvf
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Haemate P 1000 i.m. Fviii/2400 i.m. Vvf – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














